The Growth Factors and Cytokines of Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome May Potentially Aid in Oral Cancer Proliferation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
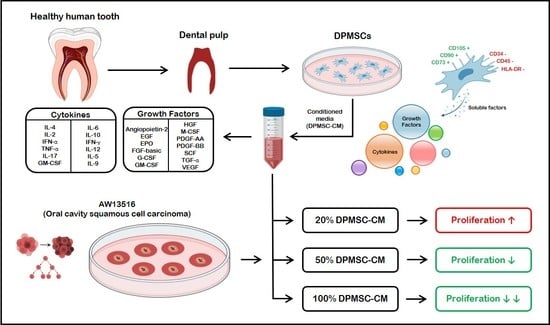
2.1. DPMSC Isolation and Characterization
2.2. DPMSC-CM Profiling
2.3. Oral Cancer Cell Lines Source and Culture in DPMSC-CM
2.4. Ki-67 Quantification by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DPMSC Characterization
3.2. Quantification of the Growth Factors and Cytokines in DPMSC-CM
3.3. Effect of the DPMSC-CM on the AW13516
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Full forms | Abbreviations |
| mesenchymal stem cells | MSC |
| MSC secretome | MSC-S |
| dental pulp MSC | DPMSC |
| DPMSC secretome | DPMSC-S |
| DPMSC conditioned media | DPMSC-CM |
| Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium | DMEM |
| phosphate-buffered saline | PBS |
| angiopoietin-2 | Ang-2 |
| epidermal growth factor | EGF |
| Erythropoietin | EPO |
| basic fibroblast growth factor | bFGF |
| granulocyte-colony stimulating factor | G-CSF |
| granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor | GM-CSF |
| hepatocyte growth factor | HGF |
| macrophage colony-stimulating factor | M-CSF |
| platelet-derived growth factor | PDGF-AA |
| platelet-derived growth factor | PDGF-BB |
| polystyrene | PS |
| stem cell factor | SCF |
| transforming growth factor | TGF- α |
| vascular endothelial growth factor | VEGF |
| interleukin 1 beta | IL-1β |
| tumor necrosis factor alpha | TNF-α |
| interleukin 17A | IL-17A |
| ;;; interleukin 12p70 | IL-12p70 |
| interferon-gamma | IFN- γ |
| C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 | CXCL10 |
| C-C motif chemokine ligand | CCL2 |
| C-C motif chemokine ligand 8 | CXCL8 |
| interleukin 2 | IL-2 |
| interleukin 4 | IL-4 |
| interleukin 6 | IL-6 |
| interleukin 10 | IL-10 |
| transforming growth factor-beta 1 | TGF-β1 |
| human third molar tooth germ stem cells | TGMSCs |
References
- Aryan, A.; Bayat, M.; Bonakdar, S.; Taheri, S.; Haghparast, N.; Bagheri, M.; Piryaei, A.; Abdollahifar, M.-A. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium promotes wound healing in deep second-degree burns in male rats. Cells Tissues Organs 2018, 206, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kandoi, S.; Misra, R.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Rajagopal, K.; Verma, R.S. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, L.; Ramos, E.; Mendiola, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Santamaria, G.; Santamaria, J.; Arteagoitia, I. Autologous dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells for inferior third molar post-extraction socket healing: A split-mouth randomised clinical trial. Med. Oral Patol. Oral y Cir. Bucal 2018, 23, e469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irastorza, I.; Luzuriaga, J.; Martinez-Conde, R.; Ibarretxe, G.; Unda, F. Adhesion, integration and osteogenesis of human dental pulp stem cells on biomimetic implant surfaces combined with plasma derived products. Eur. Cells Mater. 2019, 38, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardena, T.N.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Abu Kasim, N.H. Conditioned media derived from mesenchymal stem cell cultures: The next generation for regenerative medicine. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Rosa-Ruiz, M.D.P.; Álvarez-Pérez, M.A.; Cortés-Morales, V.A.; Monroy-García, A.; Mayani, H.; Fragoso-González, G.; Caballero-Chacón, S.; Diaz, D.; Candanedo-González, F.; Montesinos, J.J. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from dental tissues: A comparative in vitro evaluation of their immunoregulatory properties against T cells. Cells 2019, 8, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salehi, H.; Al-Arag, S.; Middendorp, E.; Gergely, C.; Cuisinier, F.; Orti, V. Dental pulp stem cells used to deliver the anticancer drug paclitaxel. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Moshy, S.; Radwan, I.A.; Rady, D.; Abbass, M.M.S.; El-Rashidy, A.A.; Sadek, K.M.; Dörfer, C.E.; Fawzy El-Sayed, K.M. Dental stem cell-derived secretome/conditioned medium: The future for regenerative therapeutic applications. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 7593402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kheur, S.; Sanap, A.; Kharat, A.; Gupta, A.A.; Raj, A.T.; Kheur, M.; Bhonde, R. Hypothesizing the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in oral submucous fibrosis. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, A.; Demirci, S.; Apdik, H.; Apdik, E.A.; Şahin, F. Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) increase prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration under in vitro conditions. Tissue Cell 2017, 49, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.T.; Kheur, S.; Bhonde, R.; Gupta, A.A.; Patil, S. Assessing the effect of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned media on human cancer cell lines: A systematic review. Tissue Cell 2021, 71, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.R.; Kharat, A.H.; Kulkarni, D.G.; Kheur, S.M.; Bhonde, R.R. Long term explant culture for harvesting homogeneous population of human dental pulp stem cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandi, S.; Al Khatani, A.; Abdulaziz Sumayli, H.; Yahya Sabyei, M.; Mohammed Al Zailai, A.; Ali Sumayli, M.; Ibrahim Hakami, H.; Abdurabu Jafer, M.; Vyas, N.; Ali Baeshen, H.; et al. Comparative analysis of cytokines and growth factors in the conditioned media of stem cells from the pulp of deciduous, young, and old permanent tooth. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3559–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandi, S.; Al Kahtani, A.; Mashyakhy, M.; Alsofi, L.; Maganur, P.C.; Vishwanathaiah, S.; Testarelli, L.; Del Giudice, A.; Mehta, D.; Vyas, N.; et al. Modulation of the dental pulp stem cell secretory profile by hypoxia induction using cobalt chloride. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, D.K.; Montero, P.H.; Migliacci, J.C.; Shah, J.P.; Wong, R.J.; Ganly, I.; Patel, S.G. Survival outcomes after treatment of cancer of the oral cavity (1985–2015). Oral Oncol. 2019, 90, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvanov, A.A.; Yalvaç, M.E.; Shafigullina, A.K.; Salafutdinov, I.I.; Blatt, N.L.; Sahin, F.; Kiyasov, A.P.; Palotás, A. Interaction and self-organization of human mesenchymal stem cells and neuro-blastoma SH-SY5Y cells under co-culture conditions: A novel system for modeling cancer cell micro-environment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalvaç, M.E.; Yilmaz, A.; Mercan, D.; Aydin, S.; Dogan, A.; Arslan, A.; Demir, Z.; Salafutdinov, I.I.; Shafigullina, A.K.; Sahin, F.; et al. Differentiation and neuro-protective properties of immortalized human tooth germ stem cells. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalvaç, M.E.; Yarat, A.; Mercan, D.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Palotás, A.; Şahin, F. Characterization of the secretome of human tooth germ stem cells (hTGSCs) reveals neuro-protection by fine-tuning micro-environment. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2013, 32, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raj, A.T.; Kheur, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Sayed, M.E.; Mugri, M.H.; Almasri, M.A.; Al-Ahmari, M.M.; Patil, V.R.; Bhandi, S.; Testarelli, L.; et al. The Growth Factors and Cytokines of Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome May Potentially Aid in Oral Cancer Proliferation. Molecules 2021, 26, 5683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185683
Raj AT, Kheur S, Khurshid Z, Sayed ME, Mugri MH, Almasri MA, Al-Ahmari MM, Patil VR, Bhandi S, Testarelli L, et al. The Growth Factors and Cytokines of Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome May Potentially Aid in Oral Cancer Proliferation. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185683
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaj, A. Thirumal, Supriya Kheur, Zohaib Khurshid, Mohammed E. Sayed, Maryam H. Mugri, Mazen A. Almasri, Manea Musa Al-Ahmari, Vikrant R. Patil, Shilpa Bhandi, Luca Testarelli, and et al. 2021. "The Growth Factors and Cytokines of Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome May Potentially Aid in Oral Cancer Proliferation" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185683
APA StyleRaj, A. T., Kheur, S., Khurshid, Z., Sayed, M. E., Mugri, M. H., Almasri, M. A., Al-Ahmari, M. M., Patil, V. R., Bhandi, S., Testarelli, L., & Patil, S. (2021). The Growth Factors and Cytokines of Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome May Potentially Aid in Oral Cancer Proliferation. Molecules, 26(18), 5683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185683