Novel c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitors with an 11H-Indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one Scaffold
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Binding Affinity of Novel Compounds toward JNK1-3
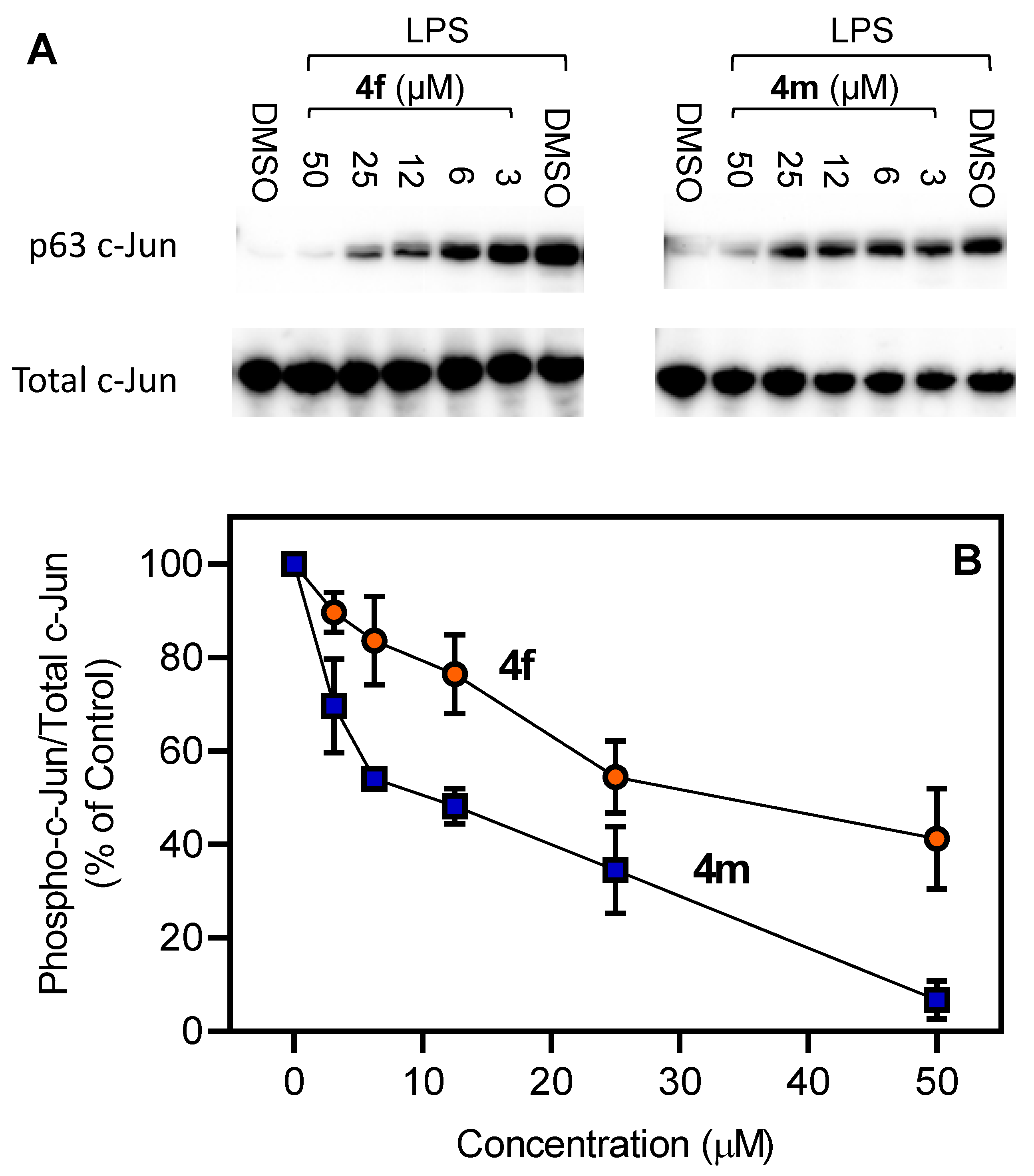
2.3. Evaluation of Compound Biological Activity
2.4. ADME Predictions
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. General Procedures for Indenoquinoxalin-11-one (3a–3o) Synthesis
4.1.2. General Procedure for Oximation of the Indenoquinoxaline Ketones
4.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
4.3. Methods for Biological Analysis
4.3.1. Kinase Kd Determination
4.3.2. Cell Culture
4.3.3. Analysis of AP-1/NF-κB Activation
4.3.4. IL-6 Analysis
4.3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3.6. Western Blotting
4.4. Molecular Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Armstrong, S.C. Protein kinase activation and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 61, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.G. The functional contrariety of JNK. Mol. Carcinog. 2007, 46, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Ngoei, K.R.; Zhao, T.T.; Yeap, Y.Y.; Ng, D.C. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling: Recent advances and challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplain, H. Salvage of ischemic myocardium: A focus on JNK. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 588, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.; Jang, M.; Cho, H.; Yang, S.; Im, D.; Moon, H.; Hah, J.M. Discovery of 3-alkyl-5-aryl-1-pyrimidyl-1H-pyrazole derivatives as a novel selective inhibitor scaffold of JNK3. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, Y.T.; Davis, R.J. Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)—from inflammation to development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998, 10, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadov, S.; Jang, S.; Agostini, B. Crosstalk between mitogen-activated protein kinases and mitochondria in cardiac diseases: Therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nijboer, C.H.; van der Kooij, M.A.; van, B.F.; Ohl, F.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. Inhibition of the JNK/AP-1 pathway reduces neuronal death and improves behavioral outcome after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Wei, J.; Wu, C. Mammalian STE20-like kinase 1 knockdown attenuates TNFα-mediated neurodegenerative disease by repressing the JNK pathway and mitochondrial stress. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.L.; Nakamura, K. The c-Jun kinase/stress-activated pathway: Regulation, function and role in human disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waetzig, V.; Herdegen, T. Context-specific inhibition of JNKs: Overcoming the dilemma of protection and damage. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guma, M.; Ronacher, L.M.; Firestein, G.S.; Karin, M.; Corr, M. JNK-1 deficiency limits macrophage-mediated antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Boehm, I.; Oakley, A.; Ketterman, A.J.; Barr, R.K. Targeting the JNK MAPK cascade for inhibition: Basic science and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1697, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Zhang, Q.G. Agents targeting c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway as potential neuroprotectants. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 14, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.X.; Zou, F.M.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.M.; Tu, M. JNK pathway in osteoarthritis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects. J. Recept. Signal. Transduct. Res. 2017, 37, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinas, G.; Becattini, B. JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, U.K.; Kini, S.G.; Garg, V.; Agrawal, S.; Tomar, P.K.; Pathak, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Gupta, P.; Malik, A. JNK pathway signaling: A novel and smarter therapeutic targets for various biological diseases. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 2065–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, W.; Jacevic, V.; Franca, T.C.C.; Wang, X.; Kuca, K. Selective inhibitors for JNK signalling: A potential targeted therapy in cancer. J. Enzym. Inhib Med. Chem 2020, 35, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plotnikov, M.B.; Aliev, O.I.; Shamanaev, A.Y.; Sidekhmenova, A.V.; Anishchenko, A.M.; Fomina, T.I.; Rydchenko, V.S.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Anfinogenova, Y.J.; Schepetkin, I.A.; et al. Antihypertensive activity of a new c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikov, M.B.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Aliev, O.I.; Smol’iakova, V.I.; Fomina, T.I.; Osipenko, A.N.; Rydchenko, V.S.; Anfinogenova, Y.J.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Schepetkin, I.A.; et al. Protective effects of a new c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor in the model of global cerebral ischemia in rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotnikov, M.B.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Smolyakova, V.I.; Aliev, O.I.; Trofimova, E.S.; Sherstoboev, E.Y.; Osipenko, A.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Anfinogenova, Y.J.; Schepetkin, I.A.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of a novel inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Cells 2020, 9, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeldt, S.C.H.; Majolo, F.; Goettert, M.I.; Laufer, S. c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors as potential leads for new therapeutics for Alzheimer’s diseases. Int J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Xia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. JNK selective inhibitor, IQ-1S, protects the mice against lipopolysaccharides-induced sepsis. Bioorg Med. Chem 2021, 30, 115945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoGrasso, P.; Kamenecka, T. Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK). Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, M.; Kuramoto, K.; Takeda, H.; Watarai, H.; Sakaki, H.; Seino, S.; Seino, M.; Suzuki, S.; Kitanaka, C. The novel JNK inhibitor AS602801 inhibits cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27021–27032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Messoussi, A.; Feneyrolles, C.; Bros, A.; Deroide, A.; Dayde-Cazals, B.; Cheve, G.; Van Hijfte, N.; Fauvel, B.; Bougrin, K.; Yasri, A. Recent progress in the design, study, and development of c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Chem Biol 2014, 21, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prause, M.; Christensen, D.P.; Billestrup, N.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. JNK1 protects against glucolipotoxicity-mediated beta-cell apoptosis. Plos One 2014, 9, e87067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, D.; Hao, F.; Hu, C.; Kong, W.; Xu, X.; Cui, M.Z. JNK1 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced CD14 and SR-AI expression and macrophage foam cell formation. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lemos, L.; Junyent, F.; Camins, A.; Castro-Torres, R.D.; Folch, J.; Olloquequi, J.; Beas-Zarate, C.; Verdaguer, E.; Auladell, C. Neuroprotective effects of the absence of JNK1 or JNK3 isoforms on kainic acid-induced temporal lobe epilepsy-like symptoms. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Cai, L.; Li, J.T.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.Y.; Wang, T.H. JNK3 involvement in nerve cell apoptosis and neurofunctional recovery after traumatic brain injury star. Neural Regen Res. 2013, 8, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, D.; Luque, M.; Pedros, I.; Ettcheto, M.; Abad, S.; Pallas, M.; Verdaguer, E.; Auladell, C.; Folch, J.; Camins, A. Evaluation of the role of JNK1 in the hippocampus in an experimental model of familial Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.L.; Sasaki, D.T.; Murray, B.W.; O’Leary, E.C.; Sakata, S.T.; Xu, W.; Leisten, J.C.; Motiwala, A.; Pierce, S.; Satoh, Y.; et al. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2001, 98, 13681–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczepankiewicz, B.G.; Kosogof, C.; Nelson, L.T.; Liu, G.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Serby, M.D.; Xin, Z.; Liu, M.; Gum, R.J.; et al. Aminopyridine-based c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors with cellular activity and minimal cross-kinase activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3563–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.W.; Pachori, A.; Howard, S.; Ganno, M.; Hansen, D., Jr.; Kamenecka, T.; Song, X.; Duckett, D.; Chen, W.; Ling, Y.Y.; et al. Small molecule c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitors protect dopaminergic neurons in a model of Parkinson’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Hanks, T.S.; Kochetkova, I.; Pascual, D.W.; Jutila, M.A.; Quinn, M.T. Identification and characterization of a novel class of c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 81, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Potapov, A.S.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Matveevskaya, V.V.; Belyanin, M.L.; Atochin, D.N.; Zanoza, S.O.; Gaidarzhy, N.M.; Lyakhov, S.A.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling of 11H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one derivatives and tryptanthrin-6-oxime as c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Eur J. Med. Chem 2019, 161, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansideri, F.; Dammann, M.; Boeckler, F.M.; Koch, P. Fluorescence polarization-based competition binding assay for c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1 and 2. Anal. Biochem 2017, 532, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirpotina, L.N.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Hammaker, D.; Kuhs, A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Quinn, M.T. Therapeutic effects of tryptanthrin and tryptanthrin-6-oxime in models of rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Hammaker, D.; Kochetkova, I.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Lyakhov, S.A.; Firestein, G.S.; Quinn, M.T. Anti-inflammatory effects and joint protection in collagen-induced arthritis after treatment with IQ-1S, a selective c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearson, B.D. Indenoquinolines. III. Derivatives of 11H-indeno-[1,2-b]quinoxaline and related indenoquinolines. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Obi-Egbedi, N.O. Indeno-1-one [2,3-b]quinoxaline as an effective inhibitor for the corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 122, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.S.; Li, X.; Li, Z.H.; Yu, Y.C.; You, Q.D.; Zhang, X.J. Discovery of nonquinone substrates for NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) as effective intracellular ROS generators for the treatment of drug-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 11280–11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deady, L.W.; Desneves, J.; Ross, A.C. Synthesis of some 11H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-ones. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 9823–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Tzeng, C.C.; Liu, W.; Chou, C.K.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, Y.L. Discovery of indeno[1,2-b]quinoxaline derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Eur J. Med. Chem 2016, 108, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatunga, M.K.P.; Thompson, S.; McKee, T.C.; Chan, M.C.; Reece, K.M.; Hardy, A.P.; Sekirnik, R.; Seden, P.T.; Cook, K.M.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Inhibition of the HIF1 alpha-p300 interaction by quinone- and indandione-mediated ejection of structural Zn(II). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 94, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matthies, D.; Hain, K. Amidoalkylierende derivate des ninhydrins. Synthesis 1973, 1973, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macrae, C.F.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Shields, G.P.; Taylor, R.; Towler, M.; van De Streek, J. Mercury: Visualization and analysis of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, F.H.; Kennard, O.; Watson, D.G.; Brammer, L.; Orpen, A.G.; Taylor, R. Tables of bond lengths determined by X-ray and neutron-diffraction. Part 1. Bond lengths in organic compounds. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1987, S1–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimhoffer, Á.; Rusznyák, Á.; Réti-Nagy, K.; Vasvári, G.; Váradi, J.; Vecsernyés, M.; Bácskay, I.; Fehér, P.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Fenyvesi, F. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery systems and their effects on biological barriers. Sci. Pharma. 2019, 87, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duma, H.I.; Sazonov, K.D.; Liakhov, L.S.; Toporov, S.V.; Liakhov, S.A. 6- and 7-aminomethyl-11H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxaline-11-ones—synthesis, DNA affinity and toxicity. Odesa Natl. Univ. Herald. Chem. 2020, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabatsos, G.J.; Taller, R.A. Structural studies by nuclear magnetic resonance. 15. Conformations and configurations of oximes. Tetrahedron 1968, 24, 3347–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doogue, M.P.; Polasek, T.M. The ABCD of clinical pharmacokinetics. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2013, 4, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, M.W.; Herrgard, S.; Treiber, D.K.; Gallant, P.; Atteridge, C.E.; Campbell, B.T.; Chan, K.W.; Ciceri, P.; Davis, M.I.; Edeen, P.T.; et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab-initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular-dichroism spectra using density-functional force-fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.A.; Dunning, T.H.; Harrison, R.J. Electron-affinities of the 1st-row atoms revisited – systematic basis-sets and wave-functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 96, 6796–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woon, D.E.; Dunning, T.H. Gaussian-basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. III. The atoms aluminum through argon. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
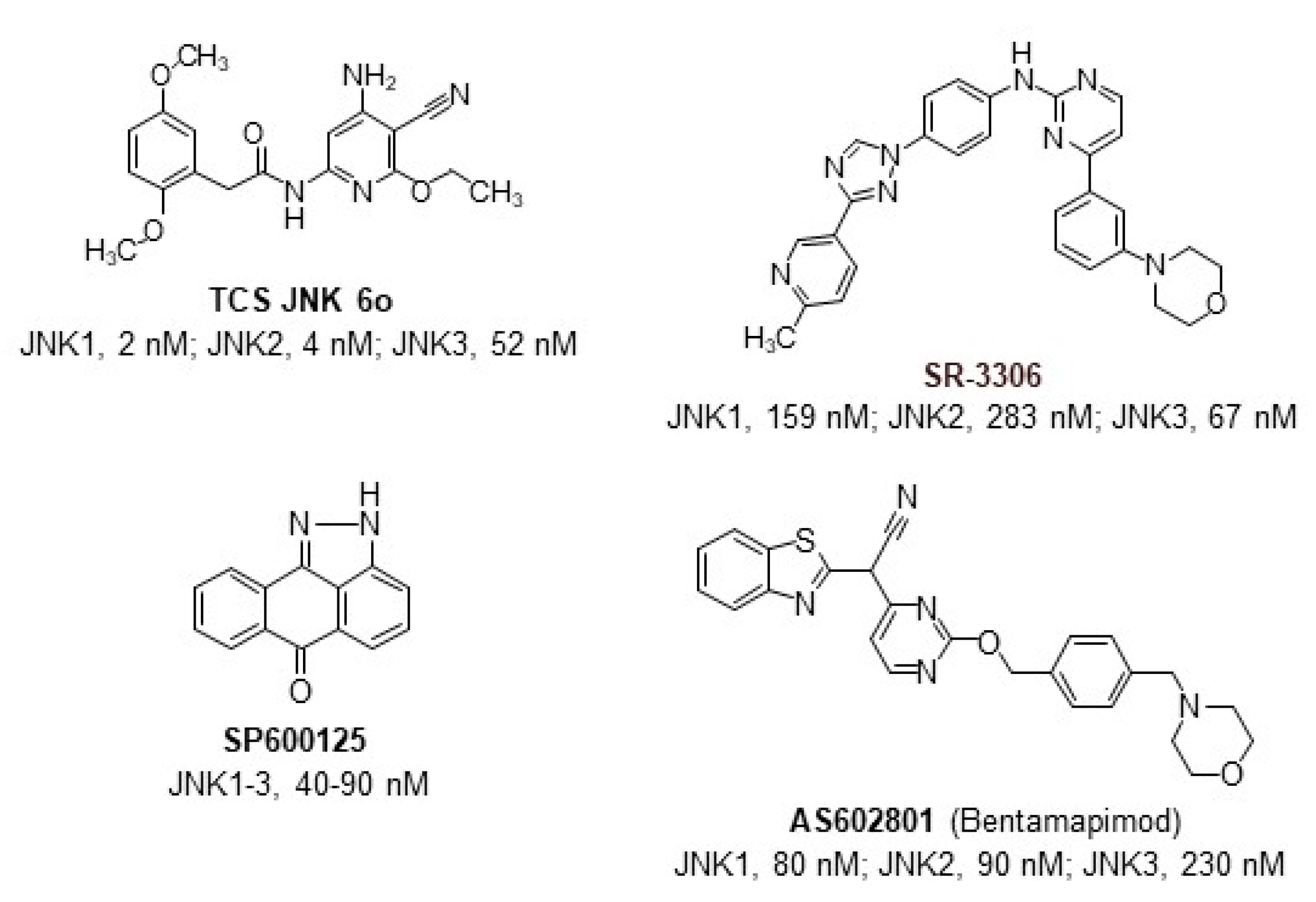





 |  | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound C | |||||||
| R1 | R2 | R3 | Kd (µM) | ||||
| JNK1 | JNK2 | JNK3 | |||||
| IQ-1 | H | H | H | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | |
| A | H | H | COOH | 2.1 | 6.0 | 3.9 | |
| B | H | NO2 | H | 6.0 | 12.0 | 4.3 | |
| C | H | H | Cl | 1.1 | 21.5 | 0.7 | |
| D | H | CH3 | H | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.3 | |
| E | H | OC2H5 | H | 2.3 | 2.0 | 0.9 | |
| F | CH3 | H | H | 3.3 | 2.5 | 6.0 | |
| G | H | CH3 | CH3 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 1.3 | |
| Diamine | Mulliken Charges on Nitrogen Atoms a | |
|---|---|---|
| N1 | N2 | |
| 2a | −0.086 | −0.072 |
| 2b | −0.117 | −0.060 |
| 2c | −0.090 | −0.097 |
| 2d | −0.033 | −0.006 |
| 2e | −0.076 | −0.118 |
| 2f | −0.077 | −0.077 |
| 2g | −0.077 | −0.092 |
| 2h | −0.107 | 0.015 |
| 2i | −0.100 | −0.034 |
| 2j | −0.121 | 0.003 |
| 2k | −0.034 | −0.084 |
| 2n | −0.101 b | 0.041 c |

| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | JNK1 | JNK2 | JNK3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd (µM) | ||||||
| IQ-1 * | H | H | H | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.10 |
| 4a | H | F | H | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 |
| 4b | Cl | H | H | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| 4c | CH3 | H | Br | N.B. | N.B. | N.B. |
| 4d | H | t-Bu | H | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 3.1 ± 0.2 |
| 4e | F | H | F | 0.92 ± 0.05 | 1.6 ± 0.01 | 0.9 ± 0.3 |
| 4f | H | F | F | 0.17 ± 0.04 | N.B. | 0.52 ± 0.3 |
| 4g | F | F | H | 0.52 ± 0.09 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
| 4h | Br | H | CF3 | N.B. | N.B. | N.B. |
| 4i | Cl | H | CF3 | N.B. | N.B. | N.B. |
| 4j | CF3 | H | CF3 | N.B. | N.B. | N.B. |
| 4k | H | F | Cl | N.B. | N.B. | 24.5 ± 2.1 |
| 4l | H | H | COOCH3 | 0.91 ± 0.16 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 0.71 ± 0.05 |
| 4m | CH2MRF | H | H | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.88 ± 0.10 | 0.91 ± 0.3 |
| Compound | THP-1Blue Cell Cytotoxicity | MonoMac-6 Cell Cytotoxicity | THP-1Blue Cell NF-κB/AP-1 | MonoMac-6 Cell IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | ||||
| IQ-1 | N.T | N.T | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 3.4 ± 0.8 |
| 4a | N.T. | N.T. | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.6 |
| 4b | N.T. | N.T. | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.4 |
| 4c | 37.5 ± 1.7 | 14.6 ± 1.2 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 4d | N.T. | N.T. | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| 4e | N.T. | N.T. | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| 4f | N.T. | N.T. | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 14.0 ± 2.8 |
| 4g | N.T. | 32.0 ± 2.2 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | n.d. |
| 4h | N.T. | 29.0 ± 2.5 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | n.d. |
| 4i | N.T. | N.T. | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 6.2 ± 0.2 |
| 4j | 36.5 ± 1.9 | N.T. | n.d. | 4.8 ± 0.5 |
| 4k | N.T. | N.T. | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.4 |
| 4l | 26.1 ± 5.3 | N.T. | n.d. | N.A. |
| 4m | N.T. | N.T. | 0.1 ± 0.05 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| Property | 4b | 4f | 4m |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | C15H8ClN3O | C15H7F2N3O | C20H18N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 281.70 | 283.23 | 346.38 |
| Heavy Atoms | 20 | 21 | 26 |
| Fraction Csp3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.25 |
| Rotatable bonds | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| H-bond Acceptors | 4 | 6 | 6 |
| H-bond Donors | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Molar Refractivity | 77.41 | 72.32 | 102.38 |
| Topological Polar Surface Area (tPSA, Å2) | 58.37 | 58.37 | 70.84 |
| Lipophilicity (Consensus Log Po/w) | 3.08 | 3.16 | 2.39 |
| BBB Permeation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liakhov, S.A.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Karpenko, O.S.; Duma, H.I.; Haidarzhy, N.M.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Bagryanskaya, I.Y.; Quinn, M.T. Novel c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitors with an 11H-Indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one Scaffold. Molecules 2021, 26, 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185688
Liakhov SA, Schepetkin IA, Karpenko OS, Duma HI, Haidarzhy NM, Kirpotina LN, Kovrizhina AR, Khlebnikov AI, Bagryanskaya IY, Quinn MT. Novel c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitors with an 11H-Indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one Scaffold. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185688
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiakhov, Serhii A., Igor A. Schepetkin, Olexander S. Karpenko, Hanna I. Duma, Nadiia M. Haidarzhy, Liliya N. Kirpotina, Anastasia R. Kovrizhina, Andrei I. Khlebnikov, Irina Y. Bagryanskaya, and Mark T. Quinn. 2021. "Novel c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitors with an 11H-Indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one Scaffold" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185688
APA StyleLiakhov, S. A., Schepetkin, I. A., Karpenko, O. S., Duma, H. I., Haidarzhy, N. M., Kirpotina, L. N., Kovrizhina, A. R., Khlebnikov, A. I., Bagryanskaya, I. Y., & Quinn, M. T. (2021). Novel c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitors with an 11H-Indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one Scaffold. Molecules, 26(18), 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185688









