Ameliorating Effect on Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Mice by Litsea cubeba Persoon Powder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Preparation and Evaluation of L. cubeba Persoon Fruit Essential Oil
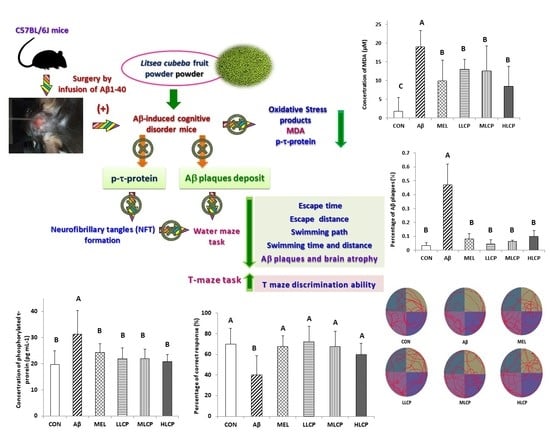
2.2. Animals and Intra-Cerebroventricular Aβ1–40 Induced Surgery Model
2.3. Administration Dosages
2.4. Water Maze Test
2.5. Reference Memory Test
2.6. Probe Test
2.7. T-Maze Test
2.8. Sacrifice and Tissue Collection
2.9. Analyses of Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.10. Determination of MDA Content in the Brain
2.11. Determination of Protein Carbonyl and Phosphorylated τ-Protein Contents in Brain
2.12. Immunohistochemical Staining of Aβ1–40 in the Brain
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Proximate Analyses and Essential Oil Content of LCP Fruits
3.2. Effects on Body Weight, Food Intake, and Relative Organ Weight
3.3. Effects on Serum Biochemical Values
3.4. Effects on Escape Time and of Reference Memory Task
3.5. Effects on Swimming Path/Time and Crossing Frequency
3.6. Effects on T-Maze Discrimination Task
3.7. Effects on the Concentration of Lipid Peroxidation Products, Protein Carbonyl, and Phosphorylated τ-Protein
3.8. Effects on Aβ Plaque Accumulation in the Brain
4. Discussion
4.1. Brain Tissue Weight and Serum Biochemical Parameters
4.2. Behavior Evaluation and Dose-Related Response
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sosa-Ortiz, A.L.; Castillo, G.I.A.; Prince, M. Epidemiology of Dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch. Med Res. 2012, 43, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthey, B. Background Paper 6.11: Alzheimer Disease and Other Dementias. A Public Health Approach to Innovation; Update on 2004 Background Paper; 2013; pp. 1–74. Available online: http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/prioritymedicines/BP611Alzheimer.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2013).
- Prince, M.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.C.; Wu, Y.T.; Matthew, P. World Alzheimer Report: The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends; Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI): London, UK, 2015; pp. 10–29. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prince, M.; Jackson, J. World Alzheimer Report: The Global Prevalence of Dementia; Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI): London, UK, 2009; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pohanka, M. Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders: Implication and counteracting of melatonin. J. Appl. Biomed. 2011, 9, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimova, B.; Kuca, K. Speech and language impairments in dementia. J. Appl. Biomed. 2016, 14, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfurth, H.W.; Laferla, F.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Berlett, B.S. Reactive Oxygen-Mediated Protein Oxidation in Aging and Disease. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1997, 10, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A.D.G.; Colombo, R. Protein carbonyl groups as biomarkers of oxidative stress. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 329, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-T.; Chu, F.-H. Molecular cloning and characterization of monoterpene synthases from Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Persoon. Tree Genet. Genomes 2011, 7, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-K.; Choi, E.-M.; Lee, J.H. Antioxidant activity of Litsea cubeba. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zeng, K.; Gao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chai, X.; Tu, P. Chemical constituents with NO production inhibitory and cytotoxic activities from Litsea cubeba. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 69, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobetsberger, C.; Buchbauer, G. Actions of essential oils on the central nervous system: An updated review. Flavour Fragr. J. 2011, 26, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.B.; Case, J.D.; Heinzelman, R.V. STRUCTURE OF MELATONIN1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 6084–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Huang, F. Anti-Amyloidogenic and Anti-Apoptotic Role of Melatonin in Alzheimer Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bejarano, I.; Monllor, F.; Marchena, A.M.; Ortiz, A.; Lozano, G.; Jiménez, M.I.; Gaspar, P.; García, J.F.; Pariente, J.A.; Rodríguez, A.B.; et al. Exogenous melatonin supplementation prevents oxidative stress-evoked DNA damage in human spermatozoa. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, C.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Antolin, I.; Herrera, F.; Martin, V.; Reiter, R.J. Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: A significant role for melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Leon, J.; Czarnocki, Z. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Biochemical mechanisms and pathophysiological implications in humans. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2003, 50, 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karolczak, K.; Watala, C. Melatonin as a Reducer of Neuro- and Vasculotoxic Oxidative Stress Induced by Homocysteine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, K.; Mogi, M.; Iwanami, J.; Min, L.-J.; Sakata, A.; Jing, F.; Iwai, M.; Horiuchi, M. Cognitive Deficit in Amyloid-β–Injected Mice Was Improved by Pretreatment With a Low Dose of Telmisartan Partly Because of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Activation. Hypertension 2009, 54, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Song, L.; Lim, G.; Tan, Y.; You, Z.; Chen, L.; Mao, J. Exacerbated mechanical hyperalgesia in rats with genetically predisposed depressive behavior: Role of melatonin and NMDA receptors. Pain 2012, 153, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis. In Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 15th ed.; AOAC International: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.H.; Huang, P.C.; Mau, J.L.; Chiang, S.S. Effect of king oyster mushroom Pleurotus eryngii basidiocarp powder to ameliorate memory and learning deficit inability in Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s disease C57BL/6J mice model. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2020, 22, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.B.; Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain: In Stereotaxic Coordinates; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-J.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chu, F.-H.; Wen, T.-Y.; Cheng, W.-W.; Chen, Y.-T.; Tsao, N.-W.; Wang, S.-Y. Neuropharmacological activities of fruit essential oil from Litsea cubeba Persoon. J. Wood Sci. 2012, 58, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Jiang, L.-K.; Zou, G.-L. Acute and Genetic Toxicity of Essential Oil Extracted from Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Pers. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M.J.; Rawlins, J.N.P. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-T.; Yang, T.-S. Antimicrobial impact of the components of essential oil of Litsea cubeba from Taiwan and antimicrobial activity of the oil in food systems. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils from Different Parts of Litsea cubeba. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Wang, C.F.; You, C.X.; Geng, Z.F.; Sun, R.Q.; Guo, S.S.; Du, S.S.; Liu, Z.L.; Deng, Z.W. Bioactivity of essential oil of Litsea cubeba from China and its main compounds against two stored product insects. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lessard-Beaudoin, M.; Laroche, M.; Demers, M.-J.; Grenier, G.; Graham, R.K. Characterization of age-associated changes in peripheral organ and brain region weights in C57BL/6 mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 63, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, N.C.; Warrington, E.K.; Freeborough, P.A.; Hartikainen, P.; Kennedy, A.M.; Stevens, J.M.; Rossor, M.N. Presymptomatic hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 1996, 119, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhoo, J.H.; Kim, H.-C.; Nabeshima, T.; Yamada, K.; Shin, E.-J.; Jhoo, W.-K.; Kim, W.; Kang, K.-S.; Jo, S.A.; Woo, J.I. β-Amyloid (1–42)-induced learning and memory deficits in mice: Involvement of oxidative burdens in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 155, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyras, L.; Cairns, N.J.; Jenner, A.; Jenner, P.; Halliwell, B. An assessment of oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA in the brain from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Stadtman, E.R. Protein oxidation processes in the aging brain. Adv. Cell Aging Gerontol. 1997, 2, 161–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Fukumoto, S.; Yokogoshi, H. Components of lemon essential oil attenuate dementia induced by scopolamine. Nutr. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuhamdah, S.; Abuhamdah, R.; Howes, M.J.; Al-Olimat, S.; Ennaceur, A.; Chazot, P.L. Pharmacological and neuroprotective profile of an essential oil derived from leaves of Aloysia citrodora Palau. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seal, T.; Chaudhuri, K.; Pillai, B.; Chakrabarti, S.; Mondal, T.; Auddy, B. Evaluation of antioxidant activities, toxicity studies and the DNA damage protective effect of various solvent extracts of Litsea cubeba fruits. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Composition | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 65.26 ± 0.04 |
| Crude ash | 1.10 ± 0.08 |
| Crude protein | 4.37 ± 0.10 |
| Crude fat | 10.18 ± 0.27 |
| Carbohydrate | 19.07 ± 0.23 |
| Essential oil recovery | 3.80 ± 0.13 |
| Times Ordinal | CON | Aβ | MEL | LLCP | MLCP | HLCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escape Latency (sec) | ||||||
| First day | a 76.46 ± 12.37 A | a 84.31 ± 10.66 A | a 77.09 ± 11.99 A | a 80.50 ± 14.32 A | a 80.25 ± 6.49 A | a 74.31 ± 14.54 A |
| Second day | b 30.31 ± 10.43 D | a 85.37 ± 6.95 A | b 48.40 ± 23.26 BC | b 37.40 ± 15.36 CD | b 49.93 ± 15.80 BC | b 56.40 ± 12.09 B |
| Third day | c 17.34 ± 10.07 C | a 77.56 ± 14.62 A | c 20.06 ± 9.85 C | c 21.25 ± 10.61 C | c 20.09 ± 7.70 C | c 33.62 ± 11.64 B |
| Escape Distance (m) | ||||||
| First day | a 9.73 ± 1.33 A | ab 10.33 ± 2.10 A | a 10.74 ± 1.57 A | a 10.30 ± 1.94 A | a 10.72 ± 1.43 A | a 9.39 ± 1.24 A |
| Second day | b 5.31 ± 1.45 C | a 10.71 ± 1.73 A | b 7.36 ± 3.21 BC | b 5.52 ± 1.66 C | b 08.55 ± 1.45 B | a 8.67 ± 1.95 B |
| Third day | c 3.00 ± 1.71 C | b 8.24 ± 2.29 A | c 2.90 ± 1.56 C | c 3.23 ± 1.65 C | c 3.52 ± 1.27 BC | b 5.07 ± 1.68 B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-T.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chiang, S.-S. Ameliorating Effect on Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Mice by Litsea cubeba Persoon Powder. Molecules 2021, 26, 5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185709
Lee K-T, Chu C-Y, Chiang S-S. Ameliorating Effect on Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Mice by Litsea cubeba Persoon Powder. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185709
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kuan-Tseng, Chen-Yeon Chu, and Shen-Shih Chiang. 2021. "Ameliorating Effect on Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Mice by Litsea cubeba Persoon Powder" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185709
APA StyleLee, K.-T., Chu, C.-Y., & Chiang, S.-S. (2021). Ameliorating Effect on Aβ-Induced Alzheimer’s Mice by Litsea cubeba Persoon Powder. Molecules, 26(18), 5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185709