Cajanin Suppresses Melanin Synthesis through Modulating MITF in Human Melanin-Producing Cells
Abstract
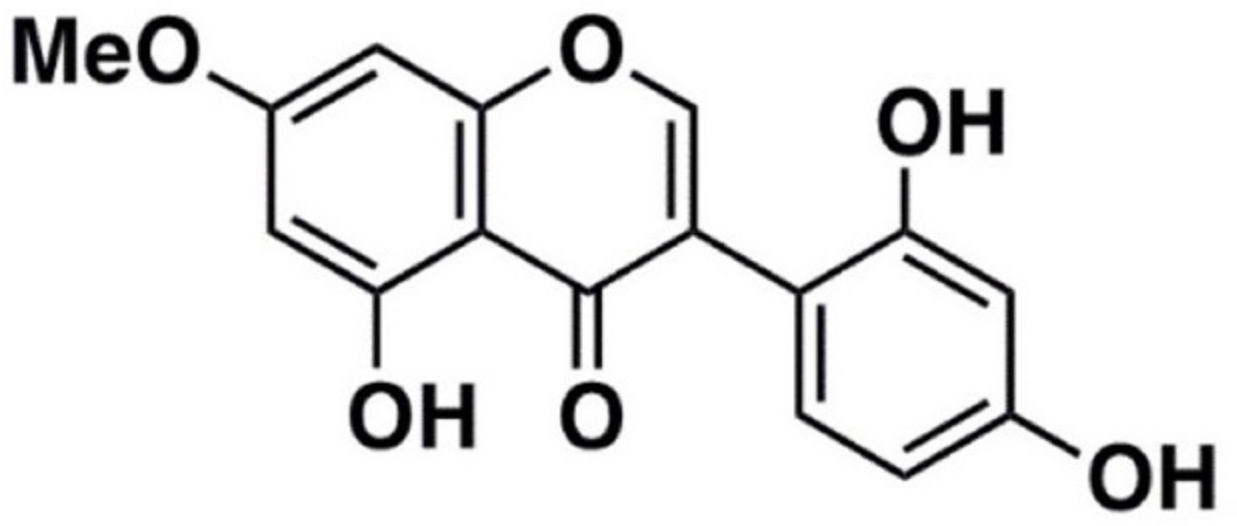
:1. Introduction
2. Results
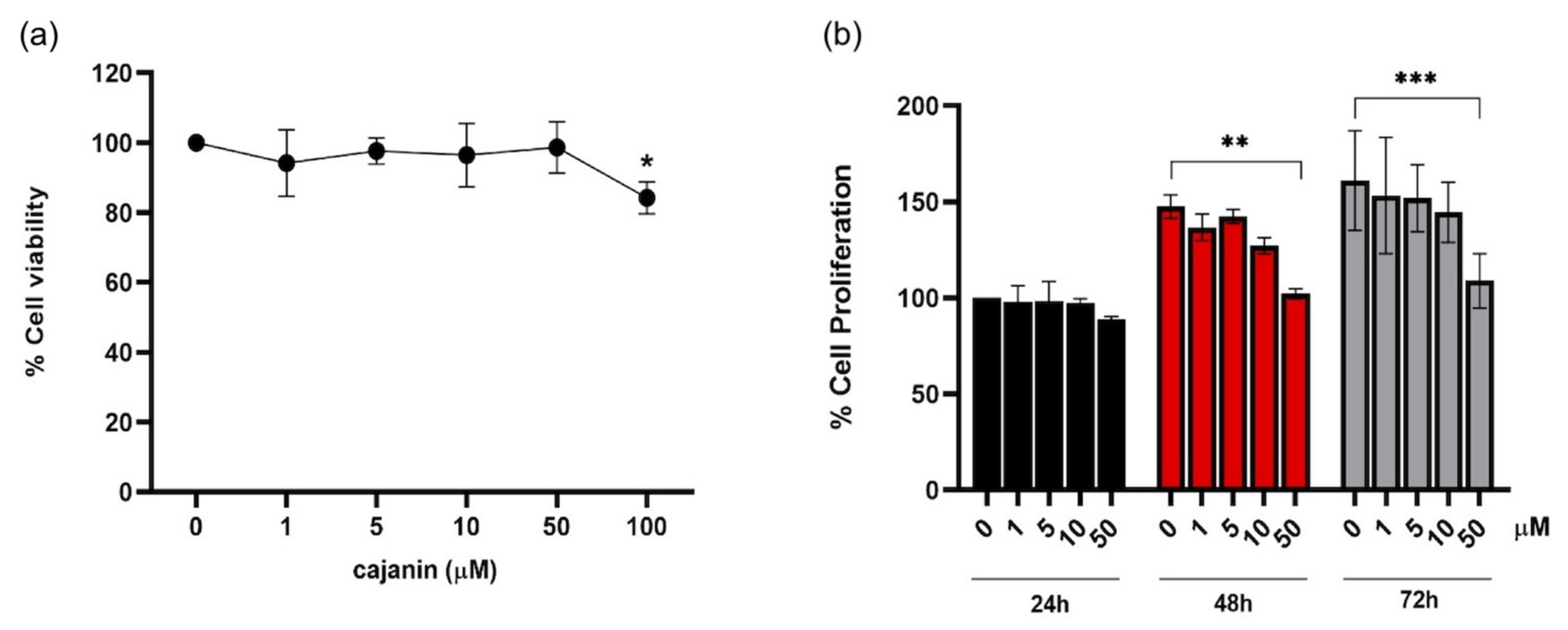
2.1. Antiproliferative Effect of Cajanin in Human Melanoma MNT1 Cells
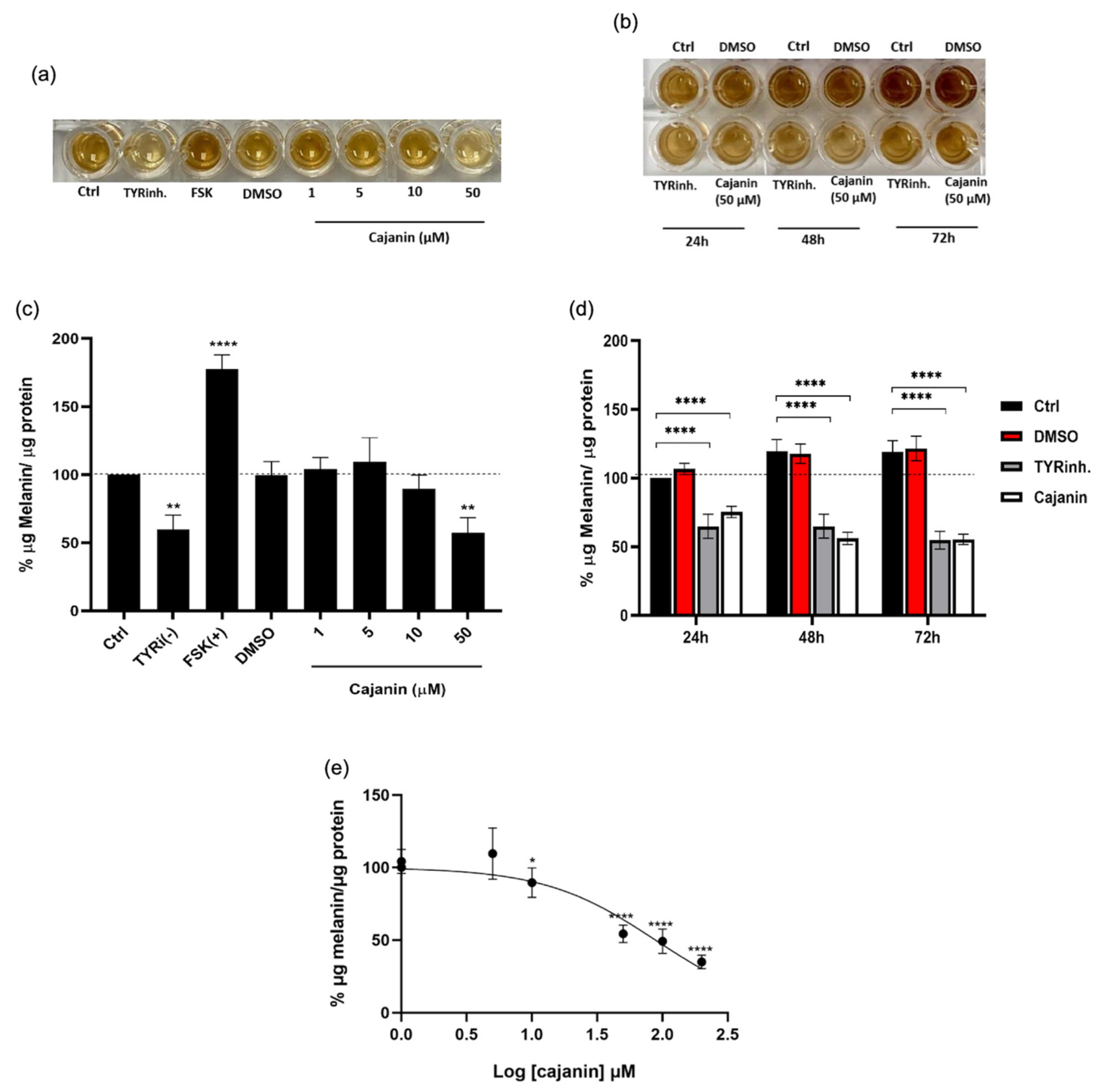
2.2. Cajanin Diminishes Melanin Content in Human Melanin-Producing Cells
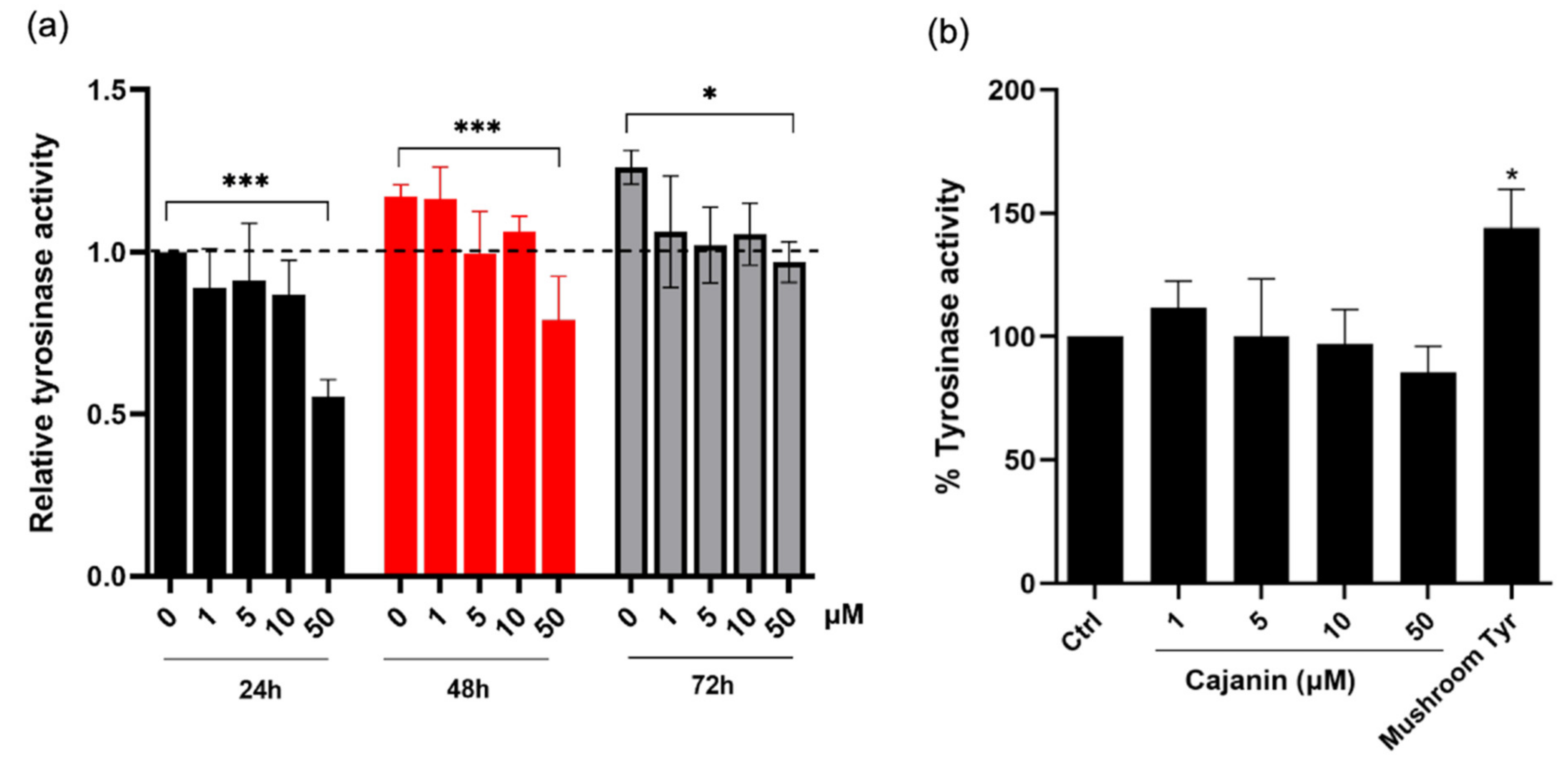
2.3. Cellular Tyrosinase Activity Suppressed by Cajanin
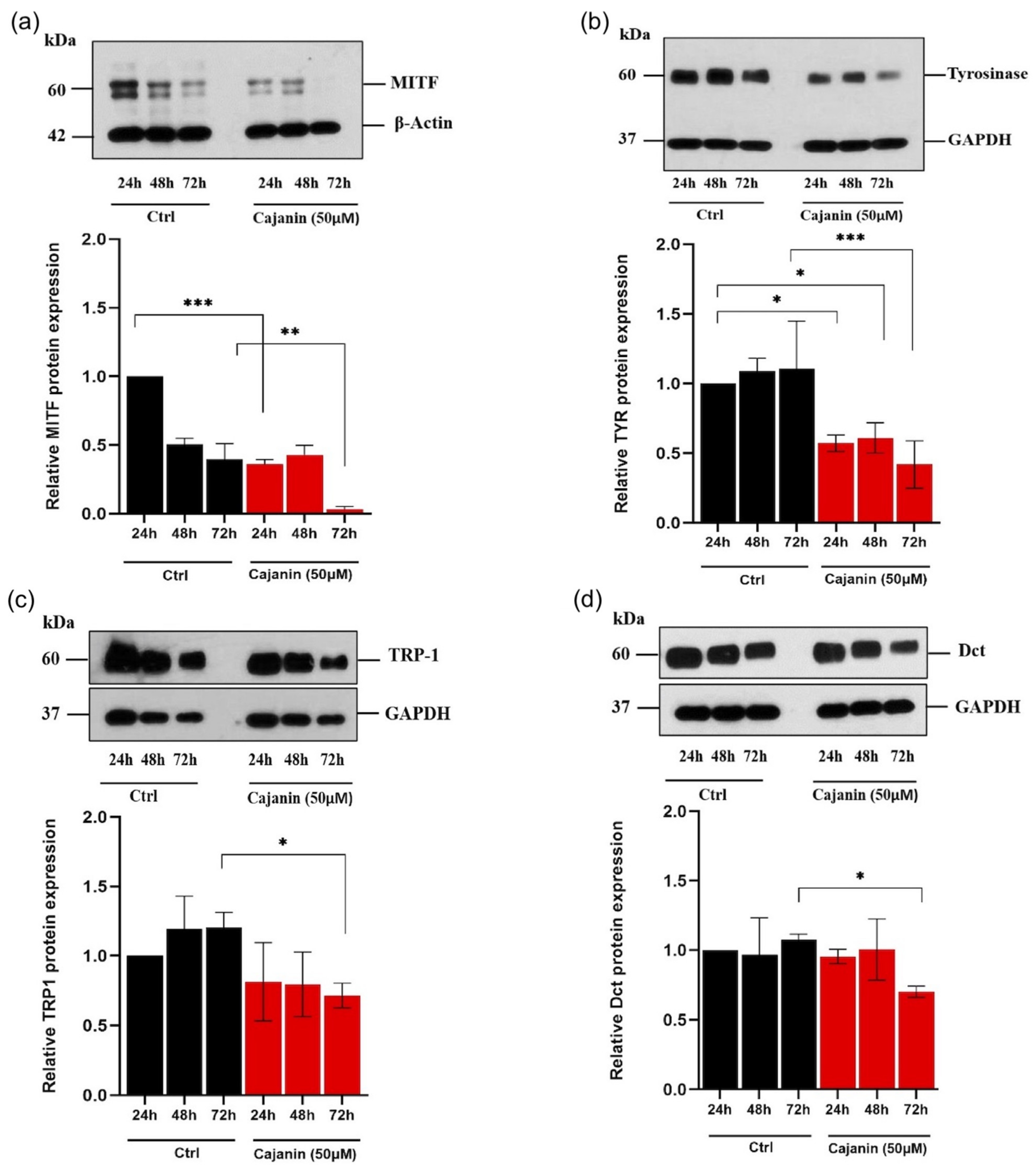
2.4. Effects of Cajanin on Melanogenesis-Related Proteins in Human MNT1 Cells
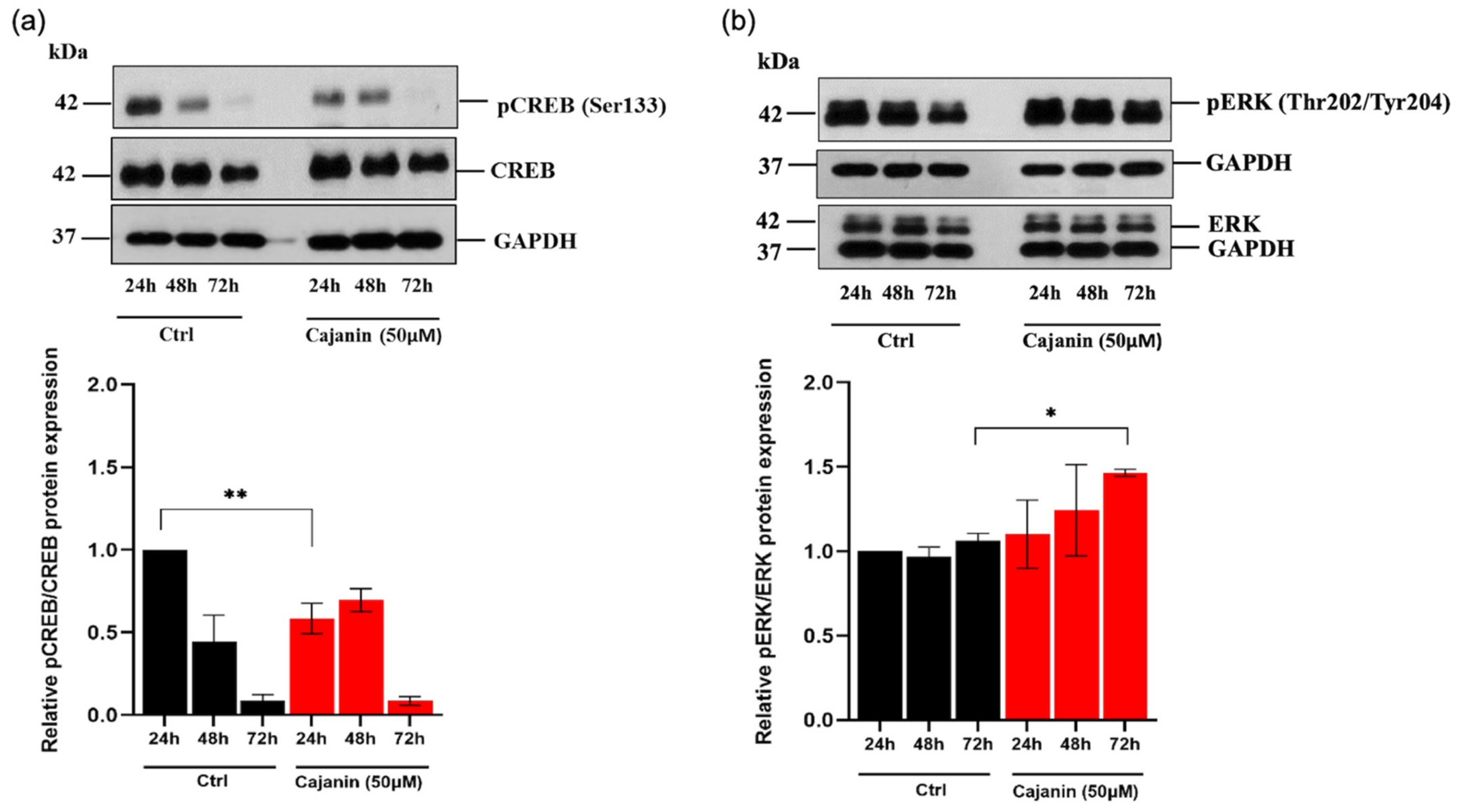
2.5. Cajanin Modulates MITF Regulating Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability and Proliferation Assay
4.4. Determination of Cellular Melanin Content
4.5. Cell-Free Tyrosinase Activity Assay
4.6. Evaluation on Cellular Tyrosinase Activity
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
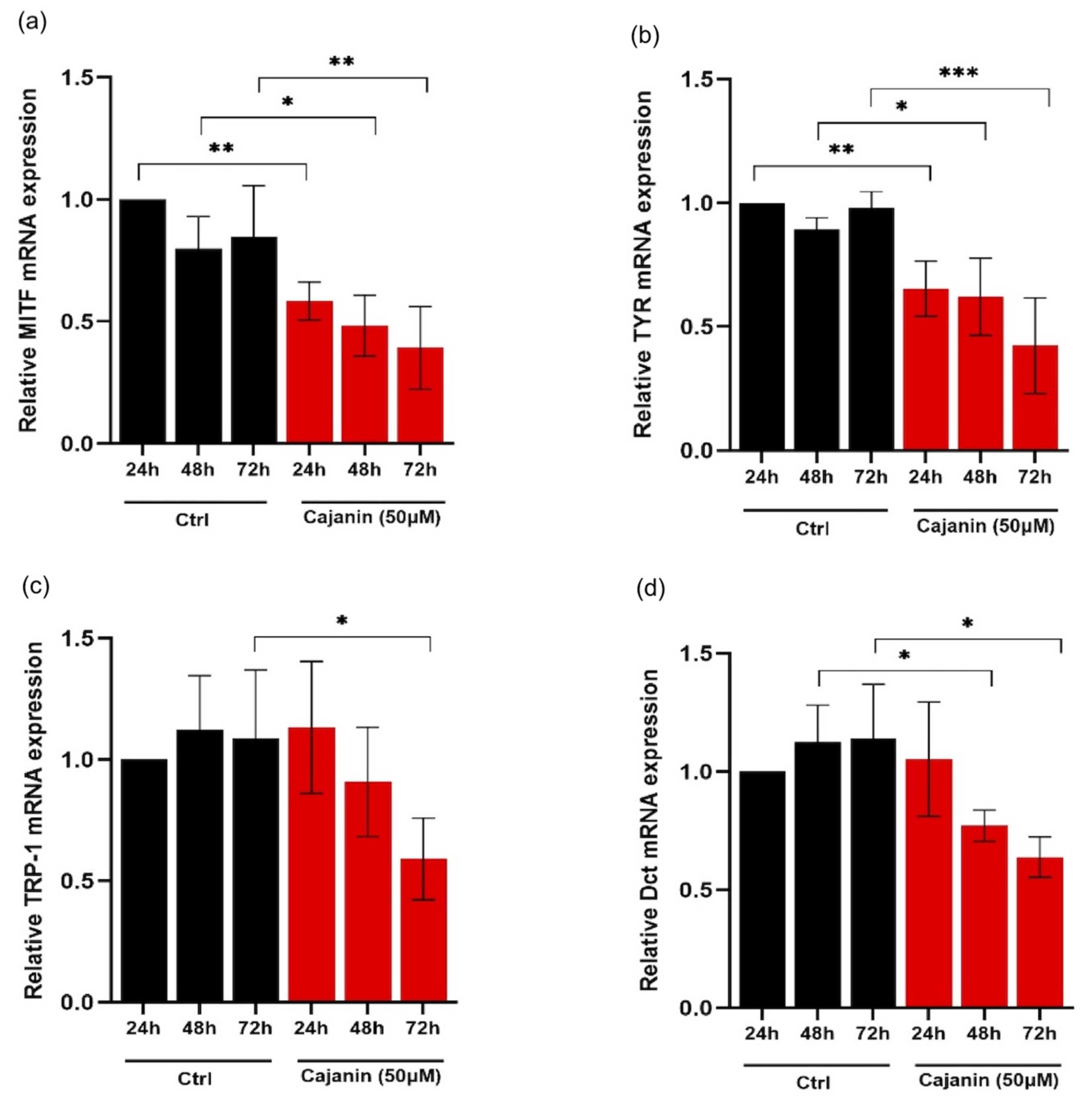
4.8. Determination of mRNA Expression Level by RT-qPCR
- -
- Human GAPDH forward primer: 5′-GAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCA-3′
- -
- Human GAPDH reverses primer: 5′-TTCAGCTCAGGGATGACCTT-3′
- -
- Human MITF forward primer: 5′-TCATCCAAAGATCTGGGCTATGACT-3′
- -
- Human MITF reverse primer: 5′-GTGACGACACAGCAAGCTCAC-3′
- -
- Human tyrosinase forward primer: 5′-TCATCCAAAGATCTGGGCTATGACT-3′
- -
- Human tyrosinase reverse primer: 5′-GTGACGACACAGCAAGCTCAC-3′
- -
- Human TRP-1 forward primer: 5′-AAGGCTACAACAAAAATCACCAT-3′
- -
- Human TRP-1 reverse primer: 5′-ATTGAGAGGCAGGGAAACAC-3′
- -
- Human Dct forward primer: 5′-GCAGCAAGAGATACACAGAAGAA-3′
- -
- Human Dct reverse primer: 5′-TCCTTTATTGTCAGCGTCAGA-3′
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, A.G.; Guevara, I.L. Disorders of hyperpigmentation. Dermatol. Clin. 2000, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Kang, M.; Chung, H.S.; Cho, C.; Hong, M.C.; Shin, M.K.; Bae, H. Survey and mechanism of skin depigmenting and lightening agents. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Arora, P.; Garg, K.V. Cosmeceuticals for hyperpigmentation: What is available? J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 6, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korner, A.; Pawelek, J. Mammalian tyrosinase catalyzes three reactions in the biosynthesis of melanin. Science 1982, 217, 1163–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Kamiya, T.; Kawakami, A.; Ogino, J.; Sohma, H.; Uhara, H.; Jimbow, K. Elucidation of melanogenesis cascade for identifying pathophysiology and therapeutic approach of pigmentary disorders and melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, B.J.; Ben-David, Y. The Role of DCT/TYRP2 in resistance of melanoma cells to drugs and radiation. In From Melanocytes to Melanoma: The Progression to Malignancy; Hearing, V.J., Leong, S.P.L., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widlund, H.R.; Fisher, D.E. Microphthalamia-associated transcription factor: A critical regulator of pigment cell development and survival. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3035–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ullah, S.; Chung, Y.C.; Hyun, C.G. Induction of melanogenesis by fosfomycin in B16F10 cells through the upregulation of p-JNK and p-p38 signaling pathways. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.S. Natural melanogenesis inhibitors acting through the down-regulation of tyrosinase activity. Materials 2012, 5, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, C.I.; Setaluri, V. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling in melanocytes and melanoma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 563, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, T.Y.; Yoon, T.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, M.R.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, C.H. Downregulation of melanin synthesis by haginin A and its application to in vivo lightening model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.S.; Park, M.; Han, J.; Lee, J.H.; Bae, I.H.; Choi, H.; Son, E.D.; Park, Y.H.; Lim, K.M. Liver X receptor activation inhibits melanogenesis through the acceleration of ERK-mediated MITF degradation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Guan, D.; Meng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Jia, H.; Dou, K.; Liu, C.; et al. MITF-siRNA formulation is a safe and effective therapy for human melasma. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Liu, W.; Zhu, D.; Cao, Y.; Tang, A.; Gong, G.; Su, H. Natural skin-whitening compounds for the treatment of melanogenesis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujimoto, N.; Watanabe, H.; Nakatani, T.; Roy, G.; Ito, A. Induction of thyroid tumours in (C57BL/6N × C3H/N)F1 mice by oral administration of kojic acid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promden, W.; Viriyabancha, W.; Monthakantirat, O.; Umehara, K.; Noguchi, H.; De-Eknamkul, W. Correlation between the potency of flavonoids on mushroom tyrosinase inhibitory activity and melanin synthesis in melanocytes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoek, K.; Rimm, D.L.; Williams, K.R.; Zhao, H.; Ariyan, S.; Lin, A.; Kluger, H.M.; Berger, A.J.; Cheng, E.; Trombetta, E.S.; et al. Expression profiling reveals novel pathways in the transformation of melanocytes to melanomas. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5270–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleszczyński, K.; Kim, T.K.; Bilska, B.; Sarna, M.; Mokrzynski, K.; Stegemann, A.; Pyza, E.; Reiter, R.J.; Steinbrink, K.; Böhm, M.; et al. Melatonin exerts oncostatic capacity and decreases melanogenesis in human MNT-1 melanoma cells. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 67, e12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, B.R.; Gareiss, P.C.; Jacobs, S.E.; Fricke, A.F.; Scott, G.A.; Miller, B.L. A potent activator of melanogenesis identified from small-molecule screening. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolbe, L.; Mann, T.; Gerwat, W.; Batzer, J.; Ahlheit, S.; Scherner, C.; Wenck, H.; Stäb, F. 4-n-butylresorcinol, a highly effective tyrosinase inhibitor for the topical treatment of hyperpigmentation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27 (Suppl. S1), 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B. The path from anti Parkinson drug selegiline and rasagiline to multifunctional neuroprotective anti Alzheimer drugs ladostigil and m30. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2006, 3, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggioli, C.; Buscà, R.; Abbe, P.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is required but is not sufficient to induce the expression of melanogenic genes. Pigment. Cell Res. 2003, 16, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Fisher, D.E. MITF and UV responses in skin: From pigmentation to addiction. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2019, 32, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vance, K.W.; Carreira, S.; Brosch, G.; Goding, C.R. Tbx2 is overexpressed and plays an important role in maintaining proliferation and suppression of senescence in melanomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, I.; Kato, T.; Motokawa, T.; Tomita, Y.; Nakamura, E.; Katagiri, T. Increase of pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA prior to tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein 1, dopachrome tautomerase, Pmel-17/gp100, and P-protein mRNA in human skin after ultraviolet B irradiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young Kang, H.; Ortonne, J.P. Melasma update. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009, 100 (Suppl. S2), 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haass, N.K.; Herlyn, M. Normal human melanocyte homeostasis as a paradigm for understanding melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2005, 10, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goding, C.; Meyskens, F.L., Jr. Microphthalmic-associated transcription factor integrates melanocyte biology and melanoma progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, W.; Choi, D.; Park, S.; Park, T. Carvone decreases melanin content by inhibiting melanoma cell proliferation via the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, K.T.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, M.; Lim, Y.H. Evaluation of the inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase and cellular tyrosinase activities of oxyresveratrol: Comparison with mulberroside A. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sakamoto, K. Citric acid promoted melanin synthesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells, but inhibited it in human epidermal melanocytes and HMV-II melanoma cells via the GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Soler-Lopez, M.; Wichers, H.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Large-scale recombinant expression and purification of human tyrosinase suitable for structural studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, T.; Gerwat, W.; Batzer, J.; Eggers, K.; Scherner, C.; Wenck, H.; Stäb, F.; Hearing, V.J.; Röhm, K.H.; Kolbe, L. Inhibition of human tyrosinase requires molecular motifs distinctively different from mushroom tyrosinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Netcharoensirisuk, P.; Abrahamian, C.; Tang, R.; Chen, C.C.; Rosato, A.S.; Beyers, W.; Chao, Y.K.; Filippini, A.; Di Pietro, S.; Bartel, K.; et al. Flavonoids increase melanin production and reduce proliferation, migration and invasion of melanoma cells by blocking endolysosomal/melanosomal TPC2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellbrock, C.; Arozarena, I. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in melanoma development and MAP-kinase pathway targeted therapy. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.B.; Babiarz, L.; Liebel, F.; Roydon Price, E.; Kizoulis, M.; Gendimenico, G.J.; Fisher, D.E.; Seiberg, M. Modulation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor gene expression alters skin pigmentation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watabe, H.; Valencia, J.C.; Yasumoto, K.; Kushimoto, T.; Ando, H.; Muller, J.; Vieira, W.D.; Mizoguchi, M.; Appella, E.; Hearing, V.J. Regulation of tyrosinase processing and trafficking by organellar pH and by proteasome activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7971–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Wong, Z.C.; Wang, C.; Fung, A.H.; Wong, E.O.; Chan, G.K.; Dong, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Tsim, K.W. Isoorientin derived from Gentiana veitchiorum Hemsl. flowers inhibits melanogenesis by down-regulating MITF-induced tyrosinase expression. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.E.; Yoo, H.; Lee, H.R.; Moon, I.J.; Lee, W.J.; Song, Y.; Chang, S.E. Carvedilol, an adrenergic blocker, suppresses melanin synthesis by inhibiting the cAMP/CREB signaling pathway in human melanocytes and ex vivo human skin culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, T.; Usami, M.; Awaji, M.; Shinohara, S.; Sato, K. Dual effects of acetylsalicylic acid on ERK signaling and Mitf transcription lead to inhibition of melanogenesis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 412, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Chang, S.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Ke, H.J.; Chang, T.M. [6]-Shogaol inhibits α-MSH-induced melanogenesis through the acceleration of ERK and PI3K/Akt-mediated MITF degradation. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 842569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Fu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Y.; Song, G.; Yun, C.; Gao, R. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits melanogenesis, melanocyte dendricity and melanosome transport by regulating ERK-mediated MITF degradation. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newton, R.A.; Cook, A.L.; Roberts, D.W.; Leonard, J.H.; Sturm, R.A. Post-transcriptional regulation of melanin biosynthetic enzymes by cAMP and resveratrol in human melanocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2216–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, K.; Nemoto, K.; Kimijima, K.; Matsushita, A.; Terada, E.; Monthakantirat, O.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Miyase, T.; Warashina, T.; Degawa, M.; et al. Estrogenic constituents of the heartwood of Dalbergia parviflora. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Eknamkul, W.; Umehara, K.; Monthakantirat, O.; Toth, R.; Frecer, V.; Knapic, L.; Braiuca, P.; Noguchi, H.; Miertus, S. QSAR study of natural estrogen-like isoflavonoids and diphenolics from Thai medicinal plants. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2011, 29, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, X.T.; Park, S.H.; Lee, Y.G.; Jeong, H.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Jeon, T.I. Protocatechuic acid from pear inhibits melanogenesis in melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Netcharoensirisuk, P.; Umehara, K.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Chaotham, C. Cajanin Suppresses Melanin Synthesis through Modulating MITF in Human Melanin-Producing Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196040
Netcharoensirisuk P, Umehara K, De-Eknamkul W, Chaotham C. Cajanin Suppresses Melanin Synthesis through Modulating MITF in Human Melanin-Producing Cells. Molecules. 2021; 26(19):6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196040
Chicago/Turabian StyleNetcharoensirisuk, Ponsawan, Kaoru Umehara, Wanchai De-Eknamkul, and Chatchai Chaotham. 2021. "Cajanin Suppresses Melanin Synthesis through Modulating MITF in Human Melanin-Producing Cells" Molecules 26, no. 19: 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196040
APA StyleNetcharoensirisuk, P., Umehara, K., De-Eknamkul, W., & Chaotham, C. (2021). Cajanin Suppresses Melanin Synthesis through Modulating MITF in Human Melanin-Producing Cells. Molecules, 26(19), 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196040





