Solid-Phase Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes for Plasma Membrane Labelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
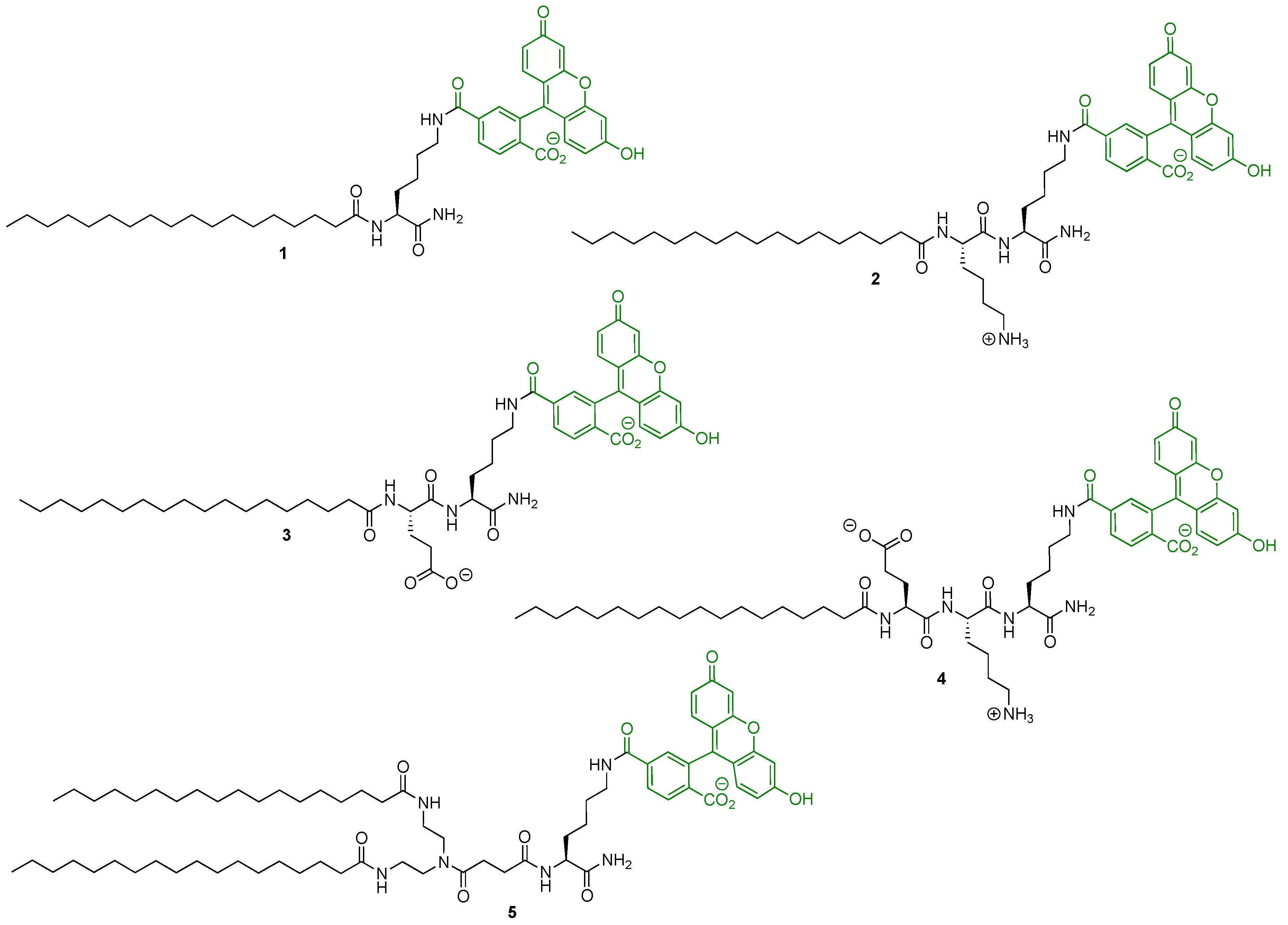
2.1. Synthesis of Fmoc-Lys(6-carboxyfluoresein diacetate)-OH
2.2. Solid-Phase Synthesis of the Fluorescent Probes
2.3. Cell Membrane Labelling
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Fmoc-Lys(6-carboxyfluoresein diacetate)-OH 6
4.2. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes 1–5
4.2.1. Synthesis of Lys(6-carboxyfluoresein diacetate)-functionalised Resin
4.2.2. General Acid Couplings
4.2.3. Fmoc Deprotection
4.2.4. Deprotection and Cleavage Off the Resin
4.2.5. Purification
4.3. Optical Properties of the Fluorescent Probes
4.4. Cell Membrane Labelling of the Fluorescent Probes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Upadhyay, A.; Kandi, R.; Rao, C.P. Wheat germ agglutinin modified magnetic iron oxide nanocomplex as a cell membrane specific receptor target material for killing breast cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5729–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedeman, J.; Mensa-Wilmot, K. A fixable probe for visualizing flagella and plasma membranes of the African trypanosome. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, N.; Zhou, H.; Liu, N.; Ren, J.; Li, W.; Yu, C. A benzoperylene self-assembly complex with turn-on excimer emission for wash-free cell membrane fluorescence imaging. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14446–14449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.G. Subcellular fate of a fluorescent cholesterol-poly (ethylene glycol) conjugate: An excellent plasma membrane imaging reagent. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10126–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Pulsipher, A.; Luo, W.; Yousaf, M.N. Synthetic chemoselective rewiring of cell surfaces: Generation of three-dimensional tissue structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8704–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fátima Martins, M.; Honório-Ferreira, A.; Martins, P.; Gonçalves, C.A. Presence of sialic acids in bronchioloalveolar cells and identification and quantification of N-acetylneuraminic and N-glycolylneuraminic acids in the lung. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collot, M.; Kreder, R.; Tatarets, A.L.; Patsenker, L.D.; Mely, Y.; Klymchenko, A.S. Bright fluorogenic squaraines with tuned cell entry for selective imaging of plasma membrane vs. endoplasmic reticulum. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17136–17139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayoob, A.M.; Peppi, M.; Tandon, V.; Langer, R.; Borenstein, J.T. A fluorescence-based imaging approach to pharmacokinetic analysis of intracochlear drug delivery. Hear. Res. 2018, 368, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Liu, H.W.; Yin, X.; Yuan, L.; Huan, S.Y.; Zhang, X.B. A cell membrane-anchored fluorescent probe for monitoring carbon monoxide release from living cells. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardone, A.; Lopez, F.; Affortunato, F.; Busco, G.; Hofer, A.M.; Mallamaci, R.; Martinelli, C.; Colella, M.; Farinola, G.M. An aryleneethynylene fluorophore for cell membrane staining. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 2808–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kucherak, O.A.; Oncul, S.; Darwich, Z.; Yushchenko, D.A.; Arntz, Y.; Didier, P.; Mély, Y.; Klymchenko, A.S. Switchable nile red-based probe for cholesterol and lipid order at the outer leaflet of biomembranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4907–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shynkar, V.V.; Klymchenko, A.S.; Kunzelmann, C.; Duportail, G.; Muller, C.D.; Demchenko, A.P.; Freyssinet, J.M.; Mely, Y. Fluorescent Biomembrane Probe for Ratiometric Detection of Apoptosis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberska, A.; Lilienkampf, A.; Unciti-Broceta, A.; Bradley, M. Solid-phase synthesis of arginine-based double-tailed cationic lipopeptides: Potent nucleic acid carriers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12774–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziarani, G.M.; Moradi, R.; Lashgari, N.; Kruger, H.G. Metal-Free Synthetic Organic Dyes, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Fluorescence Properties of Twenty Fluorescein Derivatives: Lifetime, Quantum Yield, Absorption and Emission Spectra. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, A.; Aslam, T.; Bradley, M. Separating the isomers—Efficient synthesis of the N-hydroxysuccinimide esters of 5 and 6-carboxyfluorescein diacetate and 5 and 6-carboxyrhodamine B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3186–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, R.; Mader, O.; Jung, G.; Brock, R. Extending the Applicability of Carboxyfluorescein in Solid-Phase Synthesis. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 14, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerknes, R.; Bassøe, C.F. Phagocyte C3-mediated attachment and internalization: Flow cytometric studies using a fluorescence quenching technique. Blut 1984, 49, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hed, J. Methods for distinguishing ingested from adhering particles. Methods Enzymol. 1986, 132, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hed, J.; Hallden, G.; Johansson, S.G.O.; Larsson, P. The use of fluorescence quenching in flow cytofluorometry to measure the attachment and ingestion phases in phagocytosis in peripheral blood without prior cell separation. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 101, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnemann, S.C.; Bonilha, V.L.; Marmorstein, A.D.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E. Phagocytosis of rod outer segments by retinal pigment epithelial cells requires αvβ5 integrin for binding but not for internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12932–12937. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, V.K.; Kent, S.B.; Tam, J.P.; Merrifield, R.B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 117, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



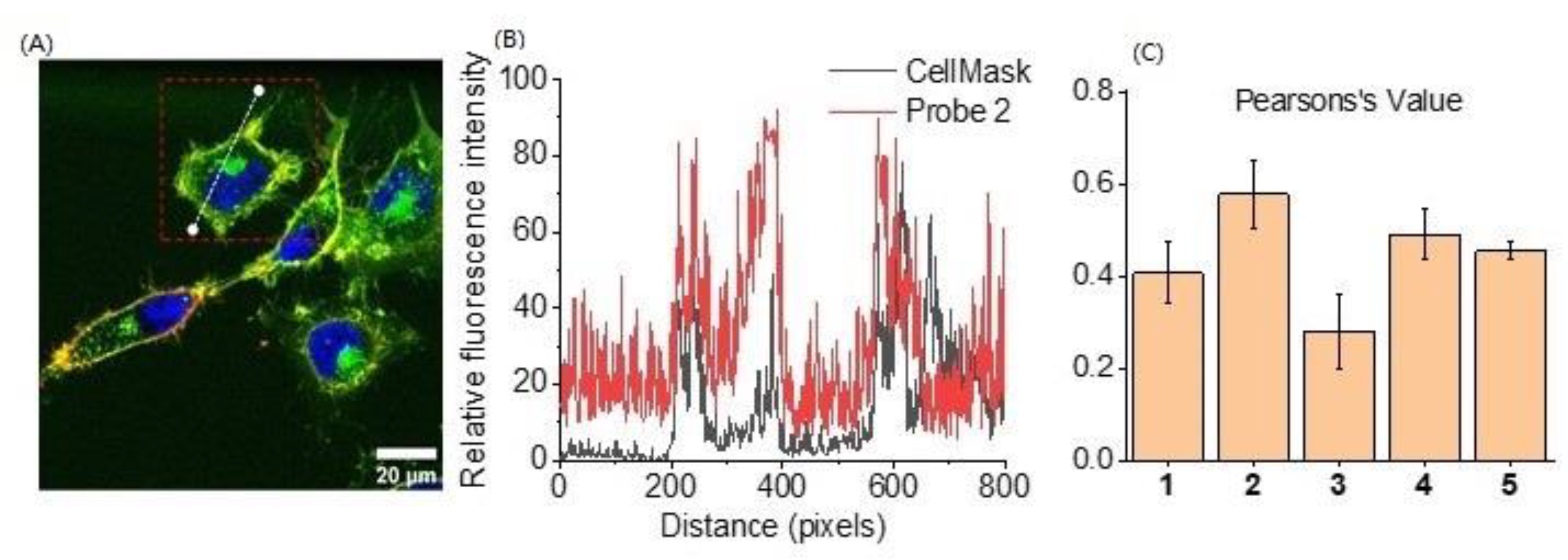

| Probe | +NH3 | COO− | Stearic Acid Tail | Cellular Labelling Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | single | Strong fluorescence staining with weak membrane selectivity | ||
| 2 | ✓ | single | Strong fluorescence staining and membrane binding for over 2 h | |
| 3 | ✓ | single | Lowest fluorescence staining with no membrane binding selectivity | |
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | single | Low fluorescence staining compared with Probe 2, with good membrane binding for over 2 h |
| 5 | double | Low fluorescence staining and high background signal |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Lilienkampf, A.; Bradley, M. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes for Plasma Membrane Labelling. Molecules 2021, 26, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020354
Zhang S, Lilienkampf A, Bradley M. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes for Plasma Membrane Labelling. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuo, Annamaria Lilienkampf, and Mark Bradley. 2021. "Solid-Phase Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes for Plasma Membrane Labelling" Molecules 26, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020354
APA StyleZhang, S., Lilienkampf, A., & Bradley, M. (2021). Solid-Phase Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes for Plasma Membrane Labelling. Molecules, 26(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020354







