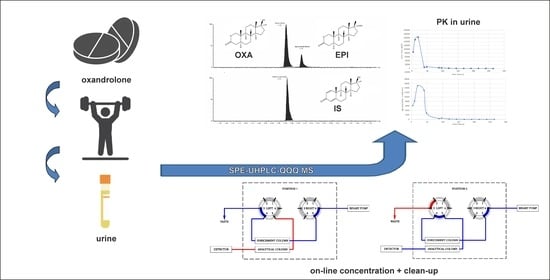
Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC—MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Liquid Chromatography—Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight (LC-QTOF) Method
2.2. SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS (QQQ) Method Optimization
2.3. SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS (QQQ) Method Validation
2.4. SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS (QQQ) Method Application
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. LC-QTOF Instrumentation and Conditions
3.3. Online SPE-UHPLC-QQQ Instrumentation and Conditions
3.4. Sample Preparation
3.4.1. Standard Solutions
3.4.2. QC Samples
3.4.3. Urine Samples
3.5. Creatinine
3.6. Method Validation
3.7. Drug Administration and Sample Collection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pappo, R.; Jung, C.J. 2-oxasteroids: A new class of biologically active compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1962, 3, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.; Fiatarone Singh, M. The anabolic androgenic steroid oxandrolone in the treatment of wasting and catabolic disorders: Review of efficacy and safety. Drugs 2004, 64, 725–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, Y.; Finnerty, C.C.; Radhakrishnan, R.S.; Herndon, D.N. Burns: An update on current pharmacotherapy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, A.; Garg, S.; She, R.W. Development of an extemporaneous oral liquid formulation of oxandrolone and its stability evaluation. Burns 2011, 37, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Moritz, T.E.; Roselle, G.A.; Morgan, T.R.; Nemchausky, B.A.; Tamburro, C.H.; Schiff, E.R.; McClain, C.J.; Marsano, L.S.; Allen, J.I.; et al. The VA Cooperative Study Group #275. Protein energy malnutrition in severe alcoholic hepatitis: Diagnosis and response to treatment. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995, 19, 258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Moritz, T.E.; Roselle, G.A.; Morgan, T.R.; Nemchausky, B.A.; Tamburro, C.H.; Schiff, E.R.; McClain, C.J.; Marsano, L.S.; Allen, J.I.; et al. The VA Cooperative Study Group #275. A study of oral nutritional support with oxandrolone in malnourished patients with alcoholic hepatitis: Results of a Department of Veterans Affairs cooperative study. Hepatology 1993, 17, 564–576. [Google Scholar]
- Bonkovsky, H.L.; Singh, R.H.; Jafri, I.H.; Fiellin, D.A.; Smith, G.S.; Simon, D.; Cotsonis, G.A.; Slaker, D.P. A randomized, controlled trial of treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with parenteral nutrition and oxandrolone. II. Short-term effects on nitrogen metabolism, metabolic balance, and nutrition. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1991, 86, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Wheeler, S.; Heller, L.; Salata, C.M.; Kaufman, F.; Loro, M.L.; Gilsanz, V.; Haight, M.; Umman, G.C.; Barton, N.; Church, J.A. Evaluation of the effects of oxandrolone on malnourished HIV-positive pediatric patients. Pediatrics 1999, 104, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaston-Blaakman, A.; Shepard, D.S.; Stone, N.; Shevitz, A.H. Cost-effectiveness of clinical interventions for AIDS wasting. AIDS Care 2007, 19, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.T.; Btaiche, I.F. Oxandrolone in pediatric patients with severe thermal burn injury. Ann. Pharmacother. 2008, 42, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demling, R.H.; DeSanti, L. Oxandrolone induced lean mass gain during recovery from severe burns is maintained after discontinuation of the anabolic steroid. Burns 2003, 29, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tarrah, K.; Moiemen, N.; Lord, J.M. The influence of sex steroid hormones on the response to trauma and burn injury. Burns Trauma 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheanon, N.M.; Backeljauw, P.F. Effect of oxandrolone therapy on adult height in Turner syndrome patients treated with growth hormone: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.M.; Cox-Martin, M.; Bardsley, M.Z.; Kowal, K.; Zeitler, P.S.; Ross, J.L. Effects of Oxandrolone on Cardiometabolic Health in Boys with Klinefelter Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.M.; Lahlou, N.; Cox-Martin, M.; Kowal, K.; Zeitler, P.S.; Ross, J.L. Oxandrolone Treatment Results in an Increased Risk of Gonadarche in Prepubertal Boys With Klinefelter Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3449–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, C.M. Anabolic steroids. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2002, 57, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demling, R.H. Comparison of the anabolic effects and complications of human growth hormone and the testosterone analog, oxandrolone, after severe burn injury. Burns 1999, 25, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, E.J.; Barnett, M.J.; Tenerowicz, M.J.; Kim, J.A.; Wei, H.; Perry, P.J. Women and anabolic steroids: An analysis of a dozen users. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2010, 20, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Cannarella, R.; Duca, Y.; Calogero, A.E. Sport, doping and female fertility. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schänzer, W.; Donike, M. Metabolism of anabolic steroids in man: Synthesis and use of reference substances for identification of anabolic steroid metabolites. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 275, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanzer, W. Metabolism of anabolic androgenic steroids. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masse, R.; Bi, H.G.; Ayotte, C.; Dugal, R. Studies on anabolic steroids. II--Gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric characterization of oxandrolone urinary metabolites in man. Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 1989, 18, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayotte, C.; Goudreault, D.; Charlebois, A. Testing for natural and synthetic anabolic agents in human urine. J. Chromatogr. B 1996, 687, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.C.; Choo, H.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Eom, K.D.; Kwon, O.S.; Suh, J.; Yang, J.; Park, J. Analysis of anabolic steroids using GC/MS with selected ion monitoring. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1990, 14, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eenoo, P.; Van Gansbeke, W.; De Brabanter, N.; Deventer, K.; Delbeke, F.T. A fast, comprehensive screening method for doping agents in urine by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelsky, A.I.; Samoshkin, A.S.; Virus, E.D.; Rodchenkov, G.M.; Revelsky, I.A. High sensitive analysis of steroids in doping control using gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass-spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, O.J.; Deventer, K.; Van Eenoo, P.; Delbeke, F.T. Efficient approach for the comprehensive detection of unknown anabolic steroids and metabolites in human urine by liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, A.; Kuuranne, T.; Kostiainen, R. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry in anabolic steroid analysis—Optimization and comparison of three ionization techniques: Electrospray ionization, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization. J. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 37, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, A.; Kuuranne, T.; Kotiaho, T.; Kostiainen, R. Screening of free 17-alkyl-substituted anabolic steroids in human urine by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids 2004, 69, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virus, E.D.; Sobolevsky, T.G.; Rodchenkov, G.M. Introduction of HPLC/orbitrap mass spectrometry as screening method for doping control. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viryus, E.D.; Sobolevskii, T.G.; Rodchenkov, G.M. Detection of oxandrolone and its metabolite in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and orbitrap detection after ceasing drug administration. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 64, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guddat, S.; Fussholler, G.; Beuck, S.; Thomas, A.; Geyer, H.; Reydevik, A.; Bondesson, U.; Hedeland, M.; Lagojda, A.; Schänzer, W.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and detection of new oxandrolone metabolites as long-term markers in sports drug testing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 8285–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzeppa, S.; Viet, L. Analysis of sulfate metabolites of the doping agents oxandrolone and danazol using high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1029–1030, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration. Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics Guidance for Industry. 2015. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Analytical-Procedures-and-Methods-Validation-for-Drugs-and-Biologics.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Kootstra, P.R.; Zoontjes, P.W.; van Tricht, E.F.; Sterk, S.S. Multi-residue screening of a minimum package of anabolic steroids in urine with GC-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 586, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WADA. Minimum Required Performance Levels for Detection and Identification of Non-Threshold Sunstances. 2014. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/WADA-TD2014MRPL-v1-Minimum-Required-Performance-Levels-EN.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- WADA. Identification Criteria for Qualitative Assay Incorporating Column Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry. 2010. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/WADA_TD2010IDCRv1.0_Identification%20Criteria%20for%20Qualitative%20Assays_May%2008%202010_EN.doc.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Tircova, B.; Bosakova, Z.; Kozlik, P. Development of an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of anabolic steroids currently available on the black market in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Compound Name | Parent (m/z) | Daughter (m/z) | Dwell (s) | Cone (V) | Collision (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxandrolone | 307.3 | 271.2 * | 0.044 | 28 | 12 |
| Oxandrolone | 307.3 | 289.3 | 0.044 | 28 | 12 |
| Oxandrolone | 307.3 | 253.1 | 0.044 | 28 | 16 |
| Oxandrolone | 307.3 | 229.1 | 0.044 | 28 | 16 |
| Oxandrolone | 307.3 | 92.9 | 0.044 | 28 | 36 |
| Metandienone (IS) | 301.3 | 149.2 | 0.044 | 28 | 12 |
| Parameter | Oxandrolone |
|---|---|
| Linear range [pg·mL−1] | 81.63–5000 |
| Rt [min] | 5.23 |
| SDRt [min] | 0.03 |
| RSDRt [%] | 0.57 |
| W1/2 [min] | 0.09 |
| N | 18730 |
| H [mm] | 0.00534 |
| Slope (a) | 0.000779 |
| SDa | 0.0000201 |
| Intercept (b) | 0.01517 |
| SDb | 0.00635 |
| r2 | 0.99704 |
| LOD [pg·mL−1] | 24.49 |
| LOQ [pg·mL−1] | 81.63 |
| QC Level | Intraday (n = 5, Single Batch) | Interday (n = 15, 5 From Each Batch) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Spiked Concentration [pg·mL−1] | Mean Concentration | RSD % | Accuracy % | Mean Concentration | RSD % | Accuracy % |
| Oxandrolone | 100 | 109.5 | 3.26 | 109.5 | 106.5 | 10.98 | 106.5 |
| 250 | 231.5 | 7.42 | 92.61 | 233.6 | 7.42 | 93.43 | |
| 1000 | 1012 | 2.38 | 101.2 | 1007 | 2.77 | 100.7 | |
| Compound | Spiked Concentration [pg·mL−1] | Mean Concentration (n = 5) | Recovery % (n = 5) | Matrix Effect % (without IS), n = 5 | Matrix Effect (with IS), n = 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxandrolone | 75 | 80.33 | 107.1 | 61.25 | −8.63 |
| 750 | 661.9 | 88.25 | 67.30 | 15.85 | |
| 5000 | 4870 | 97.39 | 56.64 | −1.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galba, J.; Piešťanský, J.; Kováč, A.; Olešová, D.; Cehlár, O.; Kertys, M.; Kozlík, P.; Chaľová, P.; Tirčová, B.; Slíž, K.; et al. Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC—MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020480
Galba J, Piešťanský J, Kováč A, Olešová D, Cehlár O, Kertys M, Kozlík P, Chaľová P, Tirčová B, Slíž K, et al. Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC—MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020480
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalba, Jaroslav, Juraj Piešťanský, Andrej Kováč, Dominika Olešová, Ondrej Cehlár, Martin Kertys, Petr Kozlík, Petra Chaľová, Barbora Tirčová, Kristián Slíž, and et al. 2021. "Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC—MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment" Molecules 26, no. 2: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020480
APA StyleGalba, J., Piešťanský, J., Kováč, A., Olešová, D., Cehlár, O., Kertys, M., Kozlík, P., Chaľová, P., Tirčová, B., Slíž, K., & Mikuš, P. (2021). Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC—MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment. Molecules, 26(2), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020480