Achiral Molecular Recognition of Substituted Aniline Position Isomers by Crown Ether Type Chiral Stationary Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
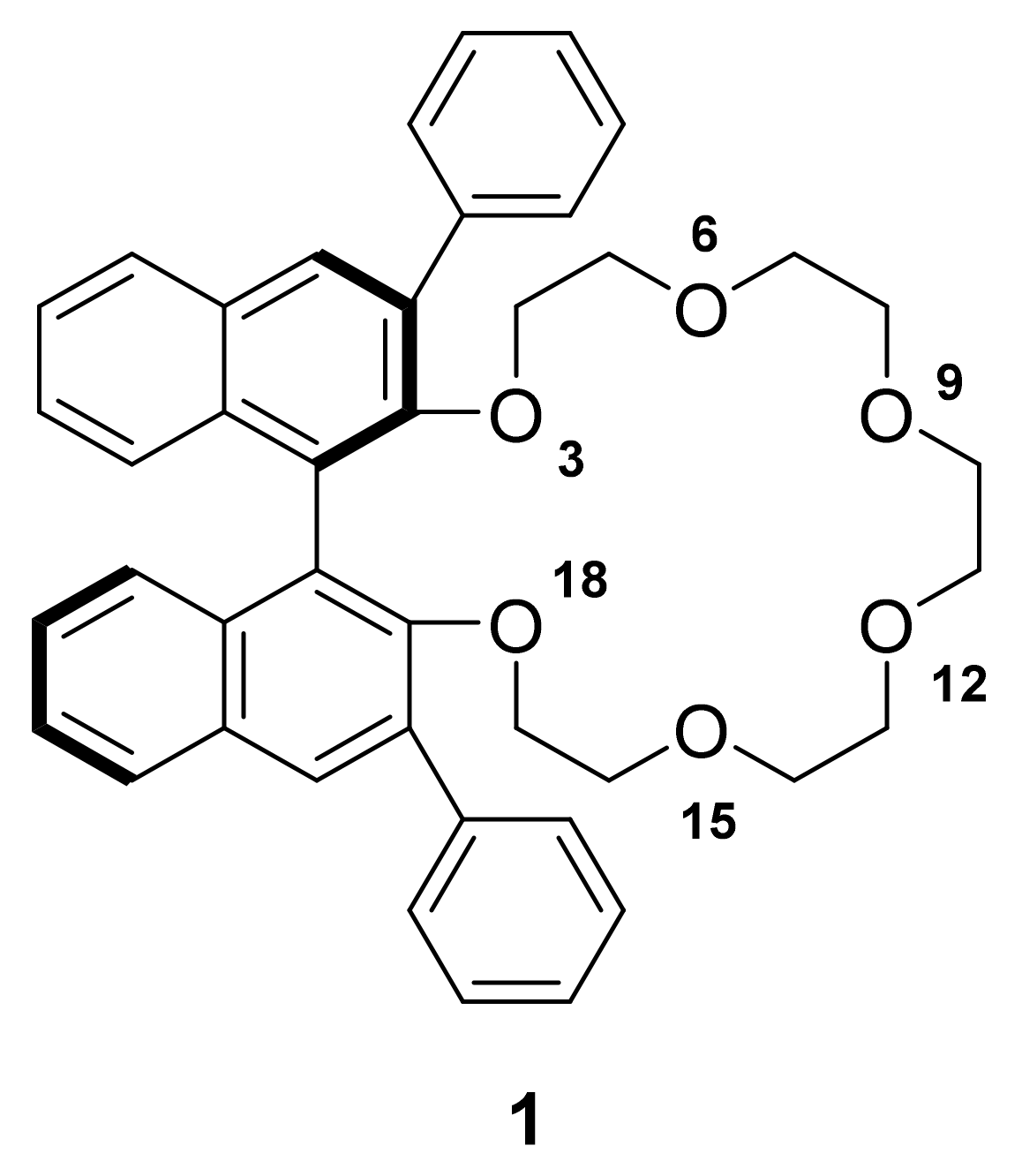
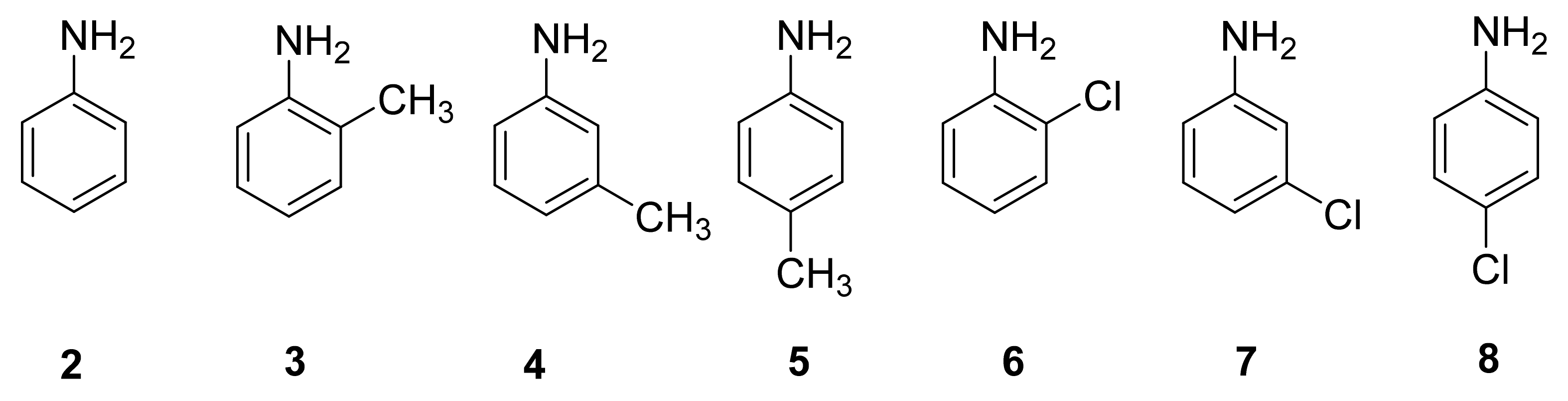
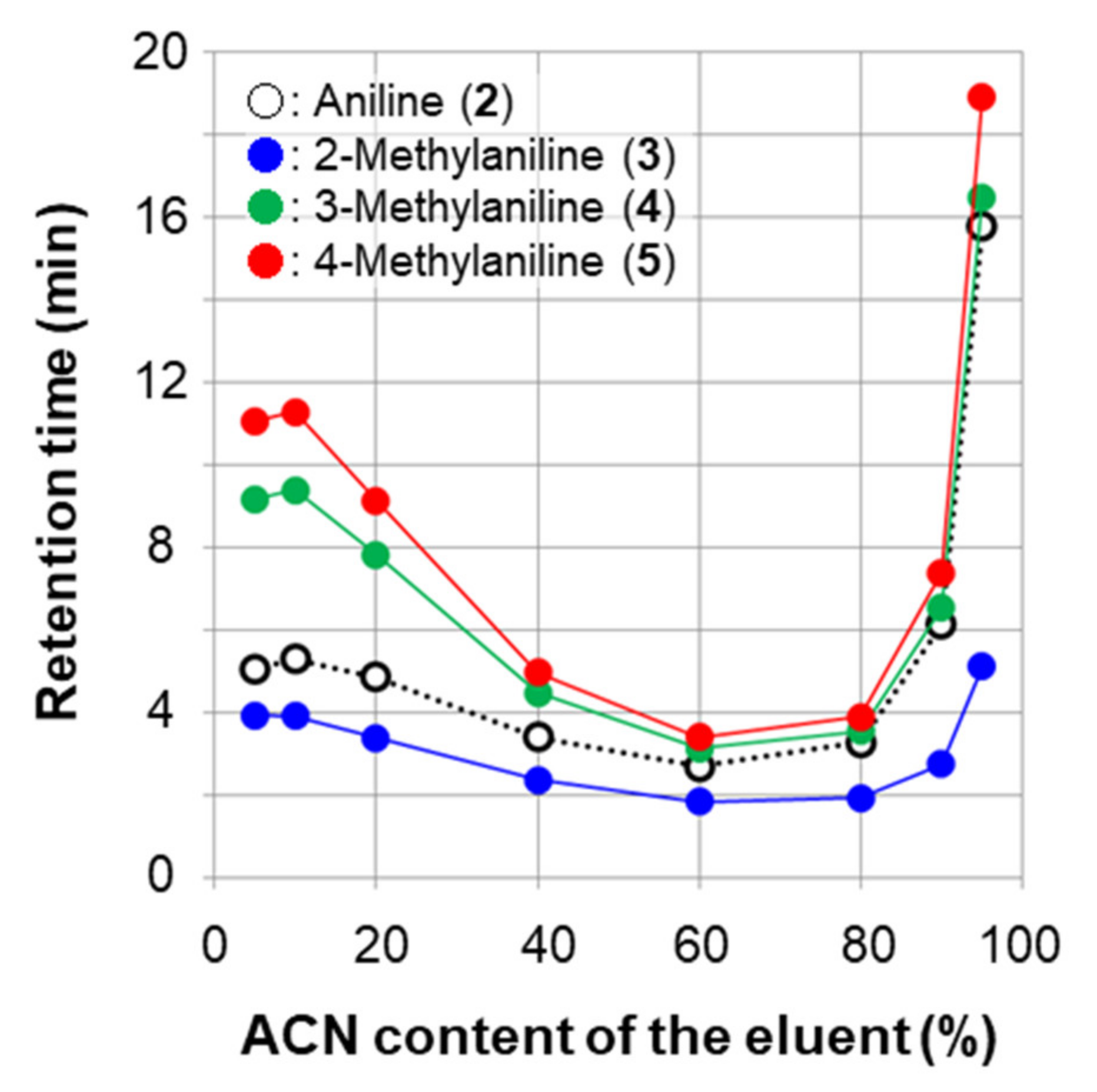
2.1. Separation of Aniline and Substituted Aniline Isomers on CROWNPAK CR-I
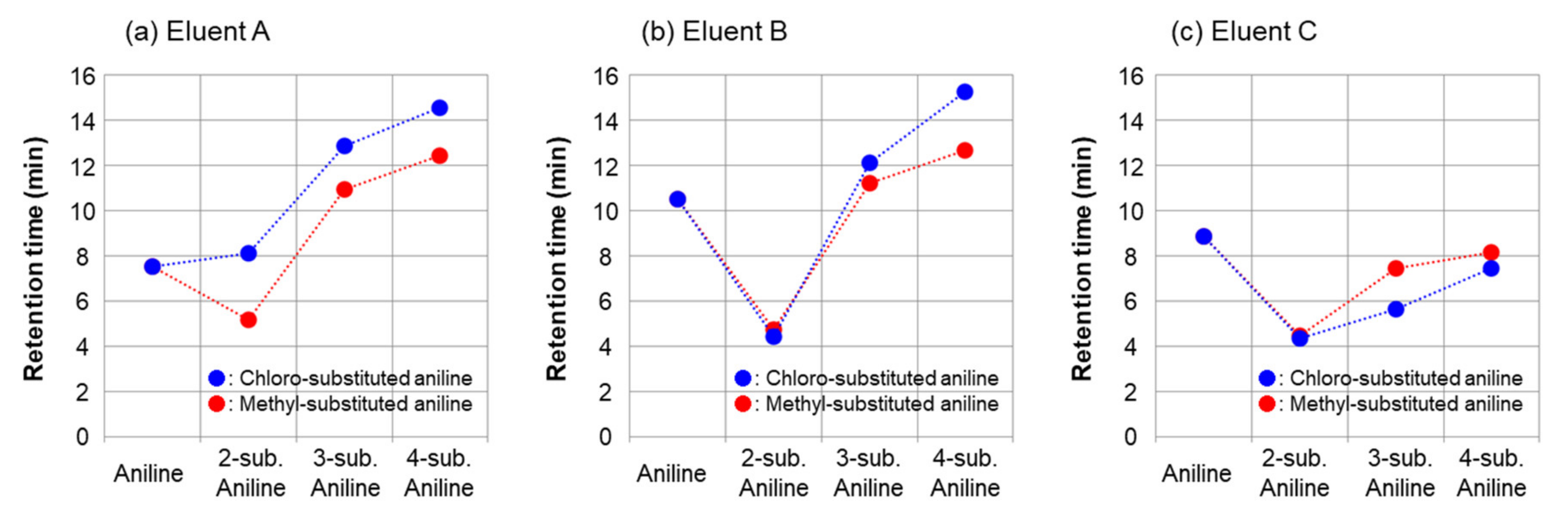
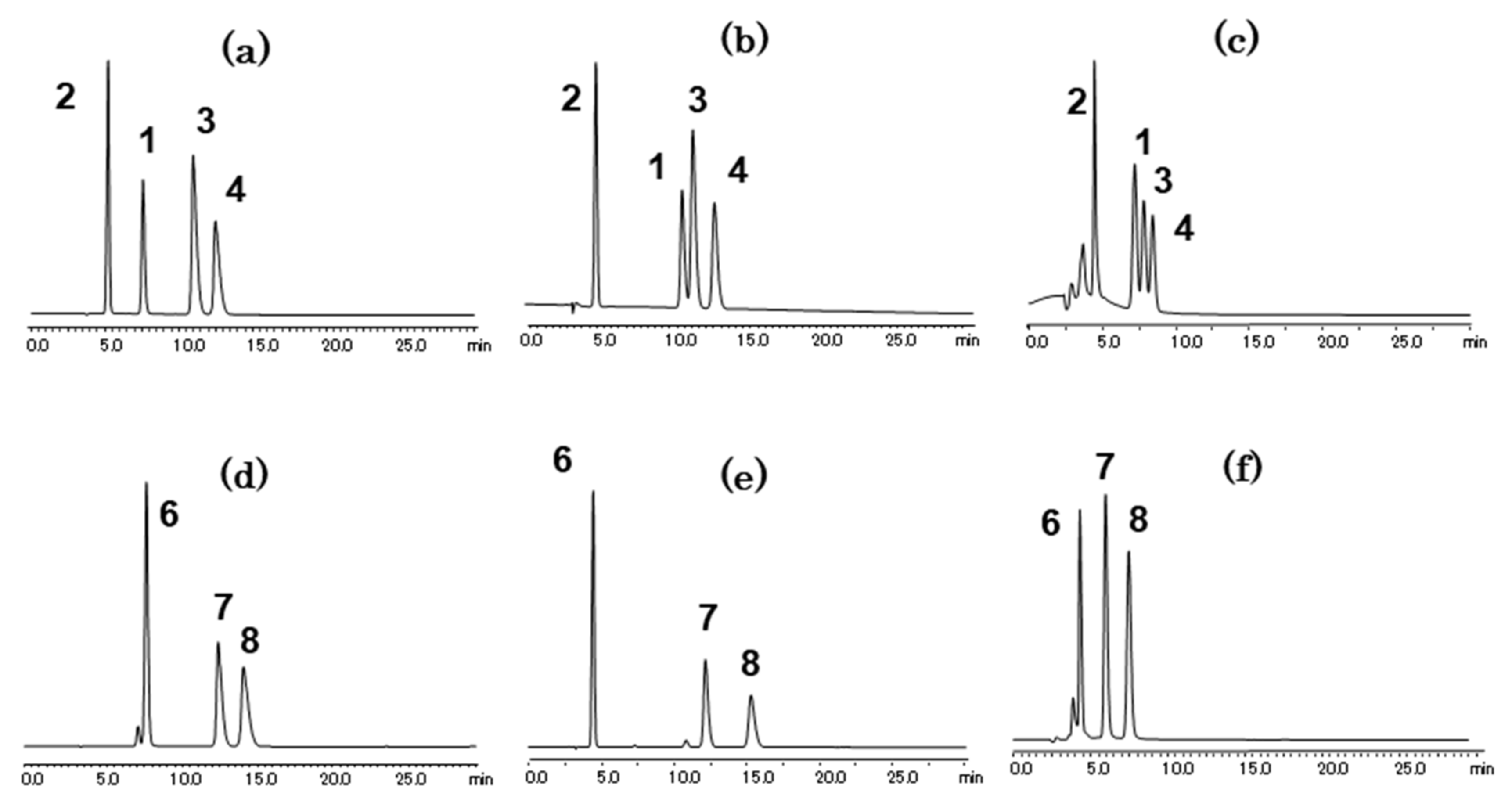
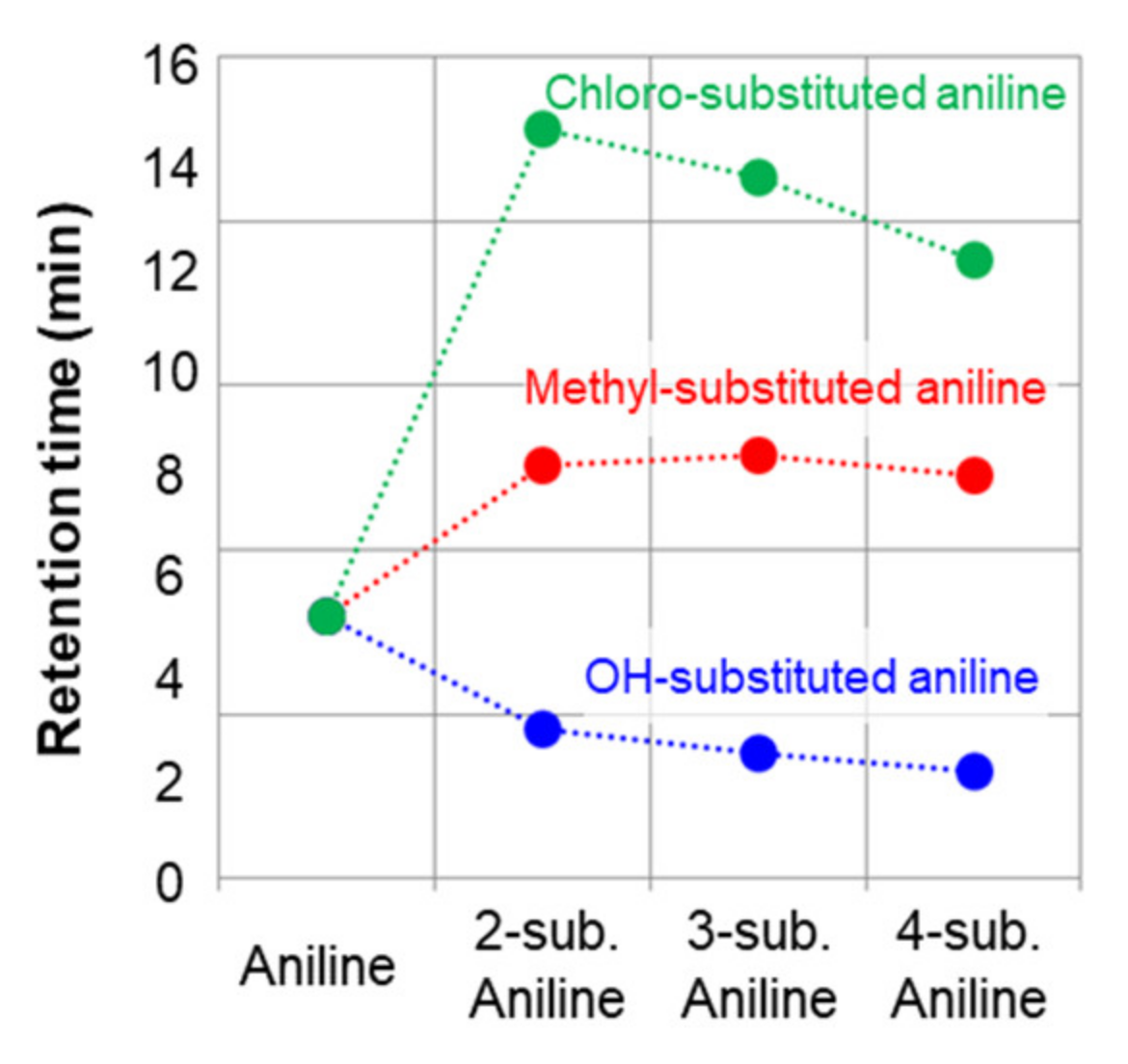
2.1.1. Separation of Aniline and Substituted Anilines
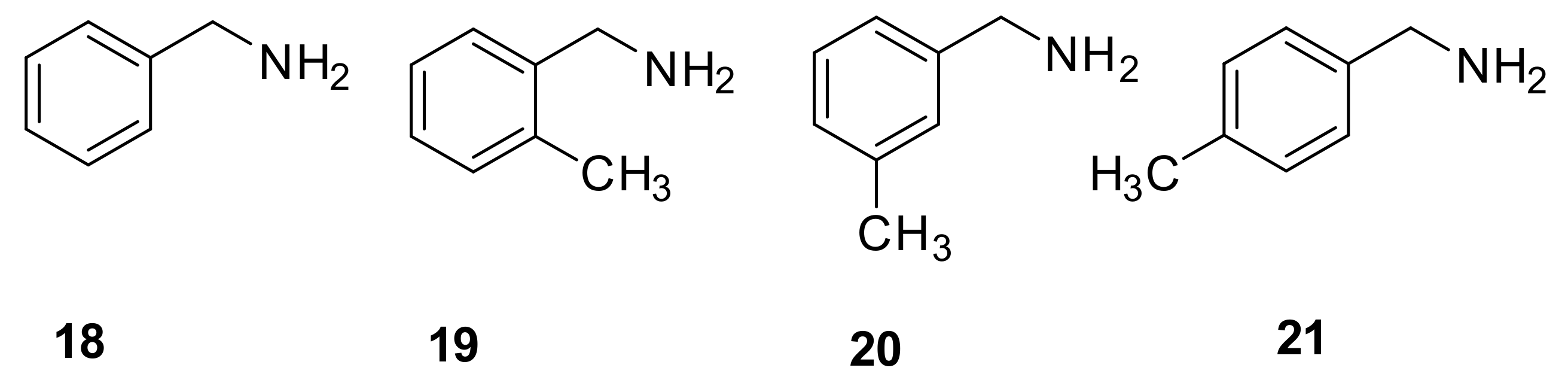
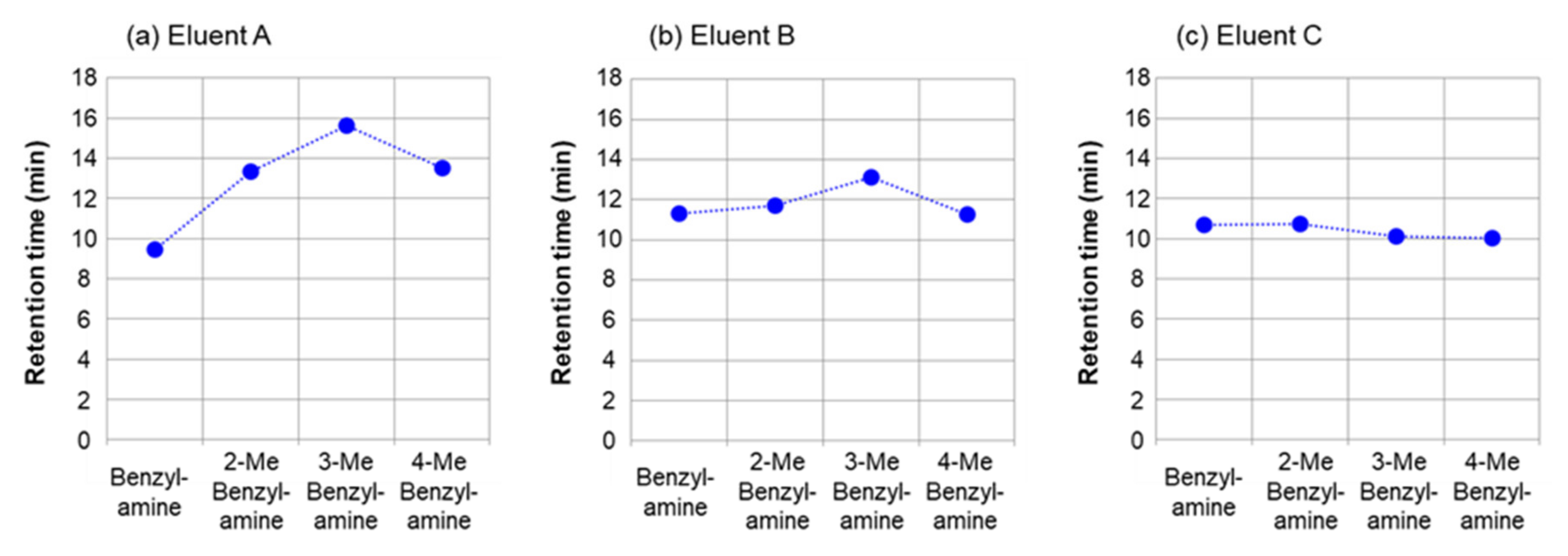
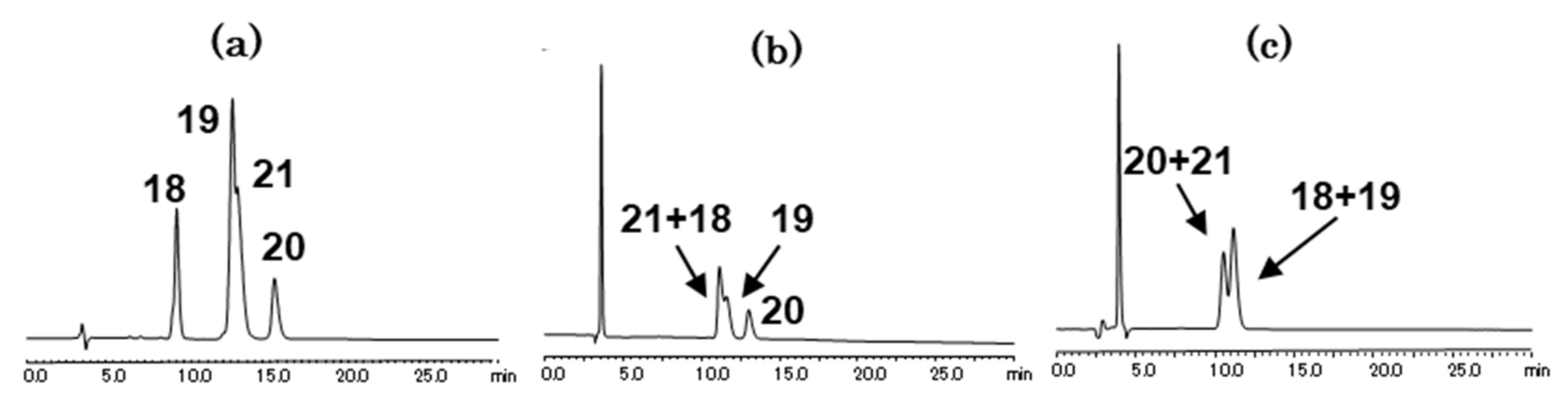
2.1.2. Separation of Benzylamine and Substituted Benzylamines
2.2. Examination of Retention Behavior by Quantum Chemical Calculation
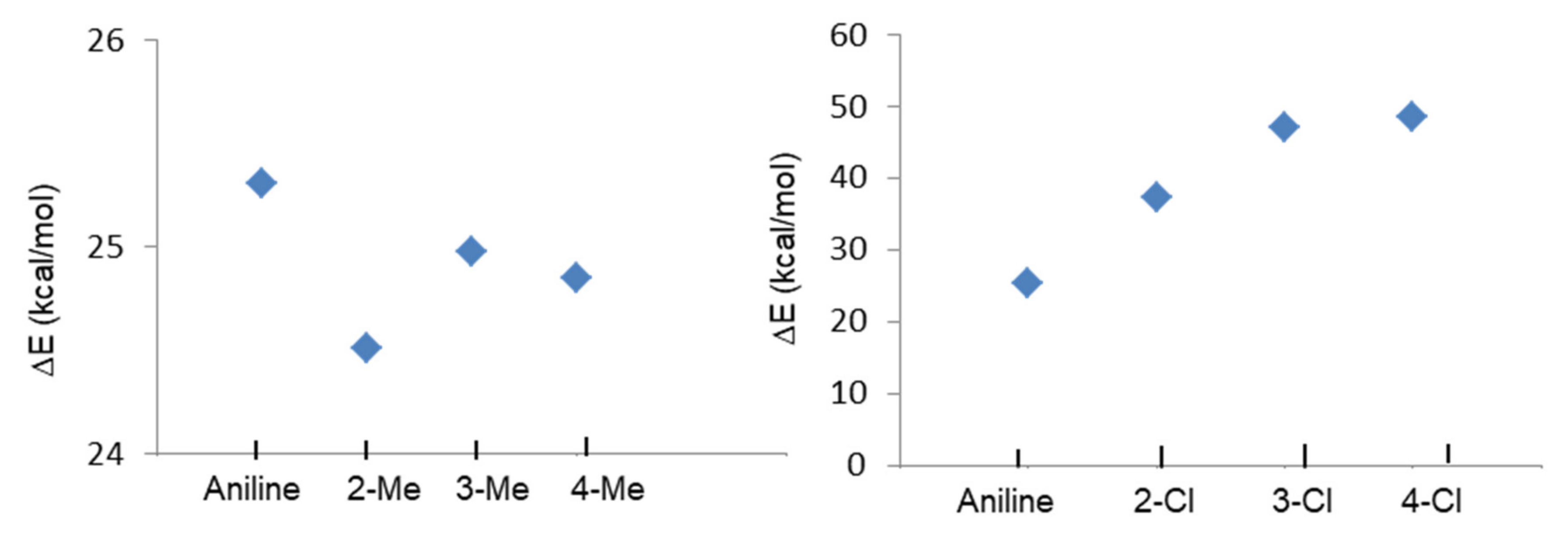
Quantum Chemical Calculation of Aniline, Methyl, and Chloroanilines
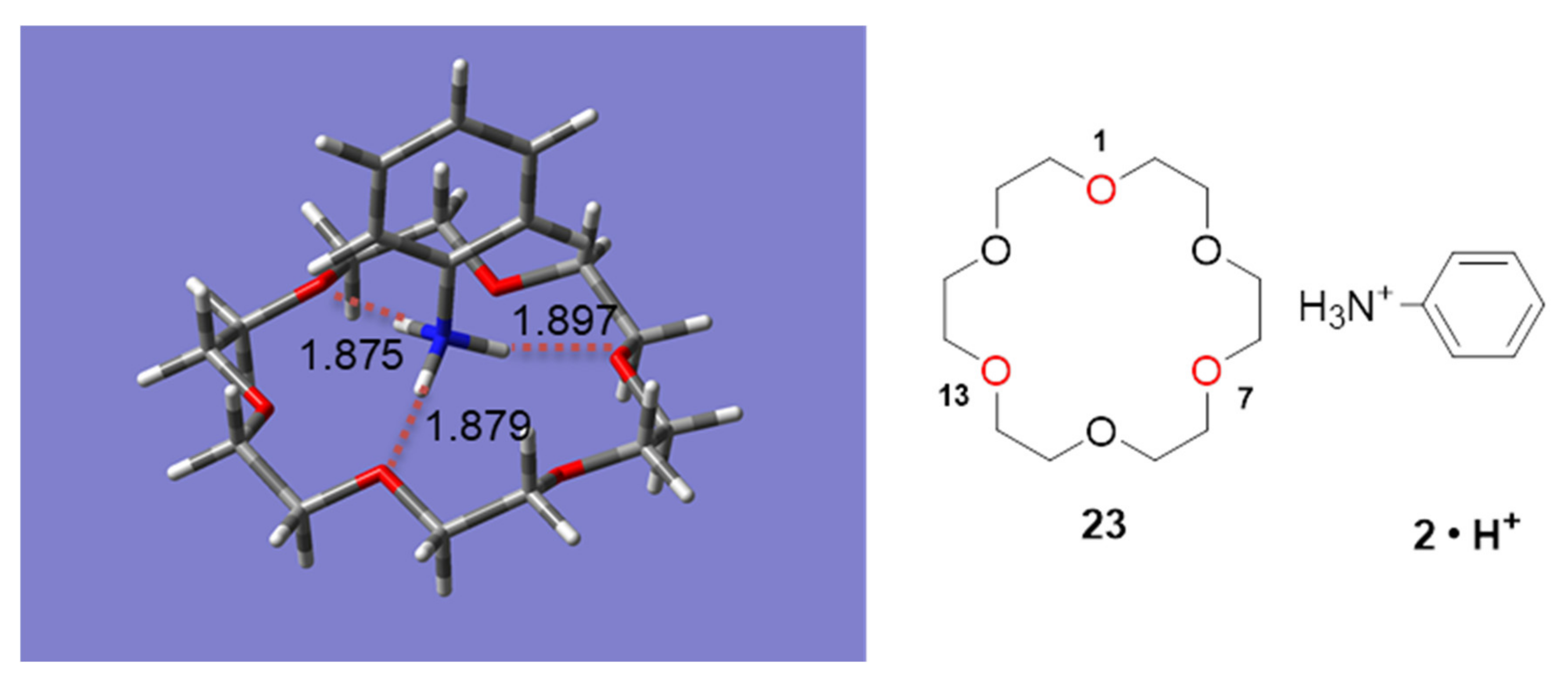
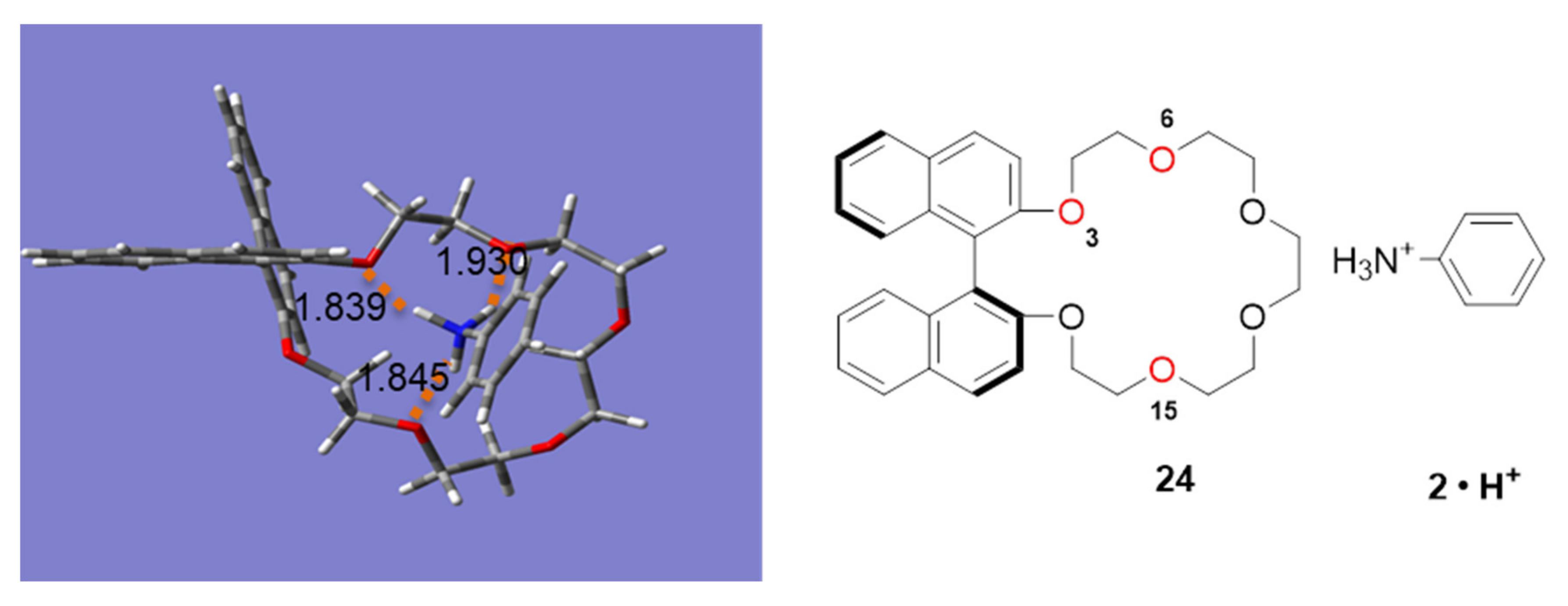
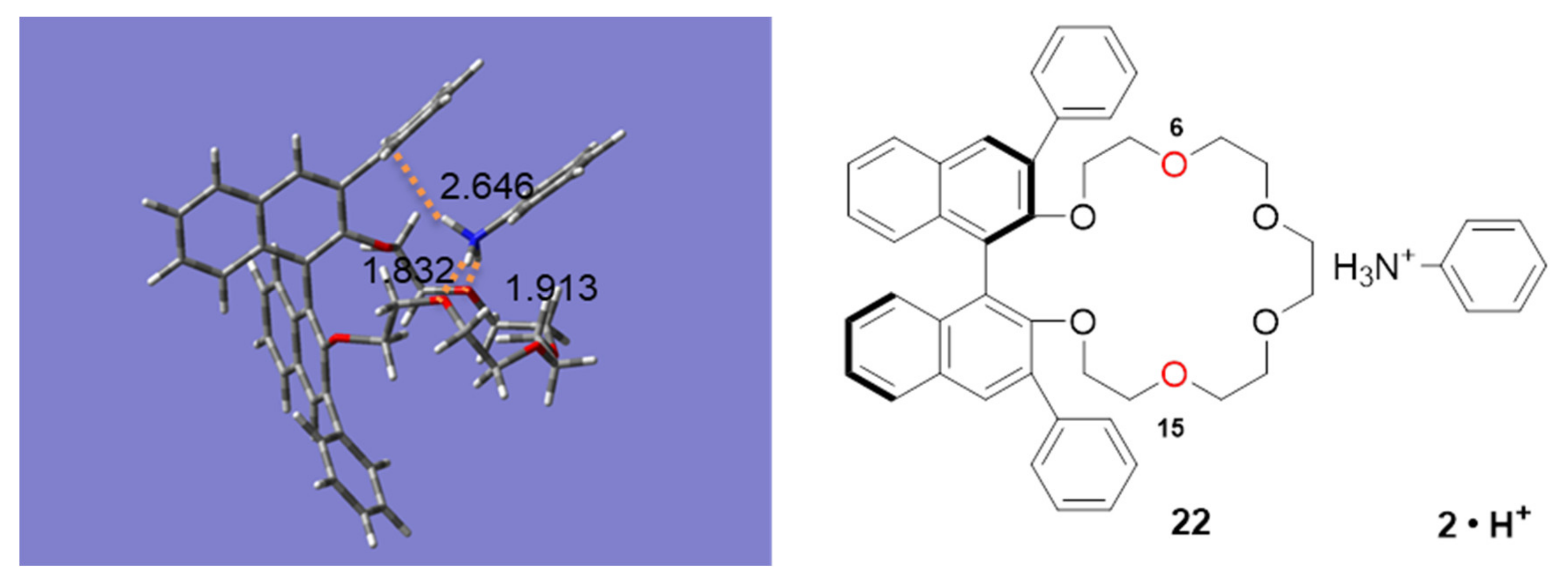
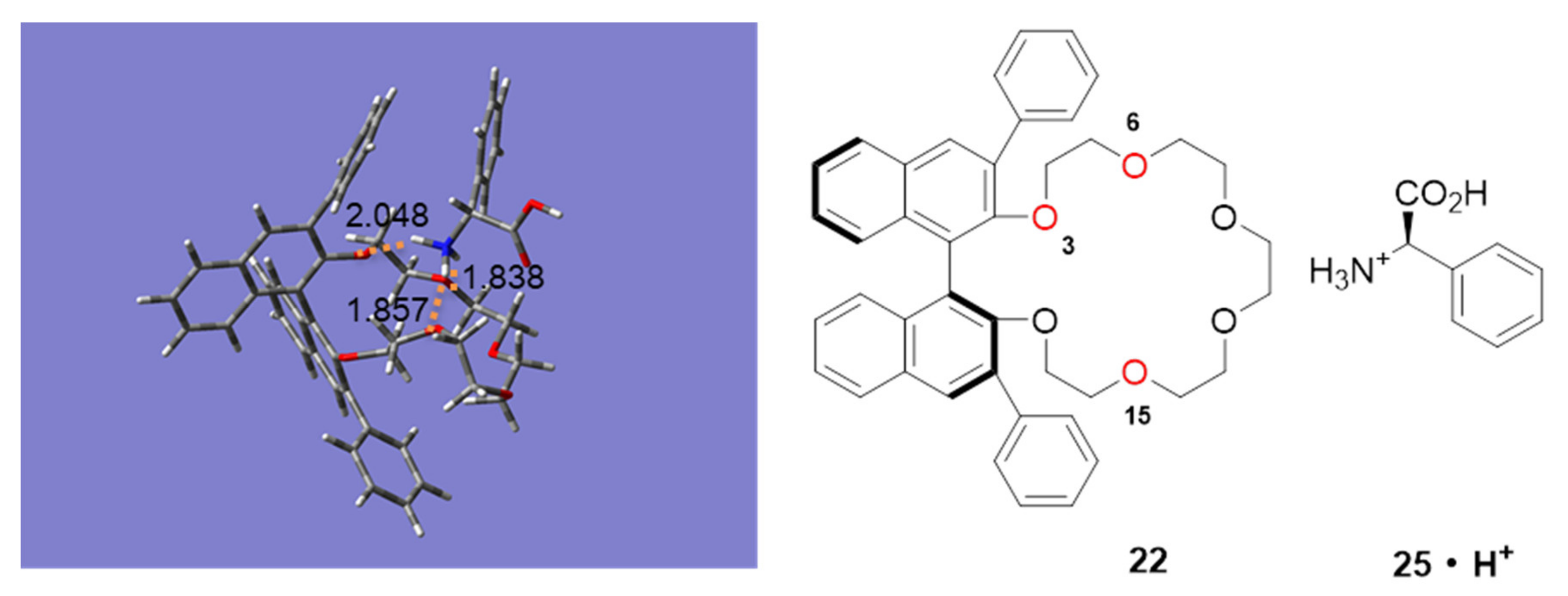
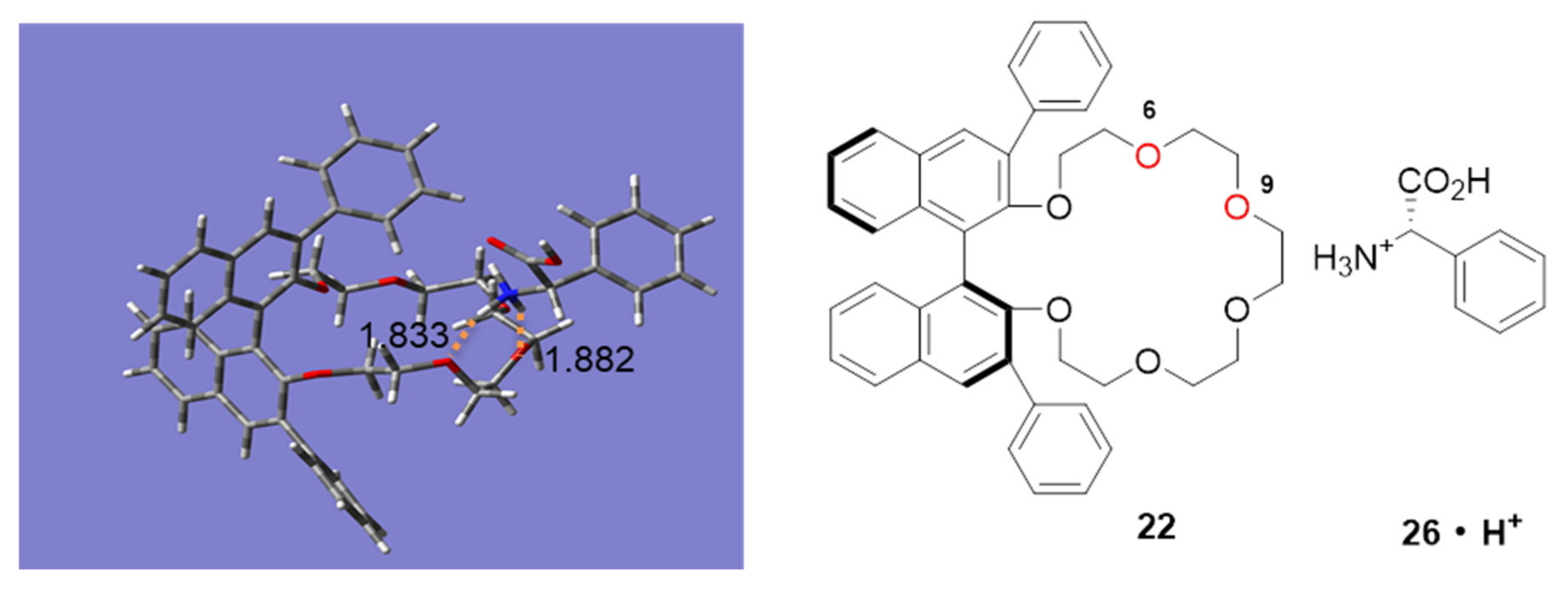
2.3. Insight into the Interaction between CR (+) Ligand and Aniline by Quantum Chemical Calculation
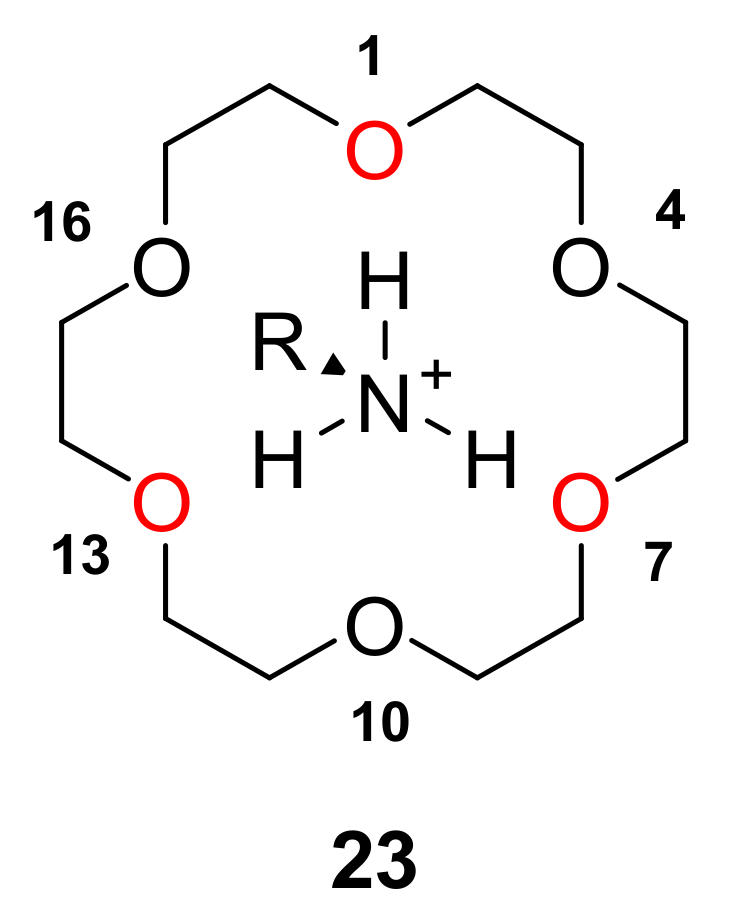
2.3.1. The Calculation Study of Various Crown Ethers and Anilines
2.3.2. Interaction of Chiral Amino Acids and CR-I(+)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Apparatus
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Eluent
3.4. HPLC Conditions
3.4.1. Analysis on a CROWNPAK CR-I (-) Column
3.4.2. Analysis of ODS Column
3.5. Calculation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Aboul-Enein, H.Y. High-performance liquid chromatographic enantioseparation of drugs containing multiple chiral centers on polysaccharide-type chiral stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 906, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, E.L.; Welch, C.J. Separation of achiral analytes using supercritical fluid chromatography with chiral stationary phases. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 67, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, M.; Enomoto, Y.; Uryu, M.; Yang, X.; Kataoka, A.; Ohnishi, A. Application of Polysaccharide-Based Chiral HPLC Columns for Separation of Nonenantiomeric Isomeric Mixtures of Organometallic Compounds. Organometallics 2019, 38, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.B.; Quirino, J.P. Chiral liquid chromatography and capillary electrochromatography: Trends from 2017 to 2018. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Shinkura, S.; Ohnishi, A.; Ueda, K. Achiral Molecular Recognition of Aromatic Position Isomers by Polysaccharide-Based CSPs in Relation to Chiral Recognition. Molecules 2017, 22, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnam, S.; Kandukuri, N.K.; Bondigalla, R.; Choppari, T.; Chennuru, L.N.; Cherla, P.M. Enantioseparation of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Immobilized Crown Ether-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Furuno, M.; Nakano, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Fukusaki, E. Mechanistic study on the high-selectivity enantioseparation of amino acids using a chiral crown ether-bonded stationary phase and acidic, highly organic mobile phase by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1578, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konya, Y.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E. Extra-facile chiral separation of amino acid enantiomers by LC-TOFMS analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, I.; Mijiddorj, B.; Kayano, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Ueda, K.; Sato, H. Separation of D-amino acid-containing peptide phenylseptin using 3,3′-phenyl-1,1′-binaphthyl-18-crown-6-ether columns. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteomics 2020, 1868, 140429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomb, M.; Cram, D.J. Effect of centered functional groups on complexing properties of cyclic polyether hosts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinbo, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nishimura, K.; Sugiura, M. Chromatographic separation of racemic amino acids by use of chiral crown ether-coated reversed-phase packings. J. Chromatogr. A 1987, 405, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, Y.; Nishi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Nakai, H.; Sato, T. Enantiomer separation of amino compounds by a novel chiral stationary phase derived from crown ether. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 805, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.H.; Jin, J.S.; Koo, H.J.; Lee, W. Liquid chromatographic resolution of racemic amines and amino alcohols on a chiral stationary phase derived from crown ether. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 837, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K.; Yongzhu, J.; Nakamura, T.; Nishioka, R.; Ueshige, T.; Tobe, Y. Preparation and evaluation of a chiral stationary phase covalently bound with chiral pseudo-18-crown-6 ether having 1-phenyl-1,2-cyclohexanediol as a chiral unit. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1078, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timko, J.M.; Helgeson, R.C.; Newcomb, M.; Gokel, G.W.; Cram, D.J. Structural parameters that control association constants between polyether host and alkylammonium guest compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 7097–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Shinkura, S.; Ohnishi, A. Retention mechanism and mobile phase design in chromatography with a crown ether based stationary phase. (In preparation)
- Dean, A.D. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, E.L.; Mazurek, U.; Bowen, J.P. Ab initio and molecular mechanics (MM3) calculations on propargyl alcohol and derivatives. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1996, 9, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Minamino, Y.; Hasebe, F.; Ito, S. Deracemization and stereoinversion to aromatic d-amino acid derivatives with ancestral l-amino acid oxidase. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10152–10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision A.03. 2016. Available online: https://gaussian.com (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.; Perdew, J.P.; Wang, Y. Derivation of a Generalized Gradient Approximation: The PW91 Density Functional BT. In Electronic Density Functional Theory: Recent Progress and New Directions; Dobson, J.F., Vignale, G., Das, M.P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 81–111. ISBN 978-1-4899-0316-7. [Google Scholar]
- Miertuš, S.; Scrocco, E.; Tomasi, J. Electrostatic interaction of a solute with a continuum. A direct utilizaion of AB initio molecular potentials for the prevision of solvent effects. Chem. Phys. 1981, 55, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditchfield, R.; Hehre, W.J.; Pople, J.A. Self-Consistent Molecular-Orbital Methods. IX. An Extended Gaussian-Type Basis for Molecular-Orbital Studies of Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 54, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
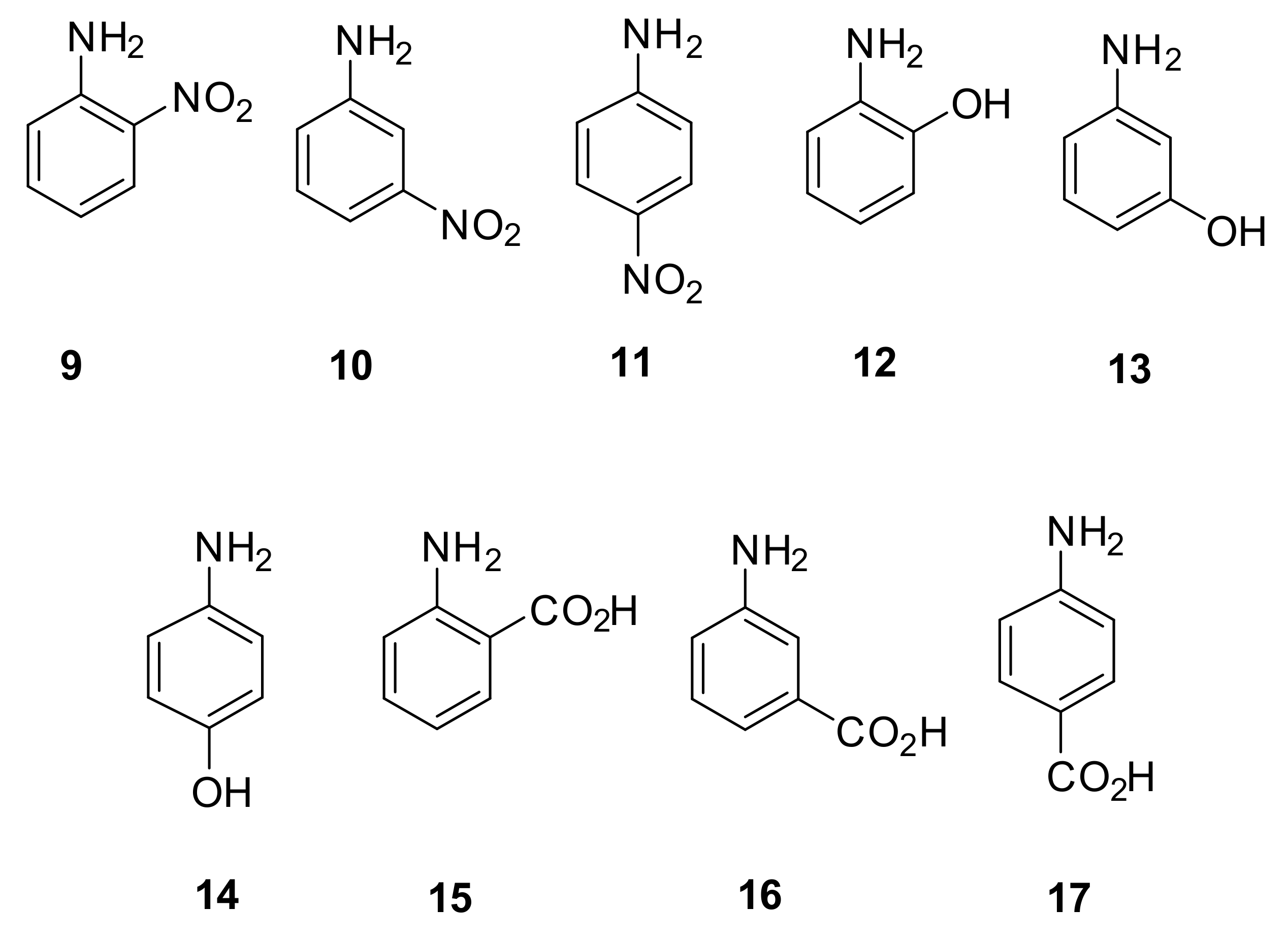



| Analytes | Retention Time (Retention Factor 2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Eluent (A) 3 | Eluent (B) 3 | Eluent (C) 3 | |
| aniline (2) | 7.55 min (1.33) | 10.52 min (2.25) | 7.80 min (1.41) |
| 2-methylaniline (3) | 5.19 min (0.60) | 4.74 min (0.47) | 4.44 min (0.37) |
| 3-methylaniline (4) | 10.95 min (2.38) | 11.23 min (2.47) | 7.18 min (1.22) |
| 4-methylaniline (5) | 12.46 min (2.85) | 12.68 min (2.92) | 8.41 min (1.60) |
| 2-chloroaniline (6) | 8.12 min (1.51) | 4.44 min (0.37) | 4.38 min (0.36) |
| 3-chloroaniline (7) | 12.89 min (2.98) | 12.14 min (2.75) | 6.08 min (0.88) |
| 4-chloroaniline (8) | 14.57 min (3.50) | 15.27 min (3.72) | 7.62 min (1.35) |
| Analytes | Retention Time (Retention Factor 2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Eluent (A) 3 | Eluent (B) 3 | Eluent (C) 3 | |
| aniline (2) | 7.55 min (1.33) | 10.52 min (2.25) | 7.80 min (1.41) |
| 2-nitroaniline (9) | 15.00 min (3.63) | 3.78 min (0.17) | 5.24 min (0.62) |
| 3-nitroaniline (10) | 11.88 min (2.67) | 8.89 min (1.75) | 6.24 min (0.93) |
| 4-nitroaniline (11) | 13.53 min (3.18) | 4.04 min (0.25) | 6.62 min (1.05) |
| 2-hydroxyaniline (12) | 6.19 min (0.91) | 7.96 min (1.46) | 8.72 min (1.70) |
| 3-hydroxyaniline (13) | 7.55 min (1.33) | 13.02 min (3.02) | 12.14 min (2.75) |
| 4-hydroxyaniline (14) | 7.41 min (1.29) | 13.13 min (3.06) | 12.42 min (2.84) |
| 2-carboxyaniline (15) | 5.85 min (0.81) | 3.50 min (0.08) | 5.12 min (0.58) |
| 3-carboxyaniline (16) | 7.49 min (1.31) | 13.18 min (3.07) | 9.21 min (1.85) |
| 4-carboxyaniline (17) | 6.90 min (1.13) | 10.40 min (2.21) | 6.51 min (1.01) |
| Analytes | Retention Time (Retention Factor 2) 3 |
|---|---|
| aniline (2) | 7.99 min (1.96) |
| 2-methylaniline (3) | 12.57 min (3.66) |
| 3-methylaniline (4) | 12.86 min (3.77) |
| 4-methylaniline (5) | 12.26 min (3.55) |
| 2-chloroaniline (6) | 22.82 min (7.46) |
| 3-chloroaniline (7) | 21.37 min (6.92) |
| 4-chloroaniline (8) | 18.81 min (5.97) |
| 2-hydroxyaniline (12) | 4.56 min (0.69) |
| 3-hydroxyaniline (13) | 3.81 min (0.41) |
| 4-hydroxyaniline (14) | 3.23 min (0.20) |
| Analytes | Retention Time (Retention Factor 2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Eluent (A) 3 | Eluent (B) 3 | Eluent (C) 3 | |
| benzylamine (18) | 9.46 min (1.92) | 11.32 min (2.50) | 10.71 min (2.31) |
| 2-methylbenzylamine (19) | 13.33 min (3.12) | 11.71 min (2.62) | 10.75 min (2.32) |
| 3-methylbenzylamine (20) | 15.65 min (3.84) | 13.11 min (3.05) | 10.11 min (2.12) |
| 4-methylbenzylamine (21) | 13.52 min (3.18) | 11.25 min (2.48) | 10.04 min (2.10) |
| Analytes | Stabilization Energy, ΔE (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| aniline (2) | 25.31 |
| 2-methylaniline (3) | 24.51 |
| 3-methylaniline (4) | 24.98 |
| 4-methylaniline (5) | 24.85 |
| 2-chloroaniline (6) | 37.48 |
| 3-chloroaniline (7) | 47.04 |
| 4-chloroaniline (8) | 48.70 |
| Chiral. Crown Ether | Amino Acid | Stabilization Energy, ΔE (kcal/mol) | Elution Order 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | (R)-Phenylglycine (25) | 19.41 | 1st |
| 22 | (S)-Phenylglycine (26) | 23.91 | 2nd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohnishi, A.; Shibata, T.; Imase, T.; Shinkura, S.; Nagai, K. Achiral Molecular Recognition of Substituted Aniline Position Isomers by Crown Ether Type Chiral Stationary Phase. Molecules 2021, 26, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020493
Ohnishi A, Shibata T, Imase T, Shinkura S, Nagai K. Achiral Molecular Recognition of Substituted Aniline Position Isomers by Crown Ether Type Chiral Stationary Phase. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020493
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhnishi, Atsushi, Tohru Shibata, Tatsuya Imase, Satoshi Shinkura, and Kanji Nagai. 2021. "Achiral Molecular Recognition of Substituted Aniline Position Isomers by Crown Ether Type Chiral Stationary Phase" Molecules 26, no. 2: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020493
APA StyleOhnishi, A., Shibata, T., Imase, T., Shinkura, S., & Nagai, K. (2021). Achiral Molecular Recognition of Substituted Aniline Position Isomers by Crown Ether Type Chiral Stationary Phase. Molecules, 26(2), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020493






