The Influence of Hydrogen Bond Donors on the CO2 Absorption Mechanism by the Bio-Phenol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
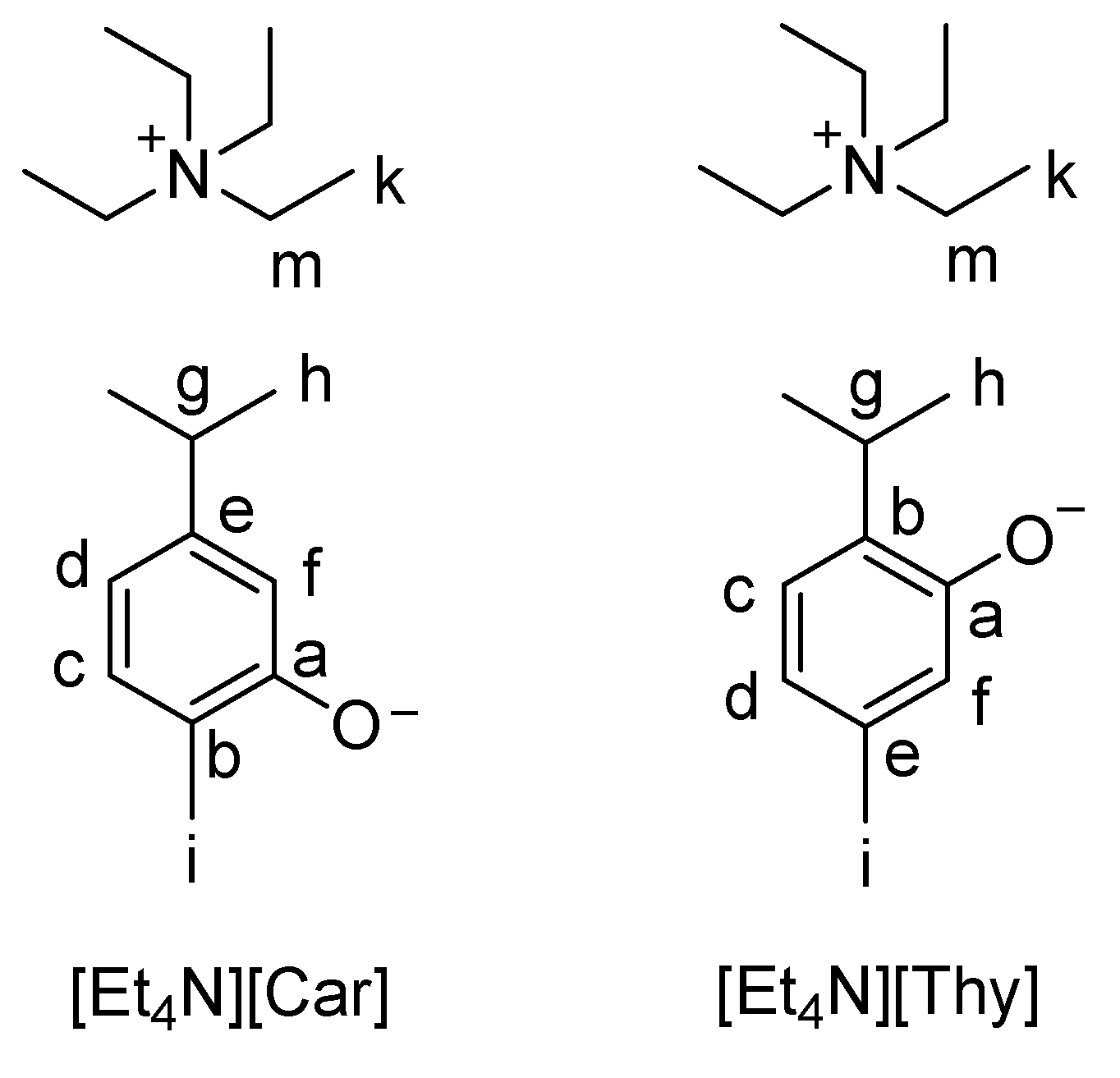
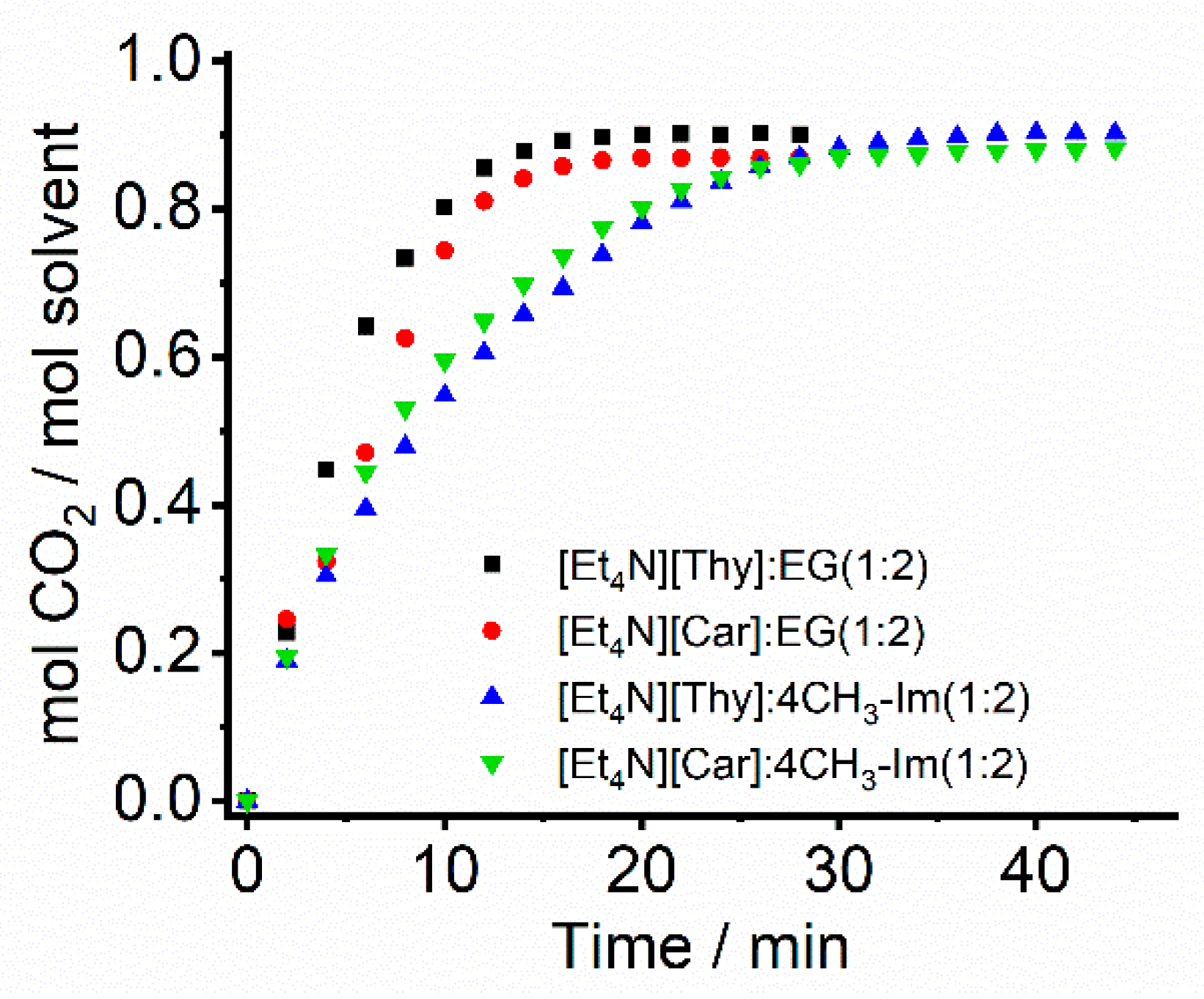
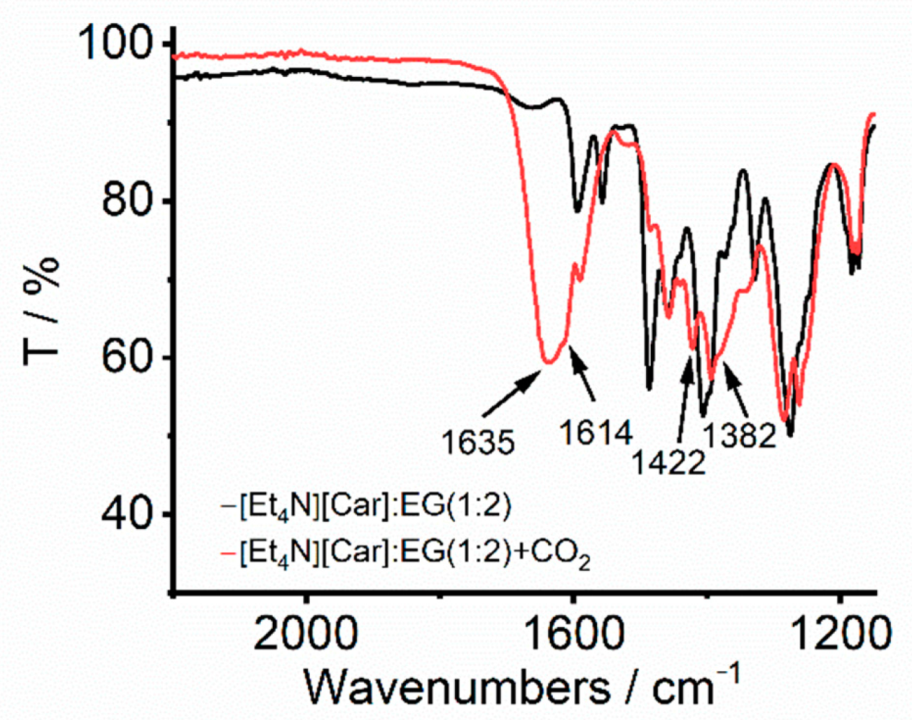
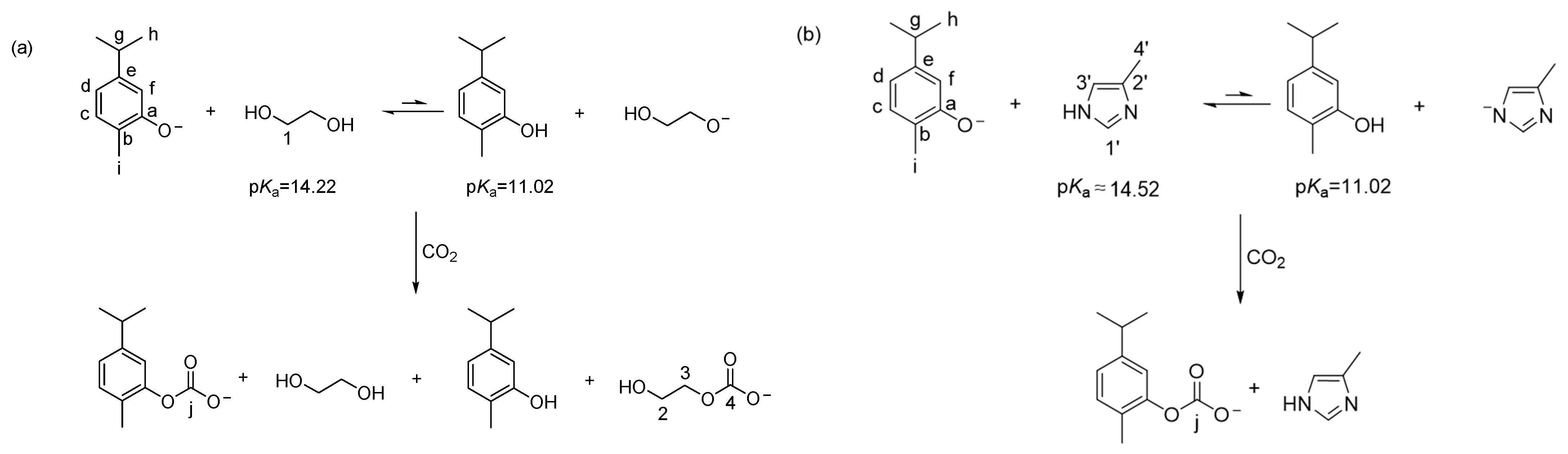
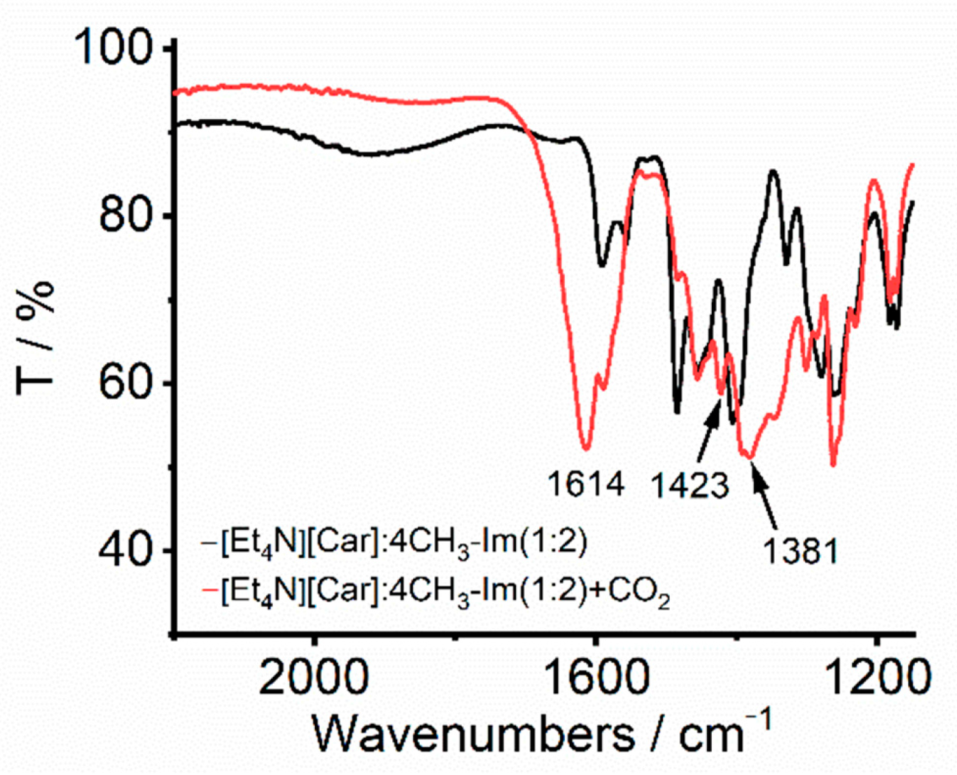
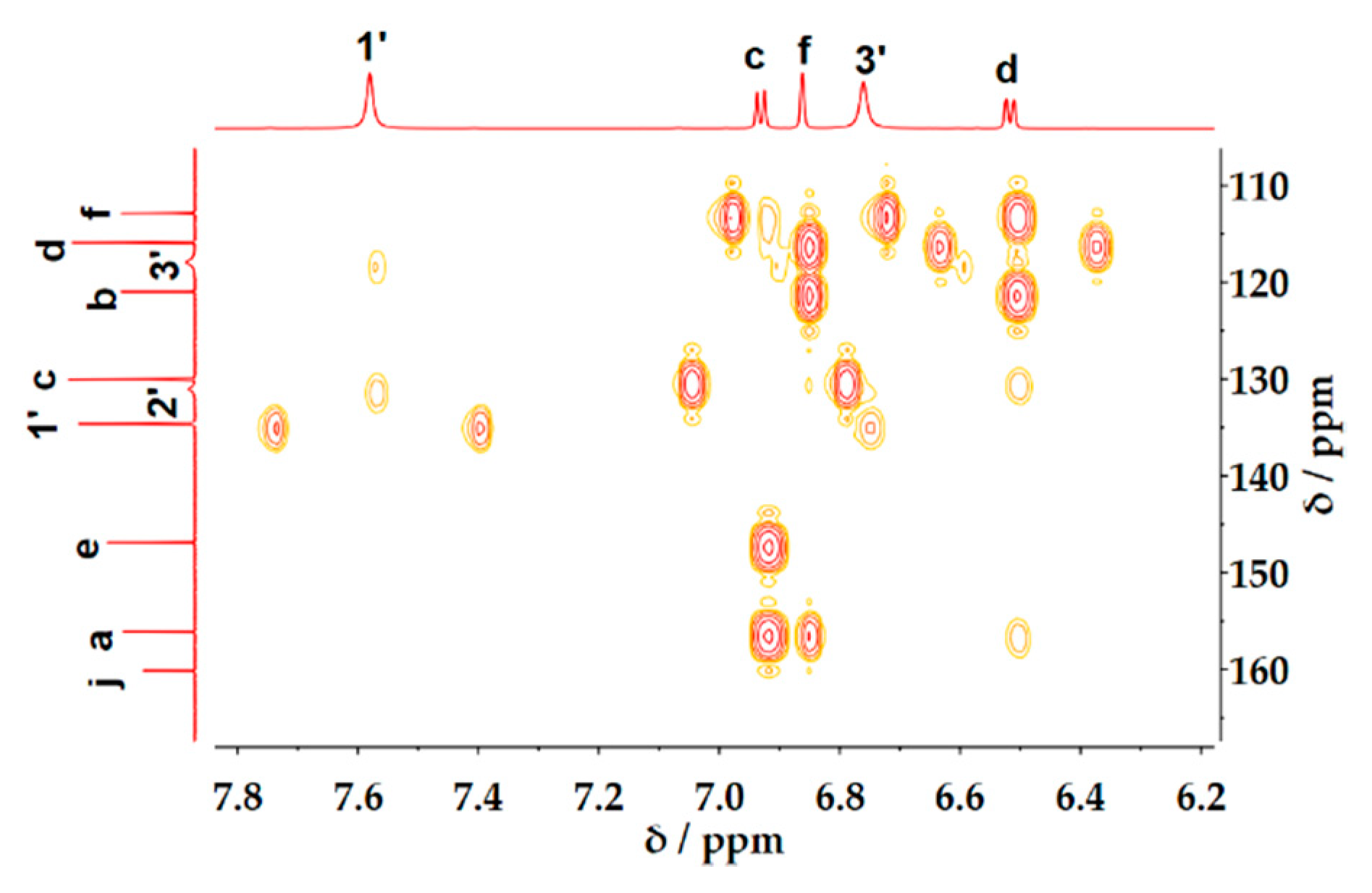
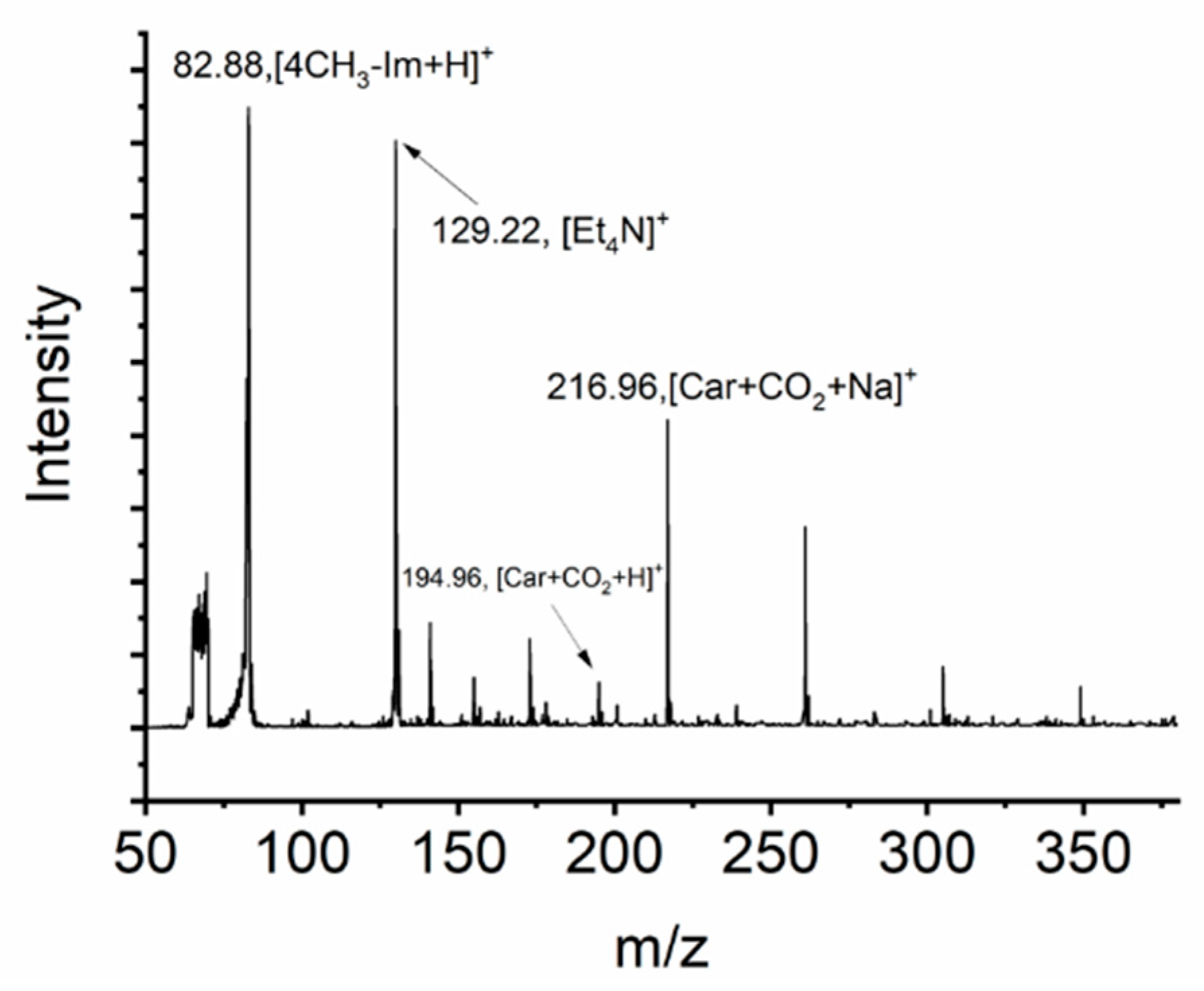
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Characterizations
3.2. Synthesis of the ILs and DESs
3.3. Absorption and Desorption of CO2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Luderer, G.; Vrontisi, Z.; Bertram, C.; Edelenbosch, O.Y.; Pietzcker, R.C.; Rogelj, J.; De Boer, H.S.; Drouet, L.; Emmerling, J.; Fricko, O.; et al. Residual fossil CO2 emissions in 1.5–2 °C pathways. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hepburn, C.; Adlen, E.; Beddington, J.; Carter, E.A.; Fuss, S.; Mac Dowell, N.; Minx, J.C.; Smith, P.; Williams, C.K. The technological and economic prospects for CO2 utilization and removal. Nature 2019, 575, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alivand, M.S.; Mazaheri, O.; Wu, Y.; Stevens, G.W.; Scholes, C.A.; Mumford, K.A. Catalytic Solvent Regeneration for Energy-Efficient CO2 Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 18755–18788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutcher, B.; Fan, M.; Russell, A.G. Amine-Based CO2 Capture Technology Development from the Beginning of 2013—A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldebrant, D.J.; Koech, P.K.; Glezakou, V.-A.; Rousseau, R.; Malhotra, D.; Cantu, D.C. Water-Lean Solvents for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture: Fundamentals, Uncertainties, Opportunities, and Outlook. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9594–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liang, S.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Xie, B.; Toe, C.Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Industrial carbon dioxide capture and utilization: State of the art and future challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8584–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lu, L.-H.; Peng, A.-Z.; Jia, G.-K.; Peng, C.; Cao, Z.; Tang, Z.; He, W.-M.; Xu, X. Ultrasound-promoted Brønsted acid ionic liquid-catalyzed hydrothiocyanation of activated alkynes under minimal solvent conditions. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3683–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, M.; Simon, N.M.; Dupont, J. The Nature of Carbon Dioxide in Bare Ionic Liquids. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, D.; Guo, W.; Mu, T. Capture of Toxic Gases by Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5410–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Ji, X. Carbon Dioxide Capture with Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents: A New Generation of Sorbents. ChemSusChem 2016, 10, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xiao, H.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Tang, M.-S.; Tang, Z.-L.; Xia, W.; Li, W.-F.; Cao, Z.; He, W.-M. Natural Deep Eutectic Sol-vent-Catalyzed Selenocyanation of Activated Alkynes via an Intermolecular H-Bonding Activation Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Zeng, S. Imidazole tailored deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture enhanced by hydrogen bonds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 27306–27316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, T.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Choi, J.W. Deep eutectic solvents as attractive media for CO2 capture. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2834–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.B.; Kumar, R. Solubility of CO2 and CH4 in sterically hindered amine-based deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mikkola, J.-P. Unusual temperature-promoted carbon dioxide capture in deep-eutectic solvents: The synergistic interactions. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3939–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W. Hydrophobic Functional Deep Eutectic Solvents Used for Efficient and Reversible Capture of CO2. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6809–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Lv, M.; Yang, D. Efficient CO2 absorption by azolide-based deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukesh, C.; Khokarale, S.G.; Virtanen, P.; Mikkola, J.-P. Rapid desorption of CO2 from deep eutectic solvents based on polyamines at lower temperatures: An alternative technology with industrial potential. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L. Highly Efficient and Reversible CO2 Capture by Task-Specific Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13321–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhao, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, F.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S. Superbase Ionic Liquid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Improving CO2 Absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Ma, J.; Yang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Tantai, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. Superbase/Acylamido-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Multiple-Site Efficient CO2 Absorption. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7569–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Pandey, S. Superbase-Added Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for CO2 Capture and Sequestration. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 11422–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzagli, F.; Mani, F.; Peruzzini, M. Efficient CO2 absorption and low temperature desorption with non-aqueous solvents based on 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP). Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control 2013, 16, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lv, M.; Chen, J. Efficient non-aqueous solvent formed by 2-piperidineethanol and ethylene glycol for CO2 absorption. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 12483–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yu, B.; Dai, S. Tuning the Physicochemical Properties of Diverse Phenolic Ionic Liquids for Equimolar CO2 Capture by the Substituent on the Anion. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; McCluskey, A.; Attalla, M.I. An FTIR Spectroscopic Study on the Effect of Molecular Structural Variations on the CO2 Absorption Characteristics of Heterocyclic Amines. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Guo, Y.; Ding, F.; Zhao, H.; Cui, G.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Significant Improvements in CO2 Capture by Pyridine-Containing Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids through Multiple-Site Cooperative Interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7053–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Dutta, P.K. Infrared Spectroscopic Study of Reaction of Carbon Dioxide with Aqueous Monoethanolamine Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6276–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, M.N.; Oliva, M.; Casero, C.; Dambolena, J.; Luna, A.; Zygadlo, J.; Demo, M. Antimicrobial combined action of terpenes against the food-borne microorganisms Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus. Flavour Fragr. J. 2009, 24, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 16th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 644. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszak, C.A.; Matuszak, A.J. Imidazole—Versatile today, prominent tomorrow. J. Chem. Educ. 1976, 53, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Yang, D. The Influence of Hydrogen Bond Donors on the CO2 Absorption Mechanism by the Bio-Phenol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237167
Wang Z, Wang Z, Chen J, Wu C, Yang D. The Influence of Hydrogen Bond Donors on the CO2 Absorption Mechanism by the Bio-Phenol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules. 2021; 26(23):7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237167
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ze, Zonghua Wang, Jie Chen, Congyi Wu, and Dezhong Yang. 2021. "The Influence of Hydrogen Bond Donors on the CO2 Absorption Mechanism by the Bio-Phenol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents" Molecules 26, no. 23: 7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237167
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, Z., Chen, J., Wu, C., & Yang, D. (2021). The Influence of Hydrogen Bond Donors on the CO2 Absorption Mechanism by the Bio-Phenol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules, 26(23), 7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237167







