Silica Hydride: A Separation Material Every Analyst Should Know About
Abstract
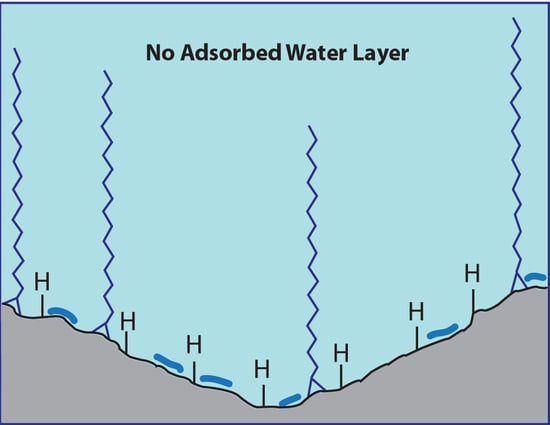
:1. Background
2. Salient Features of Silica Hydride Stationary Phases
3. Significant Applications by Column Type
3.1. Diamond Hydride
3.2. Phenyl
3.3. Amide
3.4. UDC Cholesterol
3.5. UDA (Undeceanoic Acid)
3.6. Bidentate C18
3.7. Bidentate C8
3.8. Diol
3.9. Silica C
4. General Method Development Strategies on Silica Hydride Columns
4.1. Reversed-Phase
4.1.1. Neutrals
4.1.2. Acids
4.1.3. Bases
4.2. Aqueous Normal-Phase (ANP)
4.2.1. Acids
4.2.2. Neutrals
4.2.3. Bases
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandoval, J.E.; Pesek, J.J. Synthesis and characterization of a hydride modified porous silica material as an intermediate in the preparation of chemically bonded chromatographic stationary phases. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J.E.; Pesek, J.J. Hydrolytically stable bonded chromatographic phases prepared through hydrosilation of olefins on a hydride-modified silica intermediate. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Jonsson, E.; Auvinen, M.; Pesek, J.J.; Sandoval, J.E. A new approach for the preparation of a hydride-modified substrate used as an intermediate in the synthesis of surface-bonded materials. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. The development of silica hydride stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography from conception to commercialization. Separations 2019, 6, 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Soukup, J.; Janas, P.; Jandera, P. Gradient elution in aqueous normal-phase liquid chromatography on hydrosilated silica-based stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1216, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartó, E.; Felinger, A.; Jandera, P. Investigation of the temperature dependence of water adsorption on silica-based stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1489, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsing, C.; Nolvachi, Y.; Marriott, P.; Boysen, R.; Matyska, M.; Pesek, J.; Hearn, M. Insights into the origin of the separation selectivity with silica hydride adsorbents. J. Phys. Chem. Part B 2015, 119, 3063–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, N.M.; Ashu-Arrah, B.A.; Nagle, A.P.; Omamogho, J.O.; O’Sullivan, G.P.; Friebolin, V.; Dietrich, B.; Albert, K.; Glennon, J.D. Silica hydride intermediate for octadecylsilica and phenyl bonded phase preparation via heterogeneous hydrosilation in supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Fischer, S.M.; Sana, T.R. Analysis of hydrophilic metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography—Mass spectrometry using a silica hydride-based stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1204, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naffa, R.; Holmes, G.; Ahn, M.; Harding, D.; Norris, G. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for the simultaneous quantitation of collagen and elastin crosslinks. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1478, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/90/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-03183/63/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-02318/46/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-00950/46/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-02342/46/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-00807/46/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-01023/46/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Ploumen, C.; Marginean, J.; Lurie, I.S. The utility of silica hydride-based stationary phases for dual-mode ultra high performance liquid chromatography separation of synthetic cathinone positional isomers. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.C.; Trujillo, C.; Wang, Z.; Eoh, H.; Ehrt, S.; Schnappinger, D.; Boshoff, H.I.M.; Rhee, K.Y.; Barry III, C.E.; Mizrahi, V. Validation of CoaBC as a bactericidal target in the coenzyme A pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2016, 2, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.E.; Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. Robust HPLC-refractive index analysis of simple sugars in beverages using silica hydride columns. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 12, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cífková, E.; Hájek, R.; Lísa, M.; Holčapek, M. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry of (lyso)phosphatidic acids, (yso)phosphatidylserines and other lipid classes. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1439, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Young, J.E. Analysis of thiopurines using aqueous normal phase chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 95, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, R.; Young, J.E.; Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. Separation of 1,3-dimethylamylamine and other polar compounds in dietary supplement formulation using aqueous normal phase chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2578–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.E.; Matyska, M.T.; Pesek, J.J. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry compatible approaches for the quantitation of folic acid in fortified juices and cereals using aqueous normal phase conditions. J. Chromatog. A 2011, 1218, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boysen, R.I.; Yang, Y.; Chowdhury, J.; Matyska, M.T.; Pesek, J.J.; Hearn, M.T.W. Simultaneous separation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic peptides with a silica hydride stationary phase using aqueous normal phase conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8021–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Duley, J.; Zamzami, M.; Fischer, S.M. Aqueous normal phase (ANP) retention of nucleotides on silica hydride-based columns. Method development strategies for analytes relevant in clinical analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 930–938. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Liu, F.; Holmes, E.H.; Ostrander, G.K.; Li, Q.X. Aqueous normal phase liquid chromatography coupled with tandem time-of-flight quadrupole mass spectrometry for determination of zanamivir in human serum. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 906, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villarino, G.; Guerquin-Kern, J.-L.; Sório de Carvalho, L.P.; Poquet, Y.; Neyrolles, O. Mycobacterium tuberculosis nitrogen assimilation and host colonization require aspartate. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 674–676. [Google Scholar]
- Sana, T.R.; Gordon, D.B.; Fischer, S.M.; Tichy, S.E.; Norton Kitagawa, N.; Lai, C.; Gosnell, W.L.; Chang, S.P. Global Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics Profiling of Erythrocytes Infected with Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60840. [Google Scholar]
- Marcobal, A.; Kashyap, P.C.; Nelson, T.A.; Aronov, P.A.; Donia, M.S.; Spormann, A.; Fischbach, M.A.; Sonnenburg, J.L. A metabolomic view of how the human gut microbiota impacts the host metabolome using humanized and gnotobiotic mice. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalcraft, K.R.; McCarry, B.E. Tandem LC columns for the simultaneous retention of polar and nonpolar molecules in comprehensive metabolomics analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3478–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appulage, D.K.; Schug, K.A. Silica hydride based phases for small molecule separations usingautomated liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method development. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1507, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Kim, A.M. Evaluation of silica hydride-based stationary phases for the analysis of drugs of abuse. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2760–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanova, F.A.; Vanier, N.L.; Chaves, F.C.; Pesek, J.; Matyska-Pesek, M.; Elias, M.C.; de Oliveir, M. Improvement of the quality of parboiled rice by using anti-browning agents during parboiling process. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, J.; Matyska, M.; Hoffman, J.F.; Madruga, N.; Crizel, R.L.; Elias, M.C.; Vanier, N.L.; Chaves, F.C. Analysis of mycotoxins in grains using silica hydride-based stationary phases. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Matyska-Pesek, M.T.; Berrious, J.D.J.; Takeoka, G.R.; Pesek, J.J. HPLC/ESI-TOF-MS identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in fermented/nonfermented jaboticaba fruit (myrciaria jaboticaba (vell.) O. berg). Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 3, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/93/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Tardiff, E.; Hiltz, T. Chromatographic characterization of a silica hydride-based amide stationary phase. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2728–2734. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/167/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Pesek, J.J.; Cash, T. Chemically bonded liquid crystals as stationary phases for high performance liquid chromatography. Synthesis on silica via an organochlorosilane pathway. Chromatographia 1989, 27, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Dawson, G.B.; Wilsdorf, A.; Marc, P.; Padki, M. The cholesterol bonded phase as a separation medium in high performance liquid chromatography. Evaluation of properties and applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 986, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/94/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Dang, A. Analysis of ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate using aqueous normal phase chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/99/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Young, J.E.; Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. LC-MS compatible approaches for quantitation of limonin in citrus juice. LCGC 2015, 33, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.E.; Lim, M.V.; Topete, J.; Hang, H.; Gahol, M.; Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. Improved sensitivity and specificity for trans-resveratrol in red wine analysis with HPLC-UV and LC-MS. LCGC N. Am. 2016, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/92/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Dang, A.; Sieng, M.; Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. Determination of bisphenol A in receipts and carbon paper by HPLC-UV. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 2015, 38, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/97/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/100/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Young, J.E.; Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Sanchez, B.; White, B. Quantitative analysis of uric acid metabolites in urine by high performance liquid chromatography—Mass spectrometry using a silica hydride column. Curr. Chromatogr. 2017, 4, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/146/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T.; Sharma, A. Use of hydride-based separation materials for organic normal phase chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 2008, 31, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/article/aa-01805/46/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Bawazeer, S.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Euerby, M.R.; Bawazeer, S.; David Watson, D.G. A comparison of the chromatographic properties of silica gel and silicon hydride modified silica gels. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1263, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santali, E.Y.; Edwards, D.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Bailes, S.; Euerby, M.R.; Watson, D.G. A Comparison of Silica C and Silica Gel in HILIC Mode: The Effect of Stationary Phase Surface Area. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://kb.mtc-usa.com/category/46/63/91/cogent-type-c-silica-columns/98/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pesek, J.J.; Matyska, M.T. Silica Hydride: A Separation Material Every Analyst Should Know About. Molecules 2021, 26, 7505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247505
Pesek JJ, Matyska MT. Silica Hydride: A Separation Material Every Analyst Should Know About. Molecules. 2021; 26(24):7505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247505
Chicago/Turabian StylePesek, Joseph J., and Maria T. Matyska. 2021. "Silica Hydride: A Separation Material Every Analyst Should Know About" Molecules 26, no. 24: 7505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247505
APA StylePesek, J. J., & Matyska, M. T. (2021). Silica Hydride: A Separation Material Every Analyst Should Know About. Molecules, 26(24), 7505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247505