Dynamic Changes in Glutenin Macropolymer during Different Dough Mixing and Resting Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
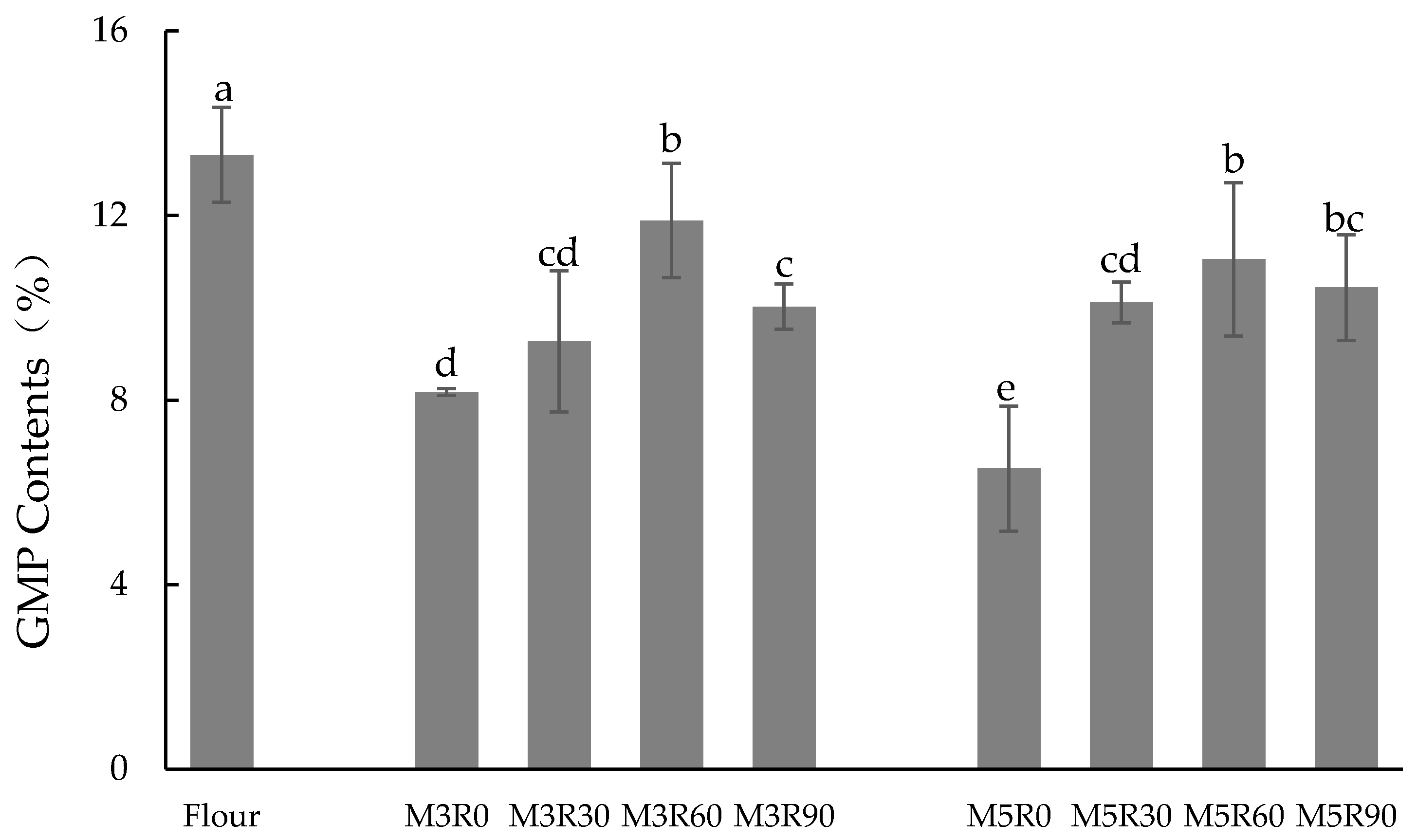
2.1. GMP Content
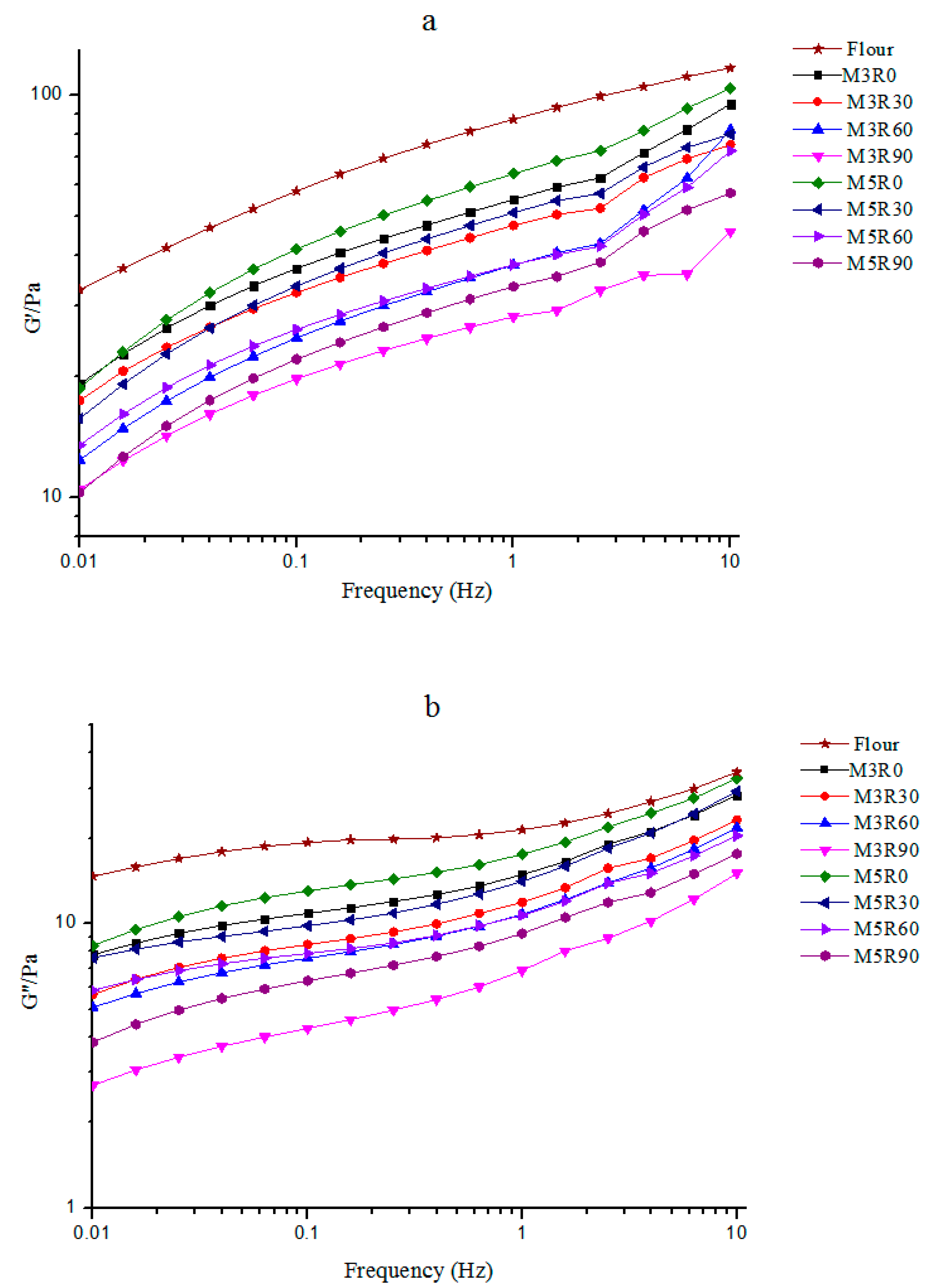
2.2. Dynamic Rheological Properties of GMP
2.3. SH/SS Exchange and SH Oxidation
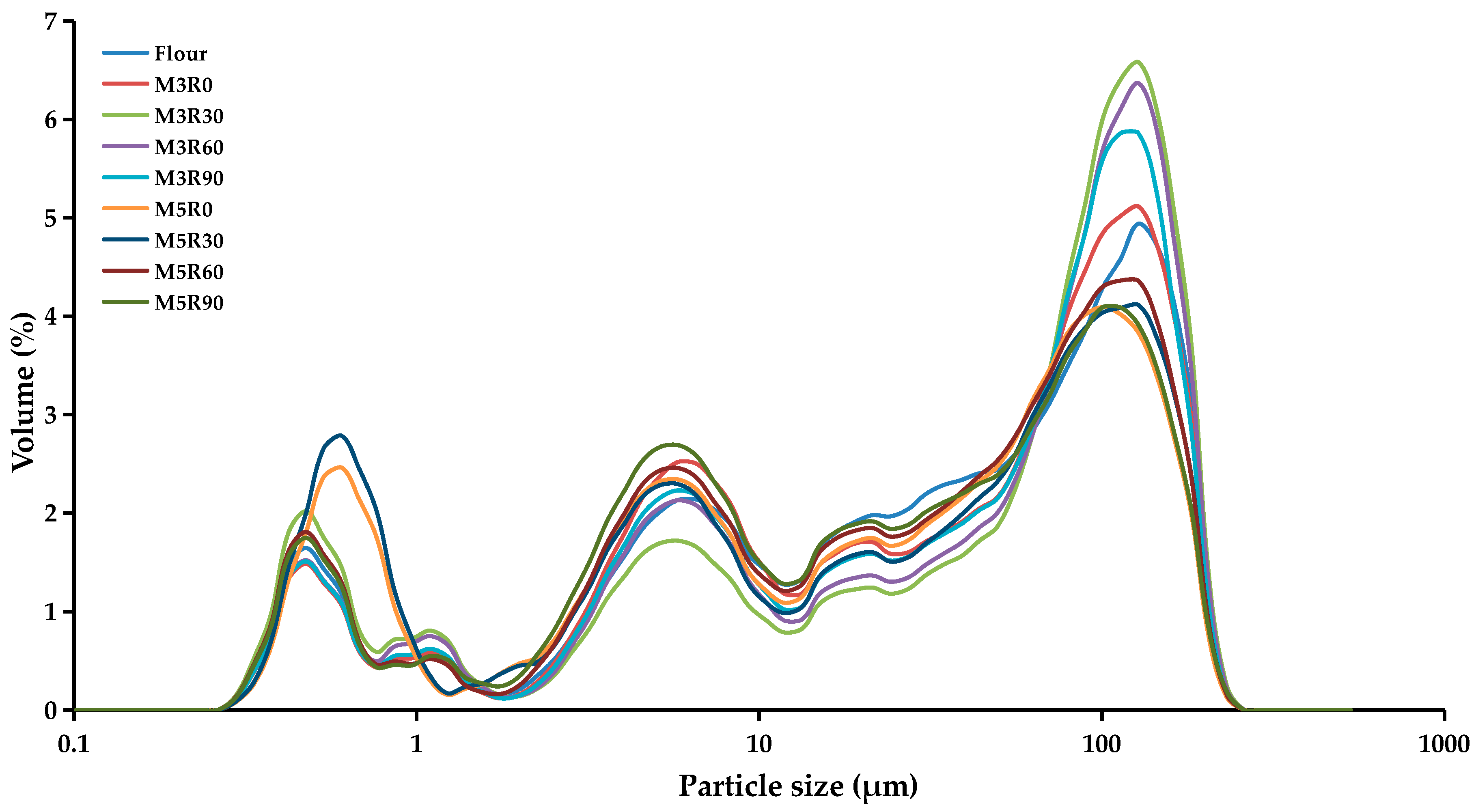
2.4. Particle Size Analysis of GMP
2.5. Secondary Structure of GMP
2.6. HMW/LMW Ratio of GMP
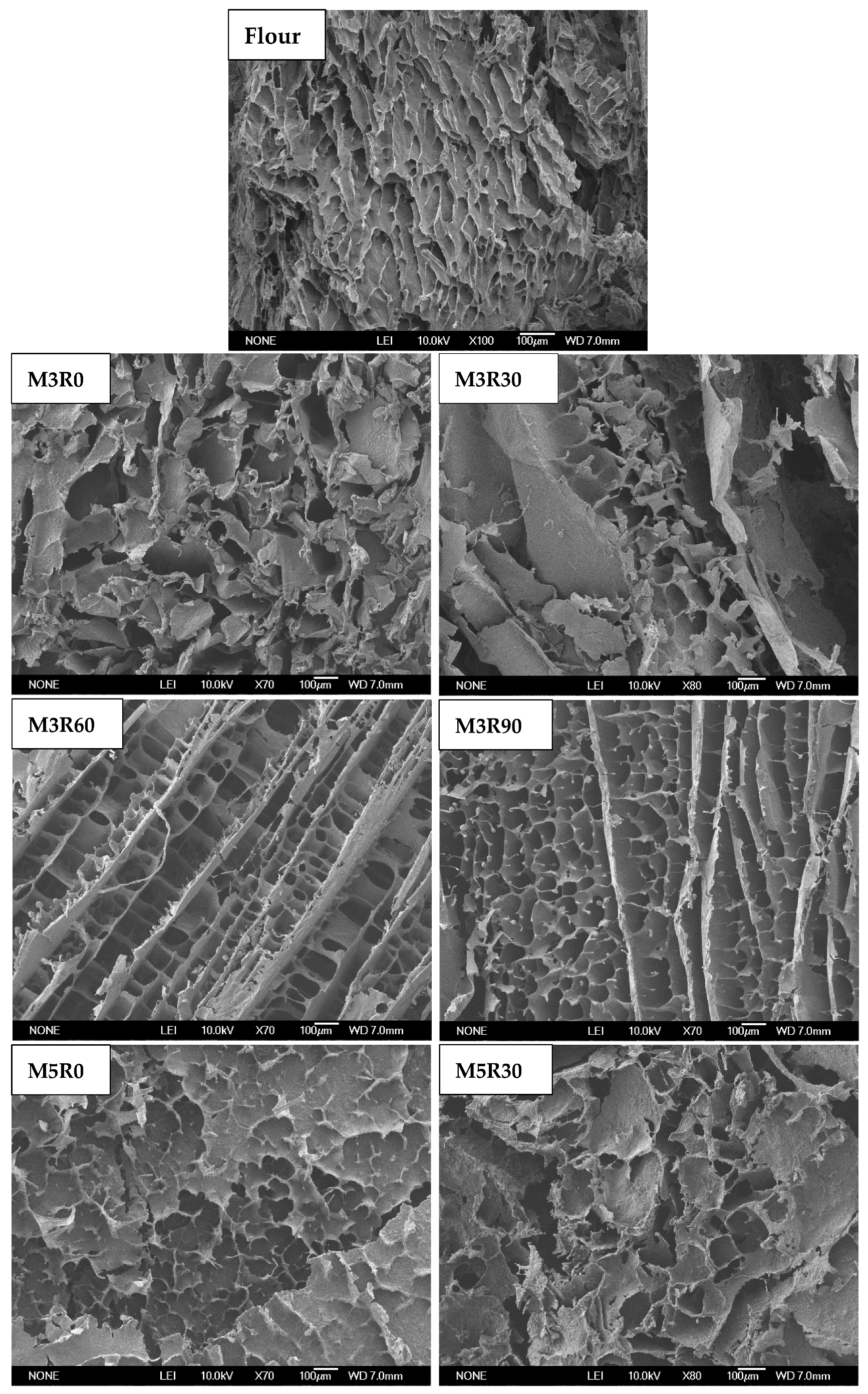
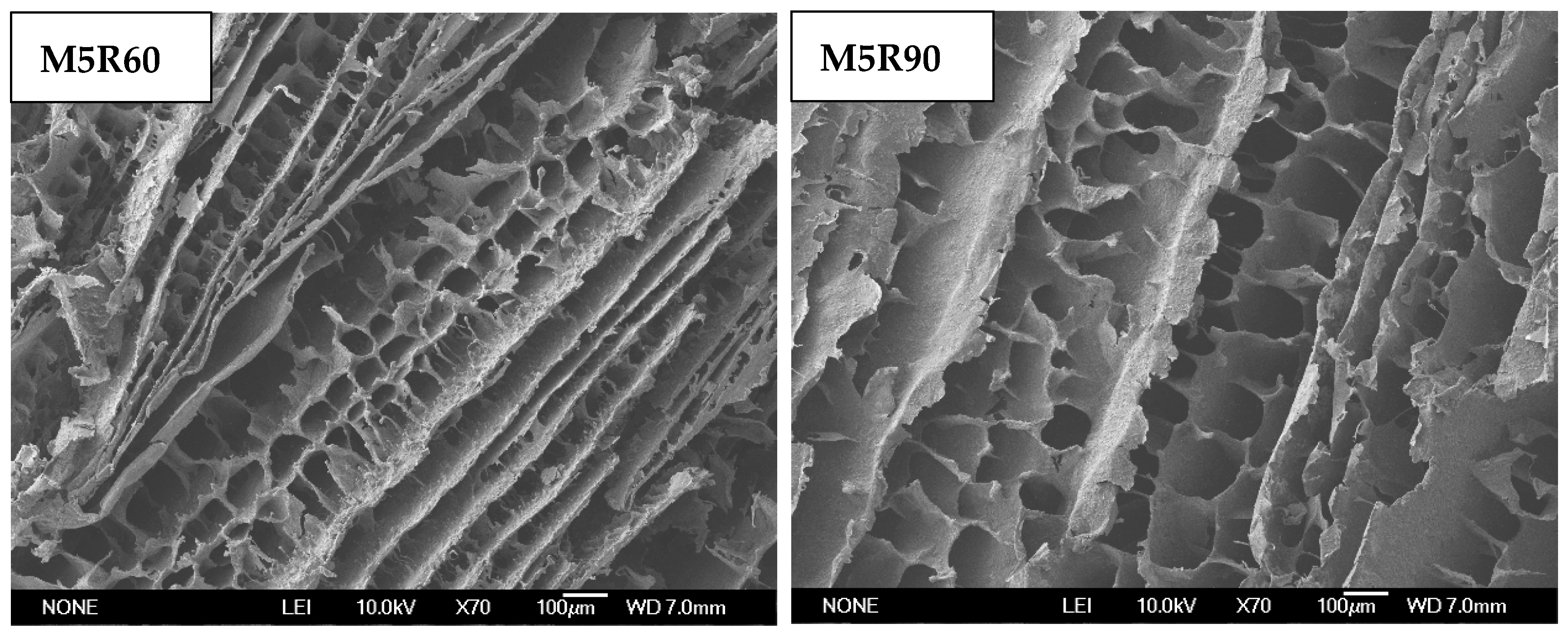
2.7. Microstructure of GMP
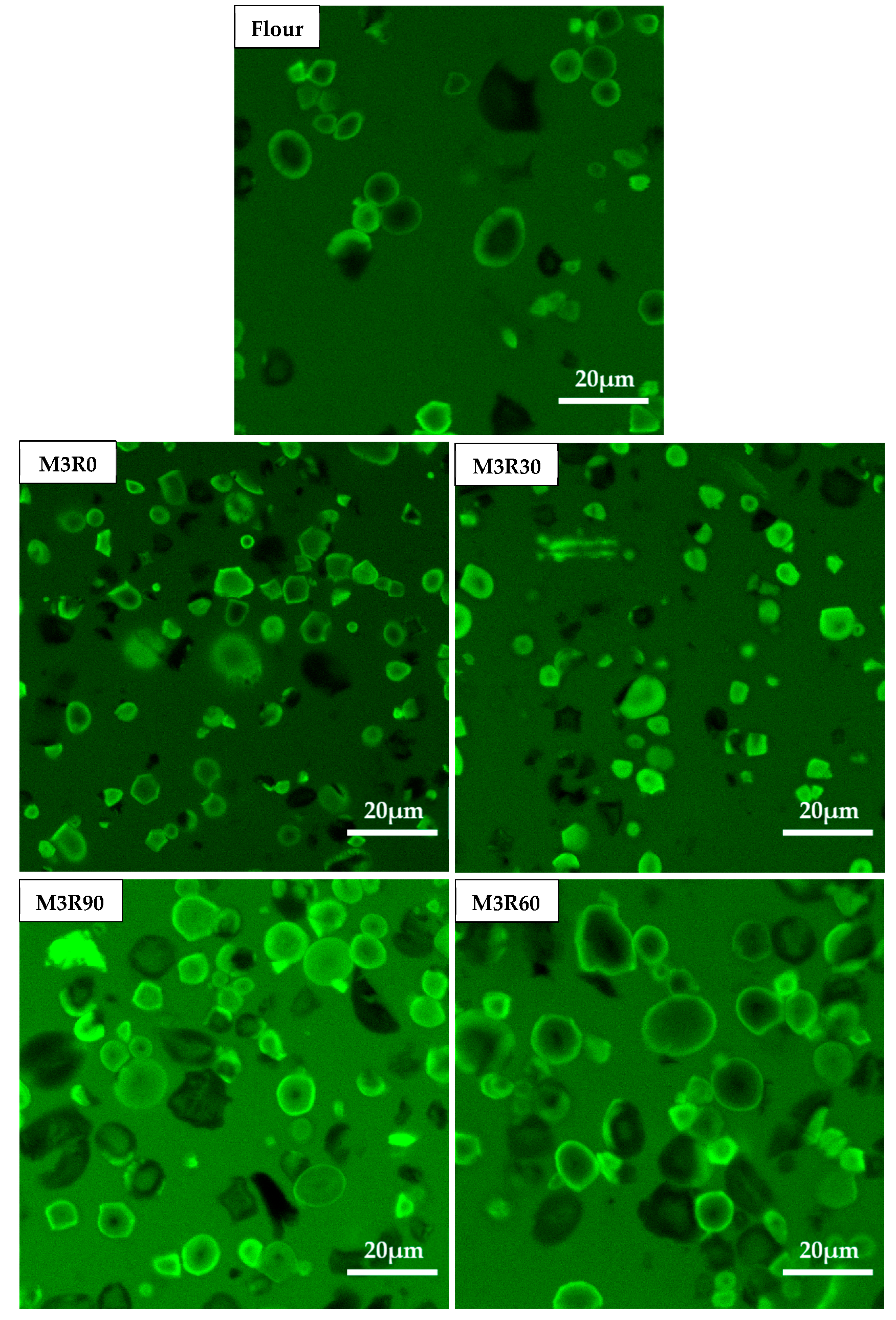
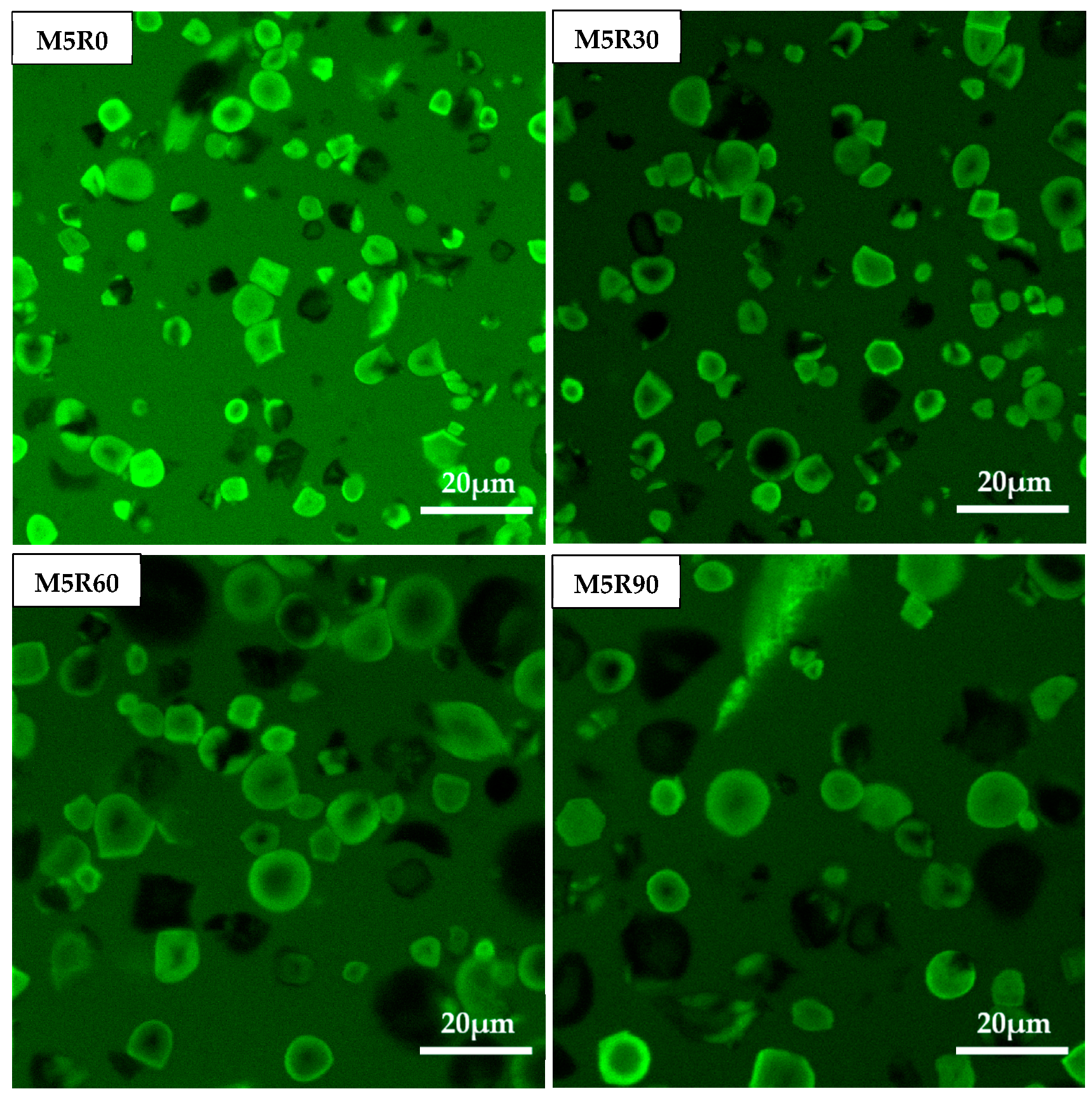
2.8. CLSM Characterization of GMP Particles
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Dough Sample Preparation (Mixing and Resting)
3.3. Isolation of GMP
3.4. GMP Content Measurements
3.5. Dynamic Rheology of GMP Gels
3.6. Thiol/Disulfide Content in GMP
3.7. Particle Size Analysis of GMP
3.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis of GMP
3.9. HMW/LMW Ratio Determination Statistical Analysis
3.10. Microstructure of GMP
3.11. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aussenac, T.; Carceller, J.L.; Kleiber, D. Changes in SDS solubility of glutenin polymers during dough mixing and resting 1. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weegels, P.L.; Pijpekamp, A.M.V.D.; Graveland, A.; Hamer, R.J.; Schofield, J.D. Depolymerisation and re-polymerisation of wheat glutenin during dough processing. I. Relationships between glutenin macropolymer content and quality parameters. J. Cereal Sci. 1996, 23, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G.; Belton, P.S.; Tatham, A.S. The structure and properties of gluten: An elastic protein from wheat grain. Philoso. Tran. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 357, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaka, V.; Khatkar, B.S. Effects of gliadin/glutenin and HMW-GS/LMW-GS ratio on dough rheological properties and bread-making potential of wheat varieties: Gluten proteins, dough rheology and bread quality. J. Food Qual. 2015, 38, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, C.; Lichtendonk, W.; Plijter, J.J.; Hamer, R.J. Glutenin macropolymer: A gel formed by glutenin particles. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonen, J.H.E.; Scheepstra, A.; Graveland, A. Use of the SDS-sedimentation test and SDS-polyacrylamidegel electrophoresis for screening breeder’s samples of wheat for bread-making quality. Euphytica 1982, 31, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanhaeuser, S.M.; Wieser, H.; Koehler, P. Correlation of quality parameters with the baking performance of wheat flours. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, P.E. The glutenin fraction (gel-protein) of wheat protein-A new tool in the prediction of baking quality. Asp. Appl. Biol. 1993, 36, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sapirstein, H.D.; Suchy, J. SDS-protein gel test for prediction of bread loaf volume. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, C.; Lichtendonk, W.J.; Plijter, J.J.; Hamer, R.J. Understanding the link between GMP and dough: From glutenin particles in flour towards developed dough. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronsmo, K.M.; Færgestad, E.M.; Longva, Å.; Schofield, J.D.; Magnus, E.M. A Study of how size distribution of gluten proteins, surface properties of gluten and dough mixing properties relate to baking properties of wheat flours. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X. Polymerization of wheat gluten and the changes of glutenin macropolymer (GMP) during the production of Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneel, C.; Lagrain, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Redox agents and N-ethylmaleimide affect the extractability of gluten proteins during fresh pasta processing. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graveland, A.; Bongers, P.; Bosveld, P. Extraction and fractionation of wheat flour proteins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 33, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.L.; Ross, A.S.; Engle, D.A. Glutenin macropolymer in salted and alkaline noodle doughs. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Don, C.; Lichtendonk, W.J.; Plijter, J.J.; van Vliet, T.; Hamer, R.J. The effect of mixing on glutenin particle properties: Aggregation factors that affect gluten function in dough. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.H.; Goot, A.J.V.D.; Hamer, R.J.; Boom, R.M. Effect of simple shear on the physical properties of glutenin macro polymer (GMP). J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 42, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraverbeke, W.S.; Courtin, C.M.; Verbruggen, I.M.; Delcour, J.A. Factors governing levels and composition of the sodium dodecyl sulphate-unextractable glutenin polymers during straight dough breadmaking. J. Cereal Sci. 1999, 29, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerritt, J.H.; Hac, L.; Bekes, F. Depolymerization of the glutenin macropolymer during dough mixing: I. Changes in levels, molecular weight distribution, and overall composition. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapirstein, H.D.; Fu, B.X. Intercultivar variation in the quantity of monomeric proteins, soluble and insoluble glutenin, and residue protein in wheat flour and relationships to breadmaking quality. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weegels, P.L.; Hamer, R.J.; Schofield, J.D. Functional properties of wheat glutenin. J. Cereal Sci. 1996, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrain, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Impact of redox agents on the physico-chemistry of wheat gluten proteins during hydrothermal treatment. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Bian, K. Effect of resting time on moisture distribution and glutenin macropolymer of stewed noodles dough. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 18, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, M.H.; Dehlon, P.; Autran, J.C.; Leygue, J.P.; Bar-L’Helgouac’h, C. Effects of temperature, sonication time, and power settings on size distribution and extractability of total wheat flour proteins as determined by size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Choi, S.G.; Kerr, W.L. Water dynamics in white bread and starch gels as affected by water and gluten content. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Z.; Lu, Q.Y. The changes of gluten ingredients during making noodle and their relationships with noodle texture difference. J. Technol. Nat. Sci. Edit. 2005, 26, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Šramková, Z.; Gregová, E.; Šturdík, E. Chemical composition and nutritional quality of wheat grain. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2009, 2, 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, J.E.; Damodaran, S. Bran-induced changes in water structure and gluten conformation in model gluten dough studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhumury, H.C.D.; Small, D.M.; Day, L. The effect of sodium chloride on gluten network formation and rheology. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byler, D.M.; Susi, H. Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers 1986, 25, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Singh, B.R. Identification of β-turn and random coil amide III infrared bands for secondary structure estimation of proteins. Biophys. Chem. 1999, 80, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Huang, W.; Rayas-Duarte, P.; Zou, Q.; Luan, Z.; Li, Y. Hydration, polymerization and rheological properties of frozen gluten-water dough as influenced by thermostable ice structuring protein extract from Chinese privet (Ligustrum vulgare) leaves. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, E.G.; Bosch, A.; Yantorno, O.; Baran, E.J. A spectroscopy approach for the study of the interactions of bioactive vanadium species with bovine serum albumin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3878–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belton, P.S. New approaches to study the molecular basis of the mechanical properties of gluten. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georget, D.M.R.; Belton, P.S. Effects of temperature and water content on the secondary structure of wheat gluten studied by FTIR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H. Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 115–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jondiko, T.O.; Tilley, M.; Awika, J.M. Effect of high molecular weight glutenin subunit composition in common wheat on dough properties and steamed bread quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2801–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ovidio, R.; Masci, S. The low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of wheat gluten. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Zhao, M.M.; Zhao, Q.Z. Correlation of glutenin macropolymer with viscoelastic properties during dough mixing. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 45, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, C.; Mann, G.; Bekes, F.; Hamer, R.J. HMW-GS affect the properties of glutenin particles in GMP and thus flour quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J. Interactions between dietary fiber and ferulic acid changed the aggregation of gluten in a whole wheat model system. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.; Antes, S.; Seilmeier, W. Quantitative determination of gluten protein types in wheat flour by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.V.; Ferrer, E.G.; Añón, M.C.; Puppo, M.C. Changes in secondary structure of gluten proteins due to emulsifiers. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1033, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | SHfree (μmol/g) | SHeq (μmol/g) | SS (μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | 1.44 ± 0.16 a | 5.51 ± 0.02 f | 2.04 ± 0.07 ef |
| M3R0 | 1.36 ± 0.07 ab | 5.62 ± 0.01 e | 2.13 ± 0.04 e |
| M3R30 | 1.13 ± 0.04 b | 6.89 ± 0.03 c | 2.88 ± 0.02 c |
| M3R60 | 1.09 ± 0.13 bc | 6.96 ± 0.04 b | 2.93 ± 0.07 b |
| M3R90 | 1.04 ± 0.13 c | 5.43 ± 0.01 g | 2.19 ± 0.05 e |
| M5R0 | 1.43 ± 0.30 a | 5.29 ± 0.03 h | 1.91 ± 0.15 f |
| M5R30 | 1.21 ± 0.05 b | 6.27 ± 0.01 c | 2.76 ± 0.02 b |
| M5R60 | 1.05 ± 0.03 c | 7.08 ± 0.01 a | 3.02 ± 0.01 a |
| M5R90 | 1.03 ± 0.12 c | 6.17 ± 0.01 d | 2.55 ± 0.05 d |
| Samples | <11 μm (%) | 11–50 μm (%) | >50 μm (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | 31.12 ± 0.25 c | 25.07 ± 0.49 a | 43.81 ± 0.55 c |
| M3R0 | 33.17 ± 0.18 b | 21.57 ± 0.07 c | 45.26 ± 0.23 b |
| M3R30 | 30.57 ± 0.77 cd | 17.30 ± 0.81 d | 52.77 ± 1.87 ab |
| M3R60 | 29.25 ± 1.23 d | 18.66 ± 2.34 d | 53.62 ± 2.35 a |
| M3R90 | 30.40 ± 0.49 cd | 21.77 ± 2.30 bc | 49.44 ± 4.29 b |
| M5R0 | 38.52 ± 0.72 a | 22.43 ± 0.46 b | 38.26 ± 1.12 d |
| M5R30 | 38.34 ± 1.41 a | 21.55 ± 0.71 c | 39.64 ± 0.70 cd |
| M5R60 | 35.02 ± 0.10 b | 24.41 ± 0.33 ab | 40.57 ± 0.38 c |
| M5R90 | 37.81 ± 0.51 a | 24.82 ± 0.33 ab | 37.92 ± 0.82 d |
| Samples | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheets (%) | β-Turns (%) | Random-Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | 26.46 ± 1.67 d | 32.74 ± 0.44 b | 26.75 ± 1.27 c | 12.27 ± 0.99 a |
| M3R0 | 29.71 ± 0.92 bc | 26.87 ± 1.72 d | 27.81 ± 1.23 b | 11.37 ± 0.01 b |
| M3R30 | 29.94 ± 0.28 bc | 31.35 ± 0.60 c | 27.58 ± 0.27 b | 10.85 ± 0.68 bc |
| M3R60 | 30.75 ± 0.17 b | 32.09 ± 0.57 bc | 28.62 ± 0.51 b | 10.21 ± 0.72 cd |
| M3R90 | 34.24 ± 2.47 a | 33.02 ± 0.32 ab | 29.68 ± 1.91 a | 8.49 ± 0.67 f |
| M5R0 | 28.58 ± 0.13 c | 32.26 ± 0.01 bc | 28.34 ± 0.31 b | 10.26 ± 0.58 cd |
| M5R30 | 29.31 ± 0.10 b | 32.50 ± 0.10 bc | 28.71 ± 0.15 b | 10.06 ± 0.04 d |
| M5R60 | 29.39 ± 0.47 bc | 32.65 ± 0.14 bc | 28.79 ± 0.24 b | 9.78 ± 0.40 e |
| M5R90 | 31.05 ± 0.81 b | 33.92 ± 1.00 a | 28.43 ± 1.55 b | 10.10 ± 0.02 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, H. Dynamic Changes in Glutenin Macropolymer during Different Dough Mixing and Resting Processes. Molecules 2021, 26, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030541
Feng Y, Zhang H, Wang J, Chen H. Dynamic Changes in Glutenin Macropolymer during Different Dough Mixing and Resting Processes. Molecules. 2021; 26(3):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030541
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yulin, Huijuan Zhang, Jing Wang, and Haitao Chen. 2021. "Dynamic Changes in Glutenin Macropolymer during Different Dough Mixing and Resting Processes" Molecules 26, no. 3: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030541
APA StyleFeng, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, J., & Chen, H. (2021). Dynamic Changes in Glutenin Macropolymer during Different Dough Mixing and Resting Processes. Molecules, 26(3), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030541






