Mechanistic Studies of the Antiallergic Activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. and Its Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. HPLC Quantification
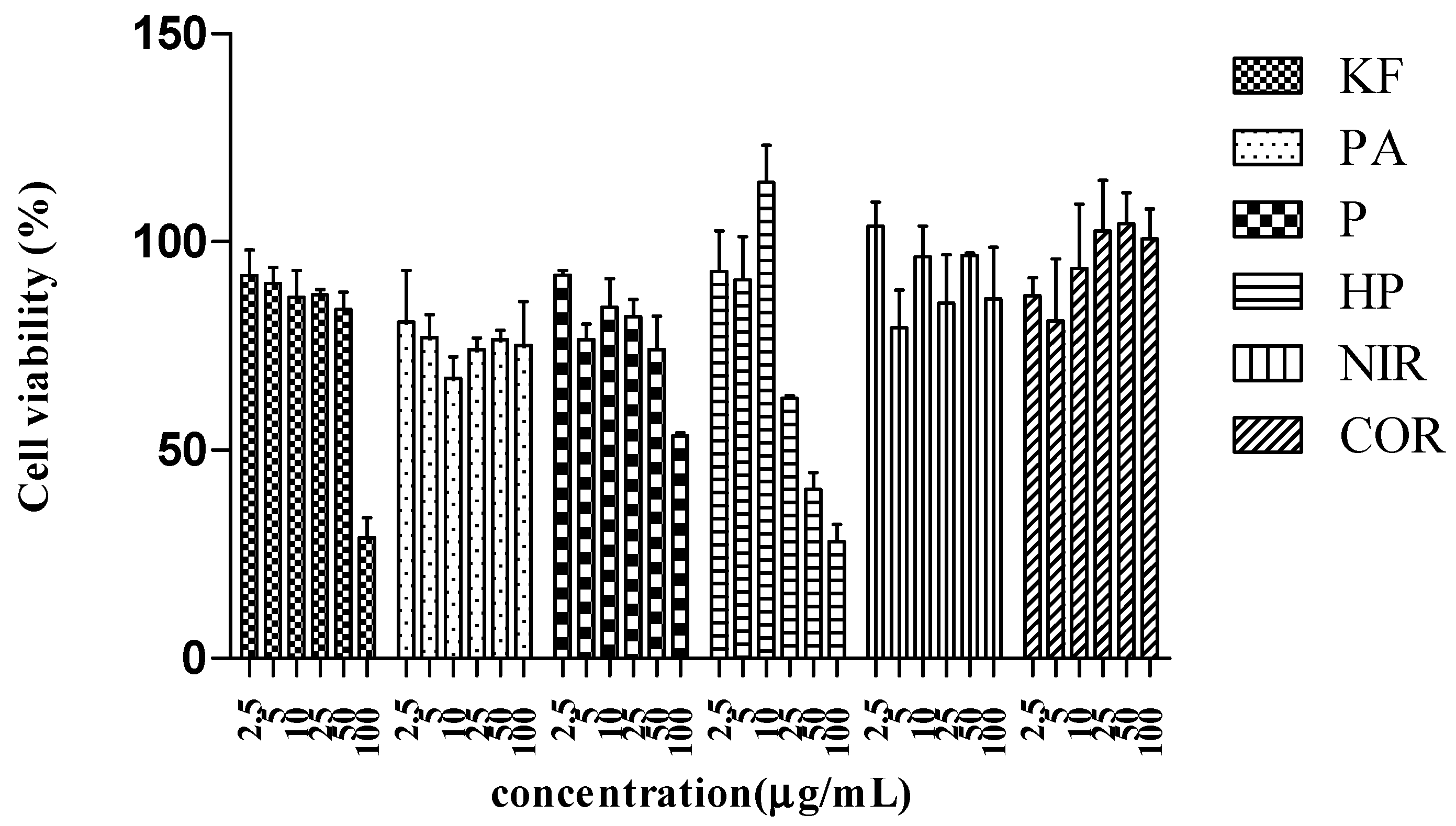
2.2. Cell Viability
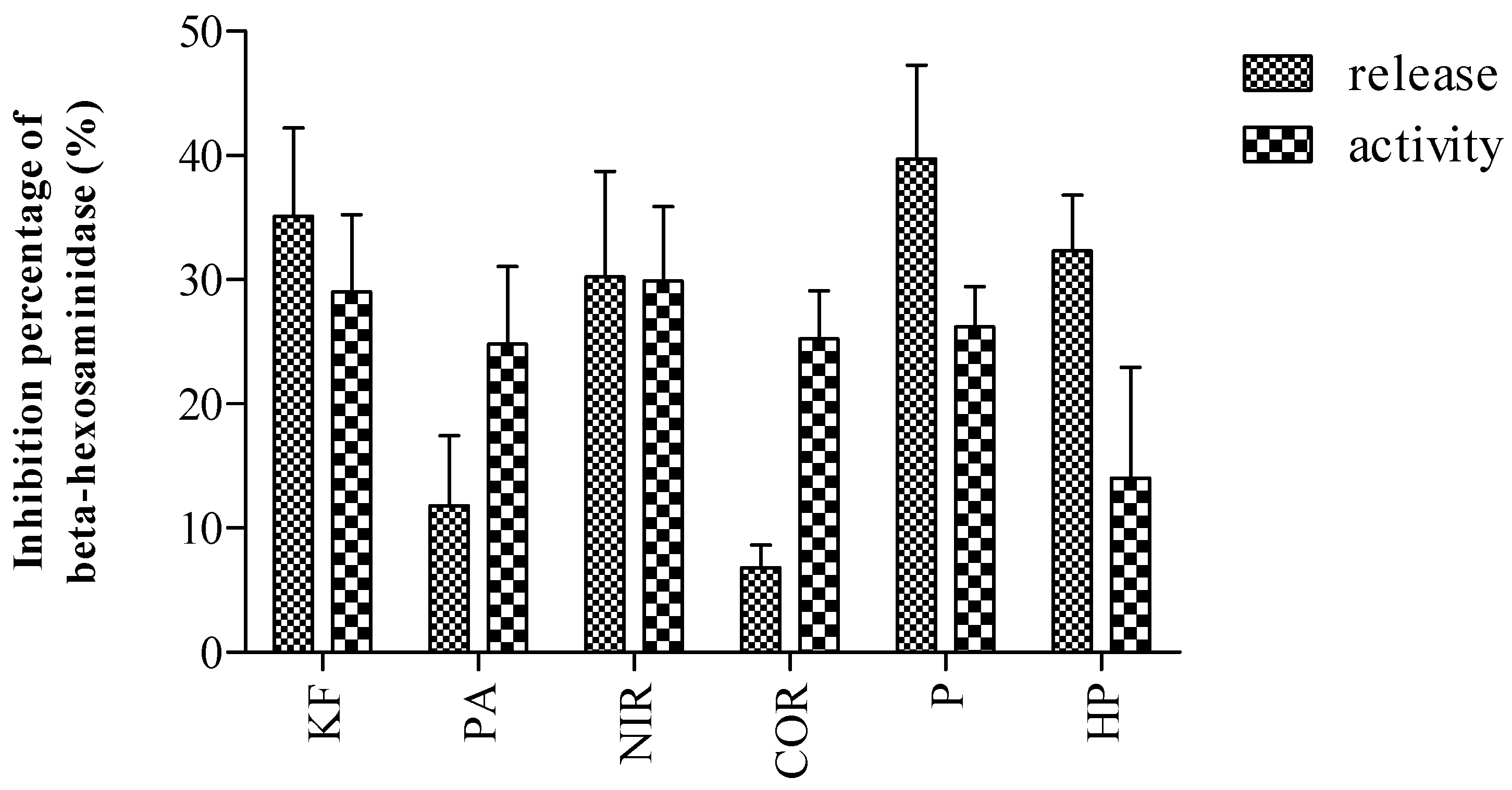
2.3. Inhibitory Activity on Beta-Hexosaminidase and Histamine Release from RBL-2H3
2.4. Inhibitory Activity on Beta-Hexosaminidase Activity
2.5. Radioligand Competition Binding Assay
2.6. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical, Reagents, and Instrument
3.2. Plant Samples and Extractions
3.3. Samples Preparation
3.4. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Condition of HPLC
3.5. Analytical Validation for HPLC Quantification
3.6. RBL-2H3 Cells
3.7. Cell Viability Assay
3.8. Inhibitory Effects on Beta-Hexosaminidase Release from RBL-2H3
3.9. Inhibitory Activity on Beta-Hexosaminidase Activity
3.10. Inhibitory Effects on Histamine Release from RBL-2H3
3.11. Radioligand Competition Binding Assay
3.12. Molecular Docking
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Sample Availability
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffman, P.; Kathriarachci, H.; Wurdack, K.J. A phylogenetic classification of Phyllanthaceae (Malpighiales; Euphorbiaceae sensu lato). Kew Bull. 2006, 61, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, P.E. Malpighiales; Enyclopaedia Britannica, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, B.; Verma, N.; Martin, J.P.; Mohanty, A. An Overview of Important Ethnomedicinal Herbs of Phyllanthus Species: Present Status and Future Prospects. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 839172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.N.; Rao, M.P.; Bhagyalakshmi, K.; Srikanth, M. Antianaphylactic Activity of Hydro Alcoholic Extract of Phyllanthus Virgatus Leaves. Int. J. Pharmtech. Res. 2015, 8, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Karmarkar, A.B. Herbal (Ayurvedic) Way of Treatment and Management of Allergic Rhinitis. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2017, 4, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, A.; Saxena, V.S.; Pratibha, N.; D’Souza, P.; Bagchi, M.; Bagchi, D.; Stohs, S.J. Mast Cell Stabilization, Lipoxygenase Inhibition, Hyaluronidase Inhibition, Antihistaminic and Antispasmodic Activities of Aller-7, A Novel Botanical Formulation for Allergic Rhinitis. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 2003, 29, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saxena, V.S.; Venkateshwarlu, K.; Nadig, P.; Barbhaiya, H.C.; Bhatia, N.; Borkar, D.M.; Gill, R.S.; Jain, R.K.; Katiyar, S.K.; Prasad, K.V.N.; et al. Multicenter Clinical Trials on A Novel Polyherbal Formulation in Allergic Rhinitis. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 24, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Unander, D.W.; Webster, G.L.; Blumberg, B.S. Uses and bioassays in Phyllanthus (Euphorbiaceae): A compilation II. The subgenus Phyllanthus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 34, 97–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.M.; Rastogi, S.; Rawat, A.K.S. Indian Traditional Ayurvedic System of Medicine and Nutritional Supplementation. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 376327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagarajan, S.P.; Subramanian, S.; Thirunalasundari, T.; Venkateswaran, P.S.; Blumberg, B.S. Effect of Phyllanthus amarus on chronic carriers of hepatitis B virus. Lancet 1988, 2, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, H.; McIntosh, H. Genus Phyllanthus for chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review. J. Viral Hepat. 2001, 8, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, H.; Liu, J.P.; Gluud, C. Phyllanthus species for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 4, CD008960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, S.; Oliveira, C.N.F.; Oliveira, R.N.; Frezza, T.F.; Rehder, V.L.G. The Use of Brazilian Medicinal Plants to Combat Schistosoma mansoni. In Schistosomiasis; Rokni, M.B., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 22–70. [Google Scholar]
- Raphael, K.R.; Kuttan, R. Inhibition of experimental gastric lesion and inflammation by Phyllanthus amarus extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 87, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.T.; Ekpo, G.I.; Ugwuoke, J.E. Immunomodulatory Potentials of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Phyllantus amarus in Wistar Rats. Pharm. Chem. J. 2017, 4, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ilangkovan, M.; Jantan, I.; Bukhari, S.N. Phyllanthin from Phyllanthus amarus inhibits cellular and humoral immune responses in Balb/C mice. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantan, I.; Husain, K. Phyltetralin, 1,7,8-trihydroxy 2-naphtaldehyde, ethyl 8-hydroxy-8-methyl-tridecanoate and 1-triacontanol from Phyllanthus amarus Schumach. & Thonn. inhibit phagocytic activity of human leucocytes. J. Pharm. Pharmcol. 2019, 71, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassuya, C.A.L.; Leite, D.F.P.; de Melo, L.V.; Rehder, V.L.G.; Calixto, J.B. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Extracts, Fractions and Lignans Isolated from Phyllanthus amarus. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Qin, R. Phyllanthin and hypophyllanthin from Phyllanthus amarus ameliorates immune-inflammatory response in ovalbumin-induced asthma: Role of IgE, Nrf2, iNOs, TNF-α, and IL’s. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 41, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyekowa, O.; Oyelakin, O.; Edjere, O. GC-MS Analysis and Antiasthmatic Activity of Hexane Extract of Phyllanthus amarus (Chanca piedra) L. in Guinea Pig. Malays. J. Chem. 2019, 21, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, S.; Van Oosterhout, A.J. Antiallergic Drugs. In Principles of Immunopharmacology; Nijkamp, F.P., Parnham, M.J., Eds.; Birkhauser Basel: Basel, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tewtrakul, S.; Itharat, A. Antiallergic Activity of Some Selected Plants in the Zingiberaceae Family. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 109, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, J. What is Allergy. In Global Atlas of Allergy; Akdis, C., Agache, I., Eds.; European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: Zurich, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kindt, T.J.; Glodsby, R.A.; Osborn, B.A.; Kuby, J. Kuby Immunology; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Larche, M.; Akdis, C.A.; Valenta, R. Immunological Mechanisms of Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C.A. The Underlying Mechanisms in Allergy. In Global Atlas of Allergy; Akdis, C.A., Agache, I., Eds.; European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: Zurich, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.V. The Role of Histamine in Allergic Diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuishi, N.; Murakami, S.; Ohno, A.; Yamanaka, N.; Matsui, N.; Fukutsuji, K.; Yamada, S.; Itoh, K.; Akagi, M. Does B-hexosaminidase Function Only as a Degranulation Indicator in Mast Cells? The Primary Role of B-hexosaminidase in Mast Cell Granules. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkovic, N.; Cekic, S.; Ristov, M.; Ristic, M.; Dukic, D.; Binic, M.; Virijevic, D. Histamine and Antihistamines. Sci. J. Fac. Med. 2015, 32, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simons, F.E.R. Advances in H1-Antihistamines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, X.; Guan, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, L. Chromatographic Fingerprint and the Simultaneous Determination of Five Bioactive Components of Geranium carolinianum L. Water Extract by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 8740–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiyah, V.; Chan, K. Determination of four lignans in Phyllanthus niruri L. by a simple high-performance liquid chromatography method with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1154, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantan, I.; Ilangkovan, M.; Yuandani; Mohamad, H.F. Correlation between the major components of Phyllanthus amarus and Phyllanthus urinaria and their inhibitory effects on phagocytic activity of human neutrophils. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahari, M.S.; Husain, K.; Kumolosasi, E.; Rajab, N.F. Histamine and Beta-Hexosaminidase Inhibitory Effects of Crude Alkaloid from Kopsia Arborea Blume in RBL-2H3 Cell Lines. Nat. Prod. Indian J. 2017, 13, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Rani, N.Z.; Kumolosasi, E.; Jasamai, M.; Jamal, J.A.; Lam, K.W.; Husain, K. In vitro antiallergic activity of Moringa oleifera Lam. extracts and their isolated compounds. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahari, M.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Kumolosasi, E.; Rajab, N.F.; Husain, K. Isolation of indole alkaloids from Kopsia larutensis King & Gamble and their effects on histamine and β-hexosaminidase inhibitory in RBL-2H3 cell line. J. Innov. Pharm. 2017, 4, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Strakhova, M.; Esbenshade, T.A. Characterization of Histaminergic Receptors. In Current Protocols in Pharmacology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diller, D.J.; Merz, M.L. High Throughput Docking for Library Design and Library Prioritization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2001, 43, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Robertson, D.H.; Brooks, C.L.I.; Vieth, M. Detailed Analysis of Grid-Based Molecular Docking: A Case Study of CDOCKER—A CHARMm-Based MD Docking Algorithm. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spassov, V.Z.; Yan, L.; Flook, P.K. The Dominant Role of Side-Chain Backbone Interactions in Structural Realization of Amino Acid-Code. ChiRotor: A Side-Chain Prediction Algorithm Based on Side-Chain Backbone Interactions. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
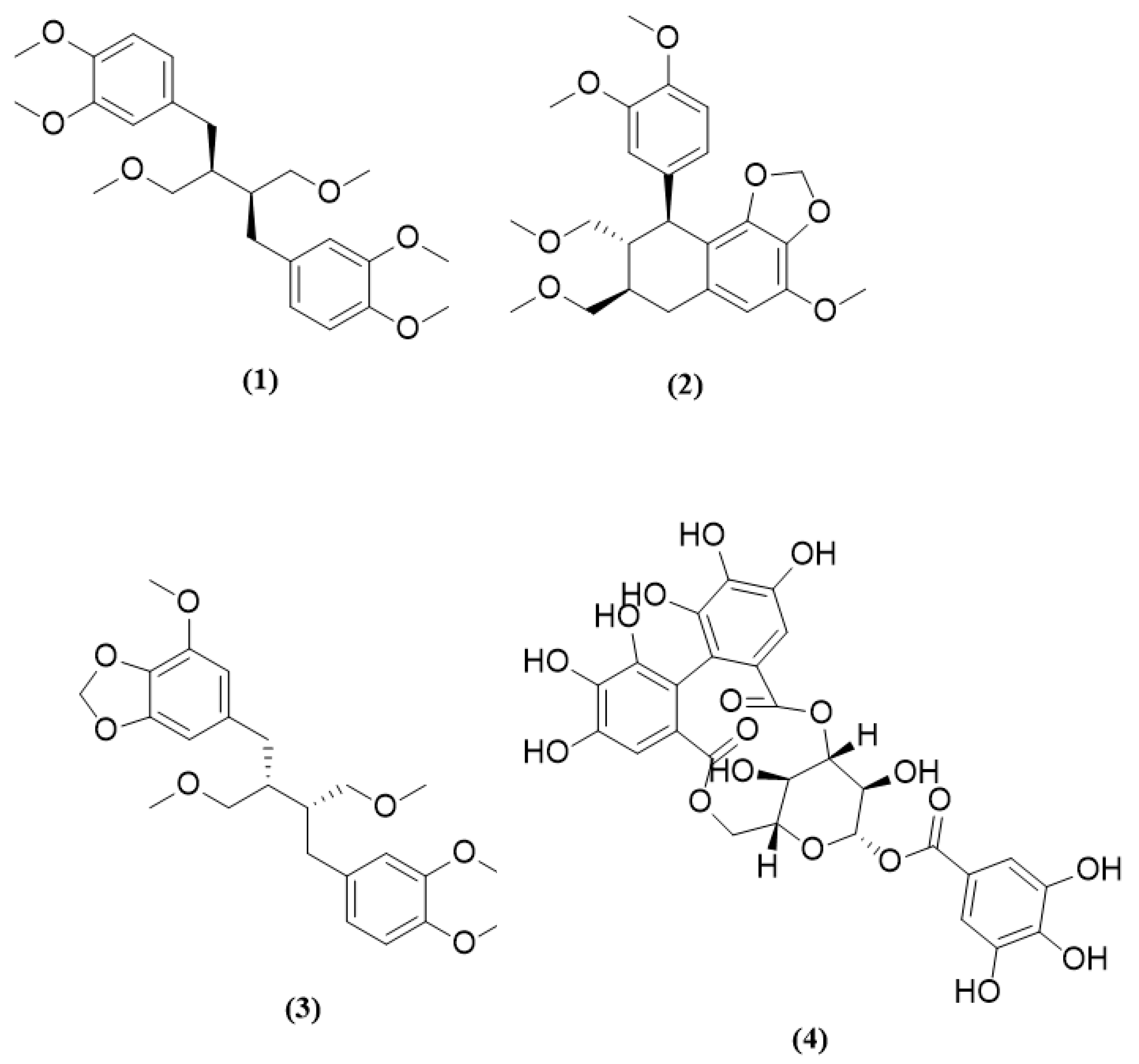
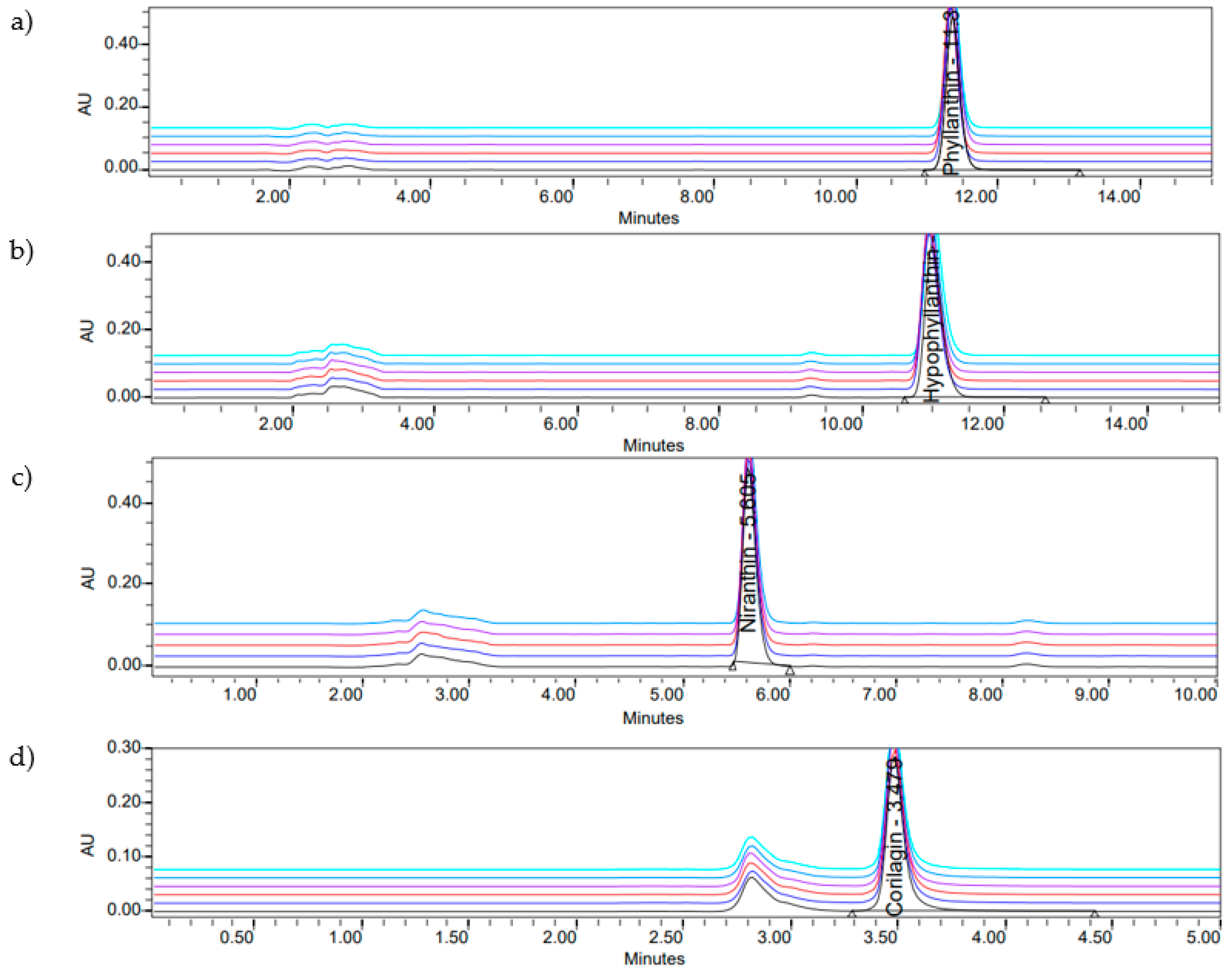
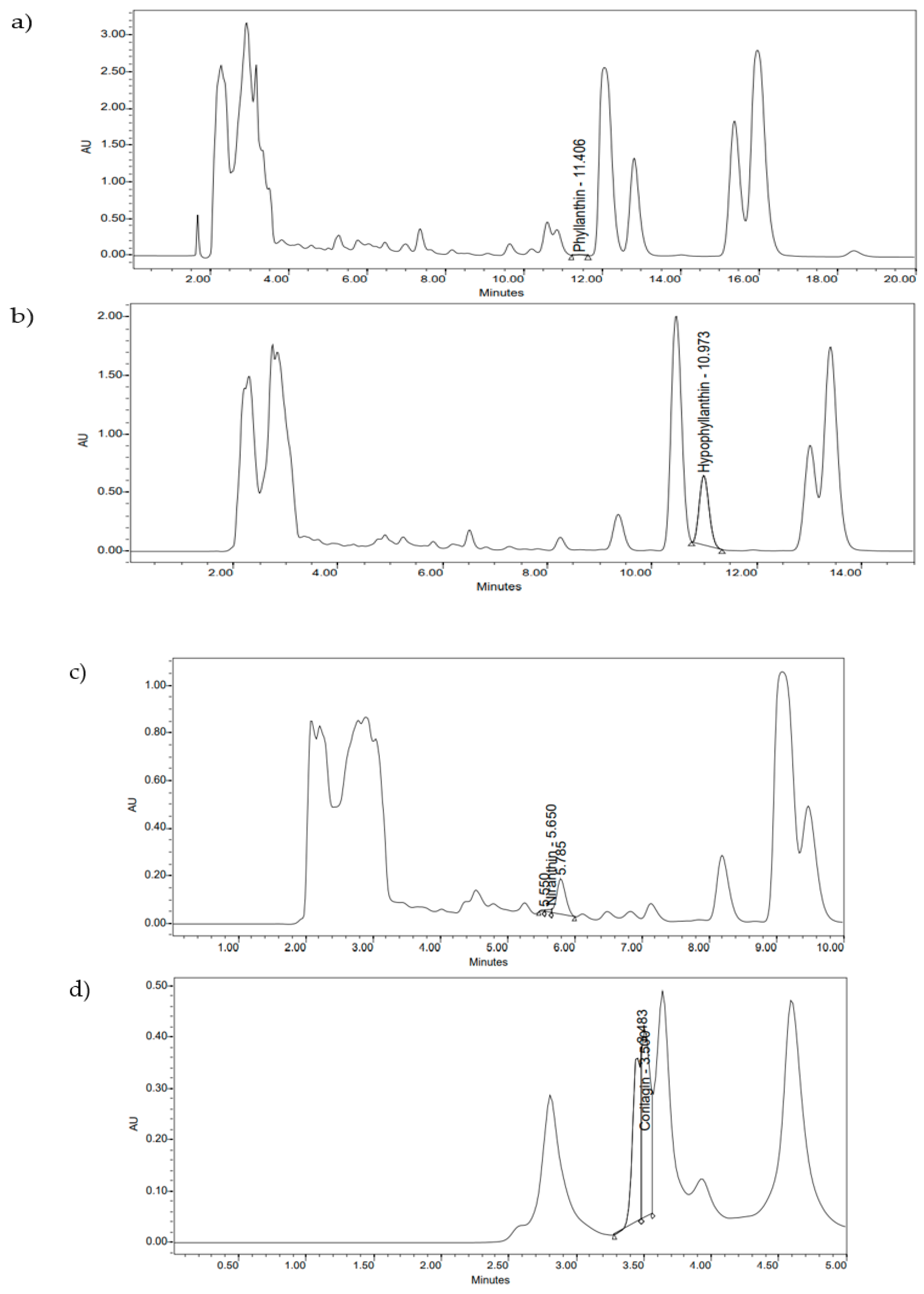


| Chemical Marker | Concentration Range (µg/mL) | Linear Equation | R-Squared Value | LOD (µg/mL) | LOQ (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phyllanthin (1) | 6.25–100 | y = 65,900x + 138,000 | 0.999747 | 3.514099 | 10.64879 |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 6.25–100 | y = 73,400x + 484,000 | 0.984817 | 13.52513 | 40.98525 |
| Niranthin (3) | 6.25–100 | y = 41,900x + 201,000 | 0.996362 | 5.452889 | 16.52391 |
| Corilagin (4) | 6.25–100 | y = 16,100x + 983,000 | 0.982418 | 14.46484 | 43.83286 |
| Chemical Marker | Concentration (µg/mL) | RSD% Retention Time | RSD% Peak Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phyllanthin (1) | 100 | 0.121 | 0.15 |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 100 | 0.175 | 0.39 |
| Niranthin (3) | 100 | 0.057 | 0.63 |
| Corilagin (4) | 100 | 0.052 | 0.91 |
| Chemical Marker | Concentration (µg/mL) | RSD% Retention Time | RSD% Peak Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phyllanthin (1) | 12.5 | 0.12 | 6.30 |
| 25 | 0.17 | 2.34 | |
| 50 | 0.20 | 1.34 | |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 12.5 | 0.67 | 8.66 |
| 25 | 0.36 | 8.36 | |
| 50 | 0.31 | 9.39 | |
| Niranthin (3) | 12.5 | 0.69 | 6.19 |
| 25 | 0.39 | 8.95 | |
| 50 | 0.19 | 6.70 | |
| Corilagin (4) | 12.5 | 0.32 | 7.86 |
| 25 | 0.40 | 18.77 | |
| 50 | 0.40 | 6.89 |
| Chemical Marker | Concentration (µg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Phyllanthin (1) | 0.22 |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 98.24 |
| Niranthin (3) | 1.89 |
| Corilagin (4) | 90.24 |
| Concentration | 2.5 µg/mL | 5 µg/mL | 10 µg/mL | 25 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL | 100 µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketotifen fumarate (positive control) | 91.93 ± 6.16 | 90.09 ± 3.89 | 86.75 ± 6.47 | 87.37 ± 1.17 | 83.84 ± 4.10 | 28.89 ± 4.87 |
| P. amarus | 80.81 ± 12.36 | 77.04 ± 5.55 | 67.25 ± 5.20 | 74.22 ± 2.69 | 76.59 ± 2.23 | 75.18 ± 10.50 |
| Phyllanthin (1) | 92.02 ± 1.13 | 76.57 ± 3.77 | 84.30 ± 6.83 | 82.10 ± 4.03 | 74.18 ± 7.99 | 53.48 ± 0.65 |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 92.96 ± 9.69 | 90.95 ± 10.40 | 114.35 ± 8.89 | 62.46 ± 0.56 | 40.58 ± 4.17 | 28.12 ± 4.13 |
| Niranthin (3) | 103.79 ± 5.79 | 79.44 ± 8.96 | 96.46 ± 7.33 | 85.37 ± 11.62 | 96.63 ± 0.63 | 86.26 ± 12.41 |
| Corilagin (4) | 87.10 ± 4.31 | 81.10 ± 14.81 | 93.71 ± 15.36 | 102.69 ± 12.10 | 104.43 ± 7.35 | 100.75 ± 7.2 |
| DMSO (solvent) | 83.25 ± 14.49 | 82.12 ± 8.73 | 88.94 ± 9.52 | 97.73 ± 6.65 | 83.74 ± 14.92 | 74.56 ± 15.31 |
| Concentration | 1.25 µg/mL | 2.5 µg/mL | 5 µg/mL | 10 µg/mL | 25 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketotifen fumarate (positive control) | - | - | 17.71 ± 1.05 | 22.23 ± 0.75 *** | 27.43 ± 0.58 *** | - |
| P. amarus | - | - | 6.14 ± 3.82 | 9.88 ± 5.22 | 11.80 ± 5.62 | - |
| Phyllanthin (1) | - | 26.35 ± 3.18 * | 37.93 ± 6.51 ** | 38.40 ± 8.72 ** | - | - |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 23.94 ± 3.31 ** | 32.33 ± 4.99 *** | 32.32 ± 4.51 *** | - | - | - |
| Niranthin (3) | - | - | - | 29.29 ± 5.81 * | 31.28 ± 7.43 * | 32.09 ± 7.27 * |
| Corilagin (4) | - | - | - | 2.43 ± 3.26 | 5.12 ± 2.09 | 6.68 ± 1.71 |
| Concentration | 1.25 µg/mL | 2.5 µg/mL | 5 µg/mL | 10 µg/mL | 25 µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketotifen fumarate (positive control) | - | - | 3.90 ± 6.80 | 44.74 ± 23.01 | 58.74 ± 23.16 |
| P. amarus | - | 40.26 ± 27.12 | 11.22 ± 28.00 | −6.99 ± 36.16 | - |
| Phyllanthin (1) | - | −3.05 ± 7.93 | 55.80 ± 19.31 | −11.64 ± 70.80 | - |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 16.39 ± 46.64 | 11.89 ± 64.33 | 71.20 ± 34.68 | - | - |
| Niranthin (3) | - | - | 34.74 ± 12.17 | 58.96 ± 22.24 | 41.22 ± 31.24 |
| Corilagin (4) | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Ligands | Radioassay (Ki) (nM) |
|---|---|
| Doxepin (positive control) | - |
| Chlorpheniramine (positive control) | 0.1447 |
| P. amarus | 104.2 ng/mL |
| Phyllanthin (1) | 129.1 |
| Hypophyllanthin (2) | 0.04 |
| Niranthin (3) | 0.4436 |
| Corilagin (4) | Not converged |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd Rani, N.Z.; Lam, K.W.; Jalil, J.; Mohamad, H.F.; Mat Ali, M.S.; Husain, K. Mechanistic Studies of the Antiallergic Activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. and Its Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030695
Abd Rani NZ, Lam KW, Jalil J, Mohamad HF, Mat Ali MS, Husain K. Mechanistic Studies of the Antiallergic Activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. and Its Compounds. Molecules. 2021; 26(3):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030695
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd Rani, Nur Zahirah, Kok Wai Lam, Juriyati Jalil, Hazni Falina Mohamad, Mohd Shukri Mat Ali, and Khairana Husain. 2021. "Mechanistic Studies of the Antiallergic Activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. and Its Compounds" Molecules 26, no. 3: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030695
APA StyleAbd Rani, N. Z., Lam, K. W., Jalil, J., Mohamad, H. F., Mat Ali, M. S., & Husain, K. (2021). Mechanistic Studies of the Antiallergic Activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. and Its Compounds. Molecules, 26(3), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030695







