Pervaporation Zeolite-Based Composite Membranes for Solvent Separations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Aspects of Pervaporation
3. Latest Insights into Zeolite-Based Membranes for Pervaporation
3.1. Dehydration of Organics
3.2. Separation of Organics from Diluted Azeoptropic Mixtures
3.3. Separation of Organic-Organic Azeoptropic Mixtures
3.4. Zeolite-Based Membrane-Aided Specific PV Applications
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Am | Active area |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| β | Separation factor |
| D | Diffusivity |
| DD3R | Deca-dodecasil 3 rhombohedral |
| DMC | Dimethyl carbonate |
| IPA | Isopropanol |
| J | Permeate flux |
| mi | Mass of compound i |
| MTBE | Methyl tert-butyl ether |
| NMP | N-methyl pyrrolidone |
| P | Permeability |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PEC | Positively charged polyelectrolyte |
| POTS | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluoroalkyltriethoxysilanes |
| PSI | Pervaporation separation index |
| PV | Pervaporation |
| S | Solubility |
| t | Time |
| ZSM-5 | Zeolite Socony Mobil–5 |
References
- Luo, Y.; Raza, W.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Lu, Y. Recent advances in acid-resistant zeolite T membranes for dehydration of organics. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, J.; Brazinha, C. Fundamentals of pervaporation. In Pervaporation, Vapour Permeation and Membrane Distillation; Basile, A., Figoli, A., Khayet, M., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawski, W.; Roszak, R. Pervaporative removal of volatile organic compounds from multicomponent aqueous mixtures. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 3559–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Buera-Gonzalez, J.; de la Iglesia, O.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Malankowska, M.; Rubio, C.; Figoli, A.; Tellez, C.; Coronas, J. Towards the dehydration of ethanol using pervaporation cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 582, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Galiano, F.; Figoli, A. Recent advances in pervaporation hollow fiber membranes for dehydration of organics. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J.; Lagzdins, R.; Figoli, A.; Kujawski, W. A New Type of Composite Membrane PVA-NaY/PA-6 for Separation of Industrially Valuable Mixture Ethanol/Ethyl Tert-Butyl Ether by Pervaporation. Materials 2020, 13, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Munoz, R.; La Iglesia, Ó.D.; Fíla, V.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Pervaporation-Assisted Esterification Reactions by Means of Mixed Matrix Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15998–16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R. Pervaporation-based membrane processes for the production of non-alcoholic beverages. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R. Pervaporation: The emerging technique for extracting aroma compounds from food systems. J. Food Eng. 2019, 253, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Matrimid®5218 dense membrane for the separation of azeotropic MeOH-MTBE mixtures by pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.; Meller, M.; Kujawski, W.; Kujawa, J. Polyamide-6 based pervaporation membranes for organic-organic separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 110, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Galiano, F.; de la Iglesia, Ó.; Fíla, V.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Figoli, A. Graphene oxide–Filled polyimide membranes in pervaporative separation of azeotropic methanol–MTBE mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) for ethanol purification through pervaporation: Current state of the art. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 565–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P. Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (COF-LZU1) based mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Iglesia, Ó.; Sorribas, S.; Almendro, E.; Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) based mixed matrix membranes for esterification of ethanol and acetic acid in a membrane reactor. Renew. Energy 2016, 88, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Castro-Muñoz, R. Breakthroughs on tailoring pervaporation membranes for water desalination: A review. Water Res. 2020, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigiz, F.U.; Dogan, H.; Hilmioglu, N.D. Pervaporation of ethanol/water mixtures using clinoptilolite and 4A filled sodium alginate membranes. Desalination 2012, 300, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Kyotani, T.; Shimotsuma, N.; Kurata, T. Laminated mordenite/ZSM-5 hybrid membranes by one-step synthesis: Preparation, membrane microstructure and pervaporation performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 160, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Nakane, T. Mass-production of tubular NaY zeolite membranes for industrial purpose and their application to ethanol dehydration by vapor permeation. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 319, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Luis, P. Pervaporation as a tool in chemical engineering: A new era? Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 4, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigen, E.M. Chapter 2 Zeolites and Molecular Sieves an Historical Perspective. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1991, 58, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Fíla, V. Progress on incorporating zeolites in matrimid® 5218 mixed matrix membranes towards gas separation. Membranes 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peydayesh, M.; Asarehpour, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Preparation and characterization of SAPO-34-Matrimid?? 5218 mixed matrix membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Martin-Gil, V.; Supinkova, T.; Lambert, P.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Hrabanek, P.; Kocirik, M.; Fila, V. Novel MMM using CO2 selective SSZ-16 and high-performance 6FDA-polyimide for CO2/CH4 separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoba, M.; Bhagiyalakshmi, M.; Alqaheem, Y.; Alomair, A.A.; Pérez, A.; Rana, M.S. Recent progress of fillers in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Inoue, T.; Ikeda, T.; Mizukami, F. Dehydration of concentrated acetic acid solutions by pervaporation using novel MER zeolite membranes. Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nakasaka, Y.; Tago, T.; Hirata, A.; Sato, Y.; Masuda, T. Preparation and optimization of mordenite nanocrystal-layered membrane for dehydration by pervaporation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 207, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Driol, E. Pervaporation Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, G.; Keshav, A.; Anandkumar, J. Review on Pervaporation: Theory, Membrane Performance, and Application to Intensification of Esterification Reaction. J. Eng. (United States) 2015, 2015, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knozowska, K.; Kujawska, A.; Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W.; Bryjak, M.; Chrzanowska, E.; Kujawski, J.K. Performance of commercial composite hydrophobic membranes applied for pervaporative reclamation of acetone, butanol, and ethanol from aqueous solutions: Binary mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.L.; Wei, Y.M.; Shen, B.J.; Zhu, K.K. High-flux NaA zeolite pervaporation membranes dynamically synthesized on the alumina hollow fiber inner-surface in a continuous flow system. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkait, K.; Sinha, M.; Mondal, P.; Singh, R. pH-Responsive Membranes. In Stimuli Responsive Polymeric Membranes; Purkait, K., Sinha, M., Mondal, P., Singh, R., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 2–244. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Cheng, Y.; Peng, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, X.; Murad, S. Fabrication and stability exploration of hollow fiber mordenite zeolite membranes for isopropanol/water mixture separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 274, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawamura, K.I.; Furuhata, T.; Sekine, Y.; Kikuchi, E.; Subramanian, B.; Matsukata, M. Zeolite Membrane for Dehydration of Isopropylalcohol-Water Mixture by Vapor Permeation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13728–13730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, T.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Cui, X.; Wu, X.; Zhu, M.; Hu, N.; Chen, X.; Kita, H.; Kondo, M. Scale-up of NaA zeolite membranes using reusable stainless steel tubes for dehydration in an industrial plant. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 583, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Kita, H.; Yogo, K. Preparation of Si-rich LTA zeolite membrane using organic template-free solution for methanol dehydration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomair, A.A.; Alqaheem, Y. The Implementation of a Carbon Precursor to Produce ZSM-5 Membranes for the Separation of Isomers in the Pervaporation System. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19005–19010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H.; Ji, M.; Gu, X. Effect of Si/Al ratio in the framework on the pervaporation properties of hollow fiber CHA zeolite membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Zheng, P.Y.; Wu, J.K.; Wang, N.X.; Ji, S.L.; Yu, Z.; An, Q.F. Facial build-up of acid-resistance skin for high-stability zeolite NaA membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 573, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhang, B. Reliable Fabrication of Thin and (h0l)-Oriented Zeolite Al-beta Membranes for Separation of Methanol/Methyl tert-Butyl Ether Mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 8271–8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, X.; Caro, J.; Huang, A. Seeding-free synthesis of high-performance MFI zeolite membranes on superhydrophobic supports inspired by “like grows like” principle. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, L.; Wang, B.; Cao, X.; et al. Hollow monocrystalline silicalite-1 hybrid membranes for efficient pervaporative desulfurization. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Jiang, J.; Peng, L.; Liu, H.; Gu, X. Choline chloride templated CHA zeolite membranes for solvents dehydration with improved acid stability. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 284, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Yamada, S.; Watanabe, T.; Negishi, H.; Okuno, T.; Tawarayama, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Oumi, Y. Hydrophobic *BEA-type zeolite membranes on tubular silica supports for alcohol/water separation by pervaporation. Membranes 2019, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Raisi, A.; Pazuki, G. Mixed matrix membrane of ZSM-5/poly (ether-block-amide)/polyethersulfone for pervaporation separation of ethyl acetate from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 263, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Raisi, A.; Pazuki, G. Three-component mixed matrix membrane containing [Hmim][PF6] ionic liquid and ZSM-5 nanoparticles based on poly (ether-block-amide) for the pervaporation process. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, A. Copper-exchanged LTA zeolite membranes with enhanced water flux for ethanol dehydration. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 1204–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Shi, B. Performance of various Si/Al ratios of ZSM-5-filled polydimethylsiloxane/polyethersulfone membrane in butanol recovery by pervaporation. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hong, Z.; Du, P.; Song, Q.; Gu, X. All-silica DD3R zeolite membrane with hydrophilic-functionalized surface for efficient and highly-stable pervaporation dehydration of acetic acid. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 581, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, S.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, N.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. Effect of flouride on preparation and pervaporation performance of NaY zeolite membrane for EtOH/ETBE mixture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 282, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ru, X.; Zhu, Y.T.; Guo, Y.; Teng, L. jun Poly(vinyl alcohol)/ZSM-5 zeolite mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol/water solution through response surface methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 144, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.K.; Xiao, K.; Xue, C.; Yang, S.T. High-Performance n-Butanol Recovery from Aqueous Solution by Pervaporation with a PDMS Mixed Matrix Membrane Filled with Zeolite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7777–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Gao, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gu, X. Fabrication of stainless steel hollow fiber supported NaA zeolite membrane by self-assembly of submicron seeds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Hong, S.; Nam, S.E.; Park, Y.I.; Choi, N.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, J. On the effects of water exposure of as-synthesized LTA membranes on their structural properties and dehydration performances. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurşun, F. Application of PVA-b-NaY zeolite mixture membranes in pervaporation method. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1201, 127170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Saulat, H.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. Manipulation on microstructure of MFI membranes by binary structure directing agents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 299, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Wu, H.; Saulat, H.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of ethanol perm-selective MFI zeolite membranes by binary structure directing agents. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 598, 117647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Ding, H.; Lyu, J.; Fu, T.; Bai, P.; Guo, X.; Tsapatsis, M. Fabrication of a sandwiched silicalite-1 membrane in a 2D confined space for enhanced alcohol/water separation. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 12586–12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirfendereski, S.M.; Lin, J.Y.S. High-performance MFI zeolite hollow fiber membranes synthesized by double-layer seeding with variable temperature secondary growth. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 618, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Ofoghi, S.; Parnia-Baran, A.; Rahim-Khorasani, M. Evaluation ethylcellulose membrane modified with NaA and NaX zeolites for the dehydration of hydrazine hydrate by pervaporation process. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, D.; Zhu, M.; Sun, X.; Xue, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Gui, T.; Kumakiri, I.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. Formation process and pervaporation of high aluminum ZSM-5 zeolite membrane with fluoride-containing and organic template-free gel. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Hu, N.; Zhang, F.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. Scale-up of high performance mordenite membranes for dehydration of water-acetic acid mixtures. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 564, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, A.; Irhamsyah, A.; Permatasari, A.D.; Desa, S.S.; Irfanita, R.; Wahyuni, S. Pervaporation membrane based on laterite zeolite-geopolymer for ethanol-water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.L.; Chang, C.K.; Kang, Y.H.; Chen, J.J.; Kang, D.Y. Enhanced pervaporation performance of zeolite membranes treated by atmospheric-pressure plasma. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 116, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, F.; Gui, T.; Hu, N.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. Preparation of chabazite zeolite membranes by a two-stage varying-temperature hydrothermal synthesis for water-ethanol separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, C.; Xu, K.; Caro, J.; Huang, A. Seeding-free synthesis of large tubular zeolite FAU membranes for dewatering of dimethyl carbonate by pervaporation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 292, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Lin, L.C. Potential and Design of Zeolite Nanosheets as Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 12845–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronas, J.; Santamaria, J. Separations using zeolite membranes. Sep. Purif. Methods 1999, 28, 127–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyozumi, Y.; Nemoto, Y.; Nishide, T.; Nagase, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Mizukami, F. Synthesis of acid-resistant Phillipsite (PHI) membrane and its pervaporation performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinov, N.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Hensen, E.J.M. Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 499, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Ma, J.; Xu, D.; Li, R. Adsorption and diffusion of xylene isomers on mesoporous Beta zeolite. Catalysts 2015, 5, 2098–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Lin, Y.S.; Yang, W. Molecular Sieving MFI-Type Zeolite Membranes for Pervaporation Separation of Xylene Isomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4776–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien-Abraham, J.; Kanezashi, M.; Lin, Y.S. Effects of adsorption-induced microstructural changes on separation of xylene isomers through MFI-type zeolite membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 320, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.; Dong, J.; Lin, Y.S. Polycrystalline MFI zeolite membranes: Xylene pervaporation and its implication on membrane microstructure. J. Memb. Sci. 1999, 158, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabande, G.T.P.; Noack, M.; Avhale, A.; Kölsch, P.; Georgi, G.; Schwieger, W.; Caro, J. Permeation properties of bi-layered Al-ZSM-5/Silicalite-1 membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 98, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, S.; Hanebuth, M.; Mabande, G.T.P.; Avhale, A.; Schwieger, W.; Dittmeyer, R. On the use of a catalytic H-ZSM-5 membrane for xylene isomerization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 96, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeon, M.Y.; Stottrup, B.L.; Tsapatsis, M. para-Xylene Ultra-selective Zeolite MFI Membranes Fabricated from Nanosheet Monolayers at the Air–Water Interface. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xomeritakis, G.; Lai, Z.; Tsapatsis, M. Separation of xylene isomer vapors with oriented MFI membranes made by seeded growth. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsufuji, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsukata, M.; Ueyama, K. Separation of butane and xylene isomers with MFI-type zeolitic membrane synthesized by a vapor-phase transport method. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 178, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Pervaporation dehydration of ethyl acetate via PBI/PEI hollow fiber membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3082–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluemke, W.; Schrader, J. Integrated bioprocess for enhanced production of natural flavors and fragrances by Ceratocystis moniliformis. Biomol. Eng. 2001, 17, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.T.; Tan, S.H. Pervaporation separation of a ternary azeotrope containing ethyl acetate, ethanol and water using a buckypaper supported ionic liquid membrane. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, H.P.; Yu, C.C.; Hung, S.B.; Lee, M.J. Design of reactive distillations for acetic acid esterification. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.G.; Uribe, I.O. Mathematical modeling of the pervaporative separation of methanol-Methylterbutyl ether mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.Y.; Rostovtseva, V.; Faykov, I.; Toikka, A. Application of Polymer Membranes for a Purification of Fuel Oxygenated Additive. Methanol/Methyl Tert-butyl Ether (MTBE) Separation via Pervaporation: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.W.; Wijmans, J.G.; Huang, Y. Permeability, permeance and selectivity: A preferred way of reporting pervaporation performance data. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 348, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, A.; Min, B.; Ganesan, A.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Grosz, A.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. AEL Zeolite Nanosheet-Polyamide Nanocomposite Membranes on α-Alumina Hollow Fibers with Enhanced Pervaporation Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 14789–14796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Chen, S.; Peng, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C. Polyamide membranes with nanoscale Turing structures for water purification. Science 2018, 360, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Raza, W.; Liu, G.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. Microwave synthesis of NaA zeolite membranes on coarse macroporous α-Al2O3 tubes for desalination. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 306, 110360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, E.; Dou, T.; Ding, S.; Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Yi, W.; Li, J.; Ding, J. Membrane dehydration-enhanced esterification for biodiesel production from a potential feedstock of Firmiana platanifolia L.f. seed oil. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 153, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Peng, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.; Gu, X. Extraction of butanol from ABE solution by MFI zeolite membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, B.; Li, H.; Jin, H.; Wu, D.; Li, Y. A pervaporation-crystallization (PC) process for simultaneous recovery of ethanol and sodium pyruvate from waste centrifugal mother liquid. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 619, 118749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, B.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Jin, H.; Li, Y. Mass produced NaA zeolite membranes for pervaporative recycling of spent N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone in the manufacturing process for lithium-ion battery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 115741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonowicz, M.E.; Lawton, J.A.; Lawton, S.L.; Rubin, M.K. MCM-22: A Molecular Sieve with Two Independent calcined. Science 1994, 264, 1910–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Kumakiri, I.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. Preparation and catalytic performance of Ti-MWW zeolite membrane for phenol hydroxylation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 268, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

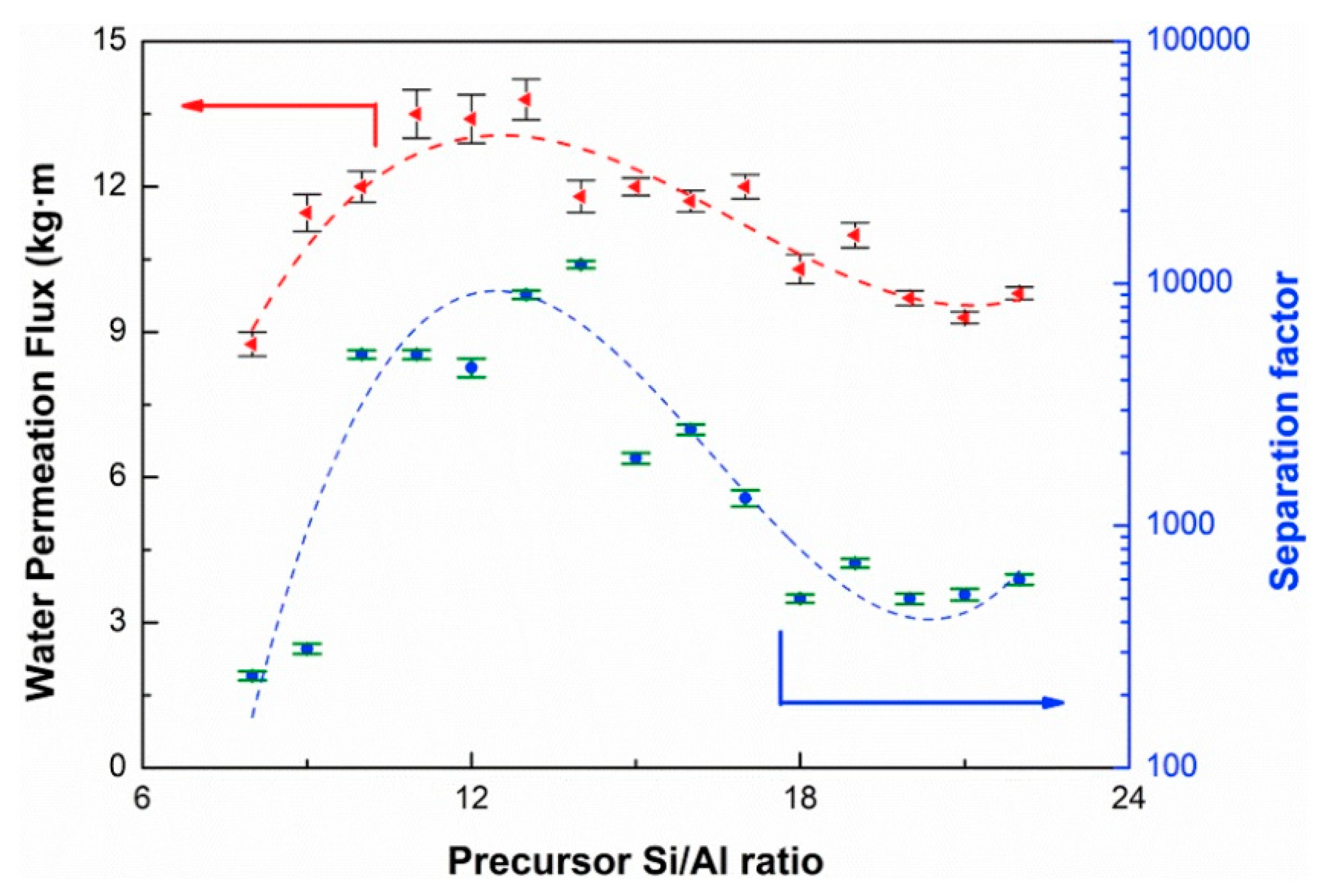
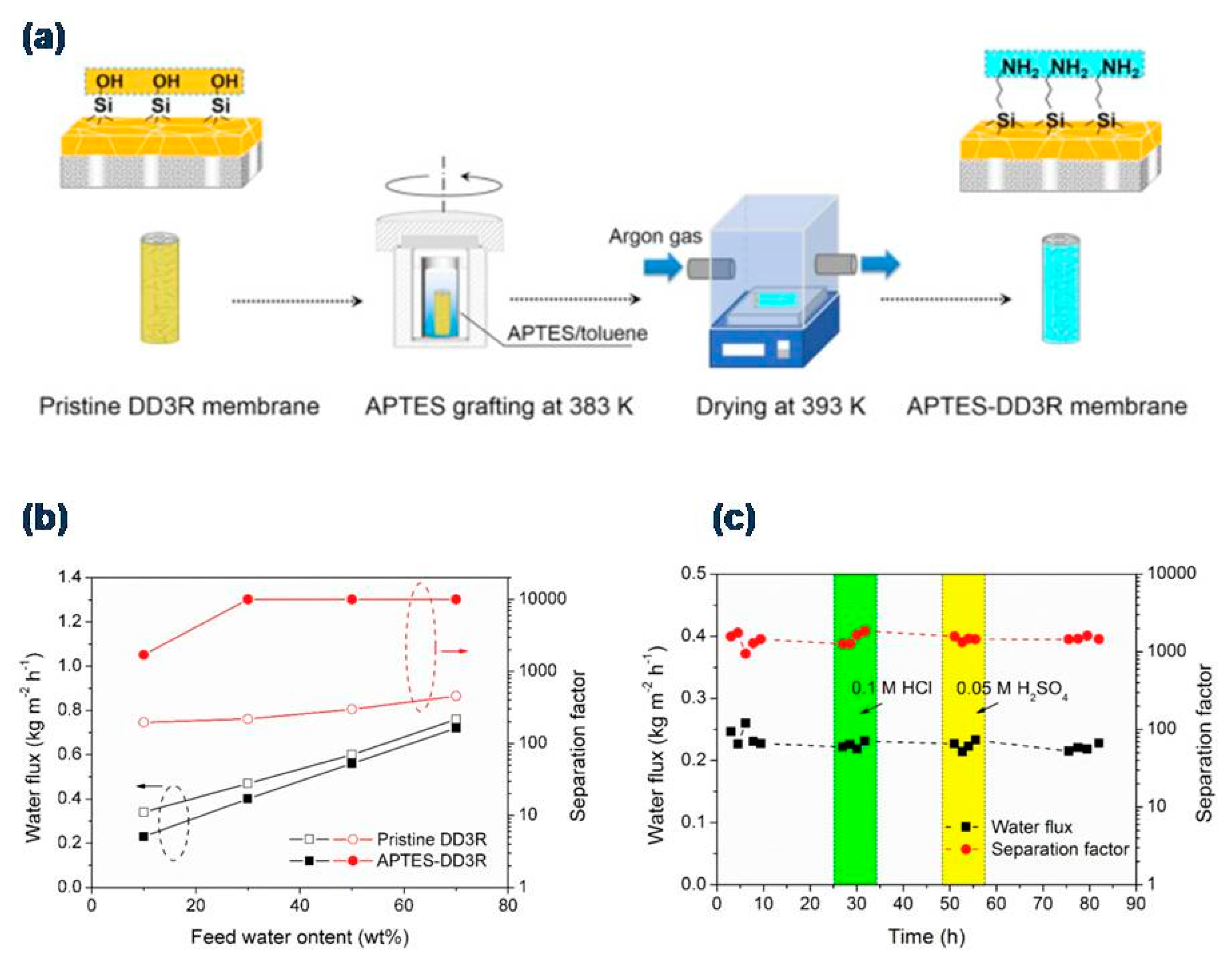
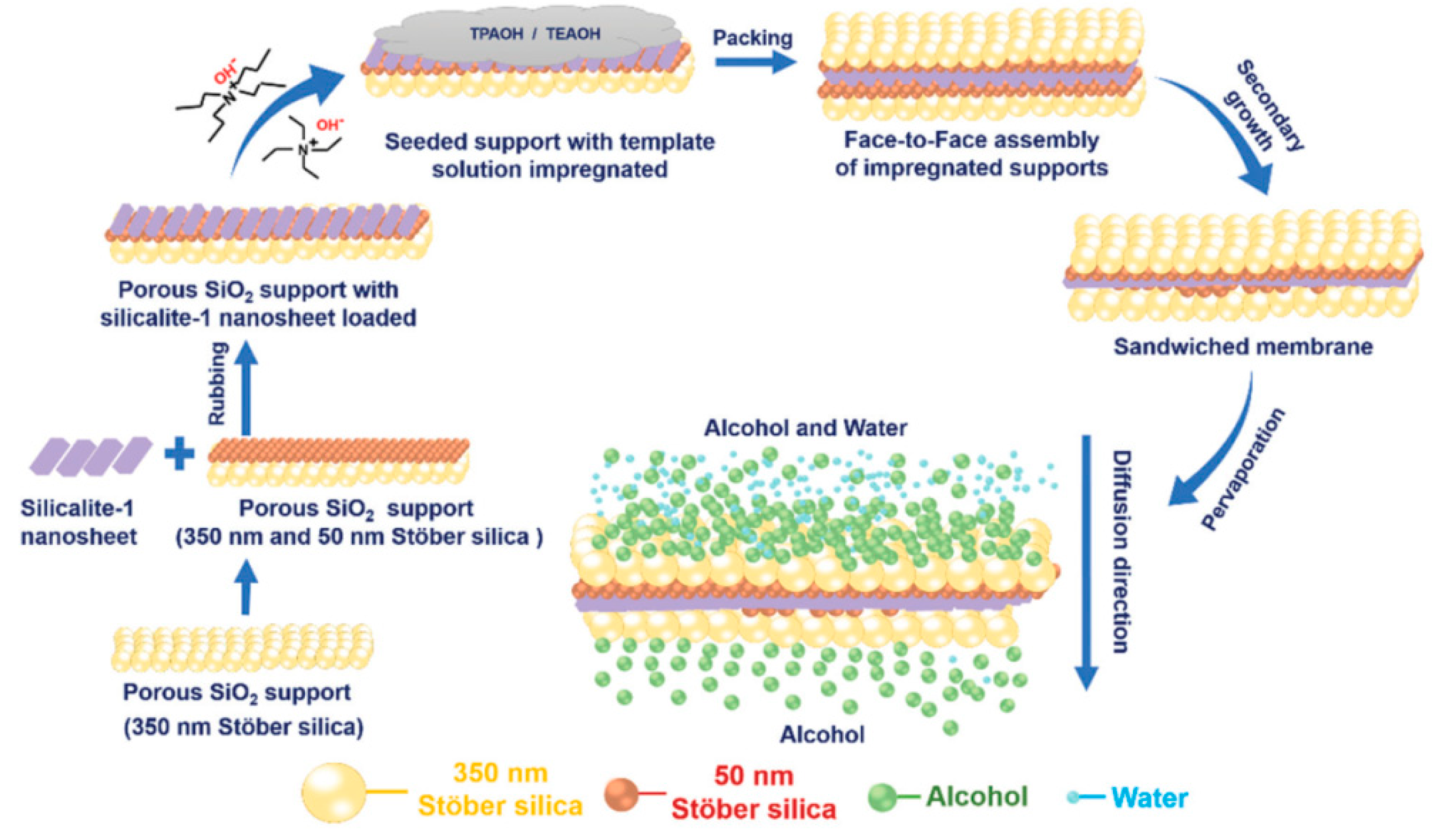
| Zeolites | Metal-Organic Frameworks | Silicas | Carbon Molecular Sieves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defined pore size | Coordinative bonds | Alter the molecular packing of polymer chains | High affinity to glassy polymers |
| High temperature stability | Flexibility in molecular sieving | Increase the free volume of polymers | High adsorptive capacity |
| High stability in water presence | Cations interconnected by organic anions | Low permeability of nonporous silica | Well-defined molecular sieving |
| Limitation in chemical modification | Rather flexible and dynamic frameworks | Weak interaction among silica-polymer | Great potential in MMMs preparation |
| Pore size crystallographically controlled | Soft structure/flexible pore size | Generate interfacial voids | Goods adhesion at interface |
| Potential as supported thin film | Low hydrothermal stability | Suitable for chemical modification (silane coupling) | High productivity/excellent separation |
| Create dense structures | Suitable for chemical modification and blending | Wide opening with constricted apertures | |
| Well-defined molecular sieving | Great potential for thin structures | ||
| Acceptable sorption and diffusion properties | Offer accessible open metals | ||
| Good mechanical stability |
| Membrane | Azeotropic Mixture | Operating Parameters | Flux (kg m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor (β) | PSI | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaA hollow fiber | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C | 19.7 | >80,000 | 157,600 | [32] |
| Modernite hollow fiber | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, <200 Pa | 1.01 | 4684 | 4730 | [34] |
| Water/IPA | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, <200 Pa | 1.45 | 6963 | 10,096 | ||
| Water/acetic acid | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, <200 Pa | 0.47 | 2150 | 1010 | ||
| ZSM-5−carbon | p-xylene/o-xylene | 50 wt.% water, 25 °C, 8 Pa | 0.12 | 1.45 | 0.174 | [38] |
| NaA supported stainless-steel | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C | 8.28 | 11,000 | 91,080 | [36] |
| CHA hollow fiber | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, 200 Pa | 12.0* | 10,000 | 120,000 | [39] |
| PEC/NaA composite | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 45 °C, 100 Pa | 0.87 | - | - | [40] |
| (h0l)-oriented zeolite Al-beta membranes | Methanol/MTBE | 20 wt.% methanol, 50 °C, 133 Pa | 1.83 | 20.3 | 37.1 | [41] |
| MFI zeolite membranes supported onPOTS | Ethanol/water | 5 wt.% ethanol, 75 °C | 2.56 | 103 | 263.6 | [42] |
| Hollow monocrystalline silicalite-1-filled Pebax | Thiophene/n-octane removal from water | 500 ppm sulfur content, 60 °C, 500 Pa | 20.6 | 6 | 123.6 | [43] |
| Choline chloride templated CHA zeolite membranes | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, 200 Pa | 4.7 | >2000 | 9400 | [44] |
| Water/IPA | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, 200 Pa | 5.6 | >2000 | 11,200 | ||
| BEA-type zeolite membranes | Butanol/water | 1 wt.% butanol, 45 °C, 200 Pa | 0.62 | 229 | 141.98 | [45] |
| ZSM-5/poly (ether-block-amide)/PES | Ethyl acetate/water | 5 wt.% ethyl acetate, 50 °C | 1.89 | 108 | 204.12 | [46] |
| [Hmim][PF6] ionic liquid/ZSM/ poly (ether-block-amide). | Ethyl acetate/water | 5 wt.% ethyl acetate, 50 °C | 1.03 | 50.9 | 52.427 | [47] |
| Copper-exchanged LTA zeolite membranes | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 70 °C | 3.52 | 3591 | 12,640 | [48] |
| ZSM-5-filledpolydimethylsiloxane/PES | Butanol/water | 4.5 wt.% water, 31 °C, 1800 Pa | 0.11 | 30 | 3.3 | [49] |
| APTES -DD3R membrane | Water/acetic acid | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, <200 Pa | 0.56* | >10,000 | 5600 | [50] |
| NaYzeolite membrane | Ethanol/ethyl tert-butyl ether | 20 wt.% ethanol, 60 °C | 1.30 | 1100 | 1430 | [51] |
| ZSM-5 filled PVA membrane | Water/IPA | 20 wt.% water, 90 °C, 100 Pa | 2.3 | >100 | 230 | [52] |
| ZSM-5 filled PDMS membrane | Butanol/water | 1.5 wt.% butanol, 47 °C, 50 kPa | 0.100 | 77 | 7.7 | [53] |
| Hollow fiber supported NaA zeolite membrane | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C | 4.22 | 10,000 | 42,200 | [54] |
| LTA membranes | Water/methanol | 10 wt.% water, 50 °C, 1000 Pa | 0.31* | 860 | 266.6 | [55] |
| PVA-NaY/PA-6 composite | Ethanol/ethyl tert-butyl ether | 20 wt.% ethanol, 30 °C | - | 2.3 | - | [6] |
| PVA-NaY composite | Water/IPA | 12.3 wt.% water, 35 °C, 50 Pa | 0.005 | 2690 | 13.4 | [56] |
| MFI zeolite membranes | Ethanol/water | 5 wt.% ethanol, 60 °C, 50 kPa | 1.85 | 59 | 109.1 | [57] |
| MFI zeolite membranes | Ethanol/water | 3 wt.% ethanol, 60 °C, 50 kPa | 1.40 | 79 | 110.6 | [58] |
| LTA membranes | Water/methanol | 10 wt.% water, 60 °C, 1 kPa | 0.16 | 10,000 | 1600 | [37] |
| Water/ethanol | 9.6 wt.% water, 75 °C, 1 kPa | 0.74 | >100,000 | 74,000 | ||
| Water/IPA | 9.7 wt.% water, 75 °C, 1 kPa | 1.20 | >100,000 | 120,000 | ||
| Sandwiched (SiO2)/(silicalite-1)/(SiO2) | Ethanol/water | 5 wt.% ethanol, 60 °C | 2.3 | 136 | 312.8 | [59] |
| n-butanol/water | 5 wt.% n-butanol, 60 °C | 2.2 | 113 | 248.6 | ||
| MFI zeolite hollow fiber | Ethanol/water | 5 wt.% ethanol, 25 °C, 100 kPa | 3 | 160 | 480 | [60] |
| NaA membrane | Water/hydrazine hydrate | 20 wt.% water, 25 °C, 1333 Pa | 0.064 | 12 | 0.76 | [61] |
| NaX/ethylcellulose membrane | Water/hydrazine hydrate | 20 wt.% water, 25 °C, 1333 Pa | 0.012 | 9 | 0.10 | |
| ZSM-5 membrane | Water/acetic acid | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C | 0.98 | 3200 | 3136 | [62] |
| Modernite membranes | Water/acetic acid | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C | 0.97 | 1200 | 1164 | [63] |
| Laterite zeolite-geopolymer membrane | Ethanol/water | 8 wt.% ethanol, 70 °C | 537 | 0.48 | 257.7 | [64] |
| FER zeolite membrane | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, 6 Pa | 0.045 | 377 | 16.9 | [65] |
| Chabazite zeolite membranes | Water/ethanol | 10 wt.% water, 75 °C, <200 Pa | 6.25 | 1950 | 12,187 | [66] |
| Zeolite FAU membrane | Water/DMC | 10 wt.% water, 80 °C, <100 Pa | 3.60 | >10,000 | 36,000 | [67] |
| MFI nanosheet membrane layer | Ethanol/water | 40 wt.% ethanol, 60 °C | 58.8 | 20.7 | 1217 | [68] |
| Membrane | Temperature (°C) | Flux (kg m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor (β) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM-5−carbon supported stainless-steel | 25 | 0.12 | 1.46 | [38] |
| Silicalite supported alumina | 25 | 0.024 | 16 | [73] |
| Oriented MFI supported alumina | 25 | 0.15 | 2.3 | [74] |
| MFI supported alumina | 25 | 0.16 | 0.94 | [75] |
| Al-ZSM-5/silicalite-1 supported stainless-steel | 110 | 0.191 | 5 | [76] |
| H-ZSM-5supported stainless-steel | 100 | 0.027 | 2.29 | [77] |
| MFI supported nanosheet | 250 | 0.015 | 7700 | [78] |
| MFI supported alumina | 125 | 3.0 | 66 | [79] |
| MFI supported alumina | 26 | 0.050 | 0.18 | [80] |
| Membrane | Operating Parameters | Flux (kg m−2 h−1) | NaCl Rejection (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEL zeolite-polyamide nanocomposite | 2 g L−1 NaCl, 25 °C | 4.3 | 99.9 | [88] |
| AEL zeolite-polyamide nanocomposite | 36 g L−1 NaCl, 25 °C | 3.3 | 99.9 | |
| NaA zeolite membranes | 35 g L−1 NaCl, 75 °C, <400 Pa | 9.58 | 99.9 | [90] |
| NaA zeolite membranes | 35 g L−1 KCl, 75 °C, <400 Pa | 8.62 | 99.9 | |
| NaA zeolite membranes | 35 g L−1 CaCl2, 75 °C, <400 Pa | 9.35 | 99.9 | |
| NaA zeolite membranes | 35 g L−1 MgCl2, 75 °C, <400 Pa | 8.69 | 99.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G. Pervaporation Zeolite-Based Composite Membranes for Solvent Separations. Molecules 2021, 26, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051242
Castro-Muñoz R, Boczkaj G. Pervaporation Zeolite-Based Composite Membranes for Solvent Separations. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051242
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro-Muñoz, Roberto, and Grzegorz Boczkaj. 2021. "Pervaporation Zeolite-Based Composite Membranes for Solvent Separations" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051242
APA StyleCastro-Muñoz, R., & Boczkaj, G. (2021). Pervaporation Zeolite-Based Composite Membranes for Solvent Separations. Molecules, 26(5), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051242







