MCH-R1 Antagonist GPS18169, a Pseudopeptide, Is a Peripheral Anti-Obesity Agent in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Peptide Design, Syntheses, and Characterization
2.2. Peptide Molecular Pharmacology
2.2.1. S-S Bridge Bearing Pseudopeptides
2.2.2. Lactam Bridge Bearing Pseudopeptides
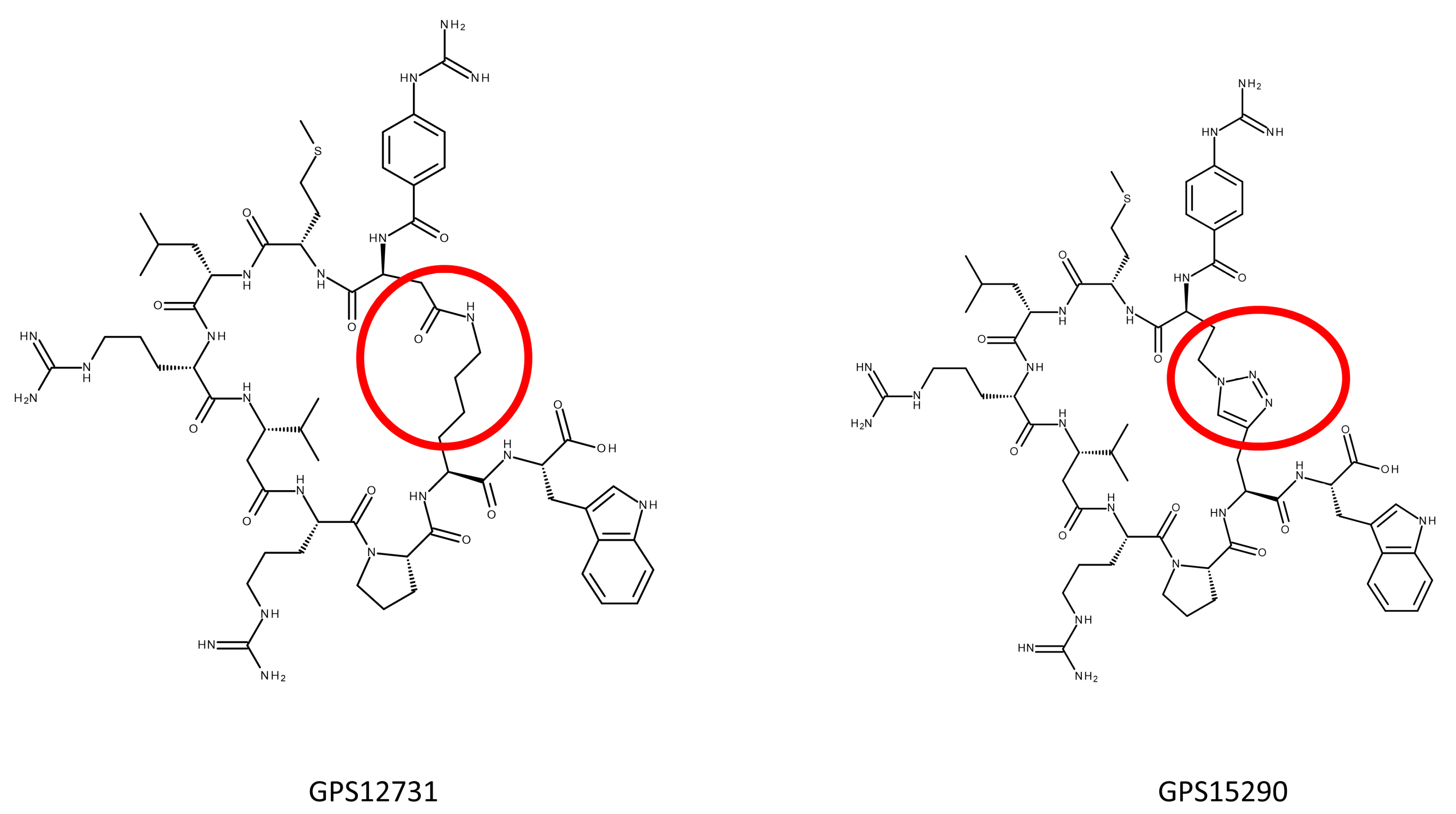
2.2.3. Triazole Bearing Pseudopeptides
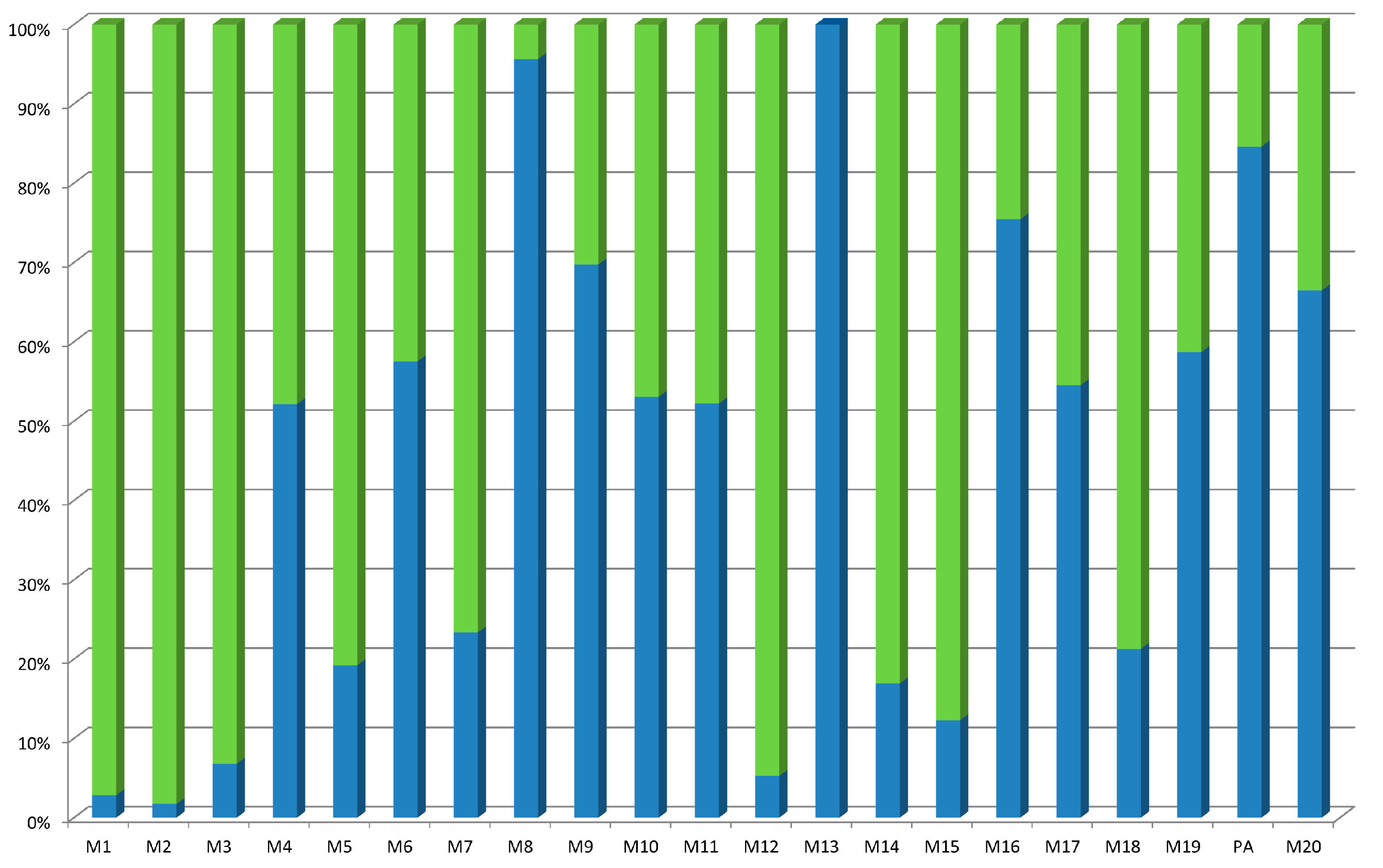
2.3. Stability of Some of the Pseudopeptides
2.4. From GPS15290 to GPS18169
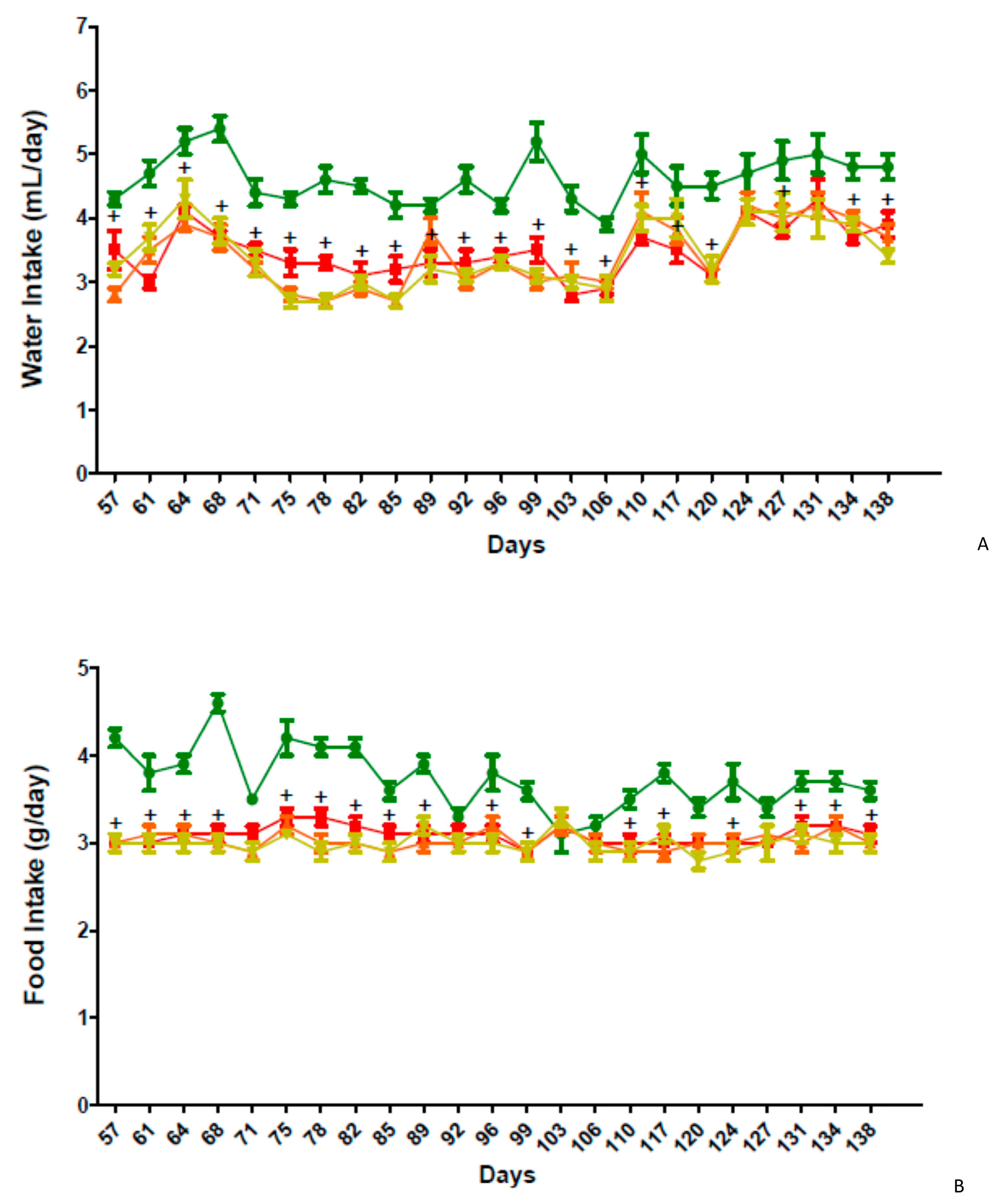
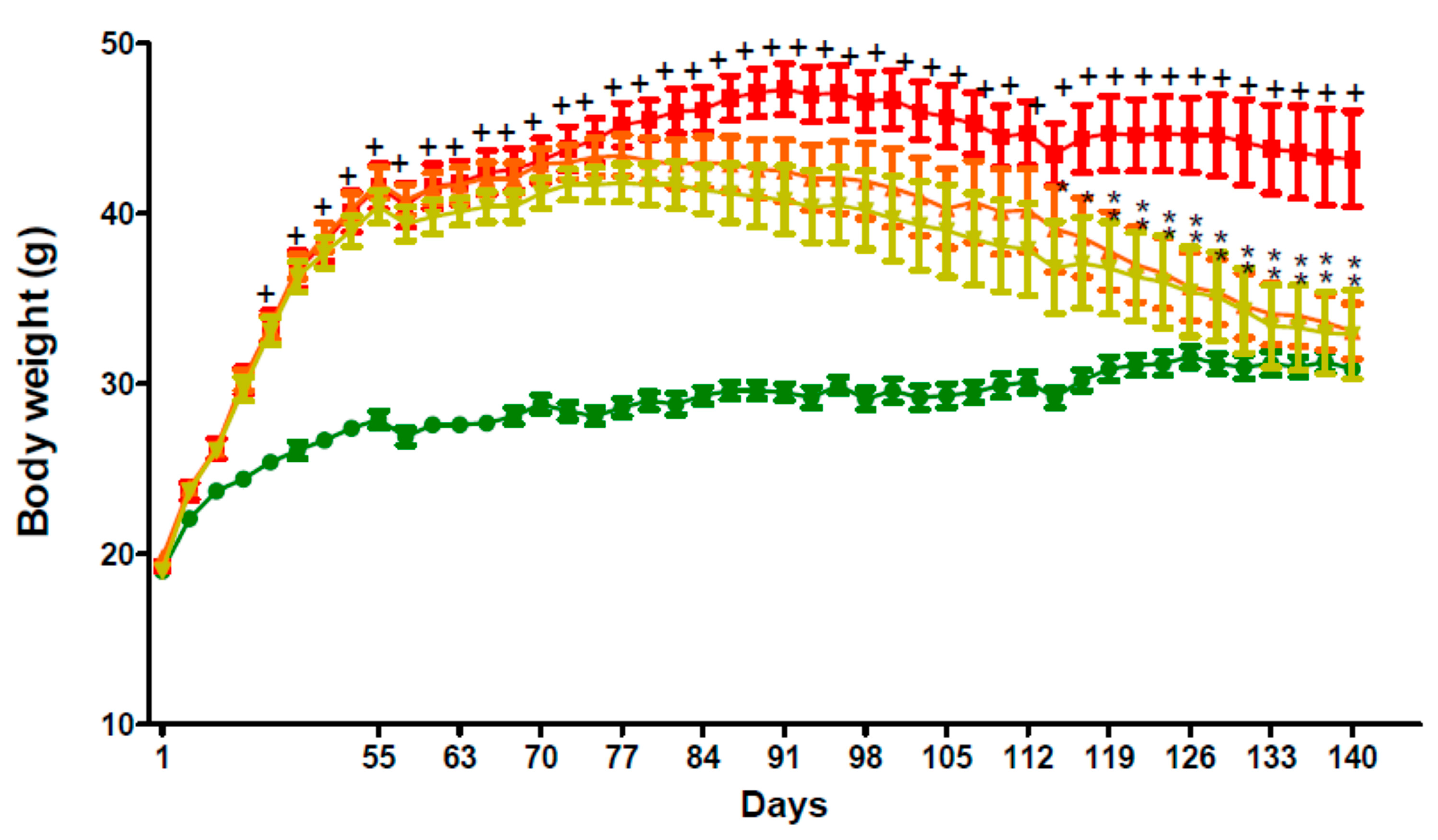
2.5. In Vivo Activity of GPS18169 in the Diet-Induced Obesity Model in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. Peptide Synthesis
4.2.1. Synthesis of Peptides with Lactam Bridge
4.2.2. Synthesis of Peptides with a Disulfide Bridge
4.2.3. Synthesis of Peptides with Triazole Bridge on a Solid Support
4.3. Purification and Analyses
4.4. Establishment of a Stable Cell Line Expressing Human MCH Receptor
4.5. Membrane Preparation and Binding
4.6. MCH Functional Cellular Assay: MCH-Induced Cytosolic Ca2+ Ion Mobilization
4.7. Stability of Pseudopeptides, Plasma and Microsomes from Mouse, Rat and Man
4.7.1. Plasma Stability
4.7.2. Mouse and Rat Hepatocytes
4.7.3. Mouse, Rat and Human Hepatic Microsomes
4.8. Evaluation of Metabolic Stability of the Candidate Pseudopeptides: GPS15290 and GPS18169
4.9. Diet-Induced Obesity Experiments
4.9.1. Animals
4.9.2. Origin of Biochemical Tests
4.9.3. Diet-induced Obesity Protocol
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, F.J.; Monistrol-Mula, A.; Cardellach, F.; Garrabou, G. Nutrition, Bioenergetics, and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byaruhanga, J.; Atorkey, P.; McLaughlin, M.; Brown, A.; Byrnes, E.; Paul, C.; Wiggers, J.; Tzelepis, F. Effectiveness of Individual Real-Time Video Counseling on Smoking, Nutrition, Alcohol, Physical Activity, and Obesity Health Risks: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.J. The Role of Anti-Obesity Medication in Prevention of Diabetes and Its Complications. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 28, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, K.C.; Riera, R.; Martimbianco, A.L.C.; Ward, L.S.; Cunha, L.L. Body Mass Index and Prognosis of COVID-19 Infection. A Systematic Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Zuana, O.; Presse, F.; Ortola, C.; Duhault, J.; Nahon, J.-L.; Levens, N. Acute and chronic administration of melanin-concentrating hormone enhances food intake and body weight in Wistar and Sprague–Dawley rats. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinaud, B.; Darré-Toulemonde, F.; Duhault, J.; Boutin, J.A.; Nahon, J.-L. Comparative analysis of melanin-concentrating hormone structure and activity in fishes and mammals. Peptides 2004, 25, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, G.B.; Bittencourt, J.C. The Melanin-Concentrating Hormone (MCH) System: A Tale of Two Peptides. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audinot, V.; Boutin, J.A.; Lakaye, B.; Nahon, J.-L.; Saito, Y. Melanin-concentrating hormone receptors (version 2019.4) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. GtoPdb CITE 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkotou, E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Marino, F.E.; Carlson, M.; Trombly, D.J.; Maratos-Flier, E. Mice with MCH ablation resist diet-induced obesity through strain-specific mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R117–R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomori, A.; Ishihara, A.; Ito, M.; Matsushita, H.; Mashiko, S.; Iwaasa, H.; Matsuda, M.; Bednarek, M.A.; Qian, S.; Macneil, D.J.; et al. Blockade of MCH1 receptor signalling ameliorates obesity and related hepatic steatosis in ovariectomized mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D.J.; Weingarth, D.T.; Novi, D.E.; Chen, H.Y.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Chen, A.S.; Guan, X.-M.; Jiang, M.M.; Feng, Y.; Camacho, R.E.; et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone 1 receptor-deficient mice are lean, hyperactive, and hyperphagic and have altered metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3240–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisse, C.; Reiter, J.F.; Berbari, N.F. Cilia and Obesity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okada, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Takei, N.; Sekino, Y.; Koganezawa, N.; Shirao, T.; Saito, Y. Characterization of Functional Primary Cilia in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganstern, I.; Gulati, G.; Leibowitz, S.F. Role of melanin-concentrating hormone in drug use disorders. Brain Res. 2020, 1741, 146872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.T.; Liu, Q.F.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.; Samidurai, M.; Jo, J.; Pak, S.C.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, S. Nasal Cavity Administration of Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Improves Memory Impairment in Memory-Impaired and Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Models. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 8076–8086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Cui, X.-Y.; Ding, H.; Cui, S.-Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.-T.; Zhao, H.-L.; Zhang, Y.-H. Melanin-Concentrating Hormone (MCH) and MCH-R1 in the Locus Coeruleus May Be Involved in the Regulation of Depressive-Like Behavior. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaru, S.S.; Khanday, M.A.; Ibrahim, N.; Naganuma, F.; Vetrivelan, R. Sleep-Wake Control by Melanin-Concentrating Hormone (MCH) Neurons: A Review of Recent Findings. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, M.J.; Hebert, A.J.; Briançon, N.; Flaherty, S.E.; Pissios, P.; Maratos-Flier, E. Conditional deletion of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 from GABAergic neurons increases locomotor activity. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, F.X.; Al-Barazanji, K.A.; Bigham, E.C.; Bishop, M.J.; Britt, C.S.; Carlton, D.L.; Feldman, P.L.; Goetz, A.S.; Grizzle, M.K.; Guo, Y.C.; et al. Potent, Selective, and Orally Efficacious Antagonists of Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Receptor 1. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7095–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Löfberg, C.; Antonsson, M.; Von Unge, S.; Hayes, M.A.; Judkins, R.; Ploj, K.; Benthem, L.; Lindén, D.; Brodin, P.; et al. Discovery of (3-(4-(2-Oxa-6-azaspiro3.3heptan-6-ylmethyl)phenoxy)azetidin-1-yl)(5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)methanone (AZD1979), a Melanin Concentrating Hormone Receptor 1 (MCHr1) Antagonist with Favorable Physicochemical Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2497–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-H.; Li, Q.-Y.; Boutin, J.A.; Renard, M.P.; Ding, Y.-X.; Hao, X.-J.; Zhao, W.-M.; Wang, M.-W. High-throughput screening of novel antagonists on melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, S.; Egner, B.J.; Gradén, H.; Gradén, J.; Morgan, D.G.; Inghardt, T.; Giordanetto, F. Optimization of piperidin-4-yl-urea-containing melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH-R1) antagonists: Reducing hERG-associated liabilities. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4274–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A. Recent progress in the discovery of melanin-concentrating hormone 1-receptor antagonists. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2011, 21, 905–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, F.; Bandaru, S.S.; Absi, G.; Mahoney, C.E.; Scammell, T.E.; Vetrivelan, R. Melanin-concentrating hormone neurons contribute to dysregulation of rapid eye movement sleep in narcolepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 120, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audinot, V.; Beauverger, P.; Lahaye, C.; Suply, T.; Rodriguez, M.; Ouvry, C.; Lamamy, V.; Imbert, J.; Rique, H.; Nahon, J.-L.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Melanin-concentrating Hormone (MCH)-related Peptide Ligands at SLC-1, the Human MCH Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13554–13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audinot, V.; Lahaye, C.; Suply, T.; Beauverger, P.; Rodriguez, M.; Galizzi, J.-P.; Fauchère, J.-L.; A Boutin, J.A. 125 I-S36057: A new and highly potent radioligand for the melanin-concentrating hormone receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audinot, V.; Della Zuana, O.; Fabry, N.; Ouvry, C.; Nosjean, O.; Henlin, J.-M.; Fauchère, J.-L.; Boutin, J.A. S38151 p-guanidinobenzoyl-Des-Gly(10)-MCH(7-17) is a potent and selective antagonist at the MCH(1) receptor and has an-ti-feeding properties in vivo. Peptides 2009, 30, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Zuana, O.; Audinot, V.; Levenez, V.; Ktorza, A.; Presse, F.; Nahon, J.-L.; Boutin, J.A. Peripheral injections of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonist S38151 decrease food intake and body weight in rodent obesity models. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molek, P.; Strukelj, B.; Bratkovic, T. Peptide Phage Display as a Tool for Drug Discovery: Targeting Membrane Receptors. Molecules 2011, 16, 857–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.-H. Cyclic Peptides as Therapeutic Agents and Biochemical Tools. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.L.; Dunn, M.K. Therapeutic peptides: Historical perspectives, current development trends, and future directions. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.-L.; Harris, J.L.; Khanna, K.K.; Hong, J.-H. A Comprehensive Review on Current Advances in Peptide Drug Development and Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosgerau, K.; Hoffmann, T. Peptide therapeutics: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, J.A.; Tartar, A.L.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Vaudry, H. General lack of structural characterization of chemically synthesized long peptides. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T. A Scale of Agonism and Allosteric Modulation for Assessment of Selectivity, Bias, and Receptor Mutation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.A.; Legros, C. The five dimensions of receptor pharmacology exemplified by melatonin receptors: An opinion. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, C.; Dupré, C.; Brasseur, C.; Bonnaud, A.; Bruno, O.; Valour, D.; Shabajee, P.; Giganti, A.; Nosjean, O.; Kenakin, T.P.; et al. Characterization of the various functional pathways elicited by synthetic agonists or antagonists at the melatonin MT 1 and MT 2 receptors. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Nishiguchi, M.; Funakoshi, T.; Iijima, M.; Ito, A.; Kanuma, K.; Sekiguchi, Y. Antidepressant/anxiolytic potential and adverse effect liabilities of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists in animal models. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 135, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaki, S.; Funakoshi, T.; Hirota-Okuno, S.; Nishiguchi, M.; Shimazaki, T.; Iijima, M.; Grottick, A.J.; Kanuma, K.; Omodera, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; et al. Anxiolytic- and Antidepressant-Like Profile of ATC0065 and ATC0175: Nonpeptidic and Orally Active Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Receptor 1 Antagonists. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cippitelli, A.; Karlsson, C.; Shaw, J.L.; Thorsell, A.; Gehlert, D.R.; Heilig, M. Suppression of alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking by melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH1-R) antagonism in Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 2010, 211, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowsky, B.; Durkin, M.M.; Ogozalek, K.; Marzabadi, M.R.; DeLeon, J.; Lagu, B.; Heurich, R.; Lichtblau, H.; Shaposhnik, Z.; Daniewska, I.; et al. Antidepressant, anxiolytic and anorectic effects of a melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonist. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åstrand, A.; Bohlooly, M.-Y.; Larsdotter, S.; Mahlapuu, M.; Andersén, H.; Tornell, J.; Ohlsson, C.; Snaith, M.; Morgan, D.G.A. Mice lacking melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 demonstrate increased heart rate associated with altered autonomic activity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R749–R758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fuster, M.J.; Parks, G.S.; Clinton, S.M.; Watson, S.J.; Akil, H.; Civelli, O. The melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) system in an animal model of depression-like behavior. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühnen, P.; Wiegand, S.; Biebermann, H. Pharmacological treatment strategies for patients with monogenic obesity. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachurzok, A.; Ranke, M.B.; Flehmig, B.; Jakubek-Kipa, K.; Marcinkiewicz, K.; Mazur, A.; Petriczko, E.; Pridzun, L.; Von Schnurbein, J.; Walczak, M.; et al. Relative leptin deficiency in children with severe early-onset obesity (SEOO)—Results of the Early-onset Obesity and Leptin—German-Polish Study (EOL-GPS). J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, S.; Miao, H.; Feng, H.; Scherzinger, A.; Nardini, G.; Beghetto, B.; Roncaglia, E.; Ligabue, G.; Milic, J.; Guaraldi, G.; et al. Effects of atazanavir, darunavir, and raltegravir on fat and muscle among persons living with HIV. HIV Res. Clin. Pr. 2020, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, N.J.; Stock, M.J. Regulation of energy balance in two models of reversible obesity in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1979, 93, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlercreutz, H. Western diet and Western diseases: Some hormonal and biochemical mechanisms and associations. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 1990, 201, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, J.K. A Mouse Model of Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 821, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.; Hasselwander, S.; Li, H.; Xia, N. Effects of different diets used in diet-induced obesity models on insulin resistance and vascular dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Vandevijvere, S.; Pan, A.; McGowan, C.J.; Wallace, C.; Imamura, F.; Mozaffarian, D.; Swinburn, B.; Ezzati, M. The obesity transition: Stages of the global epidemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine, C.-E.; Moradi, H.; Streja, E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in the Obesity Paradox. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, S26–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Levine, A.S.; Murray, S.S.; Kneip, J.; Grace, M. Peptidergic regulation of stress-induced eating. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 243, R159–R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.; Audinot, V.; Dromaint, S.; Macia, C.; Lamamy, V.; Beauverger, P.; Rique, H.; Imbert, J.; Nicolas, J.P.; Boutin, J.A.; et al. Molecular identification of the long isoform of the human neuropeptide Y Y5 receptor and pharmacological comparison with the short Y5 receptor isoform. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.L.; Kokkotou, E.G.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Cheatham, B. Melanin-concentrating hormone regulates leptin synthesis and secretion in rat adipocytes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockus, A.T.; McEwen, C.M.; Lokey, R.S. Form and Function in Cyclic Peptide Natural Products: A Pharmacokinetic Perspective. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizcano, F.; Arroyave, F. Control of Adipose Cell Browning and Its Therapeutic Potential. Metabolites 2020, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, V.L.; Kim, J.T.; Long, J.Z. Adipose Tissue Lipokines: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.; Murgolo, N.; Zhang, R.; Durkin, J.P.; Yao, X.; Strader, C.D.; Graziano, M.P. Molecular Characterization of the Melanin-Concentrating Hormone/Receptor Complex: Identification of Critical Residues Involved in Binding and Activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Behan, J.; O’Neill, K.; Weig, B.; Fried, S.; Laz, T.; Bayne, M.; Gustafson, E.; Hawes, B.E. Identification and Pharmacological Characterization of a Novel Human Melanin-concentrating Hormone Receptor, mch-r2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34664–34670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Code | Sequence | Km (nM) * | n’ | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |||
| S38151 (**) | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 4,3 | 29 |
| GPS11371 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | - | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | ~100 | 26 |
| GPS11372 | Arg | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | - | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | >10,000 | 26 |
| GPS11373 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 100 | 26 |
| GPS11374 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | hArg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 3 | 29 |
| GPS11375 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 17 | 29 |
| GPS11376 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Ala | hArg | Pro | Cys | Trp | ~100 | 29 |
| GPS11377 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | - | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 27 | 26 |
| GPS11378 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Ala | Val | Ala | hArg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 18 | 29 |
| GPS11379 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Ala | Ala | - | hArg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 63 | 26 |
| GPS11380 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | 5-Ava | Pro | Cys | Trp | >100 | 29 |
| GPS11381 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Abu | Pro | Cys | Trp | 100 | 28 |
| Code | Sequence | Km nM * | n’ | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |||
| S38151 (**) | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 4,3 | 29 |
| GPS13684 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | 4-NH2-Pro | Orn | Trp | 0,36 | 29 |
| GPS13680 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Me-Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 0,4 | 29 |
| GPS13673 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Bta | 0,68 | 29 |
| GPS12744 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 0,75 | 29 |
| GPS13663 | Gua | Glu | Ethionine | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 0,75 | 29 |
| GPS13689 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | Arg | Val | Arg | Pro | Orn | Tryptamide | 0,87 | 29 | ||
| GPS15288 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | 4-NH2-Pro | Orn | Trp | 0,91 | 32 |
| GPS13675 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Me-Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 0,95 | 29 |
| GPS13682 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | hArg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1 | 29 |
| GPS13683 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Cav | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1 | 29 |
| GPS13665 | Gua | Glu | Se-Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,2 | 29 |
| GPS14509 | Gua | Glu | Se-Met | F3-Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,2 | 29 |
| GPS13686 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | 4-CF3-Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,3 | 29 |
| GPS13687 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | 4-Ph-Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,3 | 29 |
| GPS13677 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | hArg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,6 | 29 |
| GPS14511 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Me-Arg | Val | - | Me-Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,8 | 29 |
| GPS13679 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | NO-Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1,9 | 29 |
| GPS13667 | Gua | Glu | Met | Nle | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 2 | 29 |
| GPS13674 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | NO-Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 2 | 29 |
| GPS13695 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 2,2 | 32 |
| GPS13666 | Gua | Glu | Met | F3-Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 3 | 29 |
| GPS13678 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Cav | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 3 | 29 |
| GPS13672 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | N-Me-Trp | 3,4 | 29 |
| GPS15287 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Aib | Orn | Trp | 3,4 | 29 |
| GPS14514 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | - | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 3,5 | 29 |
| GPS15292 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 3,5 | 32 |
| GPS13685 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | (Me)2-Pro | Orn | Trp | 3,8 | 29 |
| GPS13681 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Cit | Pro | Orn | Trp | 3,9 | 29 |
| GPS14510 | Gua | Glu | Met | F3-Leu | - | Me-Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 4,1 | 29 |
| GPS12733 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Dab | Trp | 5,3 | 28 |
| GPS14512 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Me-Arg | Me3-Pro | Orn | Trp | 5,7 | 29 |
| GPS13676 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Cit | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 6 | 29 |
| GPS12739 | Gua | Asp | Se-Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 8,5 | 28 |
| GPS14515 | Aaba | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 8,6 | 29 |
| GPS12743 | Gua | Orn | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Asp | Trp | 9 | 28 |
| GPS12746 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Lys | Trp | 12 | 30 |
| GPS12745 | Gua | Orn | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Glu | Trp | 13 | 29 |
| GPS12737 | Gua | Asp | Ethionine | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 23 | 28 |
| GPS13661 | Gua | Glu | CH3-S-Cys | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 26 | 29 |
| GPS13668 | Gua | Glu | Met | tBut-Gly | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 28 | 29 |
| GPS12731 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Lys | Trp | 41 | 29 |
| GPS13664- Peak 1 (***) | Gua | Glu | Buthionine | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 87 | 29 |
| GPS13670 | Gua | Ala | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Ala | Trp | 110 | 0 |
| GPS12750 | Gua | Asp | Met | Nle | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 140 | 28 |
| GPS13688 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | 4-NH2-Pro | Ala | Trp | 170 | 24 |
| GPS12732 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Dap | Trp | 210 | 27 |
| GPS13669 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 220 | 0 |
| GPS13662 | Gua | Glu | β -hMet | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 250 | 30 |
| GPS14488 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | Gly | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 270 | 32 |
| GPS13664-Peak 2 (***) | Gua | Glu | Buthionine | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 330 | 29 |
| GPS11398 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Dap | Trp | 380 | 29 |
| GPS15293 | arg | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 610 | 29 |
| GPS11401 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Dab | Trp | 880 | 27 |
| GPS14489 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Cav | Pro | Orn | Trp | 900 | 0 |
| GPS12734 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | Gly | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~10,000 | 31 |
| GPS12736 | Gua | Asp | β-hMet | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~10,000 | 29 |
| GPS12742 | Arg-BZ | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~10,000 | 28 |
| GPS13628 | Gua | Asp | Met | 4-hydro-Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~10,000 | 28 |
| GPS12752 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Aib | Orn | Trp | ~10,000 | 28 |
| GPS12749 | Gua | Asp | Met | F3-Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~1000 | 28 |
| GPS12751 | Gua | Asp | Met | tBut-Gly | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~1000 | 28 |
| GPS12735 | Gua | Asp | CH3-S-Cys | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~1000 | 28 |
| GPS12738 | Gua | Asp | Buthionine | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | ~10,000 | 28 |
| GPS11400 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 26 |
| GPS11408 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | - | Ala | Ala | hArg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 26 |
| GPS11410 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Abu | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 28 |
| GPS14522 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | >10,000 | 0 | ||||||
| GPS11403 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | hArg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >1000 | 29 |
| GPS11399 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | - | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 26 |
| GPS11402 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | >10,000 | 28 |
| GPS11404 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | arg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 29 |
| GPS11405 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Ala | hArg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 29 |
| GPS11406 | Gua | Asp | Met | Leu | - | - | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Dap | Trp | >10,000 | 26 |
| GPS14523 | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | >10,000 | 0 | ||||||
| Code | Sequence | Km nM * | n’ | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |||
| S38151 (**) | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 4,3 | 29 |
| GPS14517 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 2,1 | 29 |
| GPS15290 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 0,86 | 29 |
| GPS15363 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Bta | 0,3 | 29 |
| GPS15364 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | 4-NH2-Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 0,24 | 29 |
| GPS15365 | Gua | N3-hAla | SeMet | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 0,34 | 29 |
| GPS15366 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Triptamide | 0,21 | 29 |
| GPS15367 | Gua | N3-hAla | NMeMet | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 670 | 29 |
| GPS15368 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | NMeLeu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 360 | 29 |
| GPS18169 | Gua | N3-hAla | Nle | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 1,2 | 29 |
| GPS14519 | Gua | N3-nVal | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Propargyl-Gly | Trp | 2,3 | 29 |
| GPS14516 | Gua | Propargyl-Gly | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | N3-hAla | Trp | 1,9 | 29 |
| GPS14518 | Gua | Propargyl-Gly | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | N3-nVal | Trp | 1,8 | 29 |
| GPS15291 | Gua | Propargyl-Gly | Ethionine | Leu | - | Arg | bhVal | - | Arg | Pro | N3-hAla | Trp | 91 | 29 |
| Code | Sequence | Km (nM) | n’ | Ki (pM) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S38151 | Gua | Cys | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Cys | Trp | 4.3 | 29 | 5000 |
| GPS14517 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | hPra | Trp | 2.1 | 29 | 22 |
| GPS14518 | Gua | hPra | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | N3-nVal | Trp | 1.8 | 29 | 27 |
| GPS15290 | Gua | N3-hAla | Met | Leu | - | Arg | βhVal | - | Arg | Pro | hPra | Trp | 0.86 | 29 | 28 |
| GPS18169 | Gua | N3-hAla | Nle | Leu | - | Arg | βhVal | - | Arg | Pro | hPra | Trp | 1.2 | 29 | 28 |
| GPS13695 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | Tyr | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 2.2 | 32 | 130 |
| GPS13683 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Canava | Pro | Orn | Trp | 1 | 29 | 150 |
| GPS14519 | Gua | N3-nVal | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | hPra | Trp | 2.3 | 29 | 430 |
| GPS13671 | Gua | hPra | Ethionine | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | N3-hAla | Trp | 120 | 28 | 8000 |
| GPS13670 | Gua | Ala | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Ala | Trp | 110 | 0 | 30,000 |
| GPS13669 | Gua | Glu | Met | Leu | - | Arg | Val | - | Arg | Pro | Orn | Trp | 220 | 0 | 300,000 |
| S38151 | GPS12744 | GPS13663 | GPS13684 | GPS15290 | GPS18169 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | 23 ± 1.8 | 26 ± 3 | 19 ± 1 | 26 ± 1 | 173 ± 9 | 175 ± 17 |
| Rat | 60 ± 3 | 143 ± 12 | 94 ± 3 | 135 ± 9 | 300 * | 300 * |
| Human | 14 ± 1 | 300 * | 300 * | 300 * | 300 * | 300 * |
| Insulin | Total Cholesterol | Triglyceride | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pg/mL | mg/dL | mg/dL | |||||||||
| Day 56 | Day 113 | Day 141 | Day 56 | Day 113 | Day 141 | Day 56 | Day 113 | Day 141 | |||
| Vehicle (Normal Diet) | (*) | Mean | 381.1 | 438.3 | 760.7 | 98.1 | 103.1 | 101.2 | 69.5 | 86.3 | 78.3 |
| SEM | 51.7 | 57.2 | 79.7 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 6.4 | ||
| Vehicle (High-Fat Diet) | (*) | Mean | 887.0 | 2543.0 † | 2016.6 † | 155.6 † | 163.6 † | 157.7 † | 123.4 † | 122.1 † | 123.5 † |
| SEM | 126.9 | 383.3 | 477.2 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 17.5 | 6.7 | 5.7 | 11.6 | ||
| GPS18169 (High-Fat Diet) | (*) | Mean | 1068.0 | 1549.7 | 957.0 * | 155.6 | 135.7 | 132.1 | 122.9 | 108.3 | 102.1 |
| SEM | 145.9 | 370.8 | 371.8 | 7.4 | 9.3 | 6.6 | 3.5 | 6.0 | 3.3 | ||
| GPS18169 (High-Fat Diet) | (**) | Mean | 909.5 | 1983.8 | 760.4 * | 158.3 | 143.1 | 135.6 | 121.8 | 115.3 | 108.9 |
| SEM | 125.6 | 554.7 | 201.4 | 7.0 | 13.9 | 14.6 | 4.6 | 6.0 | 9.4 | ||
| Treatment | Dose | BW (g) Day 141 | Adipose Tissue Weight (g) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epididymal | Mesenteric | Retroperitoneal | Inguinal | Brown Fat | |||||||||
| g | g | % BW | g | % BW | g | % BW | g | % BW | g | % BW | |||
| Vehicle (Normal Diet) | 10 mL/kg QD x 12 wks | Mean | 27.2 | 0.735 | 2.66 | 0.345 | 1.26 | 0.219 | 0.79 | 0.402 | 1.46 | 0.099 | 0.36 |
| SEM | 0.5 | 0.063 | 0.20 | 0.021 | 0.06 | 0.025 | 0.08 | 0.034 | 0.11 | 0.006 | 0.02 | ||
| Vehicle (High-fat Diet) | 10 mL/kg QD x 12 wks | Mean | 40.0 † | 1.972 † | 4.98 † | 0.688 † | 1.68 | 0.779 † | 1.87 † | 1.725 † | 4.16 † | 0.164 † | 0.40 |
| SEM | 2.6 | 0.152 | 0.30 | 0.082 | 0.11 | 0.116 | 0.17 | 0.222 | 0.33 | 0.018 | 0.02 | ||
| GPS18169-002 | 10 mg/kg QD x 12 wks | Mean | 29.9 * | 1.991 | 6.71 | 0.334 * | 1.08 * | 0.320 * | 1.01 * | 0.892 * | 2.77 | 0.084 * | 0.27 * |
| SEM | 1.4 | 0.141 | 0.47 | 0.047 | 0.11 | 0.064 | 0.17 | 0.206 | 0.55 | 0.009 | 0.02 | ||
| GPS18169-002 | 5 mg/kg QD x 12 wks | Mean | 29.8 * | 1,882 | 6.67 | 0.351 * | 1.08 * | 0.321 * | 0.97 * | 0.922 * | 2.69 | 0.096 * | 0.30 * |
| SEM | 2.4 | 0.148 | 0.66 | 0.094 | 0.19 | 0.093 | 0.21 | 0.314 | 0.73 | 0.023 | 0.04 | ||
| Group | Test | Route | Conc. | Dosage | Mice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Article | mg/ml | mL/kg | mg/kg | (Male) | ||
| 1 | Vehicle a,b (Normal Diet) | IP | NA | 10 | NA, QD x 12 weeks | 10 |
| 2 | Vehicle a,c (High-fat diet) | IP | NA | 10 | NA, QD x 12 weeks | 10 |
| 3 | GPS18169 a,c | IP | 1 | 10 | 10, QD x 12 weeks | 10 |
| 4 | GPS18169 a,c | IP | 0.5 | 10 | 5, QD x 12 weeks | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boutin, J.A.; Jullian, M.; Frankiewicz, L.; Galibert, M.; Gloanec, P.; Le Diguarher, T.; Dupuis, P.; Ko, A.; Ripoll, L.; Bertrand, M.; et al. MCH-R1 Antagonist GPS18169, a Pseudopeptide, Is a Peripheral Anti-Obesity Agent in Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051291
Boutin JA, Jullian M, Frankiewicz L, Galibert M, Gloanec P, Le Diguarher T, Dupuis P, Ko A, Ripoll L, Bertrand M, et al. MCH-R1 Antagonist GPS18169, a Pseudopeptide, Is a Peripheral Anti-Obesity Agent in Mice. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051291
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoutin, Jean A., Magali Jullian, Lukasz Frankiewicz, Mathieu Galibert, Philippe Gloanec, Thierry Le Diguarher, Philippe Dupuis, Amber Ko, Laurent Ripoll, Marc Bertrand, and et al. 2021. "MCH-R1 Antagonist GPS18169, a Pseudopeptide, Is a Peripheral Anti-Obesity Agent in Mice" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051291
APA StyleBoutin, J. A., Jullian, M., Frankiewicz, L., Galibert, M., Gloanec, P., Le Diguarher, T., Dupuis, P., Ko, A., Ripoll, L., Bertrand, M., Pecquery, A., Ferry, G., & Puget, K. (2021). MCH-R1 Antagonist GPS18169, a Pseudopeptide, Is a Peripheral Anti-Obesity Agent in Mice. Molecules, 26(5), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051291







