New Insights into the Metabolism of Methyltestosterone and Metandienone: Detection of Novel A-Ring Reduced Metabolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Reference Steroids
2.1.1. 17-Hydroxymethyl-17-methyl-18-nor-13-enes
2.1.2. 17β-Methyl-5β-androstane-3α,17α-diol (11)
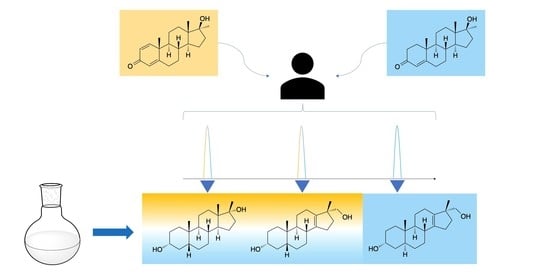
2.2. Post-Administration Urines
3. Discussion
3.1. Chemical Syntheses and Characterization of Reference Material
3.2. Urinary Metabolites
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Instrumentation
4.1.1. GC-MS/MS
4.1.2. GC-QTOF-MS
4.1.3. HPLC Purification
4.1.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
4.2. Chemicals and Reagents
4.3. Synthesis of Reference Steroids
4.3.1. Diastereomeric 17-hydroxymethyl-17-methyl-18-nor-5-androst-13-en-3-ols
4.3.2. Epi-Tetrahydromethyltestosterones
4.4. Human Administration Trial
4.5. Urine Sample Preparation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Whitelaw, M.J.; Foster, T.N.; Graham, W.H. Methandrostenolone (Dianabol): A controlled study of its anabolic and androgenic effect in children. J. Pediatrics 1966, 68, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, G.L.; Simpson, S.L. Oral methyltestosterone and jaundice. Br. Med. J. 1959, 1, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Anti-Doping Agency. The 2021 Prohibited List. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/2021list_en.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- World Anti-Doping Agency. Anti-Doping Testing Figures—Laboratory Report; World Anti-Doping Agency: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kicman, A.T. Pharmacology of anabolic steroids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicman, A.T.; Gower, D.B. Anabolic steroids in sport: Biochemical, clinical and analytical perspectives. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 40, 321–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, J.F.; Parr, M.K. Synthetic androgens as designer supplements. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schanzer, W.; Geyer, H.; Donike, M. Metabolism of metandienone in man: Identification and synthesis of conjugated excreted urinary metabolites, determination of excretion rates and gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric identification of bis-hydroxylated metabolites. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 38, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanzer, W. Metabolism of anabolic androgenic steroids. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schanzer, W.; Horning, S.; Donike, M. Metabolism of anabolic steroids in humans: Synthesis of 6 beta-hydroxy metabolites of 4-chloro-1,2-dehydro-17 alpha-methyltestosterone, fluoxymesterone, and metandienone. Steroids 1995, 60, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanzer, W.; Delahaut, P.; Geyer, H.; Machnik, M.; Horning, S. Long-term detection and identification of metandienone and stanozolol abuse in athletes by gas chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1996, 687, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schänzer, W.; Geyer, H.; Horning, S. 17,17-Dimethyl-18-nor-5a-androst-1,13-dien-3a-ol (18-normetenol) in longterm detection and confirmation of positive metandienone cases. In Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (6); Schänzer, W., Geyer, H., Gotzmann, A., Mareck-Engelke, U., Eds.; Sport und Buch Strauß: Cologne, Germany, 1999; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, M.K.; Zollner, A.; Fussholler, G.; Opfermann, G.; Schlorer, N.; Zorio, M.; Bureik, M.; Schanzer, W. Unexpected contribution of cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP11B2 and CYP21, as well as CYP3A4 in xenobiotic androgen elimination—Insights from metandienone metabolism. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 213, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo, O.J.; Lootens, L.; Van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K.; Meuleman, P.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Parr, M.K.; Schanzer, W.; Delbeke, F.T. Combination of liquid-chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in different scan modes with human and chimeric mouse urine for the study of steroid metabolism. Drug Test Anal. 2009, 1, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massé, R.; Bi, H.; Ayotte, C.; Du, P.; Gélinas, H.; Dugal, R. Studies on anabolic steroids. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1991, 562, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, A.; Pozo, O.J.; Garrostas, L.; Balcells, G.; Gomez, C.; Kotronoulas, A.; Joglar, J.; Ventura, R. LC-MS/MS detection of unaltered glucuronoconjugated metabolites of metandienone. Drug Test Anal. 2017, 9, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, C.; Pozo, O.J.; Garrostas, L.; Segura, J.; Ventura, R. A new sulphate metabolite as a long-term marker of metandienone misuse. Steroids 2013, 78, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanzer, W.; Geyer, H.; Fussholler, G.; Halatcheva, N.; Kohler, M.; Parr, M.K.; Guddat, S.; Thomas, A.; Thevis, M. Mass spectrometric identification and characterization of a new long-term metabolite of metandienone in human urine. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, M.K.; Zoellner, A.; Bureik, M.; Dragan, C.A.; Schlörer, N.; Peters, F.; Maurer, H.; Schänzer, W. Production of metandienone longterm-metabolite, 17β-hydroxymethyl-17α-methyl-18-nor-androsta-1,4,13-trien-3-one, using S. pombe based biotransformation assay. In Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (17); Schänzer, W., Geyer, H., Gotzmann, A., Mareck, U., Eds.; Sport und Buch Strauß: Cologne, Germany, 2009; pp. 95–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zollner, A.; Parr, M.K.; Dragan, C.A.; Dras, S.; Schlorer, N.; Peters, F.T.; Maurer, H.H.; Schanzer, W.; Bureik, M. CYP21-catalyzed production of the long-term urinary metandienone metabolite 17beta-hydroxymethyl-17 alpha-methyl-18-norandrosta-1,4,13-trien-3-one: A contribution to the fight against doping. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratena, N.; Enev, V.S.; Gmeiner, G.; Gartner, P. Synthesis of 17beta-hydroxymethyl-17alpha-methyl-18-norandrosta-1,4,13-trien-3-one: A long-term metandienone metabolite. Steroids 2016, 115, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolevsky, T.; Krotov, G.; Dikunets, M.; Nikitina, M.; Mochalova, E.; Rodchenkov, G. Anti-doping analyses at the Sochi Olympic and Paralympic Games 2014. Drug Test Anal. 2014, 6, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarino, M.; Orengia, M.; Botre, F. Application of fast gas chromatography/mass spectrometry for the rapid screening of synthetic anabolic steroids and other drugs in anti-doping analysis. Rapid. Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2007, 21, 4117–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schänzer, W.; Donike, M. Metabolism of anabolic steroids in man: Synthesis and use of reference substances for identification of anabolic steroid metabolites. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 275, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schänzer, W.; Opfermann, G.; Donike, M. 17-Epimerization of 17α-methyl anabolic steroids in humans: Metabolism and synthesis of 17α-hydroxy-17β-methyl steroids. Steroids 1992, 57, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Pozo, O.J.; Marcos, J.; Segura, J.; Ventura, R. Alternative long-term markers for the detection of methyltestosterone misuse. Steroids 2013, 78, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Brito, D.; Iannone, M.; Tatangelo, M.A.; Molaioni, F.; de la Torre, X.; Botre, F. A further insight into methyltestosterone metabolism: New evidences from in vitro and in vivo experiments. Rapid. Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo, O.J.; Van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K.; Lootens, L.; Van Thuyne, W.; Parr, M.K.; Schanzer, W.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernandez, F.; Meuleman, P.; et al. Detection and characterization of a new metabolite of 17alpha-methyltestosterone. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcells, G.; Pozo, O.J.; Esquivel, A.; Kotronoulas, A.; Joglar, J.; Segura, J.; Ventura, R. Screening for anabolic steroids in sports: Analytical strategy based on the detection of phase I and phase II intact urinary metabolites by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1389, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobolevsky, T.; Rodchenkov, G. Detection and mass spectrometric characterization of novel long-term dehydrochloromethyltestosterone metabolites in human urine. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 128, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsdahl, G.; Geisendorfer, T.; Goschl, L.; Pfeffer, S.; Gartner, P.; Thevis, M.; Gmeiner, G. Unambiguous identification and characterization of a long-term human metabolite of dehydrochloromethyltestosterone. Drug Test Anal. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratena, N.; Pilz, S.M.; Weil, M.; Gmeiner, G.; Enev, V.S.; Gartner, P. Synthesis and structural elucidation of a dehydrochloromethyltestosterone metabolite. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratena, N.; Pfeffer, S.; Enev, V.S.; Gmeiner, G.; Gartner, P. Synthesis of human long-term metabolites of dehydrochloromethyltestosterone and oxymesterone. Steroids 2020, 164, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, M.K.; Zapp, J.; Becker, M.; Opfermann, G.; Bartz, U.; Schanzer, W. Steroidal isomers with uniform mass spectra of their per-TMS derivatives: Synthesis of 17-hydroxyandrostan-3-ones, androst-1-, and -4-ene-3,17-diols. Steroids 2007, 72, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, A.; Loke, S.; Joseph, J.F.; Machalz, D.; de la Torre, X.; Botre, F.; Wolber, G.; Bureik, M.; Parr, M.K. Fine-mapping of the substrate specificity of human steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 194, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Stothers, J.B. 13C NMR spectra of steroids—A survey and commentary. Org. Magn. Reson. 1977, 9, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Shimahara, M.; Shiota, M. Stereochemistry of the Palladium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of 3-Oxo-4-ene Steroids1. J. Org. Chem. 1966, 31, 2394–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, M.K.; Fußhöller, G.; Gütschow, M.; Hess, C.; Schänzer, W. GC-MS(/MS) investigations on long-term metabolites of 17-methyl steroids. In Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (18); Schänzer, W., Geyer, H., Gotzmann, A., Mareck, U., Eds.; Sport und Buch Strauß: Cologne, Germany, 2010; pp. 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Joseph, J.F.; Nass, A.; Stoll, A.; de la Torre, X.; Botre, F.; Wolber, G.; Parr, M.K.; Bureik, M. Combined chemical and biotechnological production of 20betaOH-NorDHCMT, a long-term metabolite of Oral-Turinabol (DHCMT). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 183, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolevsky, T.; Rodchenkov, G. Mass spectral characterization of novel dehydrochloromethyltestosterone and oxandrolone metabolites after HPLC clean-up. In Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (19); Schänzer, W., Geyer, H., Gotzmann, A., Mareck, U., Eds.; Sportverlag Strauß: Cologne, Germany, 2011; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Guddat, S.; Fussholler, G.; Beuck, S.; Thomas, A.; Geyer, H.; Rydevik, A.; Bondesson, U.; Hedeland, M.; Lagojda, A.; Schanzer, W.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and detection of new oxandrolone metabolites as long-term markers in sports drug testing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 8285–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Álvarez, M.; Jianghai, L.; Cuervo, D.; Youxuan, X.; Muñoz-Guerra, J.A.; Aguilera, R. Detection of new Oral-Turinabol metabolites by LC-QToF. In Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (22); Schänzer, W., Geyer, H., Gotzmann, A., Mareck, U., Eds.; Sportverlag Strauß: Cologne, Germany, 2014; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, M.K.; Piana, G.L.; Stoll, A.; Joseph, J.F.; Loke, S.; Schlörer, N.; Torre, X.d.l.; Botrè, F. Tracing Back Drug Misuse—Proper Metabolite Identification Requires Synthesis. In Proceedings of the TIAFT 2019: The 57th Annual Meeting of the International Association of Forensic Toxicologists, Birmingham, UK, 6 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, B.S.; Sykes, P.J.; Adhikary, P.M.; Harkness, R.A. The identification of 17α-hydroxy-17-methyl-1,4-androstadien-3-one as a metabolite of the anabolic steroid drug 17β-hydroxy-17-methyl-1,4-androstadien-3-one in man. Steroids 1971, 18, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, F.; Gardi, R. Metabolism of 1-dehydroand rostanes in man. Steroids 1971, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| No. | Stereochemical Assignment | RT [min] | Molecular Ion (LEI) | Δm/z [ppm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 3α, 5β, 17α-CH2OH | 9.80 | 448.3162 | −5.6 |
| 8a | 3α, 5α, 17α-CH2OH | 10.13 | 448.3164 | −5.1 |
| 17α-hydroxymethyl-17β-methyl-18-nor-5β-androst-13-en-3α-ol (8) | 17α-hydroxymethyl-17β-methyl-18-nor-5α-androst-13-en-3α-ol (8a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | δC | δH | |
| 1 | 35.18 | α: 1.92 β: 1.06 | 31.93 | α: 1.35 β: 1.58 |
| 2 | 30.64 | α: 1.37 β: 1.72 | 28.93 | α: 1.66 β: 1.75 |
| 3 | 71.75 | β: 3.66 | 66.43 | β: 4.08 |
| 4 | 36.59 | α: 1.75 β: 1.56 | 35.70 | α: 1.41 β: 1.53 |
| 5 | 41.75 | β: 1.47 | 39.03 | α: 1.60 |
| 6 | 27.63 | α: 1.35 β: 1.93 | 28.86 | α: 1.25 β: 1.30 |
| 7 | 26.08 | α: 1.72 β: 1.21 | 31.47 | α: 1.04 β: 1.95 |
| 8 | 37.41 | β: 2.14 | 36.97 | β: 2.10 |
| 9 | 38.44 | α: 1.67 | 52.03 | α: 1.01 |
| 10 | 34.67 | - | 36.13 | - |
| 11 | 22.43 | α: 1.79 β: 1.14 | 22.14 | α: 1.90 β: 1.16 |
| 12 | 22.65 | α: 1.83 β: 2.02 | 22.59 | α: 1.80 β: 2.01 |
| 13 | 135.94 | - | 135.85 | - |
| 14 | 141.76 | - | 141.81 | - |
| 15 | 30.60 | α: 2.32 β: 2.12 | 30.61 | α: 2.33 β: 2.11 |
| 16 | 34.20 | α: 1.58 β: 1.97 | 34.13 | α: 1.97 β: 1.58 |
| 17 | 51.66 | - | 51.54 | - |
| 19 | 22.93 | 0.93 (s) | 10.61 | 0.78 (s) |
| 20βCH3 | 21.72 | 1.00 (s) | 21.75 | 0.99 (s) |
| 20αCH2OH | 68.97 | 3.34 (d) 3.44 (d) | 68.99 | 3.31 (d) 3.42 (d) |
| Compound (Parent Compound) | RT [min] | Ion Transitions (m/z) & Collision Energies |
|---|---|---|
| 17β-methyl-5β-androst-1-ene-3α,17α-diol (15) | 9.87 | 358.0 → 301.0 (10 eV) 358.0 → 169.0 (30 eV) 358.0 → 196.0 (10 eV) 358.0 → 194.0 (10 eV) 216.0 → 159.0 (5 eV) 268.0 → 211.0 (10 eV) 216.0 → 187.0 (5 eV) |
| 6β,17β-dihydroxy-17α-methyl-androsta-1,4-dien-3-one (13) | 16.19 | 517.5 → 229.0 (5 eV) 517.5 → 297.0 (5 eV) 517.5 → 205.0 (30 eV) 517.5 → 429.4 (5 eV) |
| 17α-hydroxy-17β-methyl-androsta-1,4-dien-3-one (14) | 13.77 | 444.4 → 206.0 (10 eV) 444.4 → 191.0 (30 eV) 339.0 → 270.0 (20 eV) 444.4 → 283.0 (30 eV) |
| 17,17-dimethyl-18-nor-5β-androsta-1,13-dien-3α-ol (16) | 6.19 | 253.0 → 185.0 (20 eV) 253.0 → 197.0 (20 eV) 253.0 → 105.0 (30 eV) 216.0 → 131.0 (20 eV) 216.0 → 145.0 (20 eV) |
| 17β-hydroxymethyl-17α-methyl-18-nor-androsta-1,4,13-trien-3-one (17) | 13.84 | 236.0 → 133.0 (5 eV) 339.0 → 193.0 (20 eV) 442.4 → 243.0 (15 eV) 442.4 → 133.0 (15 eV) 339.0 → 133.0 (20 eV) 339.0 → 243.0 (20 eV) |
| 17α-methyl-5β-androstane-3α,17β-diol (20) | 13.36 | 228.0 → 174.0 (5 eV) 270.0 → 157.0 (30 eV) 270.0 → 171.0 (30 eV) 270.0 → 199.0 (30 eV) |
| 17α-methyl-5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol (19) | 13.22 | 318.0 → 199.0 (10 eV) 318.0 → 187.0 (10 eV) 318.0 → 182.0 (10 eV) 450.4 → 365.0 (10 eV) 450.4 → 261.0 (10 eV) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loke, S.; Liu, L.; Wenzel, M.; Scheffler, H.; Iannone, M.; de la Torre, X.; Schlörer, N.; Botrè, F.; Keiler, A.M.; Bureik, M.; et al. New Insights into the Metabolism of Methyltestosterone and Metandienone: Detection of Novel A-Ring Reduced Metabolites. Molecules 2021, 26, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051354
Loke S, Liu L, Wenzel M, Scheffler H, Iannone M, de la Torre X, Schlörer N, Botrè F, Keiler AM, Bureik M, et al. New Insights into the Metabolism of Methyltestosterone and Metandienone: Detection of Novel A-Ring Reduced Metabolites. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051354
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoke, Steffen, Lingyu Liu, Maxi Wenzel, Heike Scheffler, Michele Iannone, Xavier de la Torre, Nils Schlörer, Francesco Botrè, Annekathrin Martina Keiler, Matthias Bureik, and et al. 2021. "New Insights into the Metabolism of Methyltestosterone and Metandienone: Detection of Novel A-Ring Reduced Metabolites" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051354
APA StyleLoke, S., Liu, L., Wenzel, M., Scheffler, H., Iannone, M., de la Torre, X., Schlörer, N., Botrè, F., Keiler, A. M., Bureik, M., & Parr, M. K. (2021). New Insights into the Metabolism of Methyltestosterone and Metandienone: Detection of Novel A-Ring Reduced Metabolites. Molecules, 26(5), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051354