Olea europaea Suppresses Inflammation by Targeting TAK1-Mediated MAP Kinase Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
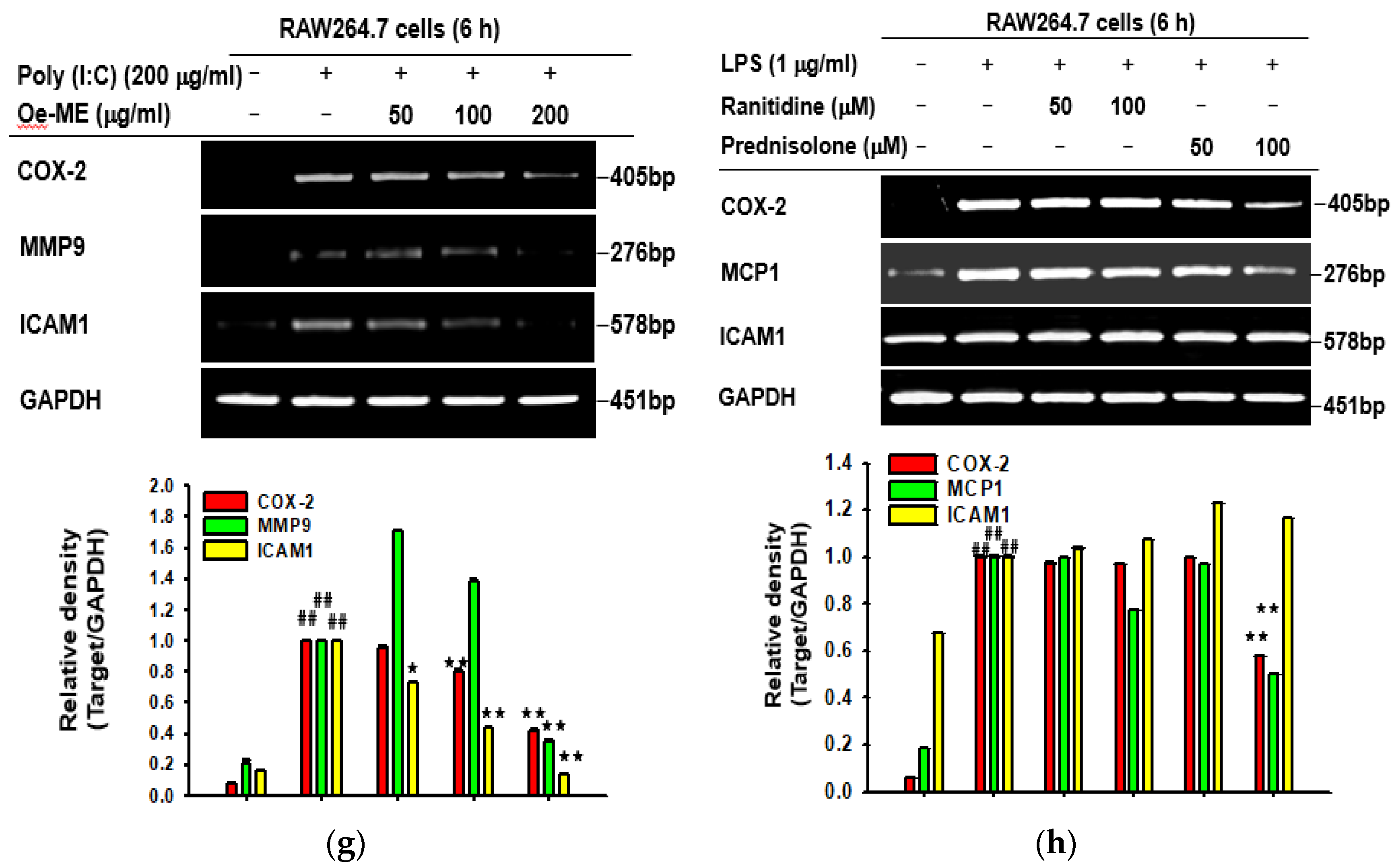
2.1. Cytotoxicity and the Effect of Oe-ME on Production of Inflammatory Genes
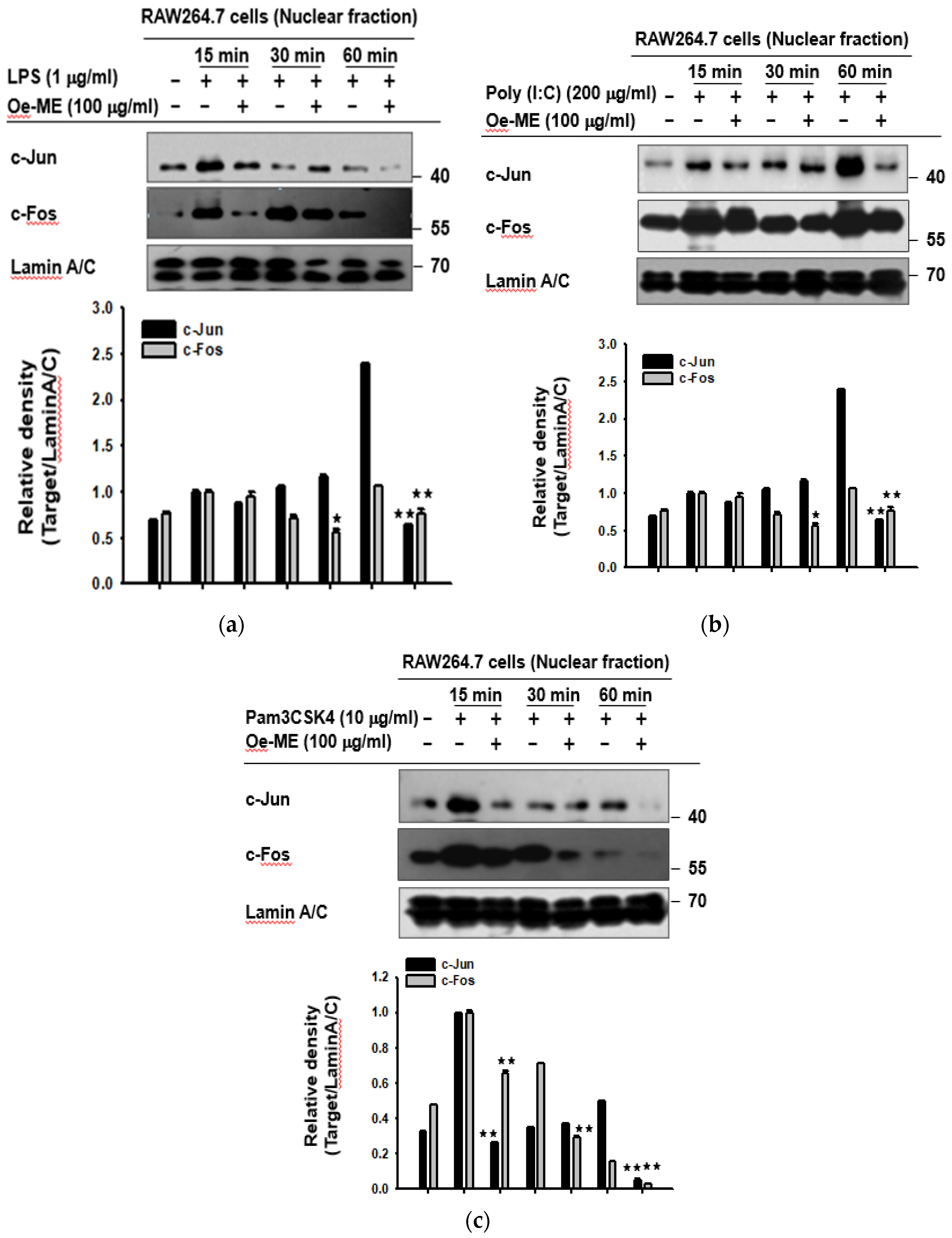
2.2. Roles of Oe-ME in Transcriptional Activation of AP-1
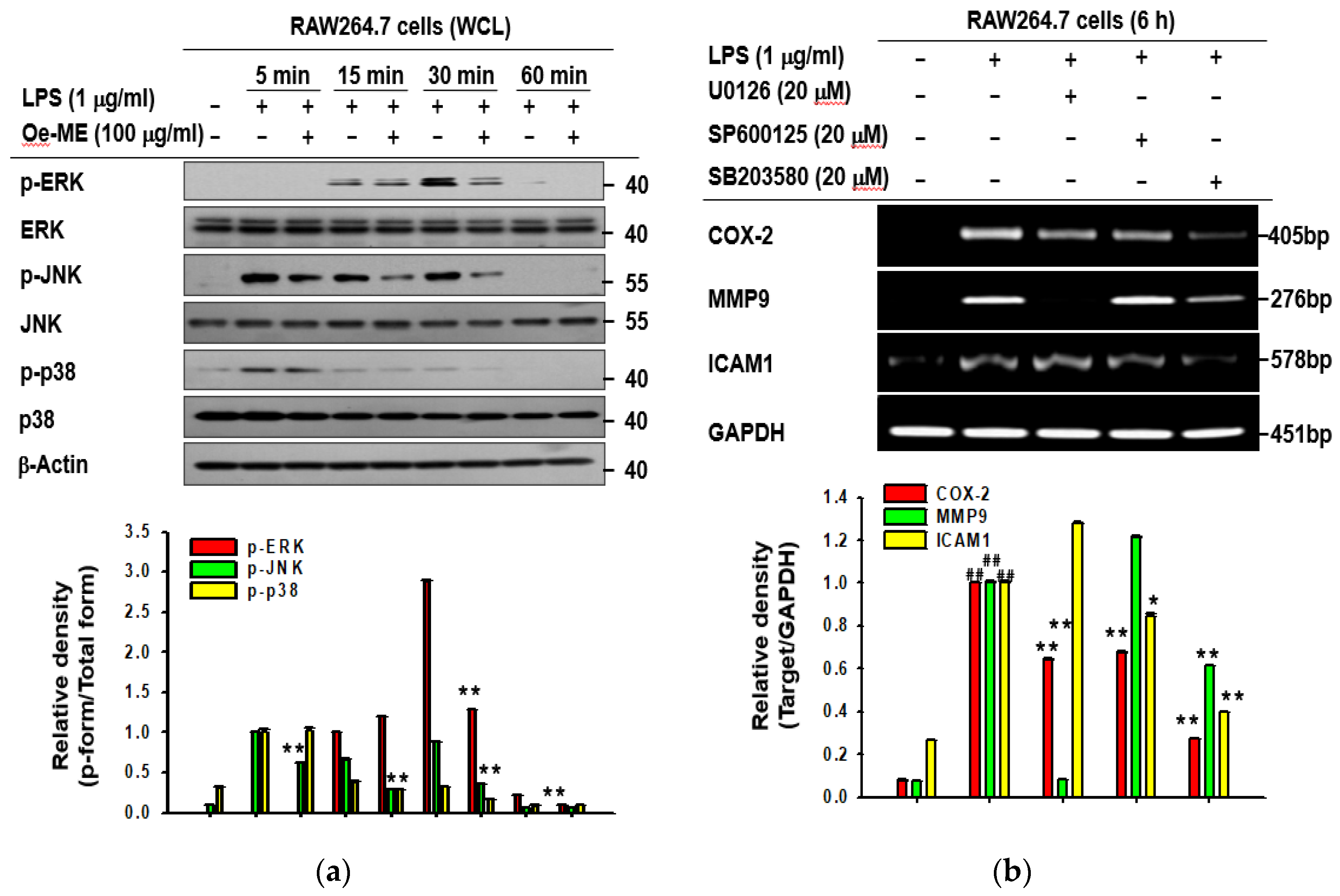
2.3. Role of Oe-ME in AP-1 Signal Transduction
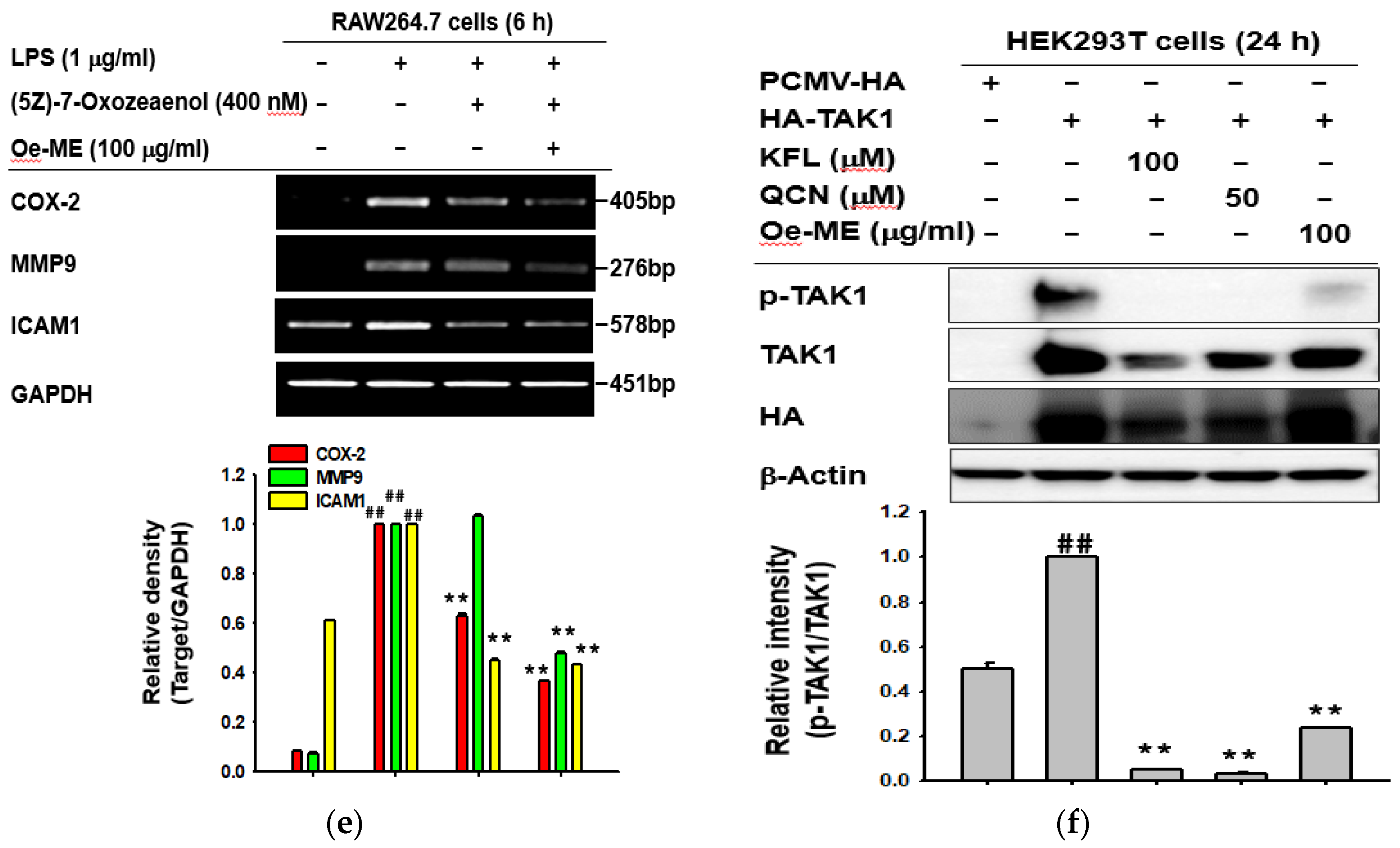
2.4. Effect of Oe-ME on TAK1 Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Oe-ME Preparation
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
4.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Production
4.6. Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Plasmid Transfection
4.8. Preparation of Nuclear and Total Samples for Immunoblotting
4.9. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.O.; Choi, E.; Shin, K.K.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, D.; Hossain, M.A.; Kim, H.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, D.; et al. Compound K, a ginsenoside metabolite, plays an antiinflammatory role in macrophages by targeting the AKT1-mediated signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, T.; Jeong, H.W.; Hong, Y.D.; Yoon, K.; Cho, J.Y.; Yoon, K.D. Identification of a novel triterpene saponin from Panax ginseng seeds, pseudoginsenoside RT8, and its antiinflammatory activity. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Yang, E.; Kim, M.-J.; Jeong, D.; Yoon, D.H.; Sung, G.-H.; Lee, S.; Yoo, B.C.; Yeo, S.-G.; Cho, J.Y. Momordica charantia inhibits inflammatory responses in murine macrophages via suppression of TAK1. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold-Smith, F.; Fernandez, A.; Bishop, K. Mangiferin and cancer: Mechanisms of action. Nutrients 2016, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Kang, Y.-G.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, T.R.; Yoo, B.C.; Jo, M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, D.; Cho, J.Y. Dehydroabietic acid suppresses inflammatory response via suppression of Src-, Syk-, and TAK1-mediated pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Luo, J.-G.; Kong, L.-Y. Bioassay-guided isolation of anti-inflammatory components from the bulbs of Lilium brownii var. viridulum and identifying the underlying mechanism through acting on the NF-κB/MAPKs pathway. Molecules 2017, 22, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.-S.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, D. Cerbera manghas methanol extract exerts anti-inflammatory activity by targeting c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the AP-1 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.; Wolf, S. ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-C.; Huang, W.-C.; SPang, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y. Quercetin inhibits the production of IL-1β-induced inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in ARPE-19 cells via the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashmi, M.A.; Khan, A.; Hanif, M.; Farooq, U.; Perveen, S. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Olea europaea (olive). Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 541591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visioli, F.; Poli, A.; Gall, C. Antioxidant and other biological activities of phenols from olives and olive oil. Med. Res. Rev. 2002, 22, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, E.; Giammanco, M.; Tabacchi, G.; Di Majo, D.; Giammanco, S.; La Guardia, M. The phenolic compounds of olive oil: Structure, biological activity and beneficial effects on human health. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2007, 18, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.H. Oleuropein in olive and its pharmacological effects. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baek, K.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Son, Y.J.; Yoo, S.; Sung, N.Y.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. In Vitro and In Vivo anti-inflammatory activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived components. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunto, S.T.; Kim, H.G.; Baek, K.S.; Jeong, D.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Loratadine, an antihistamine drug, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through suppression of the NF-kB pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 113949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.; Angel, P.; Schorpp-Kistner, M. AP-1 subunits: Quarrel and harmony among siblings. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 5965–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Kajino, T.; Ono, K.; Ohtomo, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Shiina, M.; Mihara, M.; Tsuchiya, M.; Matsumoto, K. A Resorcylic acid lactone, 5Z-7-oxozeaenol, prevents inflammation by inhibiting the catalytic activity of TAK1 MAPK kinase kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18485–18490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Powell, F.; Larsen, N.A.; Lai, Z.; Byth, K.F.; Read, J.; Gu, R.-F.; Roth, M.; Toader, D.; Saeh, J.C.; et al. Mechanism and in vitro pharmacology of TAK1 inhibition by (5Z)-7-oxozeaenol. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Hong, Y.H.; Park, J.G.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, D.; Oh, J.; Sung, G.H.; Hossain, M.A.; Taamalli, A.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Suppression of Src and Syk in the NF-κB signaling pathway by Olea europaea methanol extract is leading to its anti-inflammatory effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figenschau, S.L.; Knutsen, E.; Urbarova, I.; Fenton, C.; Elston, B.; Perander, M.; Mortensen, E.S.; Fenton, K.A. ICAM1 expression is induced by proinflammatory cytokines and associated with TLS formation in aggressive breast cancer subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parks, W.C.; Wilson, C.L.; López-Boado, Y.S. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmarsh, A.J. Regulation of gene transcription by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangnuss, S.; Cowin, A.J.; Daehn, I.S.; Hatzirodos, N.; Rothnagel, J.A.; Varelias, A.; Rayner, T.E. Regulation of MAPK activation, AP-1 transcription factor expression and keratinocyte differentiation in wounded fetal skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Jin, G.; Cai, z.; Chao, J.-I.; Lin, H.-K. K63-linked ubiquitination in kinase activation and cancer. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Truong, V.-L.; Ko, S.-Y.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.-S. Quercitrin from Toona sinensis (Juss.) M.Roem. attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver toxicity in HepG2 cells and mice through induction of antioxidant machinery and inhibition of inflammation. Nutrients 2016, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devi, K.P.; Malar, D.S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Xiao, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M. Kaempferol and inflammation: From chemistry to medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Sabir, S.; Ahmed, S.; Boligon, A.; Linde Athayde, M.; Jabbar, A.; Qamar, I.; Khan, A. Antioxidant activities and phenolic composition of olive (Olea europaea) leaves. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2015, 88, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín, M.A.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Quercetin modulates NF-κ B and AP-1/JNK pathways to induce cell death in human hepatoma cells. Nutr Cancer 2010, 62, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Ye, J.; Xia, Z.; Cheng, B. Effect of luteolin on apoptosis, MAPK and JNK signaling pathways in guinea pig chondrocyte with osteoarthritis. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Aisa, H.A. Luteolin induces apoptosis in vitro through suppressing the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.H.; Song, C.; Shin, K.K.; Choi, E.; Hwang, S.H.; Jang, Y.J.; Taamalli, A.; Yum, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.; et al. Tunisian Olea europaea L. leaf extract suppresses Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Yoon, K.Y.; Lee, O.H.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, B.Y. Oleuropein suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cell and zebrafish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, M.; Park, S.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Rhee, M.H. Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-kappaB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1452–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Sun, C.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Khan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liang, G.; et al. Kaempferol reduces K63-linked polyubiquitination to inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB and inflammatory responses in acute lung injury in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 306, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, Y. Overexpression of miR-146b-5p Ameliorates neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy by inhibiting IRAK1/TRAF6/TAK1/NF-alphaB signaling. Yonsei Med. J. 2020, 61, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, H.B.; Wu, X.P.; Guo, Y.L.; Cheng, W.D.; Qian, F. Fisetin alleviates sepsis-induced multiple organ dysfunction in mice via inhibiting p38 MAPK/MK2 signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Guo, Y.; Ping, L.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Protective effects of SIRT6 overexpression against DSS-induced colitis in mice. Cells 2020, 9, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Z.; Cao, S.; Niu, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Pan, H.; Hu, J.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific TAK1 deficiency drives RIPK1 kinase-dependent inflammation to promote liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14231–14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, M.J.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. MAPK/AP-1-targeted anti-inflammatory activities of Xanthium strumarium. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakis, G.; Timbrell, J.A. In Vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 160, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y. AKT1-targeted proapoptotic activity of compound K in human breast cancer cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S.; Grisham, M.B. Methods to detect nitric oxide and its metabolites in biological samples. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolan, T.; Hands, R.E.; Bustin, S.A. Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1559–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, H.G.; Cho, J.Y. Gastroprotective effects of the nonsaponin fraction of Korean Red Ginseng through cyclooxygenase-1 upregulation. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Syk and Src-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of aripiprazole, an atypical antipsychotic. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, W.S.; Yu, T.; Yi, Y.-S.; Park, J.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.S.; Yoon, K.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Novel anti-inflammatory function of NSC95397 by the suppression of multiple kinases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yang, W.S.; Yi, Y.-S.; Sung, G.-H.; Rhee, M.H.; Poo, H.; Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. AP-1/IRF-3 targeted anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide isolated from Andrographis paniculata. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaw, J.; Leveridge, M.; Norling, C.; Karén, J.; Molina, D.M.; O’Neill, D.; Dowling, J.E.; Davey, P.; Cowan, S.; Dabrowski, M.; et al. Determining direct binders of the androgen receptor using a high-throughput cellular thermal shift assay. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Name | Direction | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-2 | Forward | GTGCTCCTTGTCACCAGCGC |
| Reverse | GAGCCTTATGTGTTGTAAGC | |
| MMP-9 | Forward | TCTTCCCCAAAGACCTGAAA |
| Reverse | TGATGTTATGATGGTCCCAC | |
| COX-2 | Forward | GGGAGTCTGGAACATTGTGAA |
| Reverse | GCACATTGTAAGTAGGTGGACTGT | |
| MCP-1 | Forward | ACTGAAGCCAGCTCTCTCTT |
| Reverse | ACGGGTCAACTTCACATTCA | |
| ICAM1 | Forward | CAGATGCCGACCCAGGAGAG |
| Reverse | ACAGACTTCACCACCCCGAT | |
| GAPDH | Forward | CAATGAATACGGCTACAGCAAC |
| Reverse | AGGGAGATGCTCAGTGTTGG | |
| Primers Sequences Used in Real-Time PCR | ||
| COX-2 | Forward | CCAGCACTTCACGCATCAGT |
| Reverse | ACGCTGTCTAGCCAGAGTTTCAC | |
| TNF-α | Forward | TGCCTATGTCTCAGCCTCTT |
| Reverse | GAGGCCATTTGGGAACTTCT | |
| IL-6 | Forward | GCTGGAGTCACAGAAGGAGTGGC |
| Reverse | GGCATAACGCACTAGGTTTGCGC | |
| GAPDH | Forward | AGGGAGATGCTCAGTGTTGG |
| Reverse | CAATGAATACGGCTACAGCA | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, C.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Olea europaea Suppresses Inflammation by Targeting TAK1-Mediated MAP Kinase Activation. Molecules 2021, 26, 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061540
Song C, Kim M-Y, Cho JY. Olea europaea Suppresses Inflammation by Targeting TAK1-Mediated MAP Kinase Activation. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061540
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Chaoran, Mi-Yeon Kim, and Jae Youl Cho. 2021. "Olea europaea Suppresses Inflammation by Targeting TAK1-Mediated MAP Kinase Activation" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061540
APA StyleSong, C., Kim, M.-Y., & Cho, J. Y. (2021). Olea europaea Suppresses Inflammation by Targeting TAK1-Mediated MAP Kinase Activation. Molecules, 26(6), 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061540







