Correlations of Fat Content in Human Milk with Fat Droplet Size and Phospholipid Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
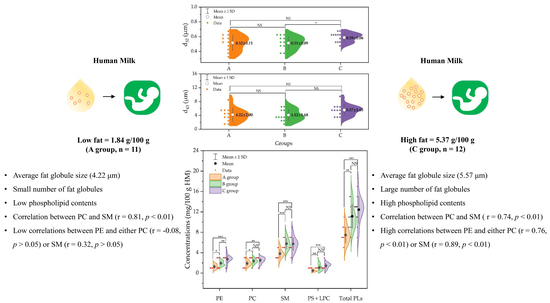
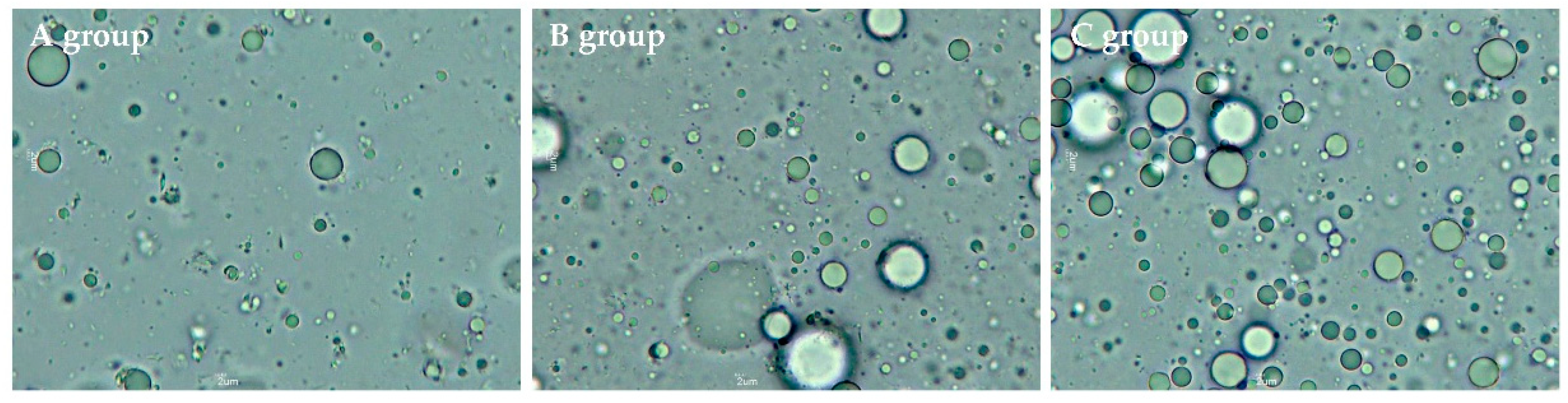
2.1. Fat Droplet Size Distribution and Diameter (d32, and d43)
2.2. Phospholipid Contents in Human Milk Samples
2.3. Correlations between Phospholipid Species
2.4. Feasibility Study of 31P NMR for Phospholipids Quantification in Human Milk
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Human Milk and Infant Formula Samples
4.3. Particle Size Analysis in Human Milk
4.4. Fat Extraction
4.5. Phospholipids Analysis
4.6. Phospholipids Analysis by 31P NMR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Keenan, T.W.; Patton, S. The Milk Lipid Globule Membrane. In Handbook of Milk Composition; Jensen, R.G., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 5–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte, M.; Bourlieu, C.; Meugnier, E.; Penhoat, A.; Cheillan, D.; Pineau, G.; Loizon, E.; Trauchessec, M.; Claude, M.; Ménard, O.; et al. Milk polar lipids affect in vitro digestive lipolysis and postprandial lipid metabolism in mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1770–1777. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/145/8/1770/4644397 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, M.; Lönnerdal, B.; Hernell, O. Supplementation of infant formula with bovine milk fat globule membranes. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 351–355. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/advances/article/8/2/351/4558143 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deeth, H.C. The role of phospholipids in the stability of milk fat globules. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1997, 52, 44–46. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hilton_Deeth/publication/37625999_The_role_of_phospholipids_in_the_stability_of_milk_fat_globules/links/004635252d9b22e2fc000000/The-role-of-phospholipids-in-the-stability-of-milk-fat-globules.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Cohn, J.S.; Wat, E.; Kamili, A.; Tandy, S. Dietary phospholipids, hepatic lipid metabolism and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2008, 19, 257–262. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/co-lipidology/FullText/2008/06000/Dietary_phospholipids,_hepatic_lipid_metabolism.7.aspx (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, K.; Sekihara, K.; Sugano, M. Hypocholesterolemic action of dietary phosphatidylethanolamine in rats sensitive to exogenous cholesterol. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1991, 2, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Huang, B.X.; Spector, A.A. Phosphatidylserine in the brain: Metabolism and function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 56, 1–18. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0163782714000289 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, G.F. Sphingolipids in inflammation: Pathological implications and potential therapeutic targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 982–993. Available online: https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00281.x (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckhardt, E.R.; Wang, D.Q.H.; Donovan, J.M.; Carey, M.C. Dietary sphingomyelin suppresses intestinal cholesterol absorption by decreasing thermodynamic activity of cholesterol monomers. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 948–956. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016508502015573 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Wang, M.; Lai, J.; Wang, X. Phospholipid Composition and Fat Globule Structure I: Comparison of Human Milk Fat from Different Gestational Ages, Lactation Stages, and Infant Formulas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13922–13928. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04247 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; MacGibbon, A.K.; Mohamed, H.J.B.J.; Loy, S.; Rowan, A.; McJarrow, P.; Fong, B.Y. Determination of phospholipid concentrations in breast milk and serum using a high performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry–multiple reaction monitoring method. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 71, 50–59. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0958694617300572 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Claumarchirant, L.; Cilla, A.; Matencio, E.; Sanchez-Siles, L.M.; Castro-Gomez, P.; Fontecha, J.; Alegría, A.; Lagarda, M.J. Addition of milk fat globule membrane as an ingredient of infant formulas for resembling the polar lipids of human milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 228–238. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0958694616301765 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakkar, S.K.; Giuffrida, F.; Cristina, C.H.; De Castro, C.A.; Mukherjee, R.; Tran, L.A.; Steenhout, P.; Lee, L.Y.; Destaillats, F. Dynamics of human milk nutrient composition of mothers from Singapore with a special focus on lipids. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2013, 25, 770–779. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ajhb.22446 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, F.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Flück, B.; Tavazzi, I.; Thakkar, S.K.; Destaillats, F.; Braun, M. Quantification of phospholipids classes in human milk. Lipids 2013, 48, 1051–1058. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11745-013-3825-z (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.Q.; Guo, Z.; Huang, J.H.; Jin, Q.Z.; Cheong, L.Z.; Wang, X.G.; Xu, X.B. Human milk fat globules from different stages of lactation: A lipid composition analysis and microstructure characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7158–7167. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf3013597 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitman, J.; Wood, D.L.; Mehta, N.R.; Hamosh, P.; Hamosh, M. Comparison of the phospholipid composition of breast milk from mothers of term and preterm infants during lactation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Nishida, Y.; Taki, M.; Murase, M.; Mukai, Y.; Itabashi, K.; Debari, K.; Iiyama, A. Is increased fat content of hindmilk due to the size or the number of milk fat globules? Int. Breastfeed. J. 2009, 4, 1–6. Available online: https://internationalbreastfeedingjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1746-4358-4-7 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiking, L.; Stagsted, J.; Björck, L.; Nielsen, J.H. Milk fat globule size is affected by fat production in dairy cows. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 909–913. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0958694604000780 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.G.; Libong, D.; Rakotomanga, M.; Gaudin, K.; Loiseau, P.M.; Chaminade, P. Comparison between charged aerosol detection and light scattering detection for the analysis of Leishmania membrane phospholipids. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1209, 88–94. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021967308012776 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alltech Associates, Phospholipids, Application Note #0024E; Alltech Associates, Inc.: Deerfield, IL, USA, 2020; pp. 60015–61899. Available online: http://www.dongmyung.co.kr/appl/0024E.pdf. (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Ji, S.; Zhang, F.; Wu, S.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. Facile preparation of polyvinyl alcohol coated SiO2 stationary phases for high performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 2014, 139, 5594–5599. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265137988_Facile_preparation_of_polyvinyl_alcohol_coated_SiO2_stationary_phases_for_high_performance_liquid_chromatography (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Fondaco, D.; AlHasawi, F.; Lan, Y.; Ben-Elazar, S.; Connolly, K.; Rogers, M.A. Biophysical aspects of lipid digestion in human breast milk and Similac™ infant formulas. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 282–291. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11483-014-9388-6 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.C.; Briard, V.; Michel, F.; Tasson, F.; Poulain, P. Size distribution of fat globules in human colostrum, breast milk, and infant formula. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 1927–1940. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002203020572868X (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernell, O.; Olivecrona, T. Human milk lipases II. Bile salt-stimulated lipase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Metab. 1974, 369, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, B.; Fauquant, C.; Daira, P.; Peretti, N.; Guichardant, M.; Michalski, M.C. Phospholipid species and minor sterols in French human milks. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 684–691. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814609012552 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Ménard, O. Human milk fat globules: Polar lipid composition and in situ structural investigations revealing the heterogeneous distribution of proteins and the lateral segregation of sphingomyelin in the biological membrane. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 29–41. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776510006041 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala-Vila, A.; Castellote, A.I.; Rodriguez-Palmero, M.; Campoy, C.; López-Sabater, M.C. Lipid composition in human breast milk from Granada (Spain): Changes during lactation. Nutrition 2005, 21, 467–473. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899900705000201 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilla, A.; Diego Quintaes, K.; Barberá, R.; Alegría, A. Phospholipids in human milk and infant formulas: Benefits and needs for correct infant nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Briard-Bion, V.; Ménard, O.; Beaucher, E.; Rousseau, F.; Fauquant, J.; Leconte, N.; Robert, B. Fat globules selected from whole milk according to their size: Different compositions and structure of the biomembrane, revealing sphingomyelin-rich domains. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 355–368. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814610010733 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Bickert, A.; Ginkel, C.; Kol, M.; Vom Dorp, K.; Jastrow, H.; Degen, J.; Jacobs, R.L.; Vance, D.E.; Winterhager, E.; Jiang, X.C.; et al. Functional characterization of enzymes catalyzing ceramide phosphoethanolamine biosynthesis in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 821–835. Available online: https://www.jlr.org/content/56/4/821.short (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis and transport in mammalian cells. Traffic 2015, 16, 1–18. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/tra.12230 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppler, C.M.; Malewicz, B.; Jenkin, H.M.; Baumann, W.J. Phosphatidylcholine as the choline donor in sphingomyelin synthesis. Lipids 1987, 22, 351–357. Available online: https://aocs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1007/BF02534005 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 11th ed.; Ross, A.C., Caballero, B., Cousins, R.J., Tucker, K.L., Ziegler, T.R., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2014; pp. 416–426. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Database for the Choline Content of Common Foods, Release 2; Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://data.nal.usda.gov/dataset/usda-database-choline-content-common-foods-release-2-2008 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Duan, B.; Shin, J.A.; Qin, Y.; Kwon, J.I.; Lee, K.T. A Study on the Relationship of Fat Content in Human Milk on Carotenoids Content and Fatty Acid Compositions in Korea. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2072. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/9/2072 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Kang, S.; Jung, B.M.; Yi, H.; Jung, J.A.; Chang, N. Breast milk fatty acid composition and fatty acid intake of lactating mothers in South Korea. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 556–561. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/breast-milk-fatty-acid-composition-and-fatty-acid-intake-of-lactating-mothers-in-south-korea/FD4676247E0D4AF5C680037E9E406D25 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacKenzie, A.; Vyssotski, M.; Nekrasov, E. Quantitative analysis of dairy phospholipids by 31P NMR. J. Am. Oil Chem Soc. 2009, 86, 757–763. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?q=Quantitative+analysis+of+dairy+phospholipids+by+31P+NMR&hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0,5 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Helmerich, G.; Koehler, P. Comparison of methods for the quantitative determination of phospholipids in lecithins and flour improvers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6645–6651. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf0345088 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Roy, R. Quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2012, 35, 5–26. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165993612000702 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Lanier, K.L.; Moore, J.D.; Smith, D.; Li, S.; Davis, B.; Shaw, W.A. Quantitative Phospholipid Analysis of Soy Lecithin and Krill Lecithin by 31P NMR. 2008. Available online: http://www.avantilipids.com/images/Analytical/AvantiPhospholipidAnalysis-AnalyticalServices.pdf. (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Puppato, A.; DuPré, D.B.; Stolowich, N.; Yappert, M.C. Effect of temperature and pH on 31P nuclear magnetic resonances of phospholipids in cholate micelles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 150, 176–185. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009308407004094 (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=A+simple+method+for+the+isolation+and+purification+of+total+lipides+from+animal+tissues&btnG= (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Shin, J.A.; Hong, S.T.; Park, S.H.; Lee, K.T. Emulsifying properties of lecithin containing different fatty acids obtained by immobilized Lecitase Ultra-catalyzed reaction. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 579–590. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Emulsifying+properties+of+lecithin+containing+different+fatty+acids+obtained+by+immobilized+Lecitase+Ultra-catalyzed+reaction&btnG= (accessed on 20 January 2021). [CrossRef]






| Total Mature Milk 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL species 2 | mg/100 g HM | Range | mg/g fat | Range | % of total PLs 3 | Range |
| PE | 2.00 ± 0.84 | 0.68–4.21 | 0.52 ± 0.21 | 0.24–1.16 | 18.89 ± 3.93 | 9.21–24.42 |
| PC | 2.26 ± 0.55 | 1.13–3.14 | 0.64 ± 0.30 | 0.30–1.46 | 22.41 ± 3.83 | 17.38–32.04 |
| SM | 5.11 ± 1.42 | 2.35–8.32 | 1.35 ± 0.49 | 0.71–2.59 | 49.64 ± 3.90 | 40.64–56.15 |
| PS + LPC | 1.01 ± 0.62 | 0.20–2.19 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | 0.07–0.47 | 9.06 ± 3.75 | 3.34–17.78 |
| Total PLs | 10.39 ± 3.11 | 4.89–17.85 | 2.74 ± 0.94 | 1.39–5.45 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, B.; Hong, E.-S.; Shin, J.-A.; Qin, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Lee, K.-T. Correlations of Fat Content in Human Milk with Fat Droplet Size and Phospholipid Species. Molecules 2021, 26, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061596
Duan B, Hong E-S, Shin J-A, Qin Y, Lee J-H, Lee C-W, Lee K-T. Correlations of Fat Content in Human Milk with Fat Droplet Size and Phospholipid Species. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061596
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Beibei, Eun-Sik Hong, Jung-Ah Shin, Yan Qin, Jeung-Hee Lee, Chi-Woo Lee, and Ki-Teak Lee. 2021. "Correlations of Fat Content in Human Milk with Fat Droplet Size and Phospholipid Species" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061596
APA StyleDuan, B., Hong, E.-S., Shin, J.-A., Qin, Y., Lee, J.-H., Lee, C.-W., & Lee, K.-T. (2021). Correlations of Fat Content in Human Milk with Fat Droplet Size and Phospholipid Species. Molecules, 26(6), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061596