Assessing the Molecular Targets and Mode of Action of Furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
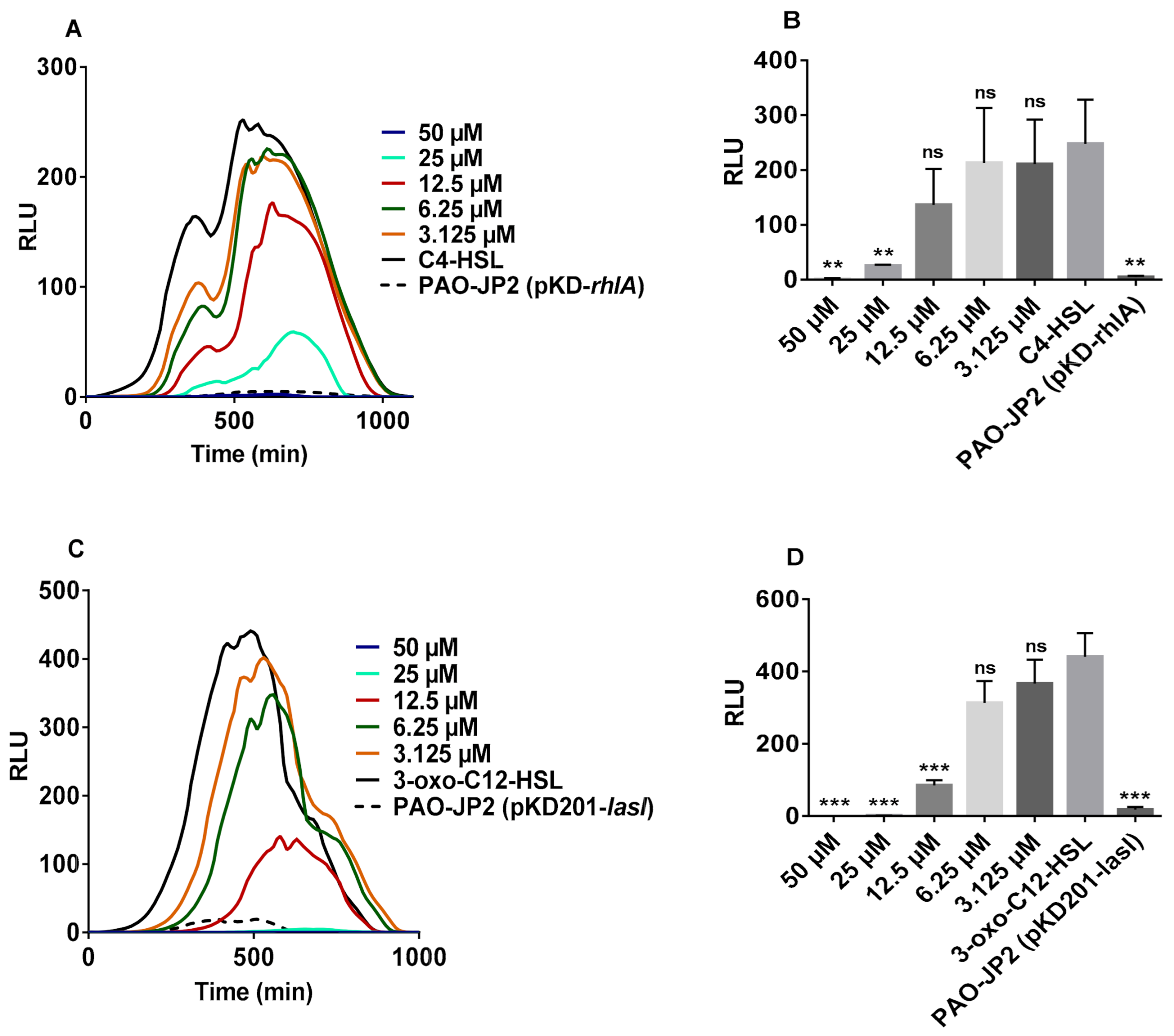
2.1. Induction of Bioluminescence
2.2. Inhibitory Actions of Furanone C-30 on RhlR and LasR
2.3. Swarming Motility Assay
2.4. Effect of Furanone C-30 on LasR Solubility
2.5. Prediction of Protein–Ligand Binding
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
4.3. Strain Cultivation
4.4. Induction of Bioluminescence
4.5. Bioluminescence Assay
4.6. Protein Expression and Purification
4.7. SDS–PAGE Analysis
4.8. Swarming Motility Assay
4.9. Computational Analyses
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Reichelt, J.L.; Borowitzka, M.A. Antimicrobial activity from marine algae: Results of a large-scale screening programme. Hydrobiologia 1984, 116, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nys, R.; Wright, A.D.; Konig, G.M.; Sticher, O. New halogenated furanones from the marine alga delisea pulchra (cf. fimbriata). Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 11213–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nys, R.; Steinberg, P.D.; Willemsen, P.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Gabelish, C.L.; King, R.J. Broad spectrum effects of secondary metabolites from the red alga Delisea pulchrain antifouling assays. Biofouling 1995, 8, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximilien, R.; de Nys, R.; Holmström, C.; Gram, L.; Givskov, M.; Crass, K.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P. Chemical mediation of bacterial surface colonisation by secondary metabolites from the red alga Delisea pulchra. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 15, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P.; Givskov, M.C.; Gram, L.; Manefield, M.; de Nys, R. Do marine natural products interfere with prokaryotic AHL regulatory systems? Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 13, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manefield, M.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Henzter, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Givskov, M. Halogenated furanones inhibit quorum sensing through accelerated LuxR turnover. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Kim, J.; Park, H.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.K.; Yoon, J. Furanone derivatives as quorum-sensing antagonists of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 80, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givskov, M.; de Nys, R.; Manefield, M.; Gram, L.; Maximilien, R.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Steinberg, P.D.; Kjelleberg, S. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gram, L.; Denys, R.; Maximilien, R.; Givskov, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelle-berg, S. Inhibitory effects of secondary metabolites from the red alga Delisea pulchra on swarming motility of Proteus mirabilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4284–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manefield, M.; de Nys, R.; Naresh, K.; Roger, R.; Givskov, M.; Peter, S.; Kjelleberg, S. Evidence that halogenated furanones from Delisea pulchra inhibit acylated homoserine lactone (AHL)-mediated gene expression by displacing the AHL signal from its receptor protein. Microbiology 1999, 145, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defoirdt, T.; Miyamoto, C.M.; Wood, T.K.; Meighen, E.A.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. The natural furanone (5Z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-butyl-2(5H)-furanone disrupts quorum sensing-regulated gene expression in Vibrio harveyi by decreasing the DNA-binding activity of the transcriptional regulator protein luxR. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, B.; Liljefors, T.; Persson, T.; Nielsen, J.; Kjelleberg, S.; Givskov, M. The LuxR receptor: The sites of interaction with quorum-sensing signals and inhibitors. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3589–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.D.; Rossi, F.M.; Welsh, M.A.; Nyffeler, K.E.; Blackwell, H.E. A Comparative Analysis of Synthetic Quorum Sensing Modulators in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New Insights into Mechanism, Active Efflux Susceptibility, Phenotypic Response, and Next-Generation Ligand Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14626–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Eberl, L.; Nielsen, J.; Givskov, M. Quorum Sensing: A Novel Target for the Treatment of Biofilm Infections. Biodrugs 2003, 17, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum-sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Heydorn, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Parsek, M.R.; Rice, S.A.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendelson, M.H.; Gurtman, A.; Szabo, S.; Neibart, E.; Meyers, B.R.; Policar, M.; Cheung, T.W.; Lillienfeld, D.; Hammer, G.; Reddy, S.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteraemia in patients with AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergie, J.E.; Shema, S.J.; Lott, L.; Crawford, R.; Patrick, C.C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteraemia in immunocompromised children: Analysis of factors associated with a poor outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltner, J.B.; Wolter, D.J.; Pope, C.E.; Groleau, M.C.; Smalley, N.E.; Greenberg, E.P.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Burns, J.; Deziel, E.; Hoffman, L.R.; et al. LasR variant cystic fibrosis isolates reveal an adaptable quorum-sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2016, 7, e01513-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stryjewski, M.E.; Sexton, D.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections in Specific Types of Patients and Clinical Settings. In Severe Infections Caused by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa; Hauser, A.R., Rello, J., Eds.; Perspectives on Critical Care Infectious Diseases; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 7, pp. 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.S.; Harris, S.G.; Phipps, R.; Iglewski, B. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Molecule N-(3-Oxododecanoyl) Homoserine Lactone Contributes to Virulence and Induces Inflammation In Vivo. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tateda, K.; Ishii, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Miyairi, S.; Pechere, J.C.; Standiford, T.J.; Ishiguro, M.; Yamaguchi, K. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer N-3-oxododecanoyl homoserine lactone accelerates apoptosis in macrophages and neutrophils. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 5785–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.S.; Iglewski, B.H.P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems, and virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Klementiev, A.D.; Whiteley, M.; Diggle, S.P. Bacterial Quorum Sensing During Infection. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Payne, G.F.; Bentley, W.E. Quorum Sensing Communication: Molecularly Connecting Cells, Their Neighbors, and Even Devices. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2020, 11, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, W.R.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; Bowden, D.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: Small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 28–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Lostroh, C.P.; Ogi, T.; Greenberg, E.P. Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: A transcriptome analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visick, L.K.; Fuqua, C. Decoding Microbial Chatter: Cell-Cell Communication in Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5507–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, V.E.; Bushnell, D.; Passador, L.; Brooks, A.I.; Iglewski, B.H. Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing regulons: Effects of growth phase and environment. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Kievit, T.R.; Iglewski, B.H. Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4839–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.E.; Buckley, D.G.; Wu, Z.; Saenphimmachak, C.; Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; Miller, S.I.; Ramsey, B.W.; Speert, D.P.; Moskowitz, S.M.; et al. Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Argenio, D.A.; Wu, M.; Hoffman, L.R.; Kulasekara, H.D.; Déziel, E.; Smith, E.E.; Nguyen, H.; Ernst, R.K.; Larson Freeman, T.J.; Spencer, D.H.; et al. Growth phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutants adapted to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Kulasekara, H.D.; Emerson, J.; Houston, L.S.; Burns, J.L.; Ramsey, B.W.; Miller, S.I. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutants are associated with cystic fibrosis lung disease progression. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2009, 8, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Rao, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Characterization of lasR-deficient clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, R.L.; Asfahl, K.L.; Van den Bossche, S.; Coenye, T.; Crabbé, A.; Dandekar, A.A. RhlR-Regulated Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Quorum Sensing in a Cystic Fibrosis Isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2020, 11, e00532-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, E.; González-Valdez, A.; Servín-González, L.; Soberón-Chávez, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing response in the absence of functional LasR and LasI proteins: The case of strain 148, a virulent dolphin isolate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Aceves, M.P.; Cocotl-Yañez, M.; Servín-González, L.; Soberón-Chávez, G. The Rhl Quorum-Sensing System Is at the Top of the Regulatory Hierarchy under Phosphate-Limiting Conditions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e00475-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, J.A.; Carty, N.L.; McDonald, N.A.; Graham, E.D.; Cheluvappa, R.; Griswold, J.A.; Hamood, A.N. Analysis of quorum sensing-deficient clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tingpej, P.; Smith, L.; Rose, B.; Zhu, H.; Conibear, T.; Al Nassafi, K.; Manos, J.; Elkins, M.; Bye, P.; Willcox, M.; et al. Phenotypic characterization of clonal and nonclonal Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from lungs of adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bukelman, O.; Amara, N.; Mashiach, R.; Krief, P.; Meijler, M.M.; Alfonta, L. Electrochemical Studies of Biofilm Formation and Inhibition. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2836–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, N.; Mashiach, R.; Amar, D.; Krief, P.; Spieser, S.A.; Bottomley, M.J.; Aharoni, A.; Meijler, M.M. Covalent inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10610–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottomley, M.J.; Muraglia, E.; Bazzo, R.; Carfì, A. Molecular insights into quorum sensing in the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the structure of the virulence regulator LasR bound to its autoinducer. J. Biol Chem. 2007, 282, 13592–13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, K.M.; Garey, J.R. The evolution of bacterial LuxI and LuxR quorum sensing regulators. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerat, E.; Moran, N.A. The evolutionary history of quorum-sensing systems in bacteria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, Y.; Nguyen, N.X.; Rogers, J.L.; Liao, J.; MacMillan, J.B.; Jiang, Y.; Sperandio, V. Structural and mechanistic roles of novel chemical ligands on the SdiA quorum-sensing transcription regulator. mBio 2015, 6, e02429-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; García-Contreras, R.; Pu, M.; Sheng, L.; Garcia, L.R.; Tomás, M.; Wood, T.K. Quorum quenching quandary: Resistance to antivirulence compounds. ISME J. 2012, 6, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O'May, C.; Tufenkji, N. The swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is blocked by cranberry proanthocyanidins and other tannin-containing materials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, T.; Curty, L.K.; Barja, F.; van Delden, C.; Pechère, J.C. Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on cell-to-cell signaling and requires flagella and pili. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5990–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blus-Kadosh, I.; Zilka, A.; Yerushalmi, G.; Banin, E. The Effect of pstS and phoB on Quorum Sensing and Swarming Motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eibergen, N.R.; Moore, J.D.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Potent and Selective Modulation of the RhlR Quorum Sensing Receptor by Using Non-native Ligands: An Emerging Target for Virulence Control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dekimpe, V.; Déziel, E. Revisiting the quorum-sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The transcriptional regulator RhlR regulates LasR-specific factors. Microbiology 2009, 155, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, L.D.; van Gennip, M.; Jakobsen, T.H.; Alhede, M.; Hougen, H.P.; Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M. Synergistic antibacterial efficacy of early combination treatment with tobramycin and quorum-sensing inhibitors against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an intraperitoneal foreign-body infection mouse model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Loughlin, C.T.; Miller, L.C.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paczkowski, J.E.; Mukherjee, S.; McCready, A.R.; Cong, J.P.; Aquino, C.J.; Kim, H.; Henke, B.R.; Smith, C.D.; Bassler, B.L. Flavonoids Suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence through Allosteric Inhibition of Quorum-sensing Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4064–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssens, J.C.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.; De Vos, D.E.; Vanderleyden, J. Small molecules for interference with cell-cell-communication systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 2144–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, K.; Eltzov, E.; Shnit-Orland, M.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A. Characterization of quorum sensing signals in coral-associated bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, K.; Golberg, K.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Marks, R.; Pushkarev, A.; Béjà, O.; Kushmaro, A. Functional marine metagenomic screening for anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity. Biofouling 2017, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skindersoe, M.E.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; de Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Phipps, R.K.; Christensen, K.B.; Jensen, P.O.; Andersen, J.B.; Koch, B.; Larsen, T.O.; Hentzer, M.; et al. Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerdt, J.P.; McInnis, C.E.; Schell, T.L.; Rossi, F.M.; Blackwell, H.E. Mutational analysis of the quorum-sensing receptor LasR reveals interactions that govern activation and inhibition by nonlactone ligands. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahumedo Monterrosa, M.; Galindo, J.F.; Vergara Lorduy, J.; Alí-Torres, J.; Vivas-Reyes, R. The role of LasR active site amino acids in the interaction with the Acyl Homoserine Lactones (AHLs) analogues: A computational study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2019, 86, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, M.C.; Dong, S.H.; Rossi, F.M.; Karlen, K.M.; Kumar, R.S.; Nair, S.K.; Blackwell, H.E. Structural and Biochemical Studies of Non-native Agonists of the LasR Quorum-Sensing Receptor Reveal an L3 Loop “Out” Conformation for LasR. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 1128–1139.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Nair, S.K. Molecular Basis for the Recognition of Structurally Distinct Autoinducer Mimics by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR Quorum-Sensing Signaling Receptor. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCready, A.R.; Paczkowski, J.E.; Henke, B.R.; Bassler, B.L. Structural determinants driving homoserine lactone ligand selection in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR quorum-sensing receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pomianek, M.E.; Semmelhack, M.F. Making bacteria behave: New agonists and antagonists of quorum sensing. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.M.; Bu, Y.; Suga, H. Induction and inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by synthetic autoinducer analogs. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McInnis, C.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of abiotic, non-lactone modulators of LuxR-type quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4812–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodgkinson, J.T.; Galloway, W.R.; Wright, M.; Mati, I.K.; Nicholson, R.L.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of non-natural modulators of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 6032–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellhammer, I.; Rarey, M. TrixX: Structure-based molecule indexing for large-scale virtual screening in sublinear time. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzler, A.M.; Urbaczek, S.; Hilbig, M.; Rarey, M. An integrated approach to knowledge-driven structure-based virtual screening. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2014, 28, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachsenberg, F.; Meyder, A.; Sommer, K.; Penner, P.; Rarey, M. A Consistent Scheme for Gradient-Based Optimization of Protein-Ligand Poses. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 6502–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volkamer, A.; Griewel, A.; Grombacher, T.; Rarey, M. Analyzing the topology of active sites: On the prediction of pockets and subpockets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markus, V.; Golberg, K.; Teralı, K.; Ozer, N.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A. Assessing the Molecular Targets and Mode of Action of Furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing. Molecules 2021, 26, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061620
Markus V, Golberg K, Teralı K, Ozer N, Kramarsky-Winter E, Marks RS, Kushmaro A. Assessing the Molecular Targets and Mode of Action of Furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061620
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkus, Victor, Karina Golberg, Kerem Teralı, Nazmi Ozer, Esti Kramarsky-Winter, Robert S. Marks, and Ariel Kushmaro. 2021. "Assessing the Molecular Targets and Mode of Action of Furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061620
APA StyleMarkus, V., Golberg, K., Teralı, K., Ozer, N., Kramarsky-Winter, E., Marks, R. S., & Kushmaro, A. (2021). Assessing the Molecular Targets and Mode of Action of Furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing. Molecules, 26(6), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061620









