Retaining Skin Barrier Function Properties of the Stratum Corneum with Components of the Natural Moisturizing Factor—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind In Vivo Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. SC Thickness
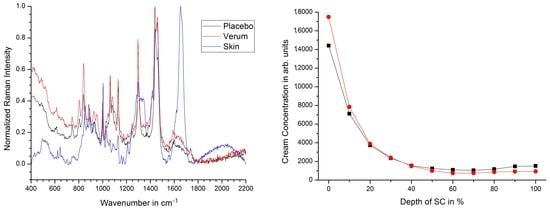
2.2. Penetration Depth
2.3. NMF Content
2.4. Lipids
2.4.1. Total Lipid Concentration
2.4.2. Lateral ICL Organization (Slat)
2.4.3. Lamellar ICL Organization (Sskeleton)
2.5. Water
2.5.1. Total Water Concentration
2.5.2. Tightly Bound Water
2.5.3. Strongly Bound Water
2.5.4. Weakly Bound Water
2.5.5. Unbound Water
2.6. Hydrogen Bonding State of Water Molecules
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Protocol
3.2. Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy (CRM)
3.3. Data Analysis
3.3.1. Penetration Depth and Content of Natural Moisturizing Factor (NMF)
3.3.2. Intercellular Lipids (ICL)
3.3.3. Water Concentration and Hydrogen Bonding State of Water
3.3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Rawlings, A.V.; Harding, C.R. Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.; Bouwstra, J. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. Stratum Corneum Barrier Function: Definitions and Broad Concepts. In Skin Barrier; Elias, P.M., Feingold, K.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, G.K.; Cleary, G.W.; Lane, M.E. The structure and function of the stratum corneum. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 435, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashtikar, M.; Matthäus, C.; Schmitt, M.; Krafft, C.; Fahr, A.; Popp, J. Non-invasive depth profile imaging of the stratum corneum using confocal Raman microscopy: First insights into the method. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.-M. The skin: An indispensable barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, D.; Uzunbajakava, N.E.; Varghese, B.; Santos, G.R.D.A.; Richters, R.J.; Van De Kerkhof, P.C.; Van Erp, P.E. Microspectroscopic Confocal Raman and Macroscopic Biophysical Measurements in the in vivo Assessment of the Skin Barrier: Perspective for Dermatology and Cosmetic Sciences. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, C.; Alonso, C.; Martí, M.; Manich, A.M.; Coderch, L.; Martí, M. Skin barrier modification with organic solvents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, M.; van Smeden, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Portale, G.; Caspers, P.J.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Kezic, S.; Wolterbeek, R.; et al. Increase in short-chain ceramides correlates with an altered lipid organization and decreased barrier function in atopic eczema patients. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doucet, J.; Potter, A.; Baltenneck, C.; Domanov, Y.A. Micron-scale assessment of molecular lipid organization in human stratum corneum using microprobe X-ray diffraction. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. A depth-dependent profile of the lipid conformation and lateral packing order of the stratum corneum in vivo measured using Raman microscopy. Analyst 2016, 141, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Dubbelaar, F.E.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M. The lipid organisation in the skin barrier. Acta Derm. Venereol. Suppl. (Stockh.) 2000, 208, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pilgram, G.S.; Pelt, A.M.E.-V.; Koerten, H.K.; Bouwstra, J.A. Electron Diffraction Provides New Information on Human Stratum Corneum Lipid Organization Studied in Relation to Depth and Temperature. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Lunter, D.J. Confocal Raman microspectroscopy as an alternative to differential scanning calorimetry to detect the impact of emulsifiers and formulations on stratum corneum lipid conformation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 121, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Kuno, H.; Kawai, M. Stratum Corneum Lipids Serve as a Bound-Water Modulator. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 96, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, V.; Pfeiffer, S.; Lanzendörfer, G.; Wenck, H.; Diembeck, W.; Gooris, G.S.; Proksch, E.; Bouwstra, J. Barrier Characteristics of Different Human Skin Types Investigated with X-ray Diffraction, Lipid Analysis, and Electron Microscopy Imaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berardesca, E.; Maibach, H.I. Transepidermal water loss and skin surface hydration in the non invasive assessment of stratum corneum function. Dermatosen Beruf und Umwelt. Occup. Environ. 1990, 38, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Grubauer, G.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. Transepidermal water loss: The signal for recovery of barrier structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 1989, 30, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskos, K.V.; Guy, R.H. Assessment of Skin Barrier Function Using Transepidermal Water Loss: Effect of Age. Pharm. Res. 1989, 6, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangia, A.; Patil, S.; Berner, B.; Boman, A.; Maibach, H. In vitro measurement of transepidermal water loss: A rapid alternative to tritiated water permeation for assessing skin barrier functions. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 170, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyumvuhore, R.; Tfayli, A.; Biniek, K.; Duplan, H.; Delalleau, A.; Manfait, M.; Dauskardt, R.; Baillet-Guffroy, A. The relationship between water loss, mechanical stress, and molecular structure of humanstratum corneum ex vivo. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrejš, P.; Pavlačková, J.; Janáčová, D.; Huťťa, M. Hydration and Barrier Properties of Emulsions with the Addition of Keratin Hydrolysate. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logger, J.G.M.; Olydam, J.I.; Woliner-van der Weg, W.; van Erp, P.E.J. Noninvasive Skin Barrier Assessment: Multiparametric Approach and Pilot Study. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gianeti, M.D.; Campos, P.M.B.G.M. Efficacy Evaluation of a Multifunctional Cosmetic Formulation: The Benefits of a Combination of Active Antioxidant Substances. Molecules 2014, 19, 18268–18282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Depth profiles of hydrogen bound water molecule types and their relation to lipid and protein interaction in the human stratum corneum in vivo. Analyst 2016, 141, 6329–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertz, P.W. Stratum corneum Lipids and Water. Exog. Dermatol. 2004, 3, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier-Sévrain, S.; Bonté, F. Skin hydration: A review on its molecular mechanisms. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2007, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, A.V.; Scott, I.R.; Harding, C.R.; Bowser, P.A. Stratum Corneum Moisturization at the Molecular Level. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 103, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, I.R.; Harding, C.R.; Barrett, J.G. Histidine-rich protein of the keratohyalin granules. Source of the free amino acids, urocanic acid and pyrrolidone carboxylic acid in the stratum corneum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1982, 719, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Topgaard, D.; Kocherbitov, V.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A.; Sparr, E. Stratum corneum hydration: Phase transformations and mobility in stratum corneum, extracted lipids and isolated corneocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 2647–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paquin, R.; Colomban, P. Nanomechanics of single keratin fibres: A Raman study of the α-helix →β-sheet transition and the effect of water. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Keratin-water-NMF interaction as a three layer model in the human stratum corneum using in vivo confocal Raman microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tfayli, A.; Jamal, D.; Vyumvuhore, R.; Manfait, M.; Baillet-Guffroy, A. Hydration effects on the barrier function of stratum corneum lipids: Raman analysis of ceramides 2, III and 5. Analyst 2013, 138, 6582–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fan, S.; Song, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhuang, P.; Zhang, Y. Desmoglein1 Deficiency Is a Potential Cause of Cutaneous Eruptions Induced by Shuanghuanglian Injection. Molecules 2018, 23, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, E.; Kang, Y.-G.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, J.K.; Hong, Y.D.; Park, W.-S.; Kim, D.; Kim, E.; Cho, J.Y. In Vitro Effects of Dehydrotrametenolic Acid on Skin Barrier Function. Molecules 2019, 24, 4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, T.; Qiao, W.; Yao, Q.; Wu, W.; Kaku, K. Treatment with Docosahexaenoic Acid Improves Epidermal Keratinocyte Differentiation and Ameliorates Inflammation in Human Keratinocytes and Reconstructed Human Epidermis Models. Molecules 2019, 24, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caspers, P.J.; Lucassen, G.W.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J. Automated depth-scanning confocal Raman microspectrometer for rapid in vivo determination of water concentration profiles in human skin. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2000, 31, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppes, S.A.; Kemperman, P.; Van Tilburg, I.; Calkoen-Kwa, F.; Engebretsen, K.A.; Puppels, G.J.; Caspers, P.J.; Kezic, S. Determination of natural moisturizing factors in the skin: Raman microspectroscopy versus HPLC. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, B.P.; Shirshin, E.A.; Schleusener, J.; Allenova, A.S.; Fadeev, V.V.; Darvin, M.E. Melanin distribution from the dermal–epidermal junction to the stratum corneum: Non-invasive in vivo assessment by fluorescence and Raman microspectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussin, J.; Groenink, H.W.W.; De Graaff, A.M.; Gooris, G.S.; Wiechers, J.W.; Van Aelst, A.C.; Bouwstra, J.A. Lipophilic and hydrophilic moisturizers show different actions on human skin as revealed by cryo scanning electron microscopy. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Choe, S.; Ri, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Stratum corneum occlusion induces water transformation towards lower bonding state: A molecular level in vivo study by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Age related depth profiles of human Stratum Corneum barrier-related molecular parameters by confocal Raman microscopy in vivo. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 172, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Analysis of Human and Porcine Skin in vivo/ex vivo for Penetration of Selected Oils by Confocal Raman Microscopy. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. In vivo confocal Raman microscopic determination of depth profiles of the stratum corneum lipid organization influenced by application of various oils. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 87, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verzeaux, L.; Vyumvuhore, R.; Boudier, D.; Le Guillou, M.; Bordes, S.; Essendoubi, M.; Manfait, M.; Closs, B. Atopic skin: In vivo Raman identification of global molecular signature, a comparative study with healthy skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, M.; Lefèvre, T.; Pouliot, R.; Auger, M.; Laroche, G. Using infrared and Raman microspectroscopies to compare ex vivo involved psoriatic skin with normal human skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 67004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Choe, S.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. A modification for the calculation of water depth profiles in oil-treated skin by in vivo confocal Raman microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e201960106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatas, G.N.; de Sterke, J.; Hauser, M.; von Stetten, O.; van der Pol, A. Lipid uptake and skin occlusion following topical application of oils on adult and infant skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 50, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-E.; Chae, E.; Balupuri, A.; Yoon, H.R.; Kang, N.S. Topological Water Network Analysis Around Amino Acids. Molecules 2019, 24, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bommannan, D.; Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Examination of Stratum Corneum Barrier Function In Vivo by Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 95, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.; Schleusener, J.; Knorr, F.; Kraft, M.; Thiede, G.; Richter, H.; Darvin, M.E.; Schanzer, S.; Gallinger, S.; Wegener, U.; et al. Influence of polyester spacer fabric, cotton, chloroprene rubber, and silicone on microclimatic and morphologic physiologic skin parameters in vivo. Ski. Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visscher, M.O.; Tolia, G.T.; Wickett, R.R.; Hoath, S.B. Effect of soaking and natural moisturizing factor on stratum corneum water-handling properties. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2003, 54, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Caspers, P.J.; Lucassen, G.W.; Wolthuis, R.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J. In vitro andin vivo Raman spectroscopy of human skin. Biospectroscopy 1998, 4, S31–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitaev, N.A.; Troyanovsky, S.M. Direct Ca2+-dependent Heterophilic Interaction between Desmosomal Cadherins, Desmoglein and Desmocollin, Contributes to Cell–Cell Adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 138, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celli, A.; Crumrine, D.; Meyer, J.M.; Mauro, T.M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Regulates Epidermal Barrier Response and Desmosomal Structure. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanno, O.; Ota, Y.; Kitamura, N.; Katsube, T.; Inoue, S. Nicotinamide increases biosynthesis of ceramides as well as other stratum corneum lipids to improve the epidermal permeability barrier. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 143, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, Y.; Taira, N.; Tsuboi, T.; Yoshioka, M.; Masaki, H.; Muraoka, O. 3- O -Laurylglyceryl ascorbate reinforces skin barrier function through not only the reduction of oxidative stress but also the activation of ceramide synthesis. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 39, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Zeng, H.; Gu, L.; Maeda, K. Water-Soluble Organic Germanium Promotes Both Cornified Cell Envelope Formation and Ceramide Synthesis in Cultured Keratinocytes. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Human skin in vivo has a higher skin barrier function than porcine skin ex vivo-comprehensive Raman microscopic study of the stratum corneum. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, T.B. The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Arch Dermatol. 1988, 124, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspers, P.J.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J.; Lucassen, G.W.; Carter, E.A. In Vivo Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy of the Skin: Noninvasive Determination of Molecular Concentration Profiles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Choe, C.-S.; Ahlberg, S.; Meinke, M.C.; Alexiev, U.; Lademann, J.M.; Darvin, M.E. Penetration of silver nanoparticles into porcine skinex vivousing fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy, Raman microscopy, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 20, 051006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lui, H.; McLean, D.I.; Zeng, H. Automated Autofluorescence Background Subtraction Algorithm for Biomedical Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascencio, S.M.; Choe, C.; Meinke, M.C.; Müller, R.H.; Maksimov, G.V.; Wigger-Alberti, W.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Confocal Raman microscopy and multivariate statistical analysis for determination of different penetration abilities of caffeine and propylene glycol applied simultaneously in a mixture on porcine skin ex vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 104, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleusener, J.; Carrer, V.; Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Surface determination of 3D confocal Raman microscopy imaging of the skin. Laser Phys. Lett. 2017, 14, 125601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Choe, S.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Modified normalization method in in vivo stratum corneum analysis using confocal Raman microscopy to compensate nonhomogeneous distribution of keratin. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, M.; Hirao, T.; Takahashi, M. In vivo Estimation of Stratum Corneum Thickness from Water Concentration Profiles Obtained with Raman Spectroscopy. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2007, 87, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ri, J.S.; Choe, S.H.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Choe, C.S.; Darvin, M.E. In vivo Tracking of DNA for Precise Determination of the Stratum Corneum Thickness and Superficial Microbiome Using Confocal Raman Microscopy. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 33, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrhauser, D.-S.; Nagelreiter, C.; Gehrig, S.; Geyer, A.; Ogris, M.; Kwizda, K.; Valenta, C. Assessment of Raman spectroscopy as a fast and non-invasive method for total stratum corneum thickness determination of pig skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, J.; Sieg, A.; Blenkiron, P.; Marcott, C.; Matts, P.; Kaczvinsky, J.; Rawlings, A. Measuring the effects of topical moisturizers on changes in stratum corneum thickness, water gradients and hydrationin vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyumvuhore, R.; Tfayli, A.; Duplan, H.; Delalleau, A.; Manfait, M.; Baillet-Guffroy, A. Raman spectroscopy: A tool for biomechanical characterization of Stratum Corneum. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q. Local statistical interpretation for water structure. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 568–569, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Qin, C. Raman OH stretching band of water as an internal standard to determine carbonate concentrations. Chem. Geol. 2011, 283, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



 /
/  —more or less ordered lateral structure of ICL in the SC.
—more or less ordered lateral structure of ICL in the SC.
 /
/  —more or less ordered lateral structure of ICL in the SC.
—more or less ordered lateral structure of ICL in the SC.


| Center Position [cm−1] | Optimi-Zation Range [cm−1] | FWHM [cm−1] | Optimi-Zation Range [cm−1] | Band Association |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2850 | 2845–2855 | 20 | 16–24 | Symmetric CH vibration: lipids |
| 2880 | 2875–2885 | 37 | 32–42 | Asymmetric CH vibration: mostly lipids, also keratin |
| 2935 | 2930–2940 | 52 | 42–65 | Symmetric CH3 stretch vibrations: mostly keratin, also lipids |
| 2980 | 2975–2985 | 35 | 30–40 | Asymmetric CH3 stretch vibrations: keratin |
| 3015 | 3005–3020 | 30 | 20–50 | Tightly bound water |
| 3065 | 3020–3090 | 40 | 20–100 | CH stretch vibrations: olefin |
| 3225 | 3190–3242 | 220 | 120–265 | Strongly bound water |
| 3330 | 3310–3350 | 40 | 10–100 | NH vibration: keratin |
| 3451 | 3450–3515 | 200 | 150–240 | Weakly bound water |
| 3633 | 3602–3645 | 80 | 50–120 | Unbound water |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schleusener, J.; Salazar, A.; von Hagen, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Retaining Skin Barrier Function Properties of the Stratum Corneum with Components of the Natural Moisturizing Factor—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind In Vivo Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061649
Schleusener J, Salazar A, von Hagen J, Lademann J, Darvin ME. Retaining Skin Barrier Function Properties of the Stratum Corneum with Components of the Natural Moisturizing Factor—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind In Vivo Study. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061649
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchleusener, Johannes, Andrew Salazar, Jörg von Hagen, Jürgen Lademann, and Maxim E. Darvin. 2021. "Retaining Skin Barrier Function Properties of the Stratum Corneum with Components of the Natural Moisturizing Factor—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind In Vivo Study" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061649
APA StyleSchleusener, J., Salazar, A., von Hagen, J., Lademann, J., & Darvin, M. E. (2021). Retaining Skin Barrier Function Properties of the Stratum Corneum with Components of the Natural Moisturizing Factor—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind In Vivo Study. Molecules, 26(6), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061649