Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Cyperus Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
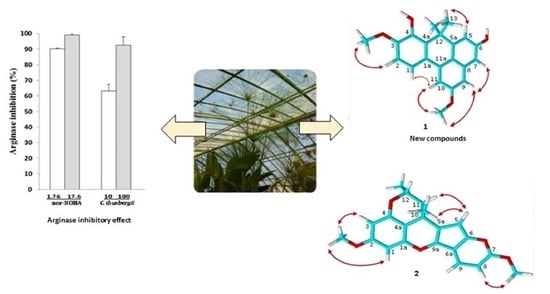
2.1. In Vitro Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Cyperus thunbergii and C. glomeratus
2.2. Ex Vivo C. thunbergii Improved Endothelial Dysfunction in Arthritic Rats
2.3. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Compounds 1–7
2.4. Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Compounds 1–7
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Identification of Pure Compounds
3.5. Measurement of Arginase Activity
3.5.1. In Vitro with Bovine Arginase
3.5.2. Ex Vivo, in Isolated Aortic Rings from Arthritic Rats
3.6. Data and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABH | (S)-amino-6-boronohexanoic acid |
| Ach | acétylcholine |
| BEC | S-(2-boronoethyl)-L-cysteine |
| COSY | correlated spectroscopy |
| DEPT | distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer |
| DMSO | dimethylsulfoxide |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| Ethanol | EtOH |
| HMBC | heteronuclear multiple bond correlations |
| (HR)ESIMS | (high resolution) electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy |
| HSQC | heteronuclear simple quantum correlation |
| J-modulated spin-echo | JMOD |
| MeCN | acetonitrile |
| MeOH | methanol |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOESY | nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy |
| nor-NOHA | Nω-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine |
| OCH3 | methoxyl |
| PLC | preparative liquid chromatography |
| SEM | standard error of mean |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SPE | solid phase extraction |
References
- Jenkinson, C.P.; Grody, W.W.; Cederbaum, S.D. Comparative properties of arginases. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 114, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, L.; Sabio, G.; Mora, A.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Ochoa, A.C.; Centeno, F.; Christianson, D.W. Crystal structure of human arginase I at 1.29-Å resolution and exploration of inhibition in the immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13058–13063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.B.; Toque, H.A.; Narayanan, S.P.; Caldwell, R.W. Arginase: An old enzyme with new tricks. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holowatz, L.A.; Kenney, W.L. Up-regulation of arginase activity contributes to attenuated reflex cutaneous vasodilatation in hypertensive humans. J. Physiol. 2007, 581, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, D.E. Structure and function of arginase. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2760S–2764S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prati, C.; Berthelot, A.; Kantelip, B.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Treatment with the arginase inhibitor Nw-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine restores endothelial function in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 14, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.N.; Liagre, B.; Girard-Thernier, C.; Demougeot, C. Research on novel anticancer agent targeting arginase inhibition. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernow, J.; Jung, C. Arginase as a potential target in the treatment of cardiovascular disease: Reversal of arginine steal? Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 98, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudlo, M.; Demougeot, C.; Girard-Thernier, C. Arginase inhibitors: A rational approach over one century. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 475–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanenkov, Y.A.; Chufarova, N.V. Small-molecule arginase inhibitors. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2014, 3, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard-Thernier, C.; Pham, T.N.; Demougeot, C. The Promise of Plant-Derived Substances as Inhibitors of Arginase. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordage, S.; Pham, T.-N.; Zedet, A.; Gugglielmetti, A.S.; Nappey, M.; Demougeot, C.; Girard-Thernier, C. investigations of mammal arginase inhibitory properties of natural ubiquitous polyphenols by using an optimized colorimetric microplate assay. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Huai, H. Diversity of wetland plants used traditionally in China: A literature review. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014, 10, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, A.S.; Ali, H.H.; Naeem, M.; Latif, M.; Bukhari, A.H.; Tanveeer, A. Cyperus rotundus L.: Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamala, A.; Middha, S.K.; Karigar, C.S. Plants in traditional medicine with special reference to Cyperus rotundus L.: A review. Biotech 2018, 8, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizbakhsh, A.; Naeemy, A. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil of Cyperus conglomeratus Rottb. from Iran. J. Chem. 2011, 8, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Thebtaranonth, C.; Thebtaranonth, Y.; Wanauppathamkul, S.; Yuthavong, Y. Antimalarial sesquiterpenes from tubers of Cyperus rotundus: Structure of 10,12-peroxycalamenene, a sesquiterpene endoperoxide. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.H.; Lee, D.U.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Anti-allergic activity of sesquiterpenes from the rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, M.; Abu-Mustafa, E.; Abdel-Razik, A.; Dawidar, A. A new flavanan isolated from Cyperus conglomeratus. Pharmazie 1998, 53, 806–807. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Mogib, M.; Bassaif, S.; Ezmirly, S. Two novel flavans from Cyperus conglomeratus. Pharmazie 2000, 55, 693–695. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, A.A.; Ross, S.A.; El-Amier, Y.A.; Khan, I. New flavans and stilbenes from Cyperus conglomeratus. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 26, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Endo, H.; Shinohara, H.; Oyama, M.; Akao, Y.; Iinuma, M. Occurrence of stilbene oligomers in Cyperus rhizomes. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraki, K.; Totoson, P.; Decendit, A.; Badoc, A.; Zedet, A.; Jolibois, J.; Pudlo, M.; Demougeot, C.; Girard-Thernier, C. Cyperaceae species are potential sources of natural mammalian arginase inhibitors with positive effects on vascular function. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Q.; Li, H.-L.; Tang, J.; Lv, Y.F.; Zhang, W.-D. A new aurone and other phenolic constituents from Veratrum schindleri Loes. f. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.; Joshi, T. Two anthochlor pigments from heartwood of Pterocarpus marsupium. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2529–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsi, A.; Majdalani, M.; Kontogiorgis, C.A.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Kefalas, P. Natural and synthetic 2′-hydroxy-chalcones and aurones: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of the antioxidant and soybean lipoxygenase inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 8073–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Su, D.; Li, L.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, J.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 387, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Han, C.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Guo, L.; Ruan, S. The Mechanism of Aureusidin in Suppressing Inflammatory Response in Acute Liver Injury by Regulating MD2. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 570776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelinger, G.; Merfort, I.; Wölfle, U.; Schempp, C.M. Anti-carcinogenic effects of the flavonoid luteolin. Molecules 2008, 13, 2628–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Schang, P.; Li, D. Luteolin: A Flavonoid that Has Multiple Cardio-Protective Effects and Its Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, H.-S.; Jeong, S.I.; Kim, S.J.; Jang, S.I. Anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects of luteolin from Perilla (P. frutescens L.) leaves. Molecules 2014, 19, 6941–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Ren, X.; Jiang, L.; Pan, Y.; Sun, C. Scirpusin A, a hydroxystilbene dimer from Xinjiang wine grape, acts as an effective singlet oxygen quencher and DNA damage protector. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattivi, F.; Reniero, R.; Korhammer, S.J. Isolation, Characterization, and Evolution in Red Wine Vinification of Resveratrol Monomers. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1995, 43, 1820–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, A.; Kumar, B. Identification and characterization of phenolics and terpenoids from ethanolic extracts of Phyllanthus species by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totoson, P.; Maguin-Gaté, K.; Prigent-Tessier, A.; Monnier, A.; Verhoeven, F.; Marie, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Etanercept improves endothelial function via pleiotropic effects in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]





| Compound | tR (min) | [M + H]+ | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyperus thunbergii | |||
| 1 | 19.7 | 337 | compound 1 |
| 2 | 21.5 | 353 | compound 2 |
| Cyperus glomeratus | |||
| 3 | 13.8 | 229 | resveratrol |
| 4 | 18.5 | 471 | trans-scirpusin A |
| 5 | 29.2 | 287 | aureusidin |
| 6 | 22.5 | 713 | trans-cyperusphenol A |
| 7 | 36.6 | 287 | luteolin |
| Position | δH(m, J in Hz) | δC, Type | COSY (H→H) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.84 (1 H, d, J = 8.4) | 121.6, CH | H2 |
| 1a | 126.5, C | ||
| 2 | 6.76 (1 H, d, J = 8.4) | 108.3, CH | H1 |
| 3 | 148.7, C | ||
| 4 | 149.2, C | ||
| 4a | 145.2, C | ||
| 5 | 6.61 (1 H, d, J = 2.2) | 117.9, CH | H7 |
| 5a | 130.2, C | ||
| 6 | 145.9, C | ||
| 7 | 7.15 (1 H, d, J = 2.2) | 125.3, CH | H5 |
| 8 | 135.3, C | ||
| 8a | 137.0, C | ||
| 9 | 6.80 (1 H, d, J = 2.2) | 98.3, CH | H11 |
| 10 | 158.5, C | ||
| 11 | 6.17 (1 H, d, J = 2.2) | 100.3, CH | H9 |
| 11a | 123.0, C | ||
| 12 | 36.9, C | ||
| 13 | 1.59 (6 H, s) | 28.5, CH3 | |
| 3-OMe | 3.81 (3 H, s) | 55.1, CH3 | |
| 10-OMe | 3.69 (3 H, s) | 54.6, CH3 |
| 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | HMBC (H→C) | Position | HMBC (H→C) |
| 1 | 2, 3, 1a, 4a | 1 | 3, 4a, 2, 1a |
| 2 | 1, 3, 1a | 3 | 1, 4a, 4, 2 |
| 5 | 8a, 6, 7, 12, 13 | 5 | 5a, 10, 6 |
| 7 | 8a, 5, 6, 8 | 8 | 9, 6, 6a, 7 |
| 9 | 7, 8, 10, 11 | 9 | 8, 7, 9a, 6a |
| 11 | 11a, 9, 10 | 11 | 10, 12, 4a, 1a, 4 |
| 13 | 4a, 5a, 12 | 12 | 12-Me, 11, 10 |
| 3-OMe | 3 | 10-Me | 10, 11, 5a |
| 10-OMe | 10 | 12-Me | 12, 11, 10 |
| 2-OMe | 2 | ||
| 7-OMe | 7 |
| Position | δH (m, J in Hz) | δC, Type | COSY (H→H) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.63 (1 H, d, J = 2.2) | 95.6, CH | H3 |
| 1a | 142.2, C | ||
| 2 | 160.5, C | ||
| 3 | 6.27 (1 H, d, J = 2.2) | 101.2, CH | H1 |
| 4 | 154.1, C | ||
| 4a | 124.6, C | ||
| 5 | 6.66 (1 H, s) | 115.5, CH | |
| 5a | 128.9, C | ||
| 6 | 144.6, C | ||
| 6a | 129.2, C | ||
| 7 | 147.2, C | ||
| 8 | 6.76 (1 H, d, J = 8.4) | 108.1, CH | H9 |
| 9 | 6.65 (1 H, d, J = 8.4) | 118.1, CH | H8 |
| 9a | 142.1, C | ||
| 10 | 38.0, C | ||
| 11 | 2.73 (1 H, dd, J = 16.2, 6.9) 2.96 (1 H, dd, J = 16.2, 9.1) | 27.3, CH | H12 |
| 12 | 3.08 (1 H, m) | 50.2, CH | H11 |
| 10-Me | 1.79 (3 H, s) | 26.2, CH3 | |
| 12-Me | 1.00 (3 H, s) | 17.9, CH3 | |
| 2-OMe | 3.79 (3 H, s) | 54.4, CH3 | |
| 7-OMe | 3.87 (3 H, s) | 55.2, CH3 |
| Compound | Arginase Inhibition, IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| nor-NOHA b | 1.7 ± 0.2 |
| 1 | 28.8 ± 2.5 |
| 2 | 74.1 ± 3.7 |
| 3 | 105.2 ± 4.1 |
| 4 | 17.6 ± 2.2 |
| 5 | 57.1 ± 2.3 |
| 6 | 19.4 ± 1.3 |
| 7 | 60.6 ± 3.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arraki, K.; Totoson, P.; Decendit, A.; Zedet, A.; Maroilley, J.; Badoc, A.; Demougeot, C.; Girard, C. Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Cyperus Species. Molecules 2021, 26, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061694
Arraki K, Totoson P, Decendit A, Zedet A, Maroilley J, Badoc A, Demougeot C, Girard C. Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Cyperus Species. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061694
Chicago/Turabian StyleArraki, Kamel, Perle Totoson, Alain Decendit, Andy Zedet, Justine Maroilley, Alain Badoc, Céline Demougeot, and Corine Girard. 2021. "Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Cyperus Species" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061694
APA StyleArraki, K., Totoson, P., Decendit, A., Zedet, A., Maroilley, J., Badoc, A., Demougeot, C., & Girard, C. (2021). Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Cyperus Species. Molecules, 26(6), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061694