Fast Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compounds in Herbal Medicines Using Bubble-Generating Magnetic Liposomes Coupled with LC–MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
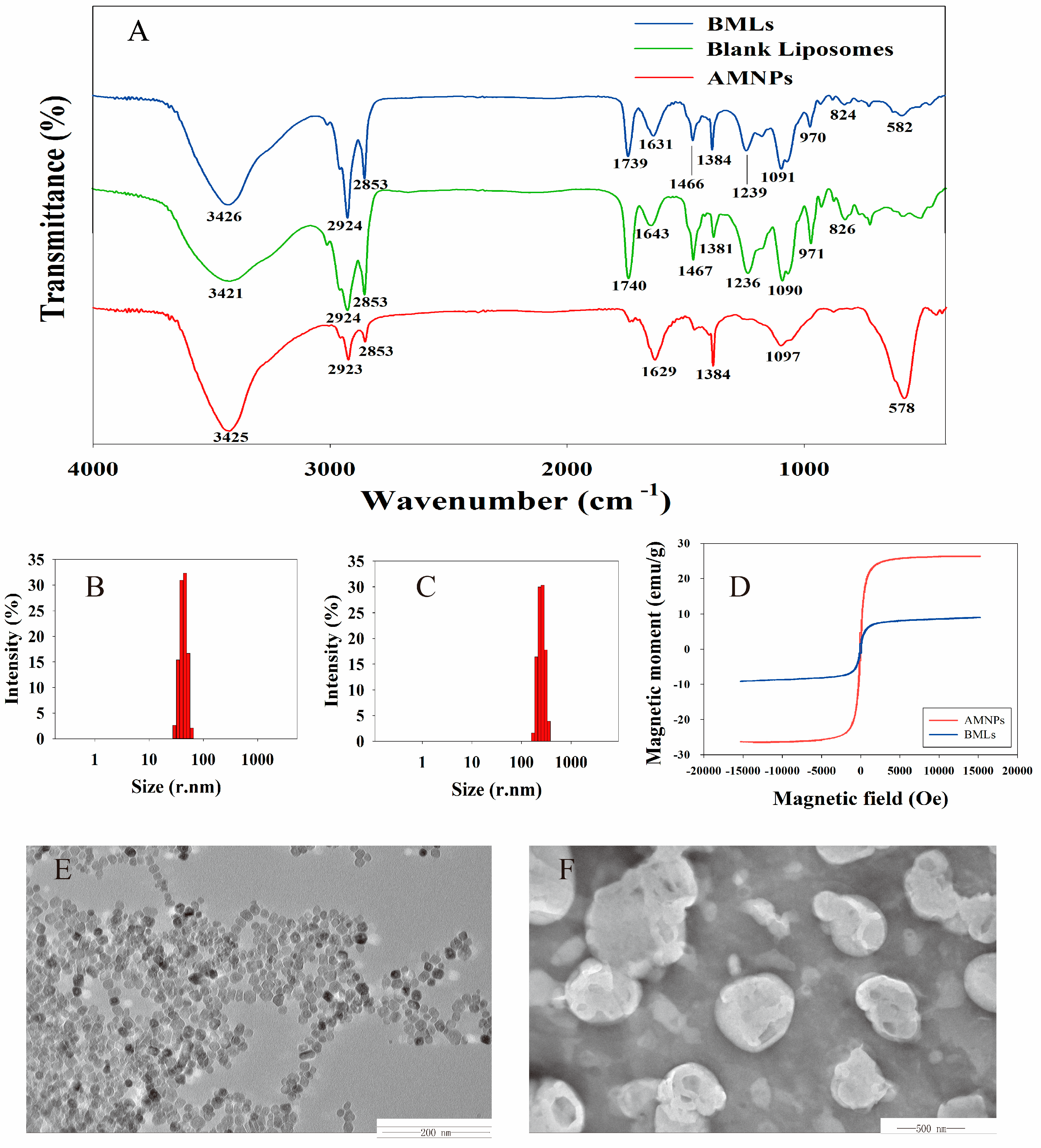
2.1. Characterization of BMLs
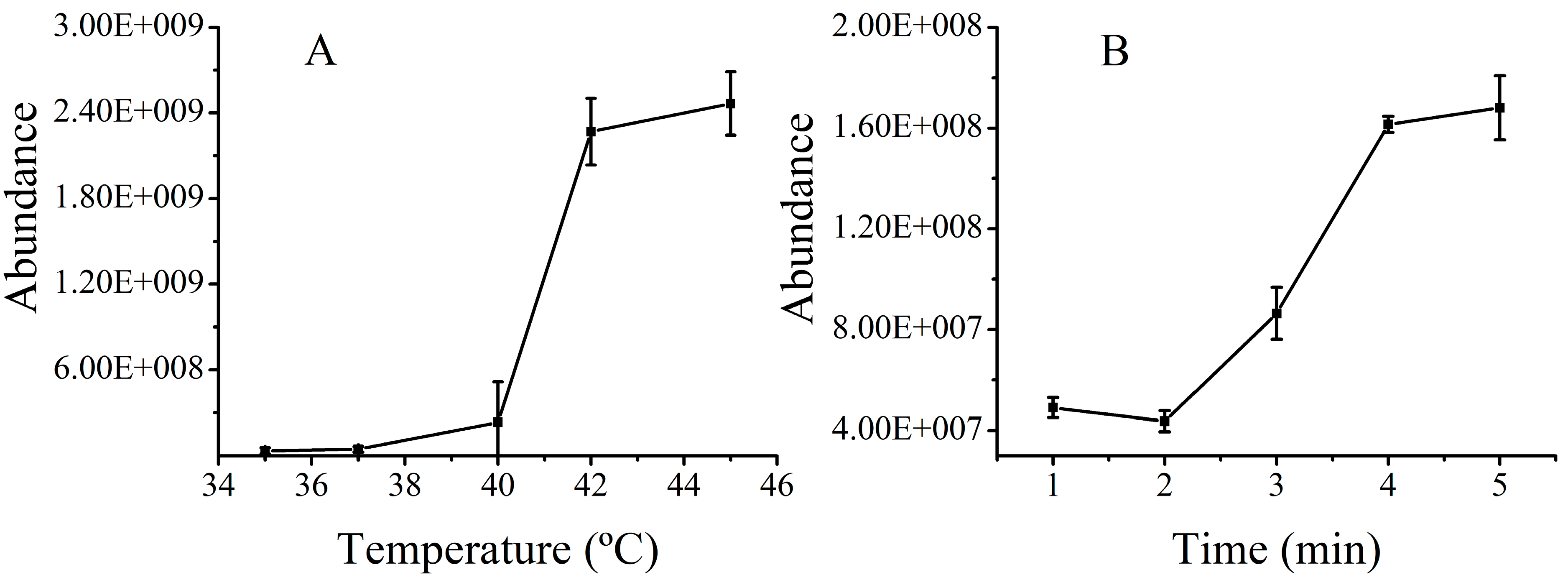
2.2. Optimization of Rlelease Condition
2.3. Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compounds in JLZS
2.4. In Vivo Animal Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Synthesis of Amino-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.4. Preparation of Bubble-Generating Magnetic Liposomes
3.5. Characterization
3.6. LC–MS Instrumentation
3.7. Optimization of Release Condition
3.8. Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compound in JLZS
3.9. In Vivo Animal Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cheung, F. TCM made in China. Nature 2011, 480, S82–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Ding, Z.; Xu, X. Frontal immunoaffinity chromatography with mass spectrometric detection: A method for finding active compounds from traditional Chinese herbs. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3994–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Song, W.; Tian, F.; Dai, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Ahmad, E.; Guo, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, H.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Temperature- and rigidity-mediated rapid transport of lipid nanovesicles in hydrogels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5362–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Han, J. Research progress on liposomes: Application in food, digestion behavior and absorption mechanism. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 104, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Lei, X.; Hu, L.; Zou, H.; Welbeck, E.; Bligh, S.W.; Wang, Z. Comprehensive two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography system with immobilized liposome chromatography column and reversed-phase column for separation of complex traditional Chinese medicine Longdan Xiegan Decoction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Shi, Z. Fast immobilized liposome chromatography based on penetrable silica microspheres for screening and analysis of permeable compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1233, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruokonen, S.K.; Dusa, F.; Rantamaki, A.H.; Robciuc, A.; Holma, P.; Holopainen, J.M.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Wiedmer, S.K. Distribution of local anesthetics between aqueous and liposome phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Z. Prediction of Human Drug Absorption Using Liposome Electrokinetic Chromatography. Chromatographia 2007, 65, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Feng, Y.; Jin, X.; Fan, X.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. Liposome electrokinetic chromatography based in vitro model for early screening of the drug-induced phospholipidosis risk. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 96, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Deng, Y.; Xue, Y.; Liang, J. Screening of bioactive compounds in Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae with liposomes and cell membranes using HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liang, J. Screening of permeable compounds in Flos Lonicerae Japonicae with liposome using ultrafiltration and HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Niu, J.; Song, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Studies on the interactions between ginsenosides and liposome by equilibrium dialysis combined with ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 923–924, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlido, L.; Azevedo, A.M.; Roque, A.C.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Magnetic separations in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Preparation, surface functionalization and application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 281, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Bu, Y.; Zhen, X.; Xu, K.; Ke, R.; Xie, X.; Wang, S. Magnetic carbon nanotubes camouflaged with cell membrane as a drug discovery platform for selective extraction of bioactive compounds from natural products. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Magnetic bead-liposome hybrids enable sensitive and portable detection of DNA methyltransferase activity using personal glucose meter. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Li, X.; Han, H.; Tao, Y. Purification and characterization of plantaricin SLG1, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lb. plantarum isolated from yak cheese. Food Control 2018, 84, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Feng, Z.; Ren, T.; Jin, W.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Tao, Y.; Dang, J. Selectively screen the antibacterial peptide from the hydrolysates of highland barley. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.F.; Chen, K.J.; Liang, H.F.; Liao, Z.X.; Chia, W.T.; Xia, Y.; Sung, H.W. A Liposomal System Capable of Generating CO2 Bubbles to Induce Transient Cavitation, Lysosomal Rupturing, and Cell Necrosis. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10236–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zou, T.; Dai, M.; He, X.Y.; Peng, N.; Wu, K.; Wang, X.Q.; Liao, C.Y.; Liu, Y. Doxorubicin loaded tumor-triggered targeting ammonium bicarbonate liposomes for tumor-specific drug delivery. Colloid Surface B 2019, 178, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, G.; Lu, Y.J.; Chen, H.A.; Hsu, H.L.; Hung, J.T.; Anilkumar, T.S.; Chen, J.P. Hyaluronic acid modified bubble-generating magnetic liposomes for targeted delivery of doxorubicin. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 474, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wu, C.; Fang, H.; Li, L.; Yan, J.; Zeng, D.; Zou, T. Thermo-responsive magnetic liposomes for hyperthermia-triggered local drug delivery. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, J. Treatment Effects of Jinlingzi Powder and Its Extractive Components on Gastric Ulcer Induced by Acetic Acid in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 7365841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. One-pot synthesis and Bioapplication of Amine-Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles and Hollow Nanospheres. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 6341–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasti, B.; Jinap, S.; Mozafari, M.R.; Yazid, A.M. Comparative study of the oxidative and physical stability of liposomal and nanoliposomal polyunsaturated fatty acids prepared with conventional and Mozafari methods. Food. Chem. 2012, 135, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Peak No. | Compound | Formula | tR (min) | MS | MS2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | RUT | C27H30O16 | 3.3 | 609 | 300, 271, 178 |
| C2 | THP | C21H25NO4 | 5.1 | 356 | 192, 174, 165 |
| C3 | PRO | C20H20NO5 | 5.1 | 354 | 336, 275, 189,188 |
| C4 | ALL | C21H24NO5 | 5.5 | 370 | 352, 290, 206, 188 |
| C5 | JAT | C20H20NO4 | 5.6 | 338 | 321, 303, 237 |
| C6 | COP | C19H14NO4 | 6.9 | 320 | 292, 277, 262, 233 |
| C7 | THC | C19H17NO4 | 7.1 | 324 | 176, 174, 149 |
| C8 | THB | C20H21NO4 | 7.7 | 340 | 176, 149, 114 |
| C9 | COR | C22H27NO4 | 7.8 | 370 | 295, 192 |
| C10 | PAL | C21H22NO4 | 8.1 | 352 | 336, 321,308 |
| C11 | BER | C20H18NO4 | 8.7 | 336 | 321, 320, 292 |
| C12 | DHC | C22H24NO4 | 9.2 | 366 | 350, 336, 322, 308 |
| C13 | TSN | C30H38O11 | 14.7, 17.3 | 573 | 531 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Di, X. Fast Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compounds in Herbal Medicines Using Bubble-Generating Magnetic Liposomes Coupled with LC–MS. Molecules 2021, 26, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061742
Gu X, Wang D, Wang X, Liu Y, Di X. Fast Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compounds in Herbal Medicines Using Bubble-Generating Magnetic Liposomes Coupled with LC–MS. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061742
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xiaoting, Dongwu Wang, Xin Wang, Youping Liu, and Xin Di. 2021. "Fast Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compounds in Herbal Medicines Using Bubble-Generating Magnetic Liposomes Coupled with LC–MS" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061742
APA StyleGu, X., Wang, D., Wang, X., Liu, Y., & Di, X. (2021). Fast Screening of Biomembrane-Permeable Compounds in Herbal Medicines Using Bubble-Generating Magnetic Liposomes Coupled with LC–MS. Molecules, 26(6), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061742





