Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Acacia nilotica (L.) Extract to Overcome Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
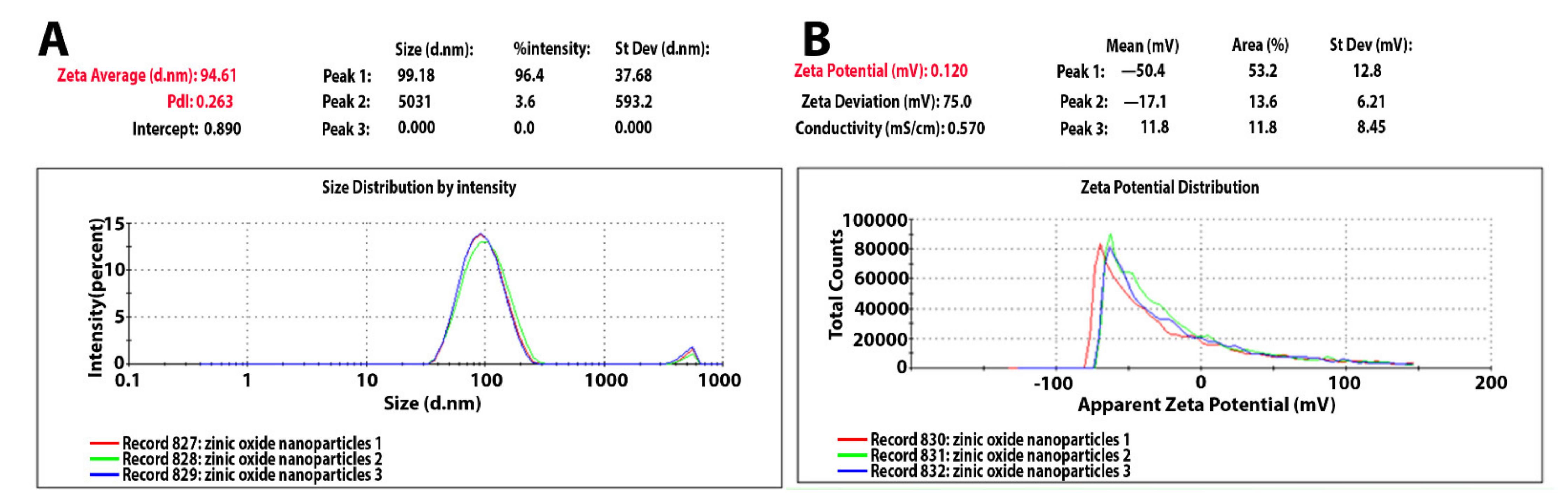
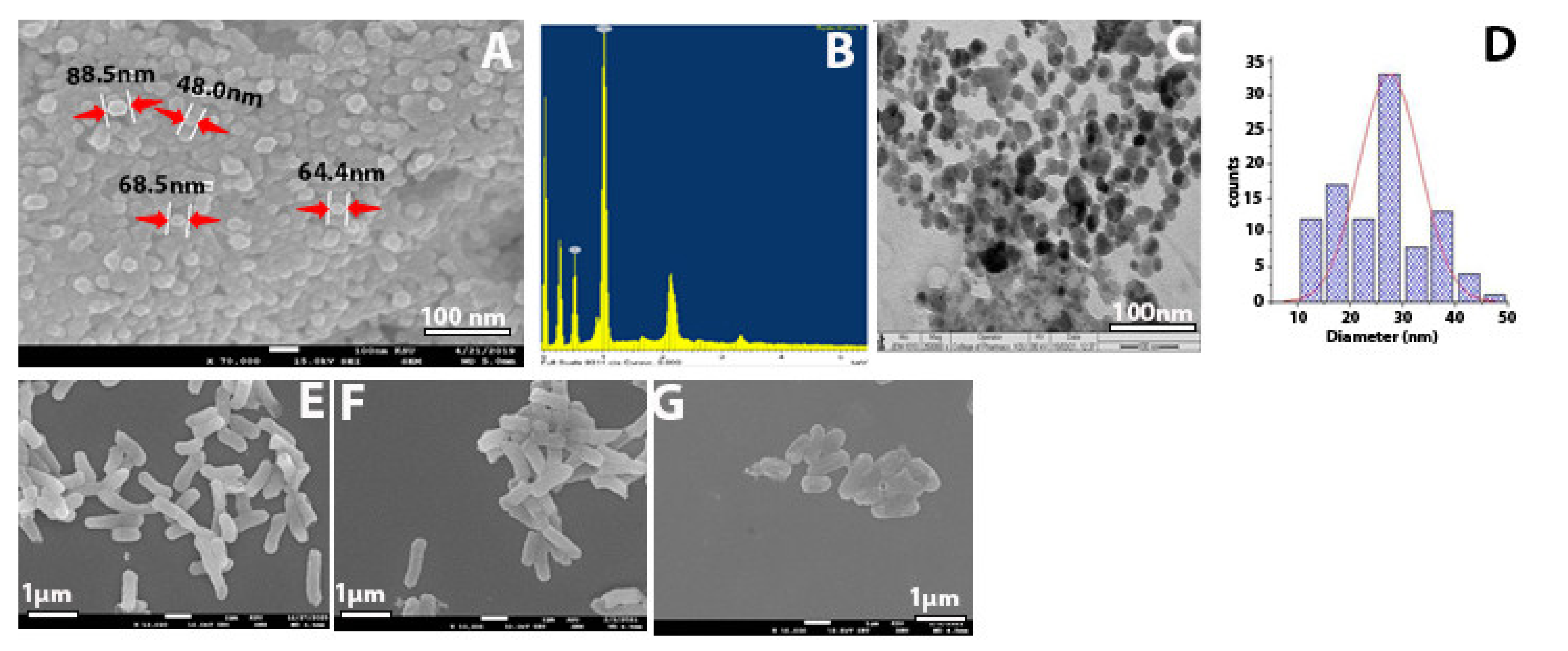
2.1. Characterization of Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
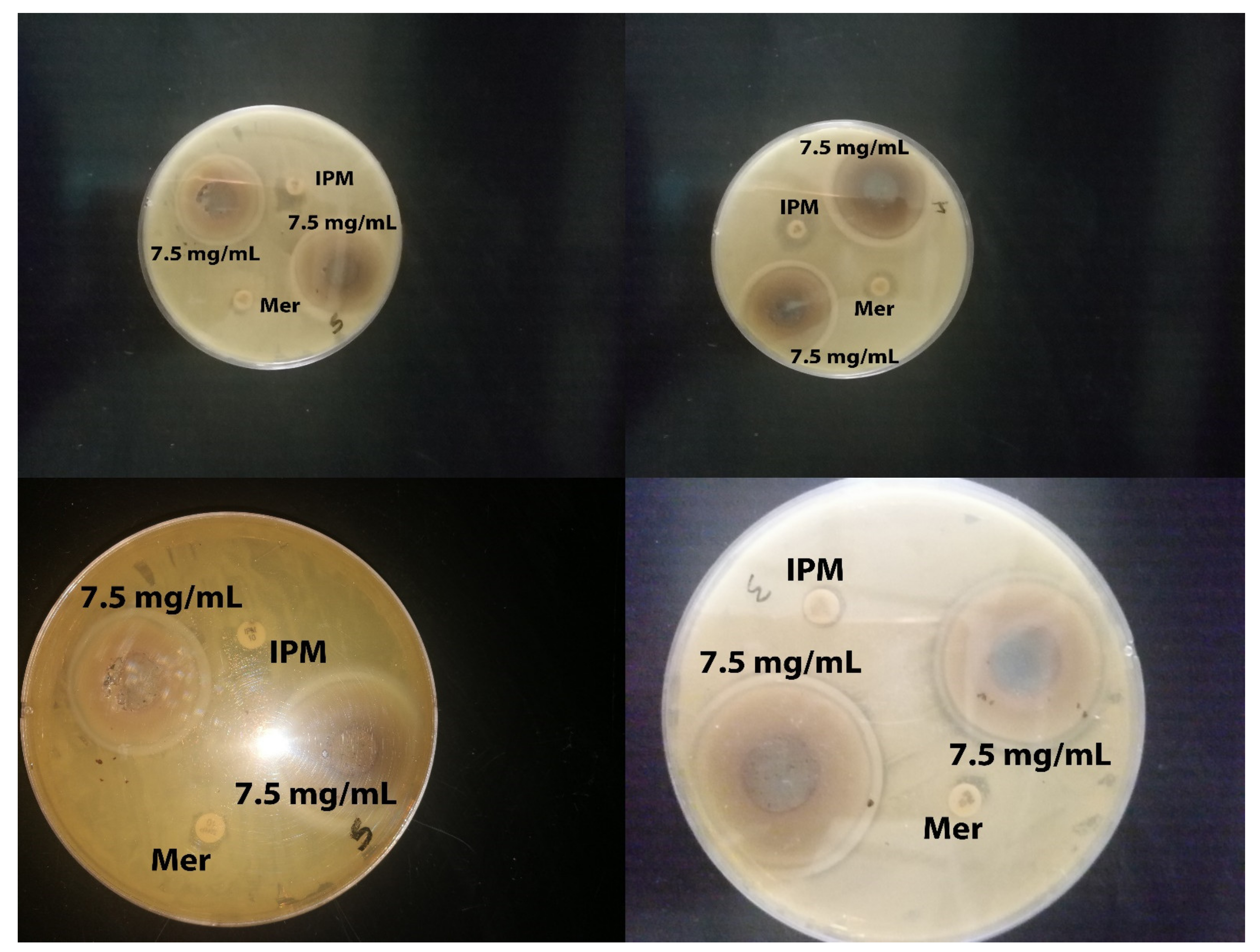
2.2. Antibacterial Activity
2.3. SEM for Bacteria
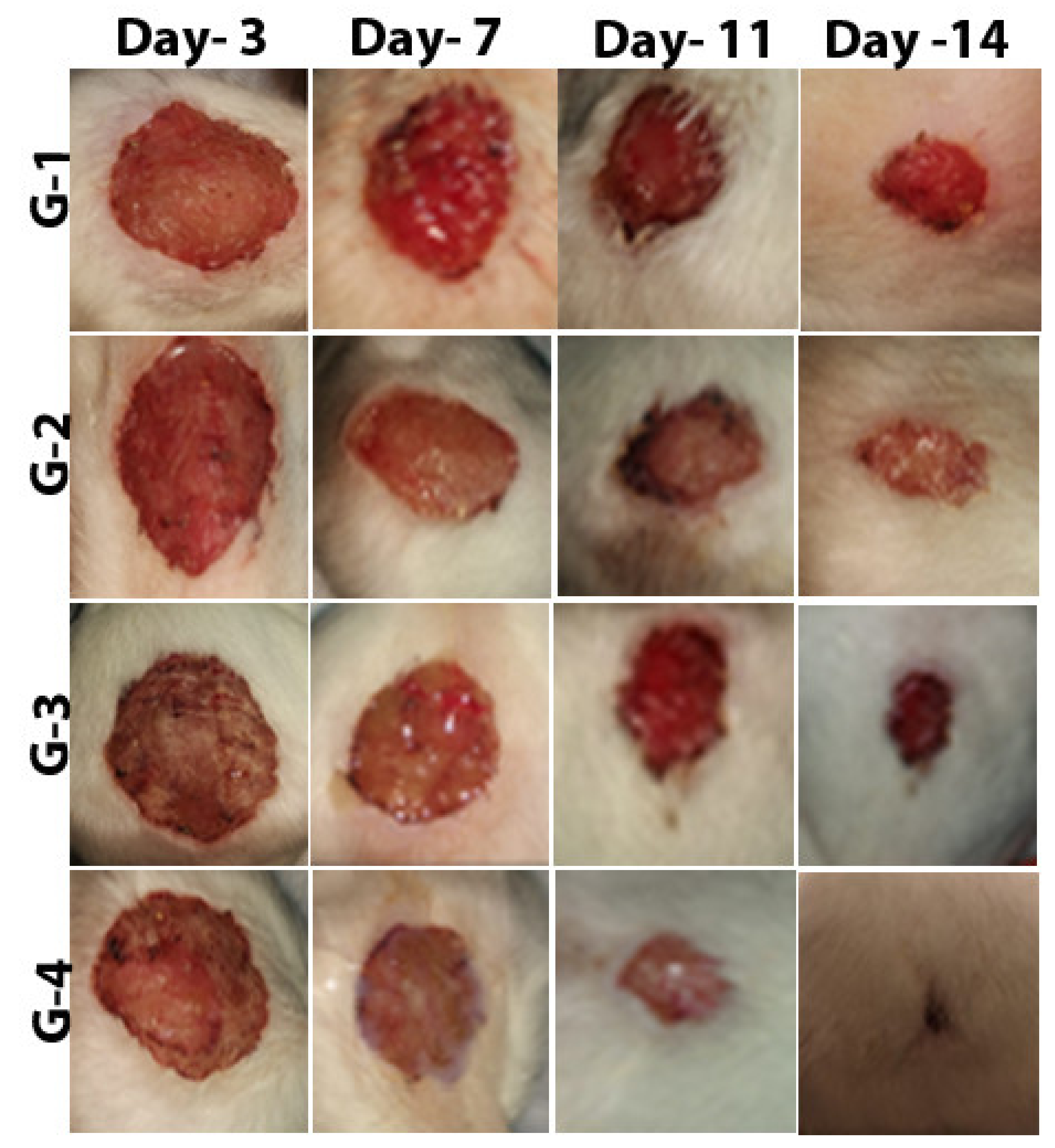
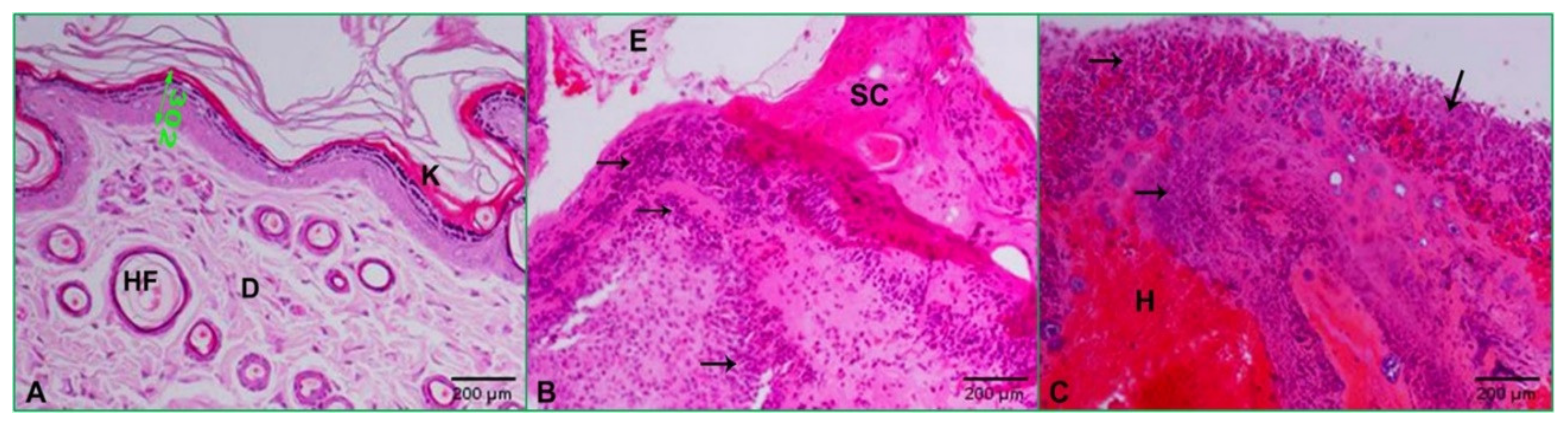
2.4. Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Improving Wound Healing
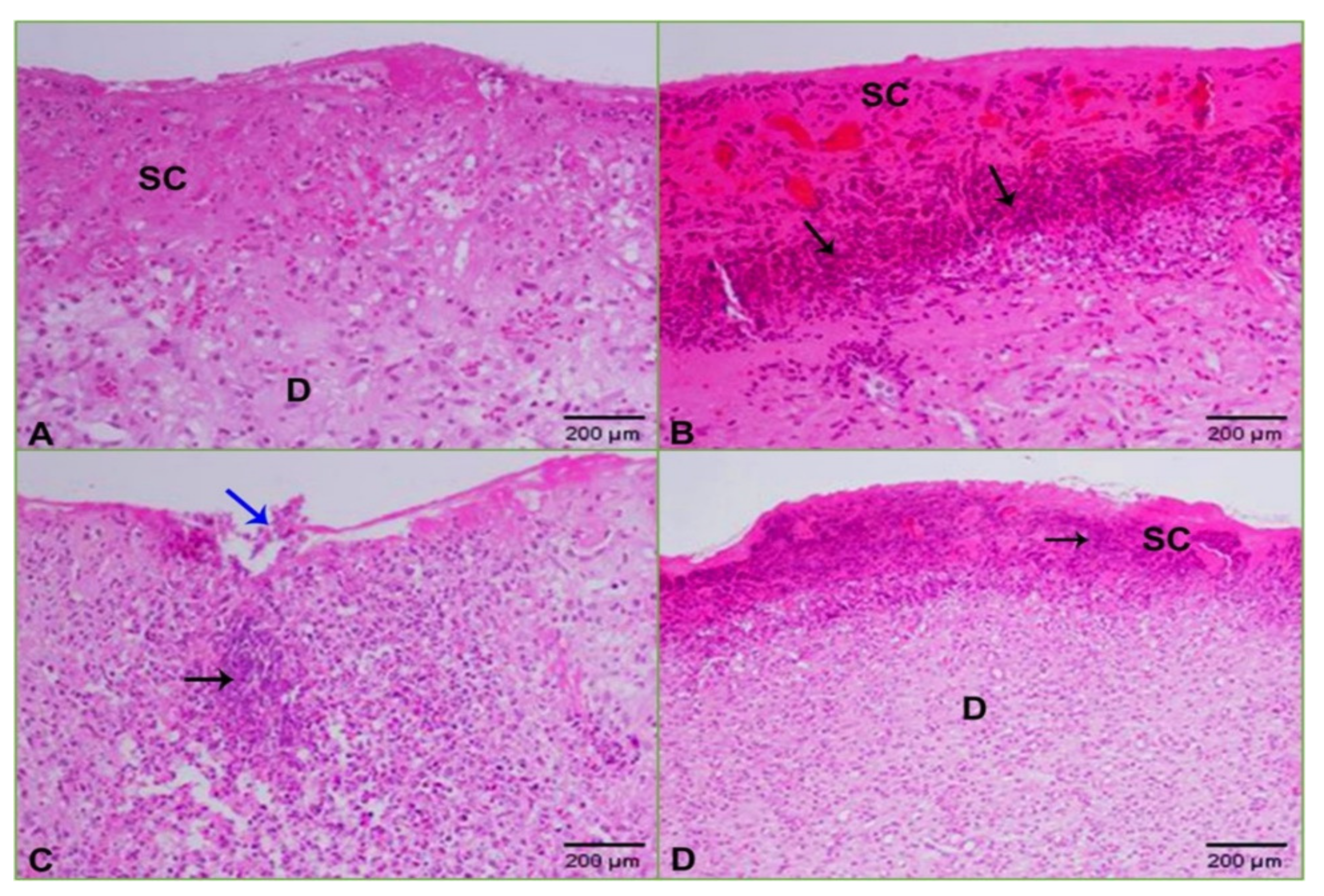
2.5. Histopathology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of ZnO-NPs Using Aqueous Plant Extract
4.2. Characterization of Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
4.3. Determination of Antibacterial Activity of ZnO-NPs by Using Agar Well Diffusion Method, Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC), and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
4.4. Preparation of Bacterial Samples for Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Animal Preparation
4.6. Wound Surgery and Induction of KPC Infection
4.7. Preparation of Gel-Based Ointments
4.8. Wound Healing and Re-Epithelialization
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Al-Saiym, R.A.; Al-Kamali, H.H.; Al-Magboul, A.Z. Synergistic Antibacterial Interaction between Trachyspermum ammi, Senna alexandrina Mill and Vachellia nilotica spp. Nilotica Extract and Antibiotics. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 18, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, R.A.; Ahmad, I.; Alsharaeh, E.; Khan, M.S.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, T.; Yusuf, M.; et al. Biogenic synthesis of Zinc oxide nanostructures from Nigella sativa seed: Prospective role as food packaging material inhibiting broad-spectrum quorum sensing and biofilm. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalbahi, A.; Alterary, S.; Almoghim, R.A.A.; Awad, M.A.; Aldosari, N.S.; Alghannam, S.F.; Alabdan, A.N.; Alharbi, S.; Alateeq, B.A.M.; Al Mohsen, A.A.; et al. Greener Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Characterization and Multifaceted Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekish, M.; Ismail, Z.B.; Albiss, B.; Nawasrah, S. In vitro antibacterial effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on multiple drug-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli: An alternative approach for antibacterial therapy of mastitis in sheep. Veter World 2018, 11, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Layton, C. Connective and other mesenchymal tissues with their stains. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. Biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Vigna radiata. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Seth, A.K.; Abercrombie, J.J.; Mustoe, T.A.; Leung, K.P. Activity of Imipenem against Klebsiella pneumoniae BiofilmsIn VitroandIn Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 58, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da’Na, E.; Taha, A.; Afkar, E. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles by Acacia nilotica Pods Extract and Its Catalytic, Adsorption, and Antibacterial Activities. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLeo, F.R.; Chen, L.; Porcella, S.F.; Martens, C.A.; Kobayashi, S.D.; Porter, A.R.; Chavda, K.D.; Jacobs, M.R.; Mathema, B.; Olsen, R.J.; et al. Molecular dissection of the evolution of carbapenem-resistant multilocus sequence type 258Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4988–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, M.; Tey, H.L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. ZnO nanoparticles as an antimicrobial tissue adhesive for skin wound closure. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S. Developing ZnO nanoparticle embedded antimicrobial starch biofilm for developing ZnO nanoparticle embedded antimicrobial starch biofilm for food. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.05083. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, F.; Jalal, R. Antimicrobial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles in combination with ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 6, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.S.H.; Karthikeyan, C.; Ahamed, A.P.; Thajuddin, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ravi, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jesline, A.; John, N.P.; Narayanan, P.M.; Vani, C.; Murugan, S. Antimicrobial activity of zinc and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavitha, S.; Dhamodaran, M.; Prasad, R.; Ganesan, M. Synthesis and characterisation of zinc oxide nanoparticles using terpenoid fractions of Andrographis paniculata leaves. Int. Nano Lett. 2017, 7, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, A.M.; Mathema, B.; Larson, E.L. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in the community: A scoping review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.S.A.; Kim, K.; Choi, M.; Lee, J.-K.; Jeong, J.; Kim, Y.-R.; Kim, M.-K.; Paek, S.; Shin, J.-H. Physicochemical properties of surface charge-modified ZnO nanoparticles with different particle sizes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.; Xu, G.; Mevers, E.E.; Clardy, J.; Watnick, P.I. A high-throughput, whole cell assay to identify compounds active against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Long, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C. Assessment of antimicrobial and wound healing effects of Brevinin-2Ta against the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae in dermally-wounded rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 111369–111385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousef, J.M.; Danial, E.N. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Zinc Oxide and Nano-particle Zinc oxide Against Pathogenic Strains. Int. J. Health Sci. 2012, 2, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumdar, R.; Bag, B.G.; Maity, N. Acacia nilotica (Babool) leaf extract mediated size-controlled rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles and study of its catalytic activity. Int. Nano Lett. 2013, 3, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malviya, S. Attributes of Acacia nilotica Linn.-A comprehensive review on ethnopharmacological claims. Int. J. of Pharm. and Life Sci. 2011, 2, 830–837. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. In Approved Standard, 9th ed.; CLSI: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 32, p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Sharma, R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using fresh peels of Punica granatum and its anti-microbial activities. Int. J. Pharma Res. Health Sci. 2015, 3, 694–699. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, S.S.; Mohammad, N.; Ghooshchian, M.; Fathizadeh, S.; Khodaii, Z.; Faramarzi, M.; Aghmiyuni, Z.F.; Roudbari, M.; Pazouki, A.; Shabestari, T.M. Comparison of the effects of Lactobacillus plantarum versus imipenem on infected burn wound healing. Med. J. Islamic Repub. Iran 2020, 34, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Okpara, E.C.; Fayemi, O.E.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Junaedi, H.; Ebenso, E.E. Green Wastes Mediated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Electrochemical Studies. Materials 2020, 13, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalia, H.; Moteriya, P.; Khara, G.; Chanda, S.; Moteiya, P. WITHDRAWN: Green synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Cinnamomum verum bark extract. OpenNano 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Guidelines—Preparation of Ketamine Anesthesia Cocktail for Rats. In Anesthesia (Guideline); University of Iowa: Iowa City, IA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Farzana, R.; Iqra, P. Antimicrobial Behavior of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and β-Lactam Antibiotics against Pathogenic Bacteria. Arch. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, M.K.; Kon, K.V. Fighting Multidrug Resistance with Herbal Extracts, Essential Oils and Their Components, 1st ed.; Mahendrakumarraimsc, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.N.; Riyazuddin; Babji, P.; Ahmad, N.; Khan, R.A.; Hassan, I.; Shahzad, S.A.; Husain, F.M. Green synthesis and structural classification of Acacia nilotica mediated-silver doped titanium oxide (Ag/TiO2) spherical nanoparticles: Assessment of its antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.M.; Harborne, J.B. Phytochemical Methods: A Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant Analysis. Second Edition. Brittonia 1990, 42, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safawo, T.; Sandeep, B.; Pola, S.; Tadesse, A. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using tuber extract of anchote (Coccinia abyssinica (Lam.) Cong.) for antimicrobial and antioxidant activity assessment. OpenNano 2018, 3, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, S.R.; Sivakumar, T. Green tea (Camellia sinensis) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanopar-ticles and studies on their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Singh, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Mishra, B.N.; Kulsoom, M.; Dasgupta, N.; Khan, S.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Haque, S. Preparation and Evaluation of the ZnO NP–Ampicillin/Sulbactam Nanoantibiotic: Optimization of Formulation Variables Using RSM Coupled GA Method and Antibacterial Activities. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiquah, A.; Hashmi, S.S.; Mushtaq, S.; Renouard, S.; Blondeau, J.P.; Abbasi, R.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Exploiting in vitro potential and characterization of surface modified Zinc oxide nanoparticles of Isodon rugosus extract: Their clinical potential towards HepG2 cell line and human pathogenic bacteria. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 671–687. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaranjani, V.; Philominathan, P. Synthesize of Titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaves and evaluation of wound healing activity. Wound Med. 2016, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnevend, Á.; Ghazawi, A.A.; Hashmey, R.; Jamal, W.; Rotimi, V.O.; Shibl, A.M.; Al-Jardani, A.; Al-Abri, S.S.; Tariq, W.U.Z.; Weber, S.; et al. Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae with High Rate of Autochthonous Transmission in the Arabian Peninsula. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Mishra, N.; Gadani, K.; Solanki, P.S.; Shah, N.A.; Tiwari, M. Mechanism of Anti-bacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshioka, C.; Ito, Y.; Nagai, N. Enhanced percutaneous absorption of cilostazol nanocrystals using aqueous gel patch systems and clarification of the absorption mechanism. Exp. Med. 2018, 15, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, E.; Pourseyedi, S.; Khatami, M.; Darezereshki, E. Simple biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using nature’s source, and it’s in vitro bio-activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1146, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Chan, E.W.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, K.; Chen, S. Nationwide Surveillance of Clinical Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Strains in China. EBioMedicine 2017, 19, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Nayak, T.R.; Hong, H.; Cai, W. Biomedical Applications of Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zowawi, H.M.; Sartor, A.L.; Balkhy, H.H.; Walsh, T.R.; Al Johani, S.M.; Aljindan, R.Y.; Alfaresi, M.; Ibrahim, E.; Al-Jardani, A.; Al-Abri, S.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council: Dominance of OXA-48 and NDM Producers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Element Line | Element Wt.% | Atom% |
|---|---|---|
| O | 16.57 | 44.80 |
| Zn | 83.43 | 55.20 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Mean ± Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|
| MIC | 0.45 ± 20 |
| MBC | 1.14 ± 50 |
| Bacterial Code | Meropenem | Imipenem |
|---|---|---|
| ATCC | >0.25 | >1 |
| 22 | >16 | >2 |
| 14 | >4 | >4 |
| 15 | >16 | >4 |
| 16 | >16 | >4 |
| 19 | >16 | >4 |
| 20 | >16 | >4 |
| 8 | >16 | >4 |
| 6 | >16 | >4 |
| 9 | >16 | >4 |
| 3 | >16 | >16 |
| 2 | >16 | >4 |
| 1 | >16 | >4 |
| 11 | >4 | >4 |
| 10 | >16 | >4 |
| 4 | >4 | >2 |
| 5 | >4 | >4 |
| 12 | >16 | >4 |
| 17 | >16 | >4 |
| 18 | >16 | >4 |
| 21 | >16 | >4 |
| Groups | Days | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Day | Day-3 | Day-7 | Day-11 | Day-14 | |
| G-1 | 2cm | 7 ± 2.739 | 17 ± 2.739 | 30 ± 5.000 | 63 ± 5.701 |
| G-2 | 2cm | 10 ± 5.000 | 18 ± 6.708 | 30 ± 7.071 | 64 ± 9.618 |
| G-3 | 2cm | 10 ± 3.536 | 39 ± 8.944 | 54 ± 4.183 | 70 ± 6.124 |
| G-4 | 2cm | 9 ± 4.183 | 57 ± 4.472 | 92 ± 5.701 | 98 ± 2.739 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasha, E.; Monerah, A.; Manal, A.; Rehab, A.; Mohammed, D.; Doaa, E. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Acacia nilotica (L.) Extract to Overcome Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Molecules 2021, 26, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071919
Rasha E, Monerah A, Manal A, Rehab A, Mohammed D, Doaa E. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Acacia nilotica (L.) Extract to Overcome Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071919
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasha, Elsayim, AlOthman Monerah, Alkhulaifi Manal, Ali Rehab, Doud Mohammed, and Elnagar Doaa. 2021. "Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Acacia nilotica (L.) Extract to Overcome Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae" Molecules 26, no. 7: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071919
APA StyleRasha, E., Monerah, A., Manal, A., Rehab, A., Mohammed, D., & Doaa, E. (2021). Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Acacia nilotica (L.) Extract to Overcome Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Molecules, 26(7), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071919






