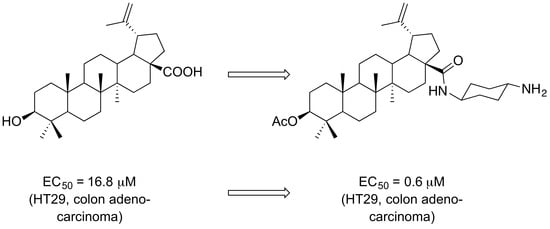
The Presence of a Cyclohexyldiamine Moiety Confers Cytotoxicity to Pentacyclic Triterpenoids
Abstract
Share and Cite
Hoenke, S.; Christoph, M.A.; Friedrich, S.; Heise, N.; Brandes, B.; Deigner, H.-P.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Csuk, R. The Presence of a Cyclohexyldiamine Moiety Confers Cytotoxicity to Pentacyclic Triterpenoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072102
Hoenke S, Christoph MA, Friedrich S, Heise N, Brandes B, Deigner H-P, Al-Harrasi A, Csuk R. The Presence of a Cyclohexyldiamine Moiety Confers Cytotoxicity to Pentacyclic Triterpenoids. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoenke, Sophie, Martin A. Christoph, Sander Friedrich, Niels Heise, Benjamin Brandes, Hans-Peter Deigner, Ahmed Al-Harrasi, and René Csuk. 2021. "The Presence of a Cyclohexyldiamine Moiety Confers Cytotoxicity to Pentacyclic Triterpenoids" Molecules 26, no. 7: 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072102
APA StyleHoenke, S., Christoph, M. A., Friedrich, S., Heise, N., Brandes, B., Deigner, H.-P., Al-Harrasi, A., & Csuk, R. (2021). The Presence of a Cyclohexyldiamine Moiety Confers Cytotoxicity to Pentacyclic Triterpenoids. Molecules, 26(7), 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072102