Glycan-Induced Protein Dynamics in Human Norovirus P Dimers Depend on Virus Strain and Deamidation Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. P Dimer Quality Control by Peptic Digest and Native MS
2.2. Bimodality of Deuterated Peak Distributions Indicates a Lower Deuterated Protein Subpopulation
2.3. Analysis of Glycan Induced Changes in P Dimers of Different Strains by HDX-MS
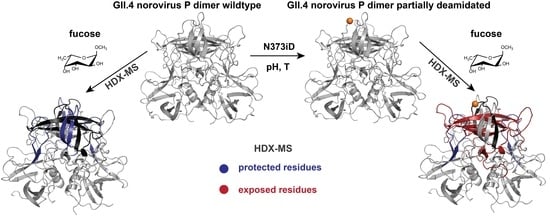
2.4. Influence of N373 Deamidation on Dynamics and Glycan Binding of GII.4 P Dimers
2.5. MD Simulations
3. Discussion
3.1. Putative Origin of Bimodal Peak Distributions
3.2. Glycan Binding in Different Strains
3.3. The Role of N373 Deamidation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expression and Purification of P Dimers
4.2. Glycan Structures

4.3. Native MS
4.4. HDX-MS
4.5. Peptide and PTM Identification
4.6. HDX Data Analysis
4.7. Experimental Design and Statistical Rationale
4.8. Structure and Sequence Alignment
4.9. Homology Modeling of GII.4 MI001 P Dimer Structure
4.10. MD Simulations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chhabra, P.; De Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.-W.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Podkolzin, A.T.; Zaytseva, E.V.; Komano, J.; Sakon, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Thanusuwannasak, T.; et al. Global Spread of Norovirus GII.17 Kawasaki 308, 2014–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graaf, M.; Van Beek, J.; Vennema, H.; Podkolzin, A.T.; Hewitt, J.; Bucardo, F.; Templeton, K.; Mans, J.; Nordgren, J.; Reuter, G.; et al. Emergence of a novel GII.17 norovirus—End of the GII.4 era? Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, L.; Cai, W.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, R.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. The resurgence of the norovirus GII.4 variant associated with sporadic gastroenteritis in the post-GII.17 period in South China, 2015 to 2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.V.V.; Hardy, M.E.; Dokland, T.; Bella, J.; Rossmann, M.G.; Estes, M.K. X-ray Crystallographic Structure of the Norwalk Virus Capsid. Science 1999, 286, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Lou, Z.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Rao, Z. Structural Basis for the Recognition of Blood Group Trisaccharides by Norovirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taube, S.; Mallagaray, A.; Peters, T. Norovirus, glycans and attachment. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 31, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Hegde, R.S.; Jiang, X. The P Domain of Norovirus Capsid Protein Forms Dimer and Binds to Histo-Blood Group Antigen Receptors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6233–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.-M.; Hutson, A.M.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V.V. Atomic resolution structural characterization of recognition of histo-blood group antigens by Norwalk virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9175–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bücher, K.S.; Yan, H.; Creutznacher, R.; Ruoff, K.; Mallagaray, A.; Grafmüller, A.; Dirks, J.S.; Kilic, T.; Weickert, S.; Rubailo, A.; et al. Fucose-Functionalized Precision Glycomacromolecules Targeting Human Norovirus Capsid Protein. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3714–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansman, G.S.; Biertümpfel, C.; Georgiev, I.; McLellan, J.S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T.; Katayama, K.; Kwong, P.D. Crystal Structures of GII.10 and GII.12 Norovirus Protruding Domains in Complex with Histo-Blood Group Antigens Reveal Details for a Potential Site of Vulnerability. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6687–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koromyslova, A.; Tripathi, S.; Morozov, V.; Schroten, H.; Hansman, G.S. Human norovirus inhibition by a human milk oligosaccharide. Virology 2017, 508, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koromyslova, A.D.; Leuthold, M.M.; Bowler, M.W.; Hansman, G.S. The sweet quartet: Binding of fucose to the norovirus capsid. Virology 2015, 483, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallagaray, A.; Creutznacher, R.; Dülfer, J.; Mayer, P.H.O.; Grimm, L.L.; Orduña, J.M.; Trabjerg, E.; Stehle, T.; Rand, K.D.; Blaum, B.S.; et al. A post-translational modification of human Norovirus capsid protein attenuates glycan binding. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallagaray, A.; Lockhauserbäumer, J.; Hansman, G.; Uetrecht, C.; Peters, T. Attachment of Norovirus to Histo Blood Group Antigens: A Cooperative Multistep Process. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12014–12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallagaray, A.; Rademacher, C.; Parra, F.; Hansman, G.; Peters, T. Saturation transfer difference nuclear magnetic resonance titrations reveal complex multistep-binding of l-fucose to norovirus particles. Glycobiology 2016, 27, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegener, H.; Mallagaray, Á.; Schöne, T.; Peters, T.; Lockhauserbäumer, J.; Yan, H.; Uetrecht, C.; Hansman, G.S.; Taube, S. Human Norovirus GII.4(MI001) P Dimer Binds Fucosylated and Sialylated Carbohydrates. Glycobiology 2017, 27, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Kitov, P.I.; Kitova, E.N.; Tan, M.; Wang, L.; Xia, M.; Jiang, X.; Klassen, J.S. Affinities of recombinant norovirus P dimers for human blood group antigens. Glycobiology 2012, 23, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zheng, R.; Richards, M.R.; Tan, M.; Kitova, E.N.; Jiang, X.; Klassen, J.S. Quantifying the binding stoichiometry and affinity of histo-blood group antigen oligosaccharides for human noroviruses. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Leuthold, M.M.; Hansman, G.S. Human Noroviruses’ Fondness for Histo-Blood Group Antigens. J. Virol. 2014, 89, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creutznacher, R.; Maass, T.; Ogrissek, P.; Wallmann, G.; Feldmann, C.; Peters, H.; Lingemann, M.; Taube, S.; Peters, T.; Mallagaray, A. NMR Experiments Shed New Light on Glycan Recognition by Human and Murine Norovirus Capsid Proteins. Viruses 2021, 13, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dülfer, J.; Kadek, A.; Kopicki, J.D.; Krichel, B.; Uetrecht, C. Structural mass spectrometry goes viral. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 105, 189–238. [Google Scholar]
- Taube, S.; Kolawole, A.O.; Höhne, M.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Handley, S.A.; Perry, J.W.; Thackray, L.B.; Akkina, R.; Wobus, C.E. A Mouse Model for Human Norovirus. mBio 2013, 4, e00450-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodge, E.A.; Benhaim, M.A.; Lee, K.K. Bridging protein structure, dynamics, and function using hydrogen/deuterium-exchange mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Rand, K.D.; Beuning, P.J.; Engen, J.R. False EX1 signatures caused by sample carryover during HX MS analyses. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 302, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.K.; Koromyslova, A.; Hefele, L.; Gürth, C.-M.; Hansman, G.S. Structural Evolution of the Emerging 2014–2015 GII.17 Noroviruses. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2710–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.W.; Tan, Y.B.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lim, B.T.; Cornvik, T.; Lescar, J.; Ng, L.F.P.; Luo, D. Chikungunya virus nsP4 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase core domain displays detergent-sensitive primer extension and terminal adenylyltransferase activities. Antivir. Res. 2017, 143, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Weis, D.D.; Engen, J.R.; Lee, K.K. Analysis of Overlapped and Noisy Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectra. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 24, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Fang, P.; Chachiyo, T.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Noroviral P particle: Structure, function and applications in virus–host interaction. Virology 2008, 382, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bereszczak, J.Z.; Barbu, I.M.; Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Jiang, X.; Van Duijn, E.; Heck, A.J. Structure, stability and dynamics of norovirus P domain derived protein complexes studied by native mass spectrometry. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 177, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. The P Domain of Norovirus Capsid Protein Forms a Subviral Particle That Binds to Histo-Blood Group Antigen Receptors. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14017–14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Cao, S.; Huang, P.; Farkas, T.; Meller, J.; Hegde, R.S.; Li, X.; Rao, Z.; Jiang, X. Elucidation of strain-specific interaction of a GII-4 norovirus with HBGA receptors by site-directed mutagenesis study. Virology 2008, 379, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bu, W.; Mamedova, A.; Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Jiang, X.; Hegde, R.S. Structural Basis for the Receptor Binding Specificity of Norwalk Virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5340–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Fang, P.-A.; Zhong, W.; McNeal, M.; Wei, C.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Norovirus P Particle, a Novel Platform for Vaccine Development and Antibody Production. J. Virol. 2010, 85, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Meller, J.; Jiang, X. C-Terminal Arginine Cluster Is Essential for Receptor Binding of Norovirus Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7322–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Fang, P.-A.; Xia, M.; Chachiyo, T.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Terminal modifications of norovirus P domain resulted in a new type of subviral particles, the small P particles. Virology 2011, 410, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hageman, T.S.; Weis, D.D. A Structural Variant Approach for Establishing a Detection Limit in Differential Hydrogen Exchange-Mass Spectrometry Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8017–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Grant, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Diehnelt, C.W.; Grigorieff, N.; Joshua-Tor, L. High-resolution cryo-EM structures of outbreak strain human norovirus shells reveal size variations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12828–12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, H.Q.; Smith, T.J. The Dynamic Capsid Structures of the Noroviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tubiana, T.; Boulard, Y.; Bressanelli, S. Dynamics and asymmetry in the dimer of the norovirus major capsid protein. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pogan, R.; Dülfer, J.; Uetrecht, C. Norovirus assembly and stability. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 31, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, M.L.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape. Viruses 2019, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pogan, R.; Schneider, C.; Reimer, R.; Hansman, G.; Uetrecht, C. Norovirus-like VP1 particles exhibit isolate dependent stability profiles. J. Physics Condens. Matter 2018, 30, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoemaker, G.K.; van Duijn, E.; Crawford, S.E.; Uetrecht, C.; Baclayon, M.; Roos, W.H.; Wuite, G.J.L.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V.V.; Heck, A.J.R. Norwalk Virus Assembly and Stability Monitored by Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trcka, F.; Durech, M.; Vankova, P.; Chmelik, J.; Martinkova, V.; Hausner, J.; Kadek, A.; Marcoux, J.; Klumpler, T.; Vojtesek, B.; et al. Human Stress-inducible Hsp70 Has a High Propensity to Form ATP-dependent Antiparallel Dimers That Are Differentially Regulated by Cochaperone Binding. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hageman, T.S.; Weis, D.D. Reliable Identification of Significant Differences in Differential Hydrogen Exchange-Mass Spectrometry Measurements Using a Hybrid Significance Testing Approach. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8008–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, D.; Berkowitz, S.A.; Engen, J.R. The Utility of Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry in Biopharmaceutical Comparability Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2071–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, J.; Hickey, J.M.; Majumdar, R.; Esfandiary, R.; Bishop, S.M.; Samra, H.S.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weis, D.D.; Volkin, D.B. Hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry reveals protein interfaces and distant dynamic coupling effects during the reversible self-association of an IgG1 monoclonal antibody. mAbs 2015, 7, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavan, D.; Man, P. MSTools—Web based application for visualization and presentation of HXMS data. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 302, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, G.R.; Burke, J.E.; Ahn, N.G.; Anand, G.S.; Borchers, C.; Brier, S.; Bou-Assaf, G.M.; Engen, J.R.; Englander, S.W.; Faber, J.; et al. Recommendations for performing, interpreting and reporting hydrogen deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) experiments. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Moretti, S.; Xenarios, I.; Orobitg, M.; Montanyola, A.; Chang, J.M.; Taly, J.F.; Notredame, C. T-Coffee: A web server for the multiple sequence alignment of protein and RNA sequences using structural information and homology extension. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W13–W17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, M.; Kiefer, F.; Biasini, M.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. Modeling protein quaternary structure of homo- and hetero-oligomers beyond binary interactions by homology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.S.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Remmert, M.; Biegert, A.; Hauser, A.; Söding, J. HHblits: Lightning-fast iterative protein sequence searching by HMM-HMM alignment. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 2010, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindahl, E.; van der Spoel, H. GROMACS 2019.1 Manual, version 2019.1; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paissoni, C.; Nardelli, F.; Zanella, S.; Curnis, F.; Belvisi, L.; Musco, G.; Ghitti, M. A critical assessment of force field accuracy against NMR data for cyclic peptides containing beta-amino acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 15807–15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, P.; Kneiszl, R.C.; Marklund, E.G. MkVsites: A tool for creating GROMACS virtual sites parameters to increase performance in all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2020, 41, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, M.W.; Jorgensen, W.L. A five-site model for liquid water and the reproduction of the density anomaly by rigid, nonpolarizable potential functions. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 8910–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nosé, S.; Klein, M. Constant pressure molecular dynamics for molecular systems. Mol. Phys. 1983, 50, 1055–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Tildesley, D. Computer Simulations of Liquids; Oxford Science Publications: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Csordas, A.; Sun, Z.; Jarnuczak, A.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Ternent, T.; Campbell, D.S.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Okuda, S.; Kawano, S.; et al. The ProteomeXchange consortium in 2017: Supporting the cultural change in proteomics public data deposition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1100–D1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaino, J.A.; Csordas, A.; Del-Toro, N.; Dianes, J.A.; Griss, J.; Lavidas, I.; Mayer, G.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Ternent, T.; et al. 2016 update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D447–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| P Dimer Dataset | Protected Residues in HDX | Fucose Binding Site 1/2 | Fucose Binding Site 3/4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GII.10 Vietnam + 100 mM fucose [14] | 311–336 | - | - |
| 337–364 | N355 (chain A) R356 (chain A) | E359 (chain A) | |
| 379–399 | D385 (chain A) | W381 (chain A) | |
| 442–458 | G451 (chain B) Y452 (chain B) | L449 (chain A) | |
| GII.10 Vietnam + 10 mM HBGA B trisaccharide [12] | 336–361 | N355 (chain A) R356 (chain A) | - |
| 379–428 | D385 (chain A) | - | |
| 440–458 | G451 (chain B) Y452 (chain B) | - | |
| 483–496 | - | - | |
| GII.17 Kawasaki + 100 mM fucose [13,27] | 269–286 | - | - |
| 333–353 | T348 (chain A) R349 (chain A) | - | |
| 434–452 | G443 (chain B) Y444 (chain B) | - | |
| - | D378 (chain A) | - | |
| GII.17 Kawasaki + 10 mM HBGA B trisaccharide [13] | 333–353 | T348 (chain A) R349 (chain A) | - |
| - | G443 (chain B) Y444 (chain B) | - | |
| GII.4 MI001 + 100 mM fucose | 283–303 | NA | NA |
| 434–449 | NA | NA | |
| GII.4 MI001 + 10 mM HBGA B trisaccharide | 283–298 | NA | NA |
| 333–353 | NA | NA | |
| 434–450 | NA | NA | |
| GII.4 Saga + 100 mM fucose / GII.4 Saga + 10 mM HBGA B trisaccharide [15,21] | 283–303 | - | - |
| no coverage | D374 (chain A) | - | |
| 434–449 | G443 (chain B) Y444 (chain B) | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dülfer, J.; Yan, H.; Brodmerkel, M.N.; Creutznacher, R.; Mallagaray, A.; Peters, T.; Caleman, C.; Marklund, E.G.; Uetrecht, C. Glycan-Induced Protein Dynamics in Human Norovirus P Dimers Depend on Virus Strain and Deamidation Status. Molecules 2021, 26, 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082125
Dülfer J, Yan H, Brodmerkel MN, Creutznacher R, Mallagaray A, Peters T, Caleman C, Marklund EG, Uetrecht C. Glycan-Induced Protein Dynamics in Human Norovirus P Dimers Depend on Virus Strain and Deamidation Status. Molecules. 2021; 26(8):2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082125
Chicago/Turabian StyleDülfer, Jasmin, Hao Yan, Maxim N. Brodmerkel, Robert Creutznacher, Alvaro Mallagaray, Thomas Peters, Carl Caleman, Erik G. Marklund, and Charlotte Uetrecht. 2021. "Glycan-Induced Protein Dynamics in Human Norovirus P Dimers Depend on Virus Strain and Deamidation Status" Molecules 26, no. 8: 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082125
APA StyleDülfer, J., Yan, H., Brodmerkel, M. N., Creutznacher, R., Mallagaray, A., Peters, T., Caleman, C., Marklund, E. G., & Uetrecht, C. (2021). Glycan-Induced Protein Dynamics in Human Norovirus P Dimers Depend on Virus Strain and Deamidation Status. Molecules, 26(8), 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082125