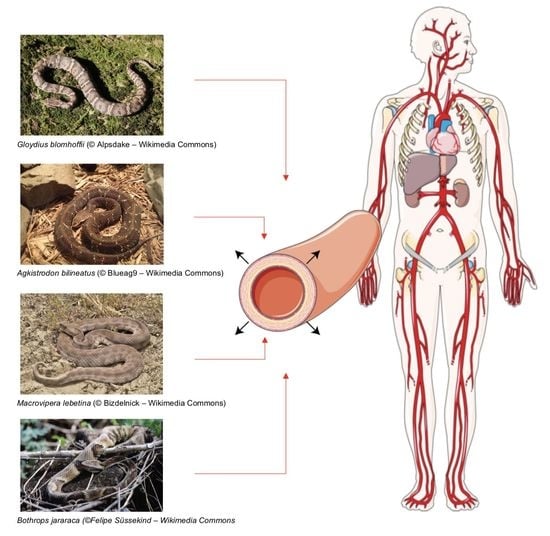
Snake Venom Components: Tools and Cures to Target Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Main Components of Snake Venom and their Effects on the Cardiovascular System
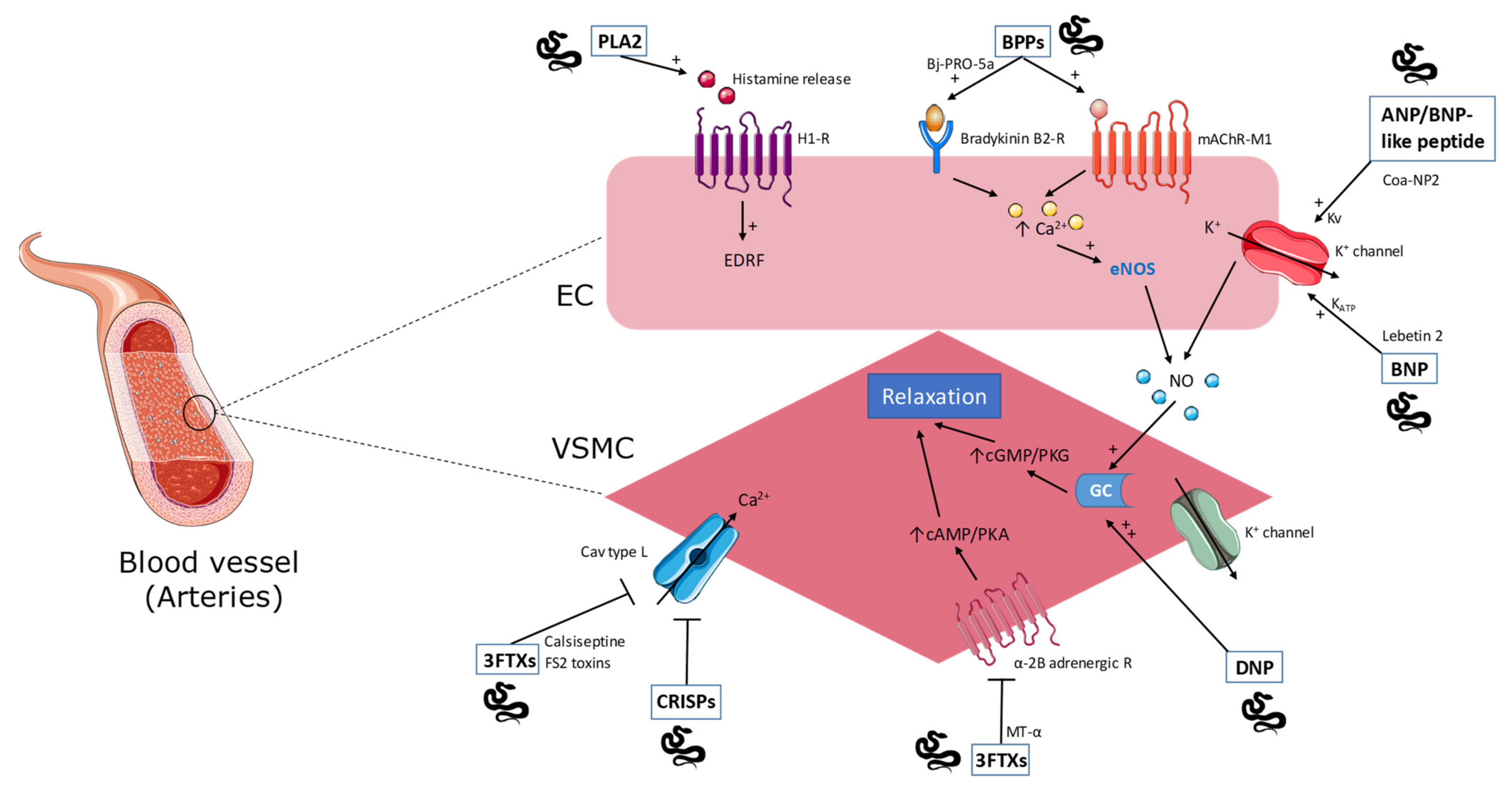
2.1. Phospholipase A2
2.2. Natriuretic Peptides
2.3. Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptides
2.4. Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins
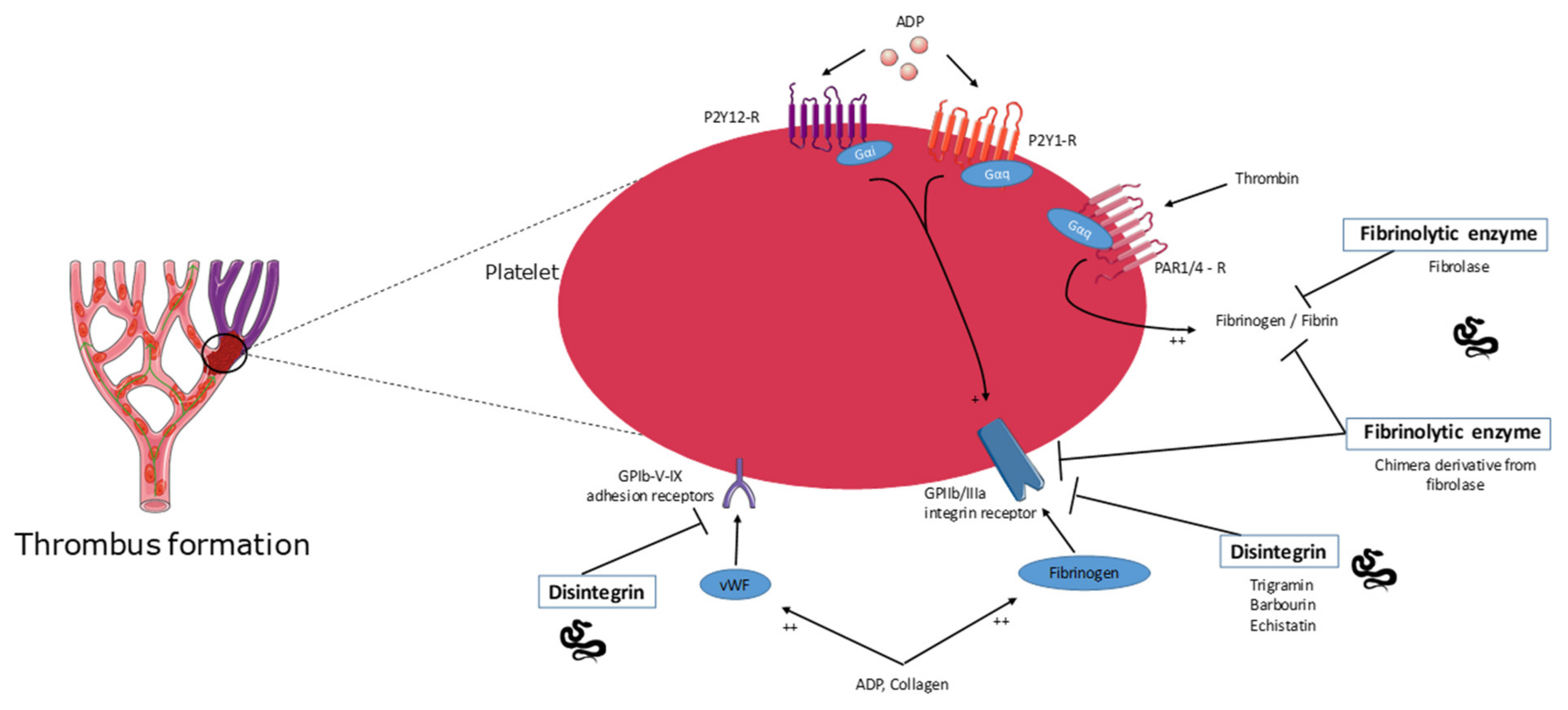
2.5. Disintegrins
2.6. Fibrinolytic Enzyme Activity
2.7. Three-Finger Toxins
3. Snake-Venom-Molecule-Based Drugs for Cardiovascular Disease
3.1. Captopril
3.2. Aggrastat
3.3. Integrilin
3.4. Defibrase
3.5. Alfimeprase
3.6. Viprinex
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fry, B.G.; Vidal, N.; Norman, J.A.; Vonk, F.J.; Scheib, H.; Ramjan, S.F.R.; Kuruppu, S.; Fung, K.; Blair Hedges, S.; Richardson, M.K.; et al. Early Evolution of the Venom System in Lizards and Snakes. Nature 2006, 439, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackessy, S.P. Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-429-18639-4. [Google Scholar]
- Utkin, Y.N. Animal Venom Studies: Current Benefits and Future Developments. WJBC 2015, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnakone, P. Snake Venoms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-94-007-6409-5. [Google Scholar]
- Amazonas, D.R.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Orefice, D.P.; Sousa, L.F.; de Martinez, M.G.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Camargo, P.B.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Evidence for Snake Venom Plasticity in a Long-Term Study with Individual Captive Bothrops Atrox. Toxins 2019, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehta, S.; Sashindran, V. Clinical Features And Management Of Snake Bite. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2002, 58, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, E.; Wilson, L.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Bhatnagar, P.; Leal, J.; Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Burns, R.; Rayner, M.; Townsend, N. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017; European Heart Network: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bordon, K.d.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Fornari-Baldo, E.C.; Pinheiro-Júnior, E.L.; Cerni, F.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A.; et al. From Animal Poisons and Venoms to Medicines: Achievements, Challenges and Perspectives in Drug Discovery. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBianco, R. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition: Unique and Effective Therapy for Hypertension and Congestive Heart Failure. Postgrad. Med. 1985, 78, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiguez, E.; Giannotti, K.C.; Viana, M.d.N.; Matsubara, M.H.; Fernandes, C.M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Teixeira, C. A Snake Venom-Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Foam Cell Formation Depending on the Activation of Factors Involved in Lipid Homeostasis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicala, C.; Cirino, G. Phospholipase A2-Induced Hypotension in the Rat and Its Pharmacological Modulation. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1993, 24, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Díaz, C.; Angulo, Y.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Role of Enzymatic Activity in Muscle Damage and Cytotoxicity Induced by Bothrops Asper Asp49 Phospholipase A2 Myotoxins: Are There Additional Effector Mechanisms Involved? PeerJ 2014, 2, e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickramaratna, J.C.; Fry, B.G.; Aguilar, M.-I.; Kini, R.M.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of a Phospholipase A2 Myotoxin from the Venom of the Irian Jayan Death Adder (Acanthophis Rugosus): Myotoxic PLA2 from A. Rugosus Venom. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakumanu, R.; Kemp-Harper, B.K.; Silva, A.; Kuruppu, S.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. An in Vivo Examination of the Differences between Rapid Cardiovascular Collapse and Prolonged Hypotension Induced by Snake Venom. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Isbister, G.K.; Tare, M.; Parkington, H.C.; Hodgson, W.C. Hypotensive and Vascular Relaxant Effects of Phospholipase A2 Toxins from Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus Scutellatus) Venom. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Mo, Y.; Qiao, L.; Wei, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xiong, Y.; He, S. Potent Histamine-Releasing Activity of Atrahagin, a Novel Snake Venom Metalloproteinase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-F.; Wei, X.; Chen, Q.-Y.; He, S.-H. Induction of Inflammatory Cell Accumulation by TM-N49 and Promutoxin, Two Novel Phospholipase A2. Toxicon 2010, 56, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, M.; Feelisch, M.; Krebber, T.; Motz, W.; Strauer, B.E. Mechanisms of Histamine-Induced Coronary Vasodilatation: H1-Receptor-Mediated Release of Endothelium-Derived Nitric Oxide. J. Vasc. Res. 1993, 30, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silveira, L.B.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Silva, F.P.; Marcussi, S.; Fuly, A.L.; Nomizo, A.; da Silva, S.L.; Stábeli, R.G.; Arantes, E.C.; et al. Isolation and Expression of a Hypotensive and Anti-Platelet Acidic Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops Moojeni Snake Venom. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 73, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, C.M.; Rey, F.M.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Sampaio, S.V.; Torqueti, M.R. Effects of Crotoxin, a Neurotoxin from Crotalus Durissus Terrificus Snake Venom, on Human Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkelä, R.; Ulvila, J.; Magga, J. Natriuretic Peptides in the Regulation of Cardiovascular Physiology and Metabolic Events. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Solinger, R. Role of Natriuretic Peptide Family in Cardiovascular Medicine. CHAMC 2009, 7, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubattu, S.; Volpe, M. Natriuretic Peptides in the Cardiovascular System: Multifaceted Roles in Physiology, Pathology and Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, T.; Otani, K.; Chiba, A.; Nishimura, H.; Tokudome, T.; Takano-Watanabe, H.; Matsuo, A.; Ishikawa, H.; Shimamoto, K.; Fukui, H.; et al. A New Secretory Peptide of Natriuretic Peptide Family, Osteocrin, Suppresses the Progression of Congestive Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J.M.; Hellermann, A. Inhibition of Cgmp Mediated Relaxation in Small Rat Coronary Arteries by Block of Ca++ Activated K+ Channels. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Nakaya, Y.; Matsuoka, S.; Saito, K.; Kuroda, Y. Atrial Natriuretic Factor and Isosorbide Dinitrate Modulate the Gating of ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels in Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johns, D.G.; Ao, Z.; Heidrich, B.J.; Hunsberger, G.E.; Graham, T.; Payne, L.; Elshourbagy, N.; Lu, Q.; Aiyar, N.; Douglas, S.A. Dendroaspis Natriuretic Peptide Binds to the Natriuretic Peptide Clearance Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitz, H.; Vigne, P.; Moinier, D.; Frelin, C.; Lazdunski, M. A New Member of the Natriuretic Peptide Family Is Present in the Venom of the Green Mamba (Dendroaspis Angusticeps). J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13928–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.L.; Dias-Junior, C.A.; Baldasso, P.A.; Damico, D.C.S.; Carvalho, B.M.A.; Garanto, A.; Acosta, G.; Oliveira, E.; Albericio, F.; Soares, A.M.; et al. Vascular Effects and Electrolyte Homeostasis of the Natriuretic Peptide Isolated from Crotalus Oreganus Abyssus (North American Grand Canyon Rattlesnake) Venom. Peptides 2012, 36, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tourki, B.; Matéo, P.; Morand, J.; Elayeb, M.; Godin-Ribuot, D.; Marrakchi, N.; Belaidi, E.; Messadi, E. Lebetin 2, a Snake Venom-Derived Natriuretic Peptide, Attenuates Acute Myocardial Ischemic Injury through the Modulation of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore at the Time of Reperfusion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, J.S.A.M.; Martins, A.M.C.; Nascimento, N.R.F.; Sousa, C.M.; Alves, R.S.; Toyama, D.O.; Toyama, M.H.; Evangelista, J.J.F.; Menezes, D.B.; de Fonteles, M.C.; et al. Renal and Vascular Effects of the Natriuretic Peptide Isolated from Crotalus Durissus Cascavella Venom. Toxicon 2008, 52, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Pierre, L.; Flight, S.; Masci, P.P.; Hanchard, K.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; de Jersey, J.; Lavin, M.F. Cloning and Characterisation of Natriuretic Peptides from the Venom Glands of Australian Elapids. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amininasab, M.; Elmi, M.M.; Endlich, N.; Endlich, K.; Parekh, N.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Schaller, J.; Mostafavi, H.; Sattler, M.; Sarbolouki, M.N.; et al. Functional and Structural Characterization of a Novel Member of the Natriuretic Family of Peptides from the Venom of Pseudocerastes Persicus. FEBS Lett. 2004, 557, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, B.G.; Wickramaratana, J.C.; Lemme, S.; Beuve, A.; Garbers, D.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P. Novel Natriuretic Peptides from the Venom of the Inland Taipan (Oxyuranus Microlepidotus): Isolation, Chemical and Biological Characterisation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianzer, D.; Konno, K.; Marques-Porto, R.; Vieira Portaro, F.C.; Stöcklin, R.; Martins de Camargo, A.C.; Pimenta, D.C. Identification of Five New Bradykinin Potentiating Peptides (BPPs) from Bothrops Jararaca Crude Venom by Using Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry after a Two-Step Liquid Chromatography. Peptides 2004, 25, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.H. A Bradykinin-Potentiating Factor (BPF) Present in the Venom of Bothrops Jararaca. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1965, 24, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Greene, L.J. Bradykinin Potentiating Peptide PCA-Lys-Trp-Ala-Pro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1971, 20, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyer, G.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Isaac, R.E.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular Recognition and Regulation of Human Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity by Natural Inhibitory Peptides. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, K.L.P.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; Bruni, F.M.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Ulrich, H.; Lameu, C. Bj-PRO-5a, a Natural Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor, Promotes Vasodilatation Mediated by Both Bradykinin B2 and M1 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negraes, P.D.; Lameu, C.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; Melo, R.L.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Ulrich, H. The Snake Venom Peptide Bj-PRO-7a Is a M1 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist. Cytometry 2011, 79A, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lameu, C.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; Guerreiro, J.R.; Oliveira, E.F.; Lebrun, I.; Pontieri, V.; Morais, K.L.P.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Ulrich, H. The Central Nervous System as Target for Antihypertensive Actions of a Proline-Rich Peptide from Bothrops Jararaca Venom. Cytometry 2010, 77, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lameu, C.; Pontieri, V.; Guerreiro, J.R.; Oliveira, E.F.; da Silva, C.A.; Giglio, J.M.; Melo, R.L.; Campos, R.R.; de Camargo, A.C.M.; Ulrich, H. Brain Nitric Oxide Production by a Proline-Rich Decapeptide from Bothrops Jararaca Venom Improves Baroreflex Sensitivity of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cintra, A.C.O.; Vieira, C.A.; Giglio, J.R. Primary Structure and Biological Activity of Bradykinin Potentiating Peptides from Bothrops Insularis Snake Venom. J. Protein Chem. 1990, 9, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.R.; Oliveira-Carvalho, A.L.; Wermelinger, L.S.; Zingali, R.B.; Ho, P.L.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.d.L.M.; Diniz, M.R.V. Identification of Novel Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptides and C-Type Natriuretic Peptide from Lachesis Muta Venom. Toxicon 2005, 46, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, A.; Zahid, A.; Negm, A.; Akrem, A.; Spencer, P.; Betzel, C. Isolation and Characterization of Bradykinin Potentiating Peptides from Agkistrodon Bilineatus Venom. Proteome Sci. 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro-Júnior, E.L.; Boldrini-França, J.; de Campos Araújo, L.M.P.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Bendhack, L.M.; Cilli, E.M.; Arantes, E.C. LmrBPP9: A Synthetic Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide from Lachesis Muta Rhombeata Venom That Inhibits the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity in Vitro and Reduces the Blood Pressure of Hypertensive Rats. Peptides 2018, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, D.M.; Junior, N.E.G.; Costa, P.P.C.; Martins, P.L.; Santos, C.F.; Carvalho, E.D.F.; Carvalho, M.D.F.; Pimenta, D.C.; Cardi, B.A.; Fonteles, M.C.; et al. A New Structurally Atypical Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide Isolated from Crotalus Durissus Cascavella Venom (South American Rattlesnake). Toxicon 2014, 90, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adade, C.M.; Carvalho, A.L.O.; Tomaz, M.A.; Costa, T.F.R.; Godinho, J.L.; Melo, P.A.; Lima, A.P.C.A.; Rodrigues, J.C.F.; Zingali, R.B.; Souto-Padrón, T. Crovirin, a Snake Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein (CRISP) with Promising Activity against Trypanosomes and Leishmania. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Koike, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Motoyoshi, K.; Wada, T.; Hishinuma, S.; Mita, M.; Morita, T. Cloning and Characterization of Novel Snake Venom Proteins That Block Smooth Muscle Contraction: Novel Proteins in Snake Venoms. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Hyodo, F.; Morita, T. Wide Distribution of Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins in Snake Venoms: Isolation and Cloning of Novel Snake Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 412, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntravat, M.; Cromer, W.E.; Marquez, J.; Galan, J.A.; Zawieja, D.C.; Davies, P.; Salazar, E.; Sánchez, E.E. The Isolation and Characterization of a New Snake Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein (SvCRiSP) from the Venom of the Southern Pacific Rattlesnake and Its Effect on Vascular Permeability. Toxicon 2019, 165, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Mercado, E.A.; Garza-Ocañas, L. Disintegrins Obtained from Snake Venom and Their Pharmacological Potential. Med. Univ. 2017, 19, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda Macedo, J.; Fox, J.; Souza Castro, M. Disintegrins from Snake Venoms and Their Applications in Cancer Research and Therapy. CPPS 2015, 16, 532–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cañas, C.A.; Castaño-Valencia, S.; Castro-Herrera, F.; Cañas, F.; Tobón, G.J. Biomedical Applications of Snake Venom: From Basic Science to Autoimmunity and Rheumatology. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.J.; Huang, T.F.; Rucinski, B.; Strzyzewski, M.; Tuma, R.F.; Williams, J.A.; Niewiarowski, S. Inhibition of Platelet Hemostatic Plug Formation by Trigramin, a Novel RGD-Peptide. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1989, 256, H1038–H1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-F.; Ouyang, C. Action Mechanism of the Potent Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor from Snake Venom. Thromb. Res. 1984, 33, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.R.; Gould, R.J.; Jacobs, J.W.; Friedman, P.A.; Polokoff, M.A. Echistatin. A Potent Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor from the Venom of the Viper, Echis Carinatus. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 19827–19832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, R.M.; Rose, J.W.; Hsu, M.A.; Phillips, D.R.; Fried, V.A.; Campbell, A.M.; Nannizzi, L.; Charo, I.F. Barbourin. A GPIIb-IIIa-Specific Integrin Antagonist from the Venom of Sistrurus m. Barbouri. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9359–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, R.M.; Naughton, M.A.; Teng, W.; Rose, J.W.; Phillips, D.R.; Nannizzi, L.; Arfsten, A.; Campbell, A.M.; Charo, I.F. Design of Potent and Specific Integrin Antagonists. Peptide Antagonists with High Specificity for Glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-F.; Wu, Y.-J.; Ouyang, C. Characterization of a Potent Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor from Agkistrodon Rhodostoma Snake Venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1987, 925, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur-Fu, H.; Chao-Zong, L.; Chaoho, O.; Che-Ming, T. Halysin, an Antiplatelet Arg-Gly-Asp-Containing Snake Venom Peptide, as Fibrinogen Receptor Antagonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Angulo, Y.; Jiménez, R.; Lomonte, B. Isolation of Bothrasperin, a Disintegrin with Potent Platelet Aggregation Inhibitory Activity, from the Venom of the Snake Bothrops Asper. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2003, 51, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Didisheim, P.; Lewis, J.H. Fibrinolytic and Coagulant Activities of Certain Snake Venoms and Proteases. Exp. Biol. Med. 1956, 93, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikha, M.; Schmitmeier, S.; Markland, F.S. Purification and Characterization of Fibrolase Isoforms from Venom of Individual Southern Copperhead (Agkistrodon Contortrix Contortrix) Snakes. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.K.; Gaddis, R.R.; Tennant, K.D.; Lacz, J.P. Biological and Thrombolytic Properties of Fibrolase—A New Fibrinolytic Protease from Snake Venom. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 1990, 20, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Bush, L.R.; Markland, F.S. Chimeric Derivative of Fibrolase, a Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Southern Copperhead Venom, Possesses Inhibitory Activity on Platelet Aggregation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 384, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siigur, J.; Samel, M.; Tõnismägi, K.; Subbi, J.; Siigur, E.; Tu, A.T. Biochemical Characterization of Lebetase, a Direct-Acting Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Vipera Lebetina Snake Venom. Thromb. Res. 1998, 90, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfimeprase. Drugs R D 2008, 9, 185–190. [CrossRef]
- Girish, V.M.; Kumar, S.; Joseph, L.; Jobichen, C.; Kini, R.M.; Sivaraman, J. Identification and Structural Characterization of a New Three-Finger Toxin Hemachatoxin from Hemachatus Haemachatus Venom. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Arrahman, A.; Xie, C.; Casewell, N.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Kool, J.; Cardoso, F.C. Multifunctional Toxins in Snake Venoms and Therapeutic Implications: From Pain to Hemorrhage and Necrosis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Weille, J.R.; Schweitz, H.; Maes, P.; Tartar, A.; Lazdunski, M. Calciseptine, a Peptide Isolated from Black Mamba Venom, Is a Specific Blocker of the L-Type Calcium Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2437–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.X.; Itahara, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Chen, Y.-N.; Kimura, T.; Sakakibara, S. Smooth Muscle Relaxing and Hypotensive Activities of Synthetic Calciseptine and the Homologous Snake Venom Peptide FS2. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 68, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koivula, K.; Rondinelli, S.; Näsman, J. The Three-Finger Toxin MTα Is a Selective Α2B-Adrenoceptor Antagonist. Toxicon 2010, 56, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, C.; Sarkar, A.; Sistla, S.; Chakrabarty, D. Anti-Platelet Activity of a Three-Finger Toxin (3FTx) from Indian Monocled Cobra (Naja Kaouthia) Venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, T.N.; Naumann, G.B.; Peixoto, P.; Rouver, W.N.; Gomes, H.L.; Campos, F.V.; Borges, M.H.; dos Santos, R.L.; Bissoli, N.S.; Sanchez, E.F.; et al. Bothrops Leucurus Venom Induces Acute Hypotension in Rats by Means of Its Phospholipase A2 (BlD-PLA2). Toxicon 2020, 185, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ye, X.; Ming, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Su, W.; Kong, Y. A Novel Direct Factor Xa Inhibitory Peptide with Anti-Platelet Aggregation Activity from Agkistrodon Acutus Venom Hydrolysates. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tadokoro, T.; M Modahl, C.; Maenaka, K.; Aoki-Shioi, N. Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins (CRISPs) from Venomous Snakes: An Overview of the Functional Diversity in a Large and Underappreciated Superfamily. Toxins 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernyshenko, V.; Petruk, N.; Korolova, D.; Kasatkina, L.; Gornytska, O.; Platonova, T.; Chernyshenko, T.; Rebriev, A.; Dzhus, O.; Garmanchuk, L.; et al. Antiplatelet and Anti-Proliferative Action of Disintegrin from Echis Multisquamatis Snake Venom. Croat. Med. J. 2017, 58, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.-J.; Chung, C.-H.; Huang, T.-F. From Discovery of Snake Venom Disintegrins to A Safer Therapeutic Antithrombotic Agent. Toxins 2019, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ondetti, M.A.; Williams, N.J.; Sabo, E.; Pluscec, J.; Weaver, E.R.; Kocy, O. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors from the Venom of Bothrops Jararaca. Isolation, Elucidation of Structure, and Synthesis. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.H.; Bartelt, D.C.; Greene, L.J. Isolation of Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptides from Bothrops Jararaca Venom. Biochemistry 1970, 9, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Carretero, O.A.; Vuljaj, N.; Liao, T.-D.; Motivala, A.; Peterson, E.L.; Rhaleb, N.-E. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: A New Mechanism of Action. Circulation 2005, 112, 2436–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaman, M.A.; Oparil, S.; Calhoun, D.A. Drugs Targeting the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millgård, J.; Hägg, A.; Sarabi, M.; Lind, L. Captopril, but Not Nifedipine, Improves Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation in Hypertensive Patients. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1998, 12, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepensky, D. Pharmacokinetics of Toxin-Derived Peptide Drugs. Toxins 2018, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valgimigli, M.; Campo, G.; Percoco, G.; Pellegrino, L.; Guardigli, G.; Ferrari, R. Tirofiban: A Critical Reappraisal of the Clinical Use, Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Future Cardiol. 2006, 2, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Juergens, C. The Role of Tirofiban in the Management of Coronary Artery Disease. CHDDT 2008, 8, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, M.J.; Lee, R.C.; Gaglia, M.A.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Torguson, R.; Pichard, A.D.; Satler, L.F.; Waksman, R. CRT-200.83 Comparison of High-Dose Bolus Tirofiban With Other Anticoagulation Strategies for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marte, F.; Sankar, P.; Cassagnol, M. Captopril. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Faruqi, A.; Jain, A. Enalapril. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovici, P.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Lelkes, P.I. From Snake Venom’s Disintegrins and C-Type Lectins to Anti-Platelet Drugs. Toxins 2019, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waheed, H.; Moin, S.F.; Choudhary, M.I. Snake Venom: From Deadly Toxins to Life-Saving Therapeutics. CMC 2017, 24, 1874–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, B.; Li, F.; Sun, Y. Meta-Analysis of Defibrase in Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2006, 119, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrör, K.; Weber, A.-A. Comparative Pharmacology of GP IIb/IIIa Antagonists. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2003, 15, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarborough, R.M. Development of Eptifibatide. Am. Heart J. 1999, 138, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Integrilin; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/integrilin (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Holleman, W.H.; Weiss, L.J. The Thrombin-like Enzyme from Bothrops Atrox Snake Venom. Properties of the Enzyme Purified by Affinity Chromatography on p-Aminobenzamidine-Substituted Agarose. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, K. Defibrinogenation with Thrombin-Like Snake Venom Enzymes. In Fibrinolytics and Antifibrinolytics; Markwardt, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 451–484. ISBN 978-3-642-66865-4. [Google Scholar]
- Toombs, C.F. Alfimeprase: Pharmacology of a Novel Fibrinolytic Metalloproteinase for Thrombolysis. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2001, 31, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.M.; Weaver, F.A.; Comerota, A.J.; Perler, B.A.; Joing, M. Efficacy and Safety of Alfimeprase in Patients with Acute Peripheral Arterial Occlusion (PAO). J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 51, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deitcher, S.R.; Toombs, C.F. Non-Clinical and Clinical Characterization of a Novel Acting Thrombolytic: Alfimeprase. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Fibrolase: Trials and Tribulations. Toxins 2010, 2, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.R.; Scher, L. Drug Evaluation: Alfimeprase, a Plasminogen-Independent Thrombolytic. IDrugs 2007, 10, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Hennerici, M.G.; Kay, R.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Lenzi, G.L.; Verstraete, M.; Orgogozo, J.M. Intravenous Ancrod for Acute Ischaemic Stroke in the European Stroke Treatment with Ancrod Trial: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathan, L.O.; Staggers, S.L. Ancrod: The Use of Snake Venom in the Treatment of Patients with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia and Thrombosis Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Nursing Management. Heart Lung 1996, 25, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempfle, C.E.; Argiriou, S.; Alesci, S.; Kucher, K.; Müller-Peltzer, H.; Rübsamen, K.; Heene, D.L. Fibrin Formation and Proteolysis during Ancrod Treatment. Evidence for Des-A-Profibrin Formation and Thrombin Independent Factor XIII Activity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 936, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Liu, M.; Counsell, C.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Lin, S.; Zhao, X. Fibrinogen Depleting Agents for Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD000091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, V.G. Ancrod Revisited: Viscoelastic Analyses of the Effects of Calloselasma Rhodostoma Venom on Plasma Coagulation and Fibrinolysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Proteins and Peptides | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic toxins | ||
| Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) | Hypotension | |
| Vasorelaxation | [21,76] | |
| Anti-atherogenic activity | ||
| Fibrinolytic enzymes | Fibrinolytic activity | [67,77] |
| Inhibition of platelet aggregation | ||
| Non-enzymatic toxins | ||
| Natriuretic peptides (NPs) | Vasorelaxation (DNP; Coa-NP2) | |
| Hypotension (Coa-NP2) | ||
| Increasing NO production (Coa-NP2) | [30,31] | |
| Cardioprotective action (Lebetin 2) | ||
| Bradykinin-potentiating peptides (BPPs) | Hypotension | [40,42,48] |
| Cysteine-rich secretory proteins (CRISPs) | Inhibition of high K+-induced contraction | [51,78] |
| Disintegrins | Inhibition of platelet aggregation | [79,80] |
| Three-finger toxins (3FTXs) | Hypotension and vasorelaxation | [73,75] |
| Inhibition of platelet aggregation | ||
| Snake Venom | Natural Peptide/Protein | Drug | Mode of Action | Indications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bothrops jararaca | Bradykinin-potentiating peptide (BPP) | Captopril/ Enalapril | ACE inhibitors | Hypertension, renal disease in diabetics and heart failure after myocardial infarction | [85,90,91] |
| Echis carinatus | Echistatin | Aggrastat/ Tirofiban | GP IIb/IIIa antagonist | Acute coronary ischemic and prevention of thrombotic complications | [58,92] |
| Sistrurus m. barbouri | Barbourin | Integrilin/ Eptifibatide | GP IIb/IIIa antagonist | Acute coronary disease and anti-thrombotic therapy | [59,80] |
| Bothrops moojeni Bothrops atrox | Batroxobin | Defibrase | Cleavage of fibrinogen Aα subunit | Acute cerebral infarction and unspecific angina pectoris (+ sudden deafness) | [93,94] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frangieh, J.; Rima, M.; Fajloun, Z.; Henrion, D.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Legros, C.; Mattei, C. Snake Venom Components: Tools and Cures to Target Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082223
Frangieh J, Rima M, Fajloun Z, Henrion D, Sabatier J-M, Legros C, Mattei C. Snake Venom Components: Tools and Cures to Target Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules. 2021; 26(8):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082223
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrangieh, Jacinthe, Mohamad Rima, Ziad Fajloun, Daniel Henrion, Jean-Marc Sabatier, Christian Legros, and César Mattei. 2021. "Snake Venom Components: Tools and Cures to Target Cardiovascular Diseases" Molecules 26, no. 8: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082223
APA StyleFrangieh, J., Rima, M., Fajloun, Z., Henrion, D., Sabatier, J. -M., Legros, C., & Mattei, C. (2021). Snake Venom Components: Tools and Cures to Target Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules, 26(8), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082223