Fabrication and Analysis of Sepiolite/Glass Microcapsules/Liquid Crystal Polymer Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
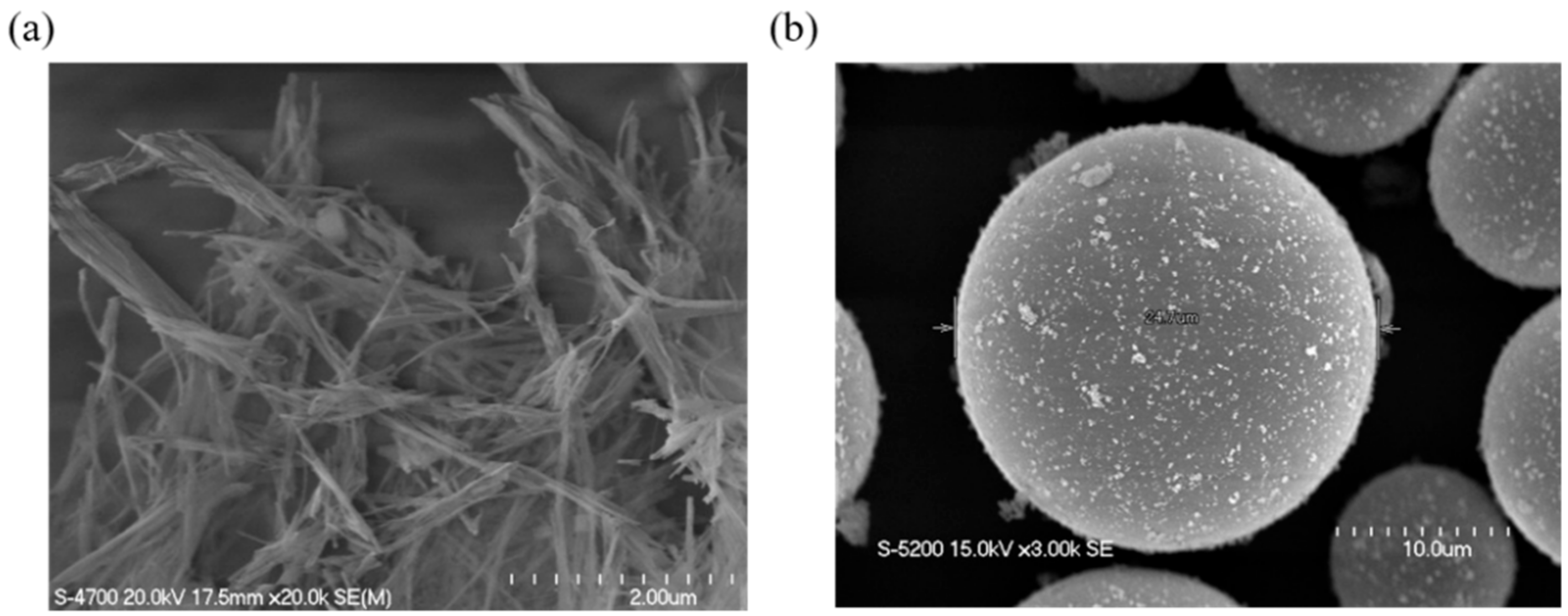
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of LCP Composites
3.3. Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability: Not available. |
References
- Aguayo, A. Opportunities for High Frequency Materials in 5G and the IoT. Microw. J. 2017, 60, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.S.; Naveena, P.; Sravani, K.G. Materials Impact on the Performance Analysis and Optimization of RF MEMS Switch for 5G Reconfigurable Antenna. Trans. Electr. Electron. 2019, 20, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Fu, X.F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.M.; Yuan, D.S.; Liu, P.G. Millimeter wave absorbing property of flexible graphene/acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber composite in 5G frequency band. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2019, 58, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maex, K.; Baklanov, M.R.; Shamiryan, D.; Iacopi, F.; Brongersma, S.H.; Yanovitskaya, Z.S. Low dielectric constant materials for microelectronics. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 8793–8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Lee, C.Y.; Hung, W.J.; Chen, G.S.; Fang, J.S. Electrical and reliability characteristics of dielectric stack with low dielectric constant SiCOH and capping SiCNH films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklanov, M.R.; Maex, K. Porous low dielectric constant materials for microelectronics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2006, 364, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.R.; Naskar, A.K.; Harrison, G.M.; Ogale, A.A. Thermal and shear flow effects on microstructure of a thermotropic liquid crystalline polymer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Mansfield, C.D.; Baird, D.G. Extrusion Blow Molding of Polymeric Blends Based on Thermotropic Liquid Crystalline Polymer and High Density Polyethylene. Int. Polym. Proc. 2017, 32, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Guo, J.; Gong, Y. Study on in situ reinforced composites of thermoplastic resins: A novel TLCP with low melting temperature. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2016, 29, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, U.; Rao, K.V.; Rakshit, A.K. Thermotropic liquid-crystalline polymers: Synthesis, characterization, and properties of poly(azomethine esters). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikrasun, S.; Bualek-Limcharoen, S.; Kohjiya, S.; Urayama, K. Thermotropic liquid-crystalline copolyester/thermoplastic elastomer in situ composites. I. Rheology, morphology, and mechanical properties of extruded strands. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 2676–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lee, K.W.; Chung, T.S.; Jaffe, M. Rheology, morphology and properties of LCP/nylon 66 composite fibers. Polym. Compos. 2000, 21, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, H.K.; Marinov, Y.G.; Hadjichristov, G.B.; Scaramuzza, N. Characterization of polymer/liquid crystal composite based electrolyte membranes for sodium ion battery applications. Solid State Ion. 2019, 335, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Tan, C.W.; Olfatnia, M.; Miao, J.M.; Barbastathis, G.; Triantafyllou, M. A liquid crystal polymer membrane MEMS sensor for flow rate and flow direction sensing applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 085006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasinski, F.; Splingart, B.; Dubois, F.; Maschke, U.; Legrand, C. Dielectric Characterization of Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal in Microwave Range—Material Integration in Specific Electronic Devices. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 542, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Song, Y.S. Thermomechanical anisotropy and flowability of talc and glass fiber reinforced multiphase polymer composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 174, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Shi, W.; Li, J.Y.; Yang, C.L.; Xia, T.; Sheng, X.M.; Wang, X.L. Structure and Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene/Liquid Crystal Polymer Blends. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2015, 54, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarev, O.L.; Strazdovskii, V.V.; Chernov, Y.V. Experimental Investigation of the Thermophysical Characteristics of a Coating Based on Hollow Glass Microspheres. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2017, 90, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ye, F.; Gao, Y. Preparation and characterization of hollow glass microsphere ceramics and silica aerogel/hollow glass microsphere ceramics having low density and low thermal conductivity. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.P.; Hu, Y.; Jia, H.Y.; Liu, P.; Du, P.; Xu, D.Y. Acoustic and dielectric properties of epoxy resin/hollow glass microsphere composite acoustic materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 135, 109105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yuan, J.; An, Z.G.; Zhang, J.J. Effect of microstructure and physical parameters of hollow glass microsphere on insulation performance. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1992–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, B.; Amos, S.E.; D’Souza, A.S.; Clemons, C.M.; Gunes, I.S.; Ista, T.K. Improvements in processing characteristics and engineering properties of wood flour-filled high density polyethylene composite sheeting in the presence of hollow glass microspheres. J. Plast. Film Sheet 2012, 28, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.N.; Kang, D.; Cheon, S.; Shim, J.K.; Hwang, S.W. The addition effect of hollow glass microsphere on the dispersion behavior and physical properties of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkutlu, M.; Dilek, C.; Bayram, G. Effects of hollow glass microsphere density and surface modification on the mechanical and thermal properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) syntactic foams. Compos. Struct. 2018, 202, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darder, M.; Lopez-Blanco, M.; Aranda, P.; Aznar, A.J.; Bravo, J.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Microfibrous chitosan-sepiolite nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Hetzer, M.; De Kee, D. PLA/clay/wood nanocomposites: Nanoclay effects on mechanical and thermal properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, N.; Ueno, T. Comparisons between characteristic lengths and fibre equivalent diameters in glass fibre and melamine foam materials of similar flow resistivity. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivato, J.B.; Marini, J.; Pollet, E.; Yamashita, F.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; Averous, L. Elaboration, morphology and properties of starch/polyester nano-biocomposites based on sepiolite clay. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 118, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Smirnov, F.A.; Pietrement, O.; Aranda, P.; Bertrand, J.R.; Ayache, J.; Le Cam, E.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Lopez, B.S. Physical interactions between DNA and sepiolite nanofibers, and potential application for DNA transfer into mammalian cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCP | 275.37 | 3.272 | 233.5 | 3.904 |
| LCP_GF5wt% | 276.53 | 3.449 | 232.67 | 4.046 |
| LCP_Sep5wt% | 276.73 | 3.258 | 233.33 | 3.528 |
| LCP_GC5wt% | 282.04 | 3.323 | 230 | 3.628 |
| LCP_GC10wt% | 281.56 | 3.333 | 229.83 | 3.668 |
| Sample | 100 Hz | 1 MHz |
|---|---|---|
| LCP | 3.30 | 3.19 |
| LCP_GF5wt% | 3.39 | 3.25 |
| LCP_Sep5wt% | 3.45 | 3.23 |
| LCP_GC5wt% | 2.33 | 2.29 |
| LCP_GC10wt% | 2.17 | 2.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-K.; Song, Y.-S. Fabrication and Analysis of Sepiolite/Glass Microcapsules/Liquid Crystal Polymer Composites. Molecules 2021, 26, 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092522
Nam J-Y, Kim H-K, Song Y-S. Fabrication and Analysis of Sepiolite/Glass Microcapsules/Liquid Crystal Polymer Composites. Molecules. 2021; 26(9):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092522
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Ji-Yun, Hyeon-Kyeong Kim, and Young-Seok Song. 2021. "Fabrication and Analysis of Sepiolite/Glass Microcapsules/Liquid Crystal Polymer Composites" Molecules 26, no. 9: 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092522
APA StyleNam, J.-Y., Kim, H.-K., & Song, Y.-S. (2021). Fabrication and Analysis of Sepiolite/Glass Microcapsules/Liquid Crystal Polymer Composites. Molecules, 26(9), 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092522







