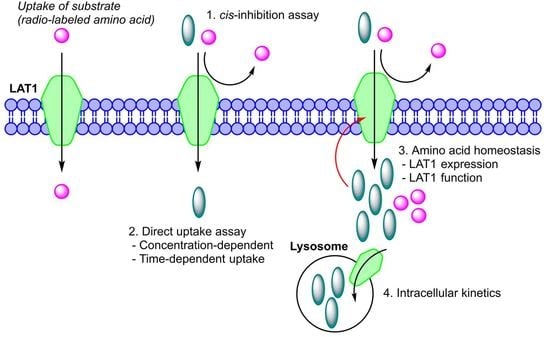
Comparison of Experimental Strategies to Study l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) Utilization by Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
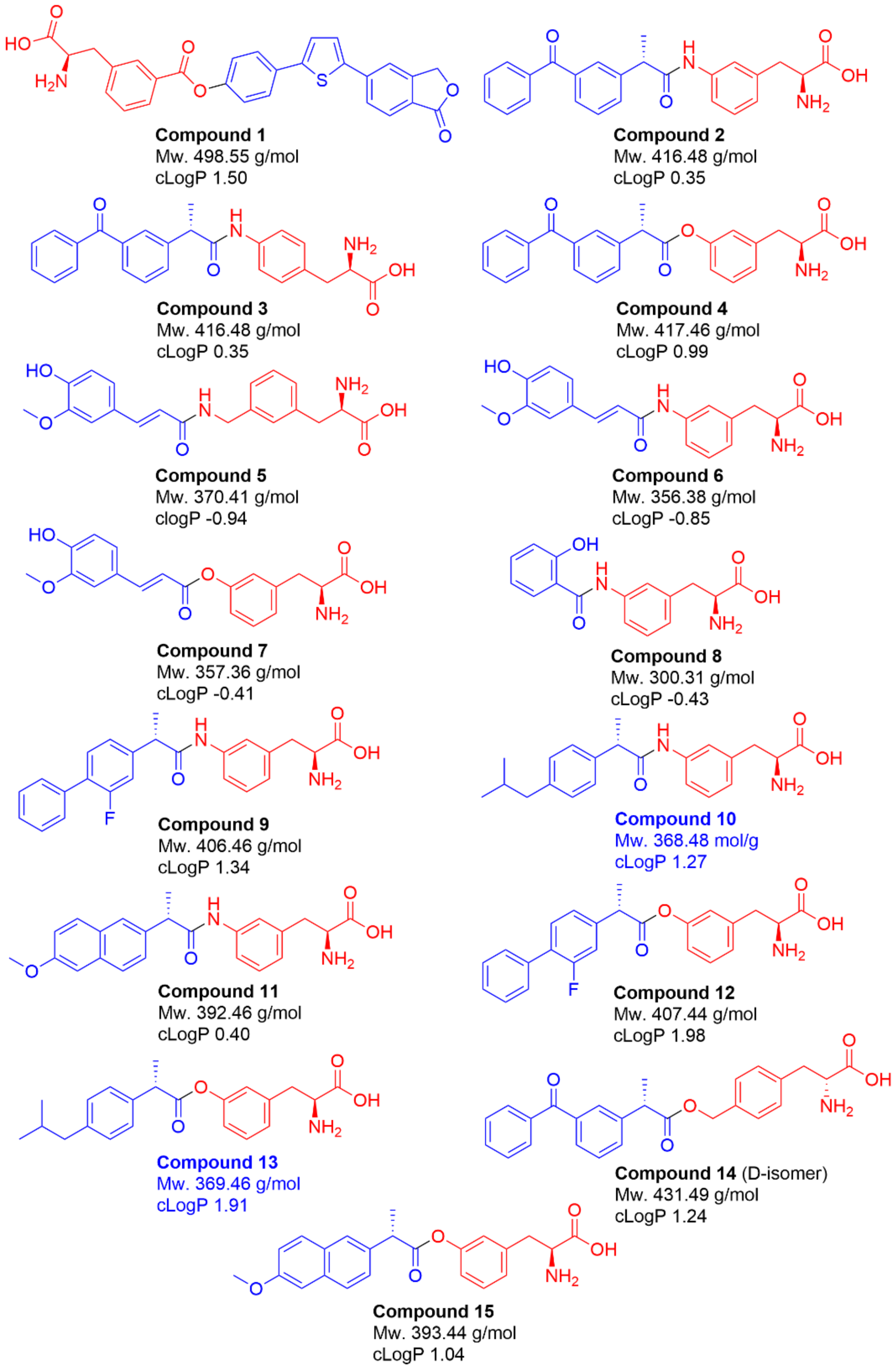
2.1. Selection of Studied Compounds
2.2. LAT1-Utilizing Compounds Can Inhibit Cellular Amino Acid Uptake
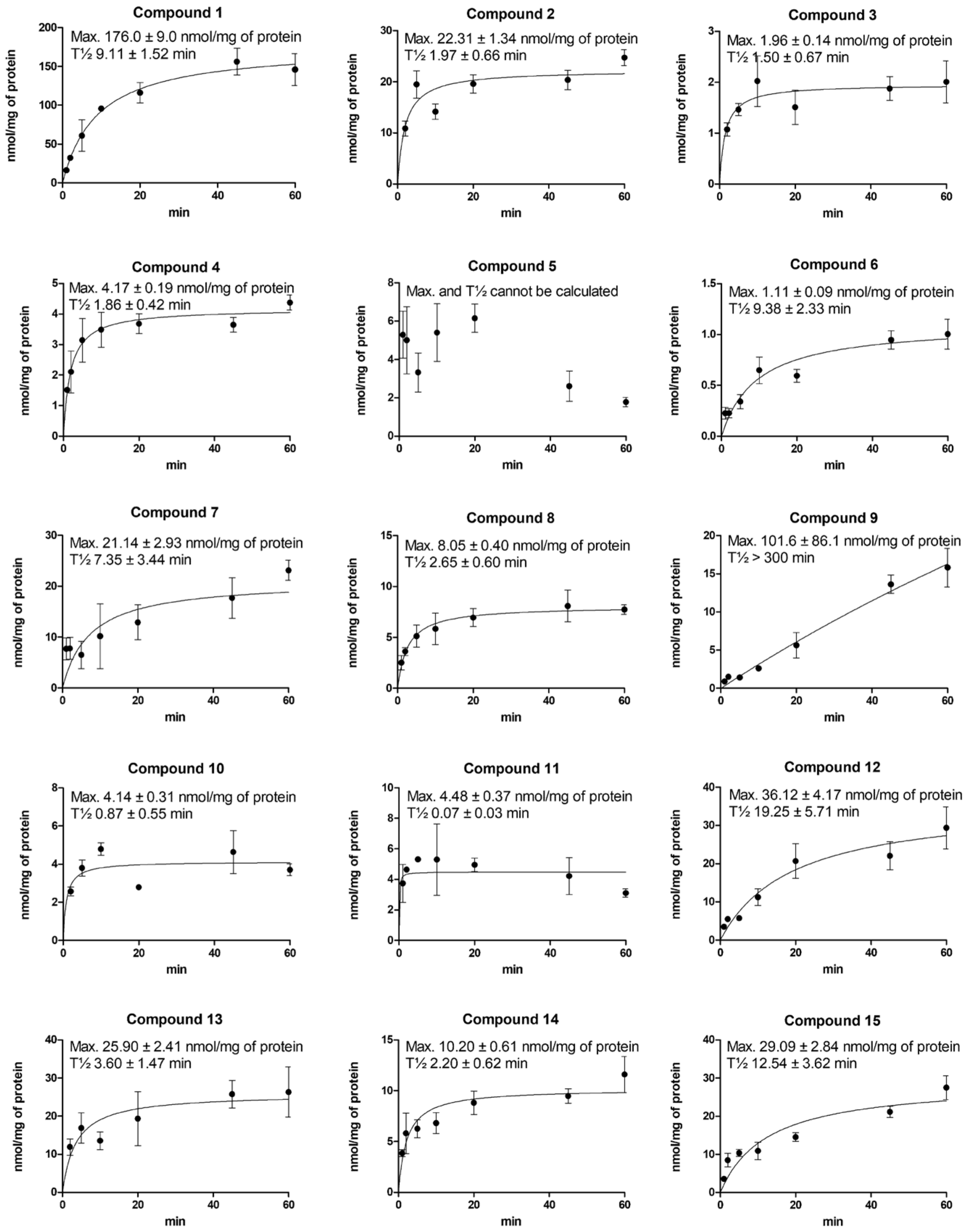
2.3. Cellular Uptake of Compounds via LAT1 Is Time- and Concentration-Dependent
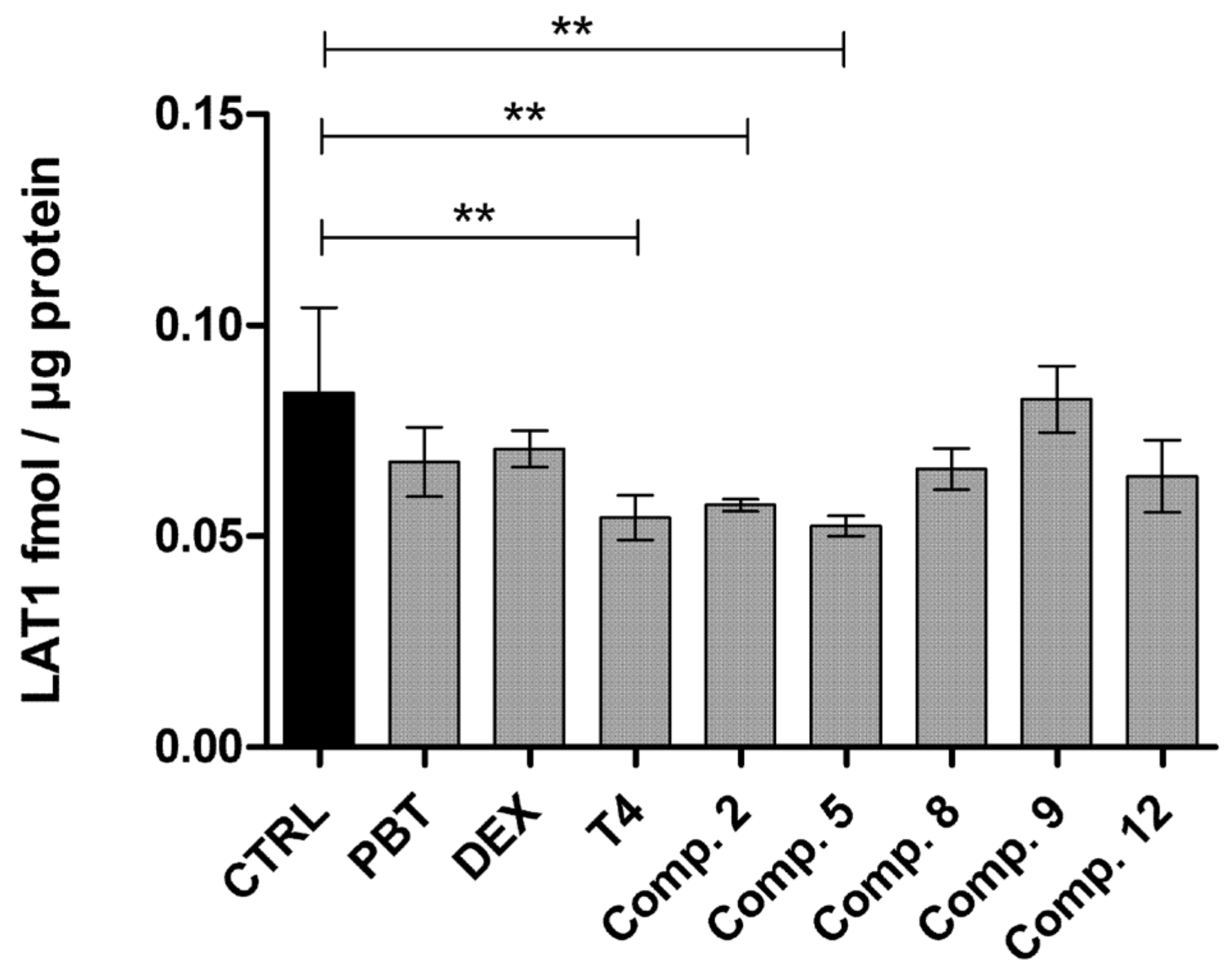
2.4. LAT1-Utilizing Prodrugs Do Not Induce the Expression or Function of LAT1
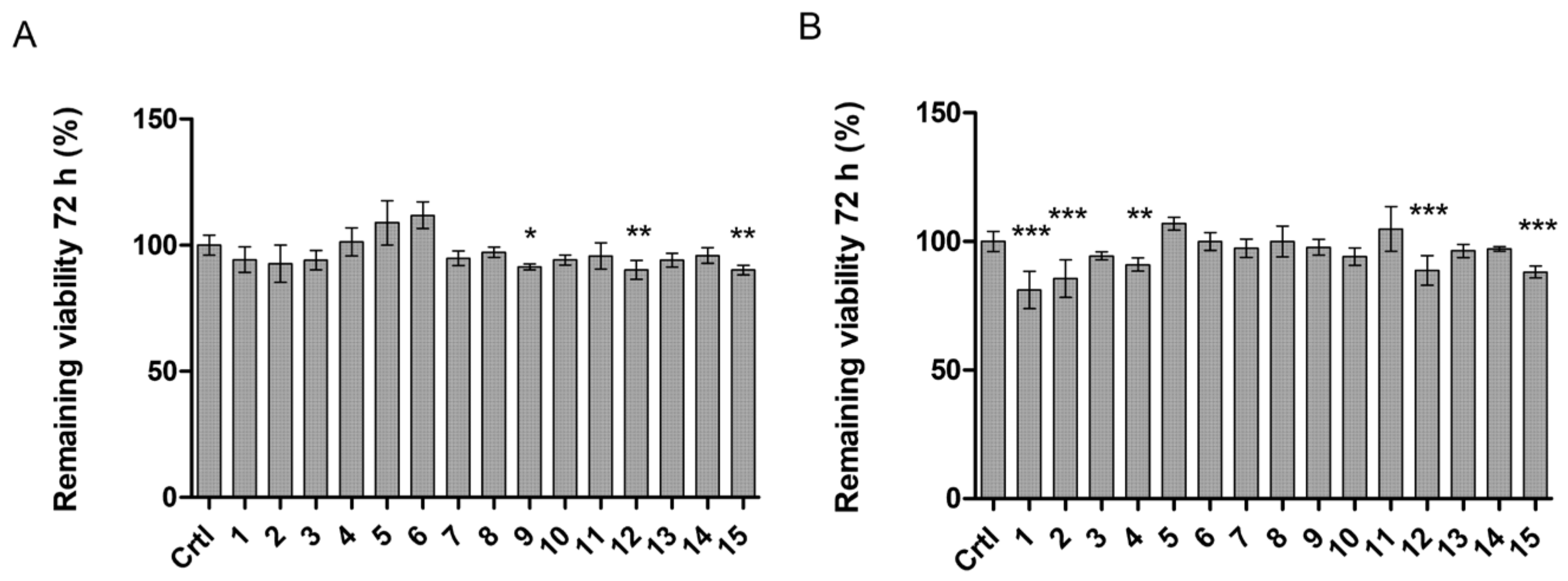
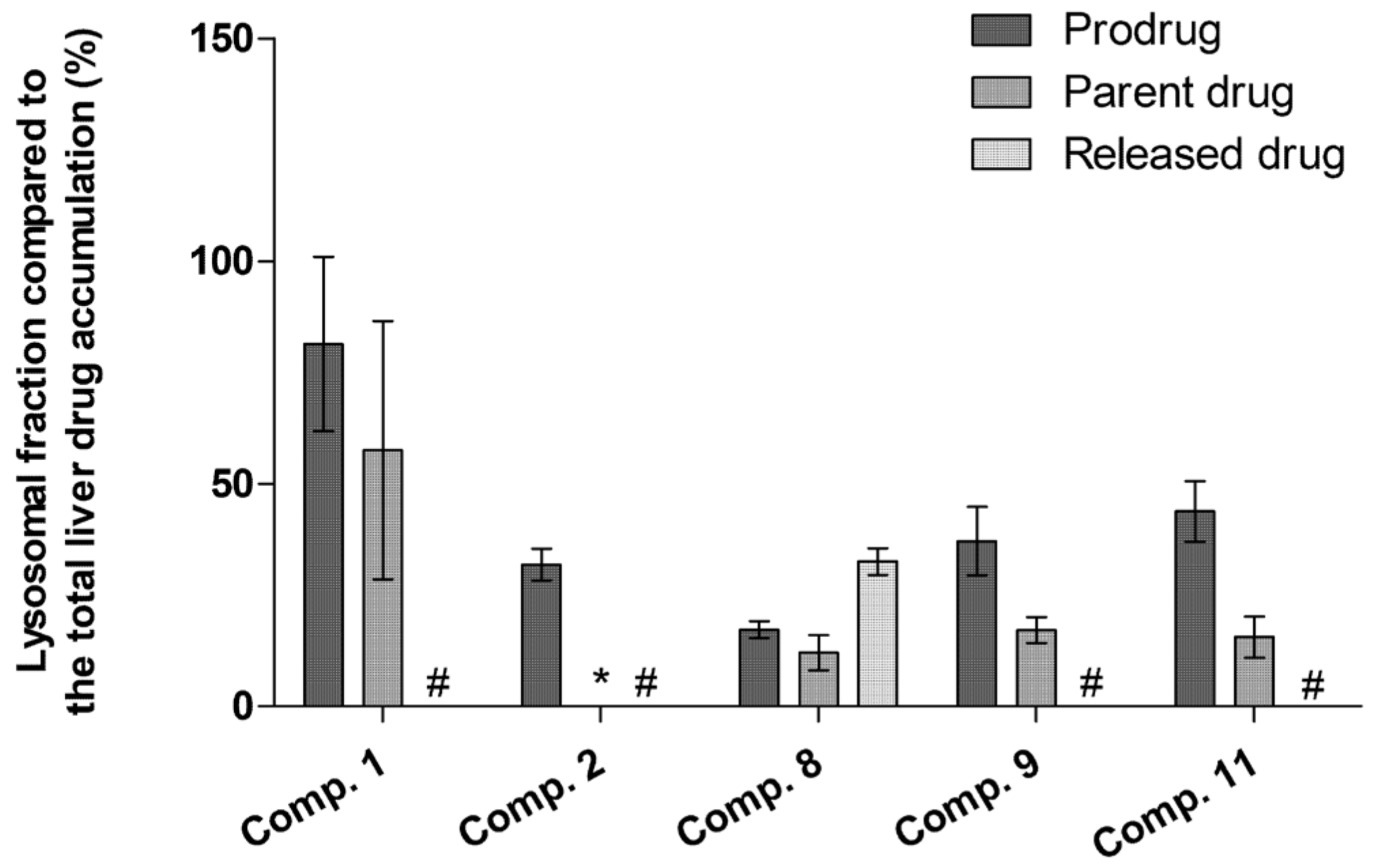
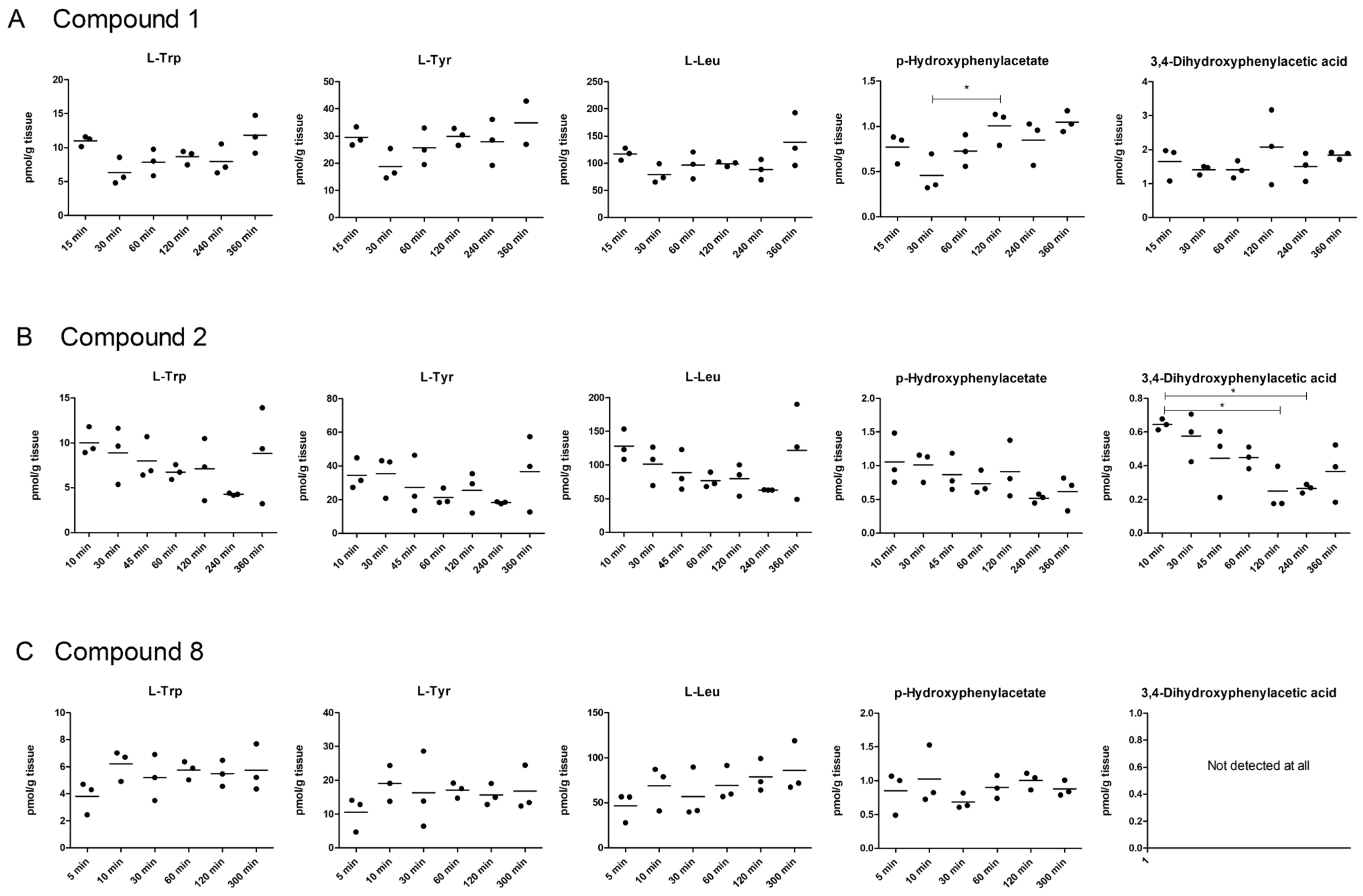
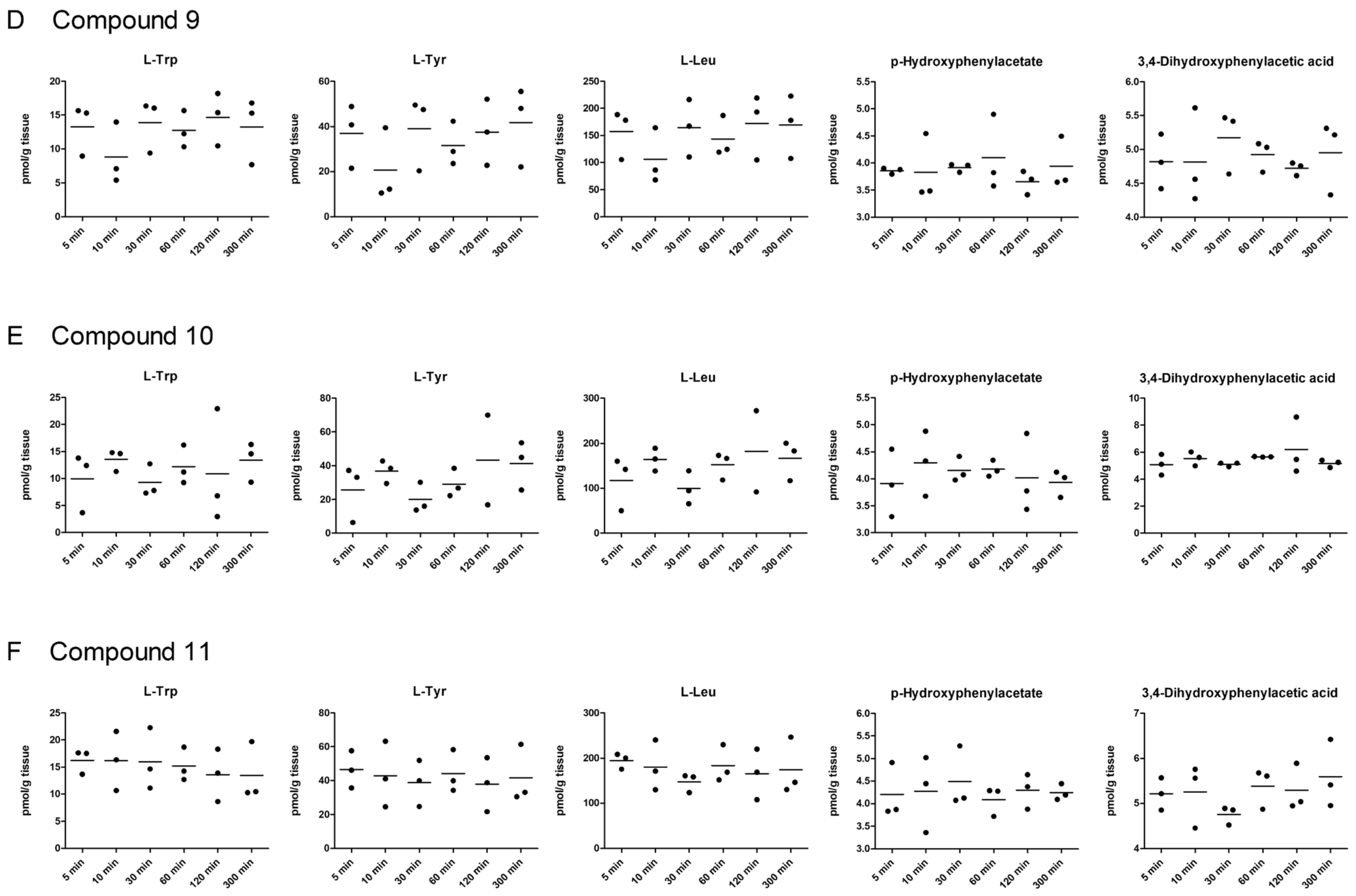
2.5. LAT1-Utilizing Compounds Accumulates into Lysosomes, but Do Not Affect Cell Viability or Brain Amino Acid Homeostasis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cis-Inhibition Studies (Ability of Compounds Bind to LAT1 and Inhibit Amino Acid Uptake)
4.4. Time-Dependent Cellular Uptake of Compounds
4.5. Concentration-Dependent Cellular Uptake of Compounds
4.6. LAT1-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Compounds
4.7. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometric (LC-MS/MS) Methods
4.8. Concentration-Dependent Cellular Uptake of L-Leucine in the Presence of the Compounds
4.9. Quantitative Expression of LAT1 on the BV2 Plasma Membrane
4.10. Cellular Viability
4.11. Animals
4.12. Lysosomal Accumulation of LAT1-Utilizing Compounds
4.13. Brain Amino Acid Homeostasis
4.14. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Uchino, H.; Kanai, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Wempe, M.F.; Chairoungdua, A.; Morimoto, E.; Anders, M.W.; Endou, H. Transport of amino acid-related compounds mediated by L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Insights into the mechanisms of substrate recognition. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalise, M.; Galluccio, M.; Console, L.; Pochini, L.; Indiveri, C. The Human SLC7A5 (LAT1): The Intriguing Histidine/Large Neutral Amino Acid Transporter and Its Relevance to Human Health. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.D.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Kekuda, R.; Rajan, D.P.; Leibach, F.H.; Ganapathy, V. Human LAT1, a subunit of system L amino acid transporter: Molecular cloning and transport function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 255, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanai, Y.; Segawa, H.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; Uchino, H.; Takeda, E.; Endou, H. Expression cloning and characterization of a transporter for large neutral amino acids activated by the heavy chain of 4F2 antigen (CD98). J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 23629–23632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Ecker, G.F. Insights into the Structure, Function, and Ligand Discovery of the Large Neutral Amino Acid Transporter 1, LAT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meier, C.; Ristic, Z.; Klauser, S.; Verrey, F. Activation of system L heterodimeric amino acid exchangers by intracellular substrates. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrey, F.; Closs, E.I.; Wagner, C.A.; Palacin, M.; Endou, H.; Kanai, Y. CATs and HATs: The SLC7 family of amino acid transporters. Pflügers Arch. 2004, 447, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanagida, O.; Kanai, Y.; Chairoungdua, A.; Kim, D.K.; Segawa, H.; Nii, T.; Cha, S.H.; Matsuo, H.; Fukushima, J.-I.; Fukasawa, Y.; et al. Human L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Characterization of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2001, 1514, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, R.; Zhao, X.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q. Structure of the human LAT1-4F2hc heteromeric amino acid transporter complex. Nature 2019, 568, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrey, F.; Jack, D.; Paulsen, I.; Saier, J.M.; Pfeiffer, R. New glycoprotein-associated amino acid transporters. J. Membr. Biol. 1999, 172, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Jin, C.; Quan, L.; Ohgaki, R.; Okuda, S.; Kusakizako, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Oda, K.; Ishitani, R.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human L-type amino acid transporter 1 in complex with glycoprotein CD98hc. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, L.; Scalise, M.; Koyioni, M.; Koutentis, P.; Catto, M.; Eberini, I.; Parravicini, C.; Palazzolo, L.; Pisani, L.; Galluccio, M.; et al. Potent inhibitors of human LAT1 (SLC7A5) transporter based on dithiazole and dithiazine compounds for development of anticancer drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 143, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustyn, E.; Finke, K.; Zur, A.A.; Hansen, L.; Heeren, N.; Chien, H.-C.; Lin, L.; Giacomini, K.M.; Colas, C.; Schlessinger, A.; et al. LAT-1 activity of meta-substituted phenylalanine and tyrosine analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2616–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chien, H.-C.; Colas, C.; Finke, K.; Springer, S.; Stoner, L.; Zur, A.A.; Venteicher, B.; Campbell, J.; Hall, C.; Flint, A.; et al. Reevaluating the Substrate Specificity of the L-Type Amino Acid Transporter (LAT1). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7358–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, E.G.; Schlessinger, A.; Fan, H.; Gable, J.E.; Irwin, J.; Sali, A.; Giacomini, K.M. Structure-based ligand discovery for the Large-neutral Amino Acid Transporter 1, LAT-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5480–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ylikangas, H.; Malmioja, K.; Peura, L.; Gynther, M.; Nwachukwu, E.O.; Leppänen, J.; Laine, K.; Rautio, J.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Huttunen, K.M.; et al. Quantitative Insight into the Design of Compounds Recognized by the L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1). ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylikangas, H.; Peura, L.; Malmioja, K.; Leppänen, J.; Laine, K.; Poso, A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Rautio, J. Structure-activity relationship study of compounds binding to large amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) based on pharmacophore modeling and in situ rat brain perfusion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, L.; Parravicini, C.; Laurenzi, T.; Guerrini, U.; Indiveri, C.; Gianazza, E.; Eberini, I. In silico Description of LAT1 Transport Mechanism at an Atomistic Level. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boado, R.J.; Li, J.Y.; Nagaya, M.; Zhang, C.; Pardridge, W.M. Selective expression of the large neutral amino acid transporter at the blood-brain barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12079–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huttunen, J.; Peltokangas, S.; Gynther, M.; Natunen, T.; Hiltunen, M.; Auriola, S.; Ruponen, M.; Vellonen, K.-S.; Huttunen, K.M. L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1/Lat1)-Utilizing Prodrugs Can Improve the Delivery of Drugs into Neurons, Astrocytes and Microglia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, B.C.; Bode, B.P. Amino acid transporters ASCT2 and LAT1 in cancer: Partners in crime? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Holst, J. L-type amino acid transport and cancer: Targeting the mTORC1 pathway to inhibit neoplasia. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nii, T.; Segawa, H.; Taketani, Y.; Tani, Y.; Ohkido, M.; Kishida, S.; Ito, M.; Endou, H.; Kanai, Y.; Takeda, E. Molecular events involved in up-regulating human Na+-independent neutral amino acid transporter LAT1 during T-cell activation. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Jutabha, P.; Endou, H.; Sagara, H.; Anzai, N. LAT1 is a critical transporter of essential amino acids for immune reactions in activated human T cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4080–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelemy, C.; André, B. Ubiquitylation and endocytosis of the human LAT1/SLC7A5 amino acid transporter. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milkereit, R.; Persaud, A.; Vanoaica, L.; Guetg, A.; Verrey, F.; Rotin, D. LAPTM4b recruits the LAT1-4F2hc Leu transporter to lysosomes and promotes mTORC1 activation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Matsushima, J.; Kimura, T.; Ueda, T.; Mizokami, A.; Kanai, Y.; Ichikawa, T. Up-Regulation of LAT1 during Antiandrogen Therapy Contributes to Progression in Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puris, E.; Gynther, M.; Huttunen, J.; Petsalo, A.; Huttunen, K.M. L-type amino acid transporter 1 utilizing prodrugs: How to achieve effective brain delivery and low systemic exposure of drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 261, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huttunen, K.M. Identification of human, rat and mouse hydrolyzing enzymes bioconverting amino acid ester prodrug of ketoprofen. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puris, E.; Gynther, M.; Huttunen, J.; Auriola, S.; Huttunen, K.M. L-type amino acid transporter 1 utilizing prodrugs of ferulic acid revealed structural features supporting the design of prodrugs for brain delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 129, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.B.; Järvinen, J.; Löffler, S.; Huttunen, J.; Auriola, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Jalkanen, A.; Huttunen, K.M. L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 Enables the Efficient Brain Delivery of Small-Sized Prodrug across the Blood-Brain Barrier and into Human and Mouse Brain Parenchymal Cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4301–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttunen, K.M.; Huttunen, J.; Aufderhaar, I.; Gynther, M.; Denny, W.A.; Spicer, J.A. L-Type amino acid transporter 1 (lat1)-mediated targeted delivery of perforin inhibitors. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 498, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampio, J.; Löffler, S.; Guillon, M.; Hugele, A.; Huttunen, J.; Huttunen, K.M. Improved l-Type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1)-mediated delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs into astrocytes and microglia with reduced prostaglandin production. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärkkäinen, J.; Gynther, M.; Kokkola, T.; Petsalo, A.; Auriola, S.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Laine, K.; Rautio, J.; Huttunen, K.M. Structural properties for selective and efficient l-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) mediated cellular uptake. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peura, L.; Malmioja, K.; Laine, K.; Leppänen, J.; Gynther, M.; Isotalo, A.; Rautio, J. Large amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) prodrugs of valproic acid: New prodrug design ideas for central nervous system delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärkkäinen, J.; Laitinen, T.; Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Montaser, A.; Lehtonen, M.; Rautio, J.; Gynther, M.; Poso, A.; Huttunen, K.M. Molecular characteristics supporting l-Type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1)-mediated translocation. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttunen, J.; Gynther, M.; Vellonen, K.-S.; Huttunen, K.M. L-Type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1)-utilizing prodrugs are carrier-selective despite having low affinity for organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs). Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 571, 118714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttunen, K.M.; Gynther, M.; Huttunen, J.; Puris, E.; Spicer, J.A.; Denny, W.A. A Selective and Slowly Reversible Inhibitor of l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) Potentiates Antiproliferative Drug Efficacy in Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5740–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, M.J.; Potter, P.M. Carboxylesterase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutzler, J.M.; Tracy, T.S. Atypical kinetic profiles in drug metabolism reactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gynther, M.; Pickering, D.S.; Spicer, J.A.; Denny, W.A.; Huttunen, K.M. Systemic and Brain Pharmacokinetics of Perforin Inhibitor Prodrugs. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2484–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorak, V.; Wiedmer, T.; Ingles-Prieto, A.; Altermatt, P.; Batoulis, H.; Bärenz, F.; Bender, E.; Digles, D.; Dürrenberger, F.; Heitman, L.H.; et al. An Overview of Cell-Based Assay Platforms for the Solute Carrier Family of Transporters. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 722889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, I.; Michard, E. High- and Low-Affinity Transport in Plants From a Thermodynamic Point of View. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forrest, L.R.; Rudnick, G. The rocking bundle: A mechanism for ion-coupled solute flux by symmetrical transporters. Physiology 2009, 24, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchida, Y.; Tachikawa, M.; Obuchi, W.; Hoshi, Y.; Tomioka, Y.; Ohtsuki, S.; Terasaki, T. A study protocol for quantitative targeted absolute proteomics (QTAP) by LC-MS/MS: Application for inter-strain differences in protein expression levels of transporters, receptors, claudin-5, and marker proteins at the blood-brain barrier in ddY, FVB, and C57BL/6J mice. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puris, E.; Gynther, M.; de Lange, E.C.; Auriola, S.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Huttunen, K.M.; Loryan, I. Mechanistic Study on the Use of the l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 for Brain Intracellular Delivery of Ketoprofen via Prodrug: A Novel Approach Supporting the Development of Prodrugs for Intracellular Targets. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3261–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Compound | IC50 (µM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14C]-L-Leu | [3H]-L-Met | [3H]-L-Trp | [3H]-L-Kynu | |
| 1 | 6.8 ± 1.4 | 8.2 ± 1.7 | 6.7 ± 1.6 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | 2.8 ± 1.5 | 3.3 ± 1.5 | 9.9 ± 1.3 | 4.3 ± 1.3 |
| 3 | 26.0 ± 1.1 | 17.1 ± 1.9 | 39.2 ± 1.5 | 11.9 ± 1.3 |
| 4 | 15.0 ± 1.3 | 26.1 ± 1.4 | 38.8 ± 3.1 | 35.3 ± 1.2 |
| 5 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 43.3 ± 1.1 |
| 6 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 54.3 ± 1.3 |
| 7 | 37.6 ± 1.8 | 13.6 ± 1.8 | 19.8 ± 1.3 | 96.8 ± 1.2 |
| 8 | 18.9 ± 1.6 1 | 12.0 ± 1.4 | 24.5 ± 2.0 | 18.1 ± 1.2 |
| 9 | 6.0 ± 1.5 1 | 1.7 ± 1.8 | 15.9 ± 7.8 | 4.7 ± 1.2 |
| 10 | 13.0 ± 1.2 1 | 9.6 ± 1.6 | 43.4 ± 1.5 | 7.7 ± 1.1 |
| 11 | 9.0 ± 1.1 1 | 10.4 ± 1.5 | 14.0 ± 1.2 | 1.8 ± 1.2 |
| 12 | 4.2 ± 1.2 1 | 4.3 ± 1.7 | 6.3 ± 1.3 | 3.0 ± 1.5 |
| 13 | 5.3 ± 1.2 1 | 9.8 ± 1.4 | 36.3 ± 1.2 | 9.7 ± 1.2 |
| 14 | 52.9 ± 1.3 1 | 32.0 ± 1.4 | 37.6 ± 1.7 | 91.5 ± 1.2 |
| 15 | 10.0 ± 1.4 1 | 25.3 ± 1.6 | 11.1 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.3 |
| Compound | IC50 (µM) | Km (µM) | Vmax (nmol/min/mg) | Inhibition Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Leu (Crtl) | - | 0.115 ± 0.007 | 3.403 ±0.055 | |
| 1 | 7 | 0.192 ± 0.0127 | 1.792 ± 0.106 | Mixed type |
| 2 | 3 | 0.202 ± 0.008 | 2.759 ± 0.066 | Mixed type |
| 3 | 10 | 0.109 ± 0.004 | 2.851 ± 0.035 | Non-competitive |
| 4 | 15 | 0.131 ± 0.020 | 1.599 ± 0.170 | Non-competitive |
| 5 | 9 | 0.057 ± 0.007 | 1.910 ± 0.057 | Un-competitive |
| 6 | 5 | 0.113 ± 0.009 | 3.224 ± 0.077 | Non-competitive |
| 7 | 38 | 0.267 ± 0.015 | 2.780 ± 0.126 | Mixed type |
| 8 | 19 | 0.071 ± 0.009 | 1.644 ± 0.073 | Un-competitive |
| 9 | 6 | 0.118 ± 0.007 | 2.422 ± 0.061 | Non-competitive |
| 10 | 13 | 0.171 ± 0.008 | 2.151 ± 0.066 | Mixed type |
| 11 | 10 | 0.098 ± 0.015 | 1.515 ± 0.125 | Non-competitive |
| 12 | 4 | 0.171 ± 0.026 | 1.513 ± 0.218 | Mixed type |
| 13 | 5 | 0.177 ± 0.028 | 2.186 ± 0.231 | Mixed type |
| 14 | 53 | 0.417 ± 0.032 | 2.622 ± 0.268 | Mixed type |
| 15 | 10 | 0.106 ± 0.012 | 1.448 ± 0.099 | Non-competitive |
| Comp. | Transport Type 1 (LAT1) | Transport Type 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vmax (pmol/mg*min) | Km (µM) | CLint (µL/min*mg) | Vmax (pmol/mg*min) | Km (µM) | CLint (µL/min*mg) | |
| 1 | 750 ± 435 | 116 ± 72 | 5067 ± 327 | 347 ± 26 | ||
| 2 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.88 ± 0.16 | 199 ± 50 | 0.004 |
| 3 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 1.9 | 49 ± 9 | 148 ± 41 | 0.33 |
| 4 | 88 ± 9 | 41 ± 6 | 2.2 | 231 ± 40 | 159 ± 45 | 1.45 |
| 5 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 77 ± 13 | 0.004 |
| 6 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 78 ± 16 | 0.003 |
| 7 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 62 ± 14 | 0.003 |
| 8 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 185 ± 10 | 41 ± 5 | 4.46 |
| 9 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | - | - | - |
| 10 | 205 ± 41 | 22 ± 6 | 9.5 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 11 | 53 ± 8 | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 44.2 | - | - | - |
| 12 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | - | - | - |
| 13 | 63 ± 8 | 8.2 ± 1.8 | 7.7 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 14 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | - | - | - |
| 15 | 280 ± 65 | 9.3 ± 2.7 | 30.1 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huttunen, J.; Agami, M.; Tampio, J.; Montaser, A.B.; Huttunen, K.M. Comparison of Experimental Strategies to Study l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) Utilization by Ligands. Molecules 2022, 27, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010037
Huttunen J, Agami M, Tampio J, Montaser AB, Huttunen KM. Comparison of Experimental Strategies to Study l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) Utilization by Ligands. Molecules. 2022; 27(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuttunen, Johanna, Mahmoud Agami, Janne Tampio, Ahmed B. Montaser, and Kristiina M. Huttunen. 2022. "Comparison of Experimental Strategies to Study l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) Utilization by Ligands" Molecules 27, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010037
APA StyleHuttunen, J., Agami, M., Tampio, J., Montaser, A. B., & Huttunen, K. M. (2022). Comparison of Experimental Strategies to Study l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) Utilization by Ligands. Molecules, 27(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010037