Implementing Complementary Approaches to Shape the Mechanism of α-Synuclein Oligomerization as a Model of Amyloid Aggregation
Abstract
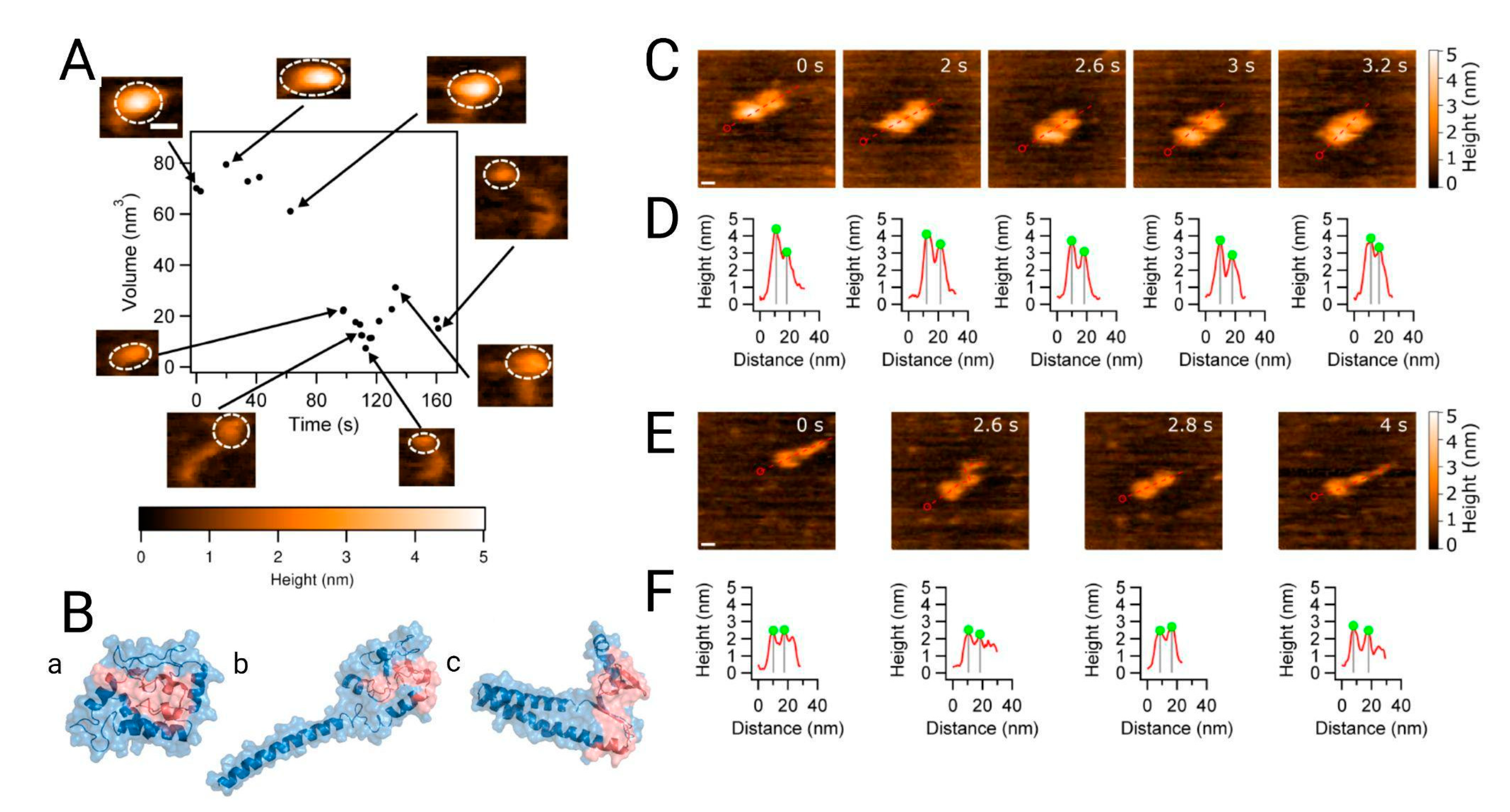
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of α-Syn Aggregation In Vitro
2.1. Monomer Aggregation Propensity Linked to Conformational Transition
2.1.1. Monomer Aggregation in the Nucleation-Polymerization Theory
2.1.2. Monomer Aggregation in Nucleation-Conversion-Polymerization Theory
2.1.3. The Conformational Dynamics of α-Syn Monomer Affect the Aggregation Process
2.1.4. Meta-Stable α-Syn Oligomers (Meta-αS-Os)
2.1.5. High and Low FRET Oligomers Subtypes
2.1.6. Towards a Combination of All Types of Aggregation Models
2.1.7. The Involvement of the Surface Hydrophobicity of Aggregates
2.2. Tetramers of α-Syn
2.3. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation
3. Mechanisms of α-Syn Aggregation in Biological Systems
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soto, C.; Pritzkow, S. Protein Misfolding, Aggregation, and Conformational Strains in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Protein Misfolding, Amyloid Formation, and Human Disease: A Summary of Progress Over the Last Decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N.; Fernández, A.; Fink, A.L. Structural and Conformational Prerequisites of Amyloidogenesis. In Protein Misfolding, Aggregation, and Conformational Diseases: Part A: Protein Aggregation and Conformational Diseases; Uversky, V.N., Fink, A.L., Eds.; Protein Reviews; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-0-387-25919-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pignataro, M.F.; Herrera, M.G.; Dodero, V.I. Evaluation of Peptide/Protein Self-Assembly and Aggregation by Spectroscopic Methods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Rahimi, F.; Sinha, S.; Maiti, P.; Bitan, G.; Murakami, K. Amyloids and Protein Aggregation-Analytical Methods. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; p. a9038. ISBN 978-0-471-97670-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, P.C.; Zhou, R.; Serpell, L.C.; Riek, R.; Knowles, T.P.; Lashuel, H.A.; Gazit, E.; Hamley, I.W.; Davis, T.P.; Fändrich, M.; et al. Half a Century of Amyloids: Past, Present and Future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5473–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Iguchi, Y.; Sahashi, K.; Katsuno, M. Significance of Oligomeric and Fibrillar Species in Amyloidosis: Insights into Pathophysiology and Treatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, H.; Katsuno, M. The Ultrastructure of Tissue Damage by Amyloid Fibrils. Molecules 2021, 26, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.T.; Scheller, R.H. Synuclein: A Neuron-Specific Protein Localized to the Nucleus and Presynaptic Nerve Terminal. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grazia Spillantini, M.; Anthony Crowther, R.; Jakes, R.; Cairns, N.J.; Lantos, P.L.; Goedert, M. Filamentous α-Synuclein Inclusions Link Multiple System Atrophy with Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 251, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating α-Synuclein Strains in Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, T.S.; Bax, A.; Cole, N.B.; Nussbaum, R.L. Structure and Dynamics of Micelle-Bound Human α-Synuclein*. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9595–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, J.; Escalona-Noguero, C.; Sot, B. Role of α-Synuclein Regions in Nucleation and Elongation of Amyloid Fiber Assembly. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Azimullah, S.; Adem, A.; Sadek, B.; Ojha, S.K. Plant Extracts and Phytochemicals Targeting α-Synuclein Aggregation in Parkinson’s Disease Models. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisi, N.; Feni, L.; Peqini, K.; Pérez-Peña, H.; Ongeri, S.; Pieraccini, S.; Pellegrino, S. α-Synuclein: An All-Inclusive Trip Around Its Structure, Influencing Factors and Applied Techniques. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 666585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.D.; Comellas, G.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Covell, D.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Kloepper, K.D.; Courtney, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Barclay, A.M.; Kendall, A.; et al. Solid-State NMR Structure of a Pathogenic Fibril of Full-Length Human α-Synuclein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremades, N.; Chen, S.W.; Dobson, C.M. Chapter Three—Structural Characteristics of α-Synuclein Oligomers. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Sandal, M., Ed.; Early Stage Protein Misfolding and Amyloid Aggregation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 329, pp. 79–143. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, G.A.P.; Silva, J.L. Alpha-Synuclein Stepwise Aggregation Reveals Features of an Early Onset Mutation in Parkinson’s Disease. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartels, T.; Choi, J.G.; Selkoe, D.J. α-Synuclein Occurs Physiologically as a Helically Folded Tetramer That Resists Aggregation. Nature 2011, 477, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, H.; Fernández, R. Navigating the Dynamic Landscape of Alpha-Synuclein Morphology: A Review of the Physiologically Relevant Tetrameric Conformation. Neural Regen Res. 2020, 15, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardenberg, M.C.; Sinnige, T.; Casford, S.; Dada, S.; Poudel, C.; Robinson, E.A.; Fuxreiter, M.; Kaminksi, C.; Kaminski-Schierle, G.S.; Nollen, E.A.A.; et al. Observation of an α-Synuclein Liquid Droplet State and Its Maturation into Lewy Body-like Assemblies. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 13, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Sahoo, B.R.; Zheng, J.; Faller, P.; Straub, J.E.; Dominguez, L.; Shea, J.-E.; Dokholyan, N.V.; De Simone, A.; et al. Amyloid Oligomers: A Joint Experimental/Computational Perspective on Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, Type II Diabetes, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 2545–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V.; Zhang, Y.; Ysselstein, D.; Rochet, J.-C.; Blanchard, S.C.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. Direct Detection of α-Synuclein Dimerization Dynamics: Single-Molecule Fluorescence Analysis. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, S.L.; Liu, D.; Wyttenbach, T.; Bowers, M.T.; Lee, J.C.; Gray, H.B.; Winkler, J.R. α-Synuclein: Stable Compact and Extended Monomeric Structures and PH Dependence of Dimer Formation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, A.S.; Gomes, A.F.; Kalapothakis, J.M.D.; Gillam, J.E.; Gasparavicius, J.; Gozzo, F.C.; Kunath, T.; MacPhee, C.; Barran, P.E. Conformational Dynamics of α-Synuclein: Insights from Mass Spectrometry. Analyst 2015, 140, 3070–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho-Cerqueira, E.; Carmo-Gonçalves, P.; Sá Pinheiro, A.; Cortines, J.; Follmer, C. α-Synuclein as an Intrinsically Disordered Monomer—Fact or Artefact? FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4915–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hashemi, M.; Lv, Z.; Williams, B.; Popov, K.I.; Dokholyan, N.V.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals Structural Dynamics of α-Synuclein Monomers and Dimers. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 123322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.N.; Jao, C.C.; Hegde, B.G.; Langen, R.; Ulmer, T.S. A Combinatorial NMR and EPR Approach for Evaluating the Structural Ensemble of Partially Folded Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8657–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uversky, V.N. The Most Important Thing Is the Tail: Multitudinous Functionalities of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Termini. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, D.; Singh, P.K.; Sahay, S.; Jha, N.N.; Jacob, R.S.; Sen, S.; Kumar, A.; Riek, R.; Maji, S.K. Structure Based Aggregation Studies Reveal the Presence of Helix-Rich Intermediate during α-Synuclein Aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliezer, D.; Kutluay, E.; Bussell, R.; Browne, G. Conformational Properties of Alpha-Synuclein in Its Free and Lipid-Associated States. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Petersen, N.O.; Claessens, M.M.A.E.; Subramaniam, V. Amyloids of Alpha-Synuclein Affect the Structure and Dynamics of Supported Lipid Bilayers. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 2585–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.W.; Drakulic, S.; Deas, E.; Ouberai, M.; Aprile, F.A.; Arranz, R.; Ness, S.; Roodveldt, C.; Guilliams, T.; De-Genst, E.J.; et al. Structural Characterization of Toxic Oligomers That Are Kinetically Trapped during α-Synuclein Fibril Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1994–E2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grupi, A.; Haas, E. Time-Resolved FRET Detection of Subtle Temperature-Induced Conformational Biases in Ensembles of α-Synuclein Molecules. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 411, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zaer, S.; Drori, P.; Zamel, J.; Joron, K.; Kalisman, N.; Lerner, E.; Dokholyan, N.V. The Structural Heterogeneity of α-Synuclein Is Governed by Several Distinct Subpopulations with Interconversion Times Slower than Milliseconds. Structure 2021, 29, 1048–1064.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhak, G.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Paik, S.R. Molecular Inscription of Environmental Information into Protein Suprastructures: Temperature Effects on Unit Assembly of α-Synuclein Oligomers into Polymorphic Amyloid Fibrils. Biochem. J. 2014, 464, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehm, L.; Svergun, D.I.; Otzen, D.E.; Vestergaard, B. Low-Resolution Structure of a Vesicle Disrupting α-Synuclein Oligomer That Accumulates during Fibrillation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3246–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenzen, N.; Nielsen, S.B.; Buell, A.K.; Kaspersen, J.D.; Arosio, P.; Vad, B.S.; Paslawski, W.; Christiansen, G.; Valnickova-Hansen, Z.; Andreasen, M.; et al. The Role of Stable α-Synuclein Oligomers in the Molecular Events Underlying Amyloid Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhak, G.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Yang, J.E.; Joo, K.; Lee, J.; Char, K.; Paik, S.R. Morphological Evaluation of Meta-Stable Oligomers of α-Synuclein with Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes-Toth, E.; Ramos, M.R.; Cappai, R.; Dalton, C.; Smith, D.P. Distinct Higher-Order α-Synuclein Oligomers Induce Intracellular Aggregation. Biochem. J. 2015, 468, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, P.; Mariani, P.; Ortore, M.G.; Plotegher, N.; Bubacco, L.; Beltramini, M.; Spinozzi, F. Comprehensive Structural and Thermodynamic Analysis of Prefibrillar WT α-Synuclein and Its G51D, E46K, and A53T Mutants by a Combination of Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering and Variational Bayesian Weighting. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 5265–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Klenerman, D. Imaging Individual Protein Aggregates to Follow Aggregation and Determine the Role of Aggregates in Neurodegenerative Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljina, M.; Garcia, G.A.; Horrocks, M.H.; Tosatto, L.; Choi, M.L.; Ganzinger, K.A.; Abramov, A.Y.; Gandhi, S.; Wood, N.W.; Cremades, N.; et al. Kinetic Model of the Aggregation of Alpha-Synuclein Provides Insights into Prion-like Spreading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1206–E1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tosatto, L.; Horrocks, M.H.; Dear, A.J.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Dalla Serra, M.; Cremades, N.; Dobson, C.M.; Klenerman, D. Single-Molecule FRET Studies on Alpha-Synuclein Oligomerization of Parkinson’s Disease Genetically Related Mutants. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Garen, C.R.; Cortez, L.M.; Petersen, N.O.; Woodside, M.T. Early Stages of Aggregation of Engineered α-Synuclein Monomers and Oligomers in Solution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rarbach, M.; Kettling, U.; Koltermann, A.; Eigen, M. Dual-Color Fluorescence Cross-Correlation Spectroscopy for Monitoring the Kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions. Methods 2001, 24, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwille, P. Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy and Its Potential for Intracellular Applications. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 34, 383–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Garen, C.R.; Petersen, N.O.; Woodside, M.T. Structural Characteristics and Membrane Interactions of Tandem α-Synuclein Oligomers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campioni, S.; Carret, G.; Jordens, S.; Nicoud, L.; Mezzenga, R.; Riek, R. The Presence of an Air–Water Interface Affects Formation and Elongation of α-Synuclein Fibrils. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Sang, J.C.; Rodrigues, M.; Carr, A.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; De, S.; Bongiovanni, M.N.; Flagmeier, P.; Dobson, C.M.; Wales, D.J.; et al. Mapping Surface Hydrophobicity of α-Synuclein Oligomers at the Nanoscale. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7494–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bongiovanni, M.N.; Godet, J.; Horrocks, M.H.; Tosatto, L.; Carr, A.R.; Wirthensohn, D.C.; Ranasinghe, R.T.; Lee, J.-E.; Ponjavic, A.; Fritz, J.V.; et al. Multi-Dimensional Super-Resolution Imaging Enables Surface Hydrophobicity Mapping. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysling, S.; Betzer, C.; Jensen, P.H.; Jorgensen, T.J.D. Characterizing the Dynamics of α-Synuclein Oligomers Using Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Monitored by Mass Spectrometry. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 9097–9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes-Toth, E.; Rempel, D.L.; Gross, M.L. Pulsed Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange Illuminates the Aggregation Kinetics of α-Synuclein, the Causative Agent for Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, R.; Lund, M.; Sparr, E.; Linse, S. Anomalous Salt Dependence Reveals an Interplay of Attractive and Repulsive Electrostatic Interactions in α-Synuclein Fibril Formation. QRB Discov. 2020, 1, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálmadóttir, T.; Malmendal, A.; Leiding, T.; Lund, M.; Linse, S. Charge Regulation during Amyloid Formation of α-Synuclein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7777–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Perovic, I.; Chittuluru, J.; Kaganovich, A.; Nguyen, L.T.T.; Liao, J.; Auclair, J.R.; Johnson, D.; Landeru, A.; Simorellis, A.K.; et al. A Soluble α-Synuclein Construct Forms a Dynamic Tetramer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17797–17802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurry, T.; Ullman, O.; Fisher, C.K.; Perovic, I.; Pochapsky, T.; Stultz, C.M. The Dynamic Structure of α-Synuclein Multimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, Y.; Delarue, P.; Scheraga, H.A.; Senet, P.; Maisuradze, G.G. From a Highly Disordered to a Metastable State: Uncovering Insights of α-Synuclein. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, A.A.; Weber, C.A.; Jülicher, F. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, S.; Singh, N.; Kumar, R.; Patel, K.; Pandey, S.; Datta, D.; Mahato, J.; Panigrahi, R.; Navalkar, A.; Mehra, S.; et al. α-Synuclein Aggregation Nucleates through Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtilerman, M.D.; Ding, T.T.; Lansbury, P.T. Molecular Crowding Accelerates Fibrillization of α-Synuclein: Could an Increase in the Cytoplasmic Protein Concentration Induce Parkinson’s Disease? Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3855–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawner, A.S.; Ray, S.; Yadav, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Panigrahi, R.; Poudyal, M.; Patel, K.; Ghosh, D.; Kummerant, E.; Kumar, A.; et al. Modulating α-Synuclein Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation. Biochemistry 2021, 48, 3676–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegert, A.; Rankovic, M.; Favretto, F.; Ukmar-Godec, T.; Strohäker, T.; Becker, S.; Zweckstetter, M. Interplay between Tau and α-Synuclein Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, R.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Ostermeier, L.; Pazurek, L.A.; Kriegler, S.; Bader, V.; Prumbaum, D.; Raunser, S.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Tatzelt, J.; et al. Remodeling of the Fibrillation Pathway of A-Synuclein by Interaction with Antimicrobial Peptide LL-III. Chemistry 2021, 27, 11845–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashuel, H.A. Rethinking Protein Aggregation and Drug Discovery in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Why We Need to Embrace Complexity? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 64, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Lewis, A.J.; Genoud, C.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castaño-Díez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease Consists of Crowded Organelles and Lipid Membranes. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trinkaus, V.A.; Riera-Tur, I.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Bäuerlein, F.J.B.; Guo, Q.; Arzberger, T.; Baumeister, W.; Dudanova, I.; Hipp, M.S.; Hartl, F.U.; et al. In Situ Architecture of Neuronal α-Synuclein Inclusions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riguet, N.; Mahul-Mellier, A.-L.; Maharjan, N.; Burtscher, J.; Croisier, M.; Knott, G.; Hastings, J.; Patin, A.; Reiterer, V.; Farhan, H.; et al. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Huntingtin Inclusions Exhibit Distinct Biochemical Composition, Interactome and Ultrastructural Properties. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, D.F.; Rodrigues, E.F.; Langohr, R.; Shahpasandzadeh, H.; Ribeiro, T.; Guerreiro, P.; Gerhardt, E.; Kröhnert, K.; Klucken, J.; Pereira, M.D.; et al. Systematic Comparison of the Effects of Alpha-Synuclein Mutations on Its Oligomerization and Aggregation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, P.; Pinho, R.; Lázaro, D.F.; Outeiro, T.F. Limelight on Alpha-Synuclein: Pathological and Mechanistic Implications in Neurodegeneration. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2013, 3, 415–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, P.J.; Kawamata, H.; Hyman, B.T. Alpha-Synuclein-Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein Fusion Proteins Form Proteasome Sensitive Inclusions in Primary Neurons. Neuroscience 2001, 104, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinknecht, A.; Popova, B.; Lázaro, D.F.; Pinho, R.; Valerius, O.; Outeiro, T.F.; Braus, G.H. C-Terminal Tyrosine Residue Modifications Modulate the Protective Phosphorylation of Serine 129 of α-Synuclein in a Yeast Model of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrington, A.J.; Yacoubian, T.A.; Slone, S.R.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A. Functional Analysis of VPS41-Mediated Neuroprotection in Caenorhabditis Elegans and Mammalian Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2142–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masaracchia, C.; König, A.; Valiente-Gabioud, A.A.; Peralta, P.; Favretto, F.; Strohäker, T.; Lázaro, D.F.; Zweckstetter, M.; Fernandez, C.O.; Outeiro, T.F. Molecular Characterization of an Aggregation-Prone Variant of Alpha-Synuclein Used to Model Synucleinopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedmon, M.M.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Christodoulou, J.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. Mapping Long-Range Interactions in α-Synuclein Using Spin-Label NMR and Ensemble Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rospigliosi, C.C.; McClendon, S.; Schmid, A.W.; Ramlall, T.F.; Barré, P.; Lashuel, H.A.; Eliezer, D. E46K Parkinson’s-Linked Mutation Enhances C-Terminal-to-N-Terminal Contacts in α-Synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 388, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Kumar, R.; Mehra, S.; Ghosh, A.; Maji, S.K.; Bhunia, A. Multitude NMR Studies of α-Synuclein Familial Mutants: Probing Their Differential Aggregation Propensities. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3605–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Nemani, V.M.; Wallender, E.K.; Kaehlcke, K.; Ott, M.; Edwards, R.H. Optical Reporters for the Conformation of α-Synuclein Reveal a Specific Interaction with Mitochondria. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12305–12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahul-Mellier, A.-L.; Burtscher, J.; Maharjan, N.; Weerens, L.; Croisier, M.; Kuttler, F.; Leleu, M.; Knott, G.W.; Lashuel, H.A. The Process of Lewy Body Formation, Rather than Simply α-Synuclein Fibrillization, Is One of the Major Drivers of Neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, C.; Sansevrino, R.; Morabito, G.; Logan, C.; Vabulas, R.M.; Ulusoy, A.; Ganzella, M.; Milovanovic, D. Synapsin Condensates Recruit Alpha-Synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giampà, M.; Amundarain, M.J.; Herrera, M.G.; Tonali, N.; Dodero, V.I. Implementing Complementary Approaches to Shape the Mechanism of α-Synuclein Oligomerization as a Model of Amyloid Aggregation. Molecules 2022, 27, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010088
Giampà M, Amundarain MJ, Herrera MG, Tonali N, Dodero VI. Implementing Complementary Approaches to Shape the Mechanism of α-Synuclein Oligomerization as a Model of Amyloid Aggregation. Molecules. 2022; 27(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiampà, Marco, María J. Amundarain, Maria Georgina Herrera, Nicolò Tonali, and Veronica I. Dodero. 2022. "Implementing Complementary Approaches to Shape the Mechanism of α-Synuclein Oligomerization as a Model of Amyloid Aggregation" Molecules 27, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010088
APA StyleGiampà, M., Amundarain, M. J., Herrera, M. G., Tonali, N., & Dodero, V. I. (2022). Implementing Complementary Approaches to Shape the Mechanism of α-Synuclein Oligomerization as a Model of Amyloid Aggregation. Molecules, 27(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010088








