Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Target Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
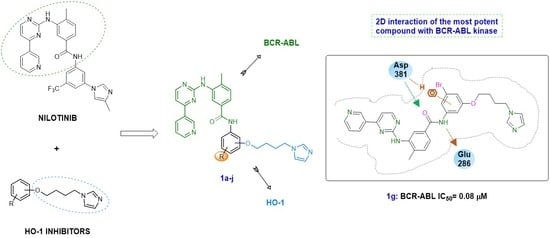
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. TK and HO-1 Inhibition
2.3. In Vitro Cytotoxic Activity on K562S and K562R Cells
2.4. Docking Studies
2.4.1. Docking Studies on BCR-ABL Kinase
2.4.2. Docking Studies on HO-1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
General Procedure for the Synthesis of Final Compounds (1a–j)
3.2. Biology
3.2.1. Preparation of Spleen Microsomal Fractions
3.2.2. Preparation of Biliverdin Reductase
3.2.3. Measurement of HO-1 Enzymatic Activity in Microsomal Fraction of Rat Spleen
3.2.4. Cell Cultures
3.2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
- (a)
- Briefly, the cell number was determined by counting the viable cells in a Burker counting chamber divided into 16 fields of 1 mm2. The percentage of viable cells was obtained by applying the following equation: % viable cells = (VC/TC) × 100, where VC = viable cells counted and TC = total cells counted (stained plus unstained cells).
- (b)
- The XTT (2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide) assay is based on the extracellular reduction of XTT by NADH produced in the mitochondria via trans-plasma membrane electron transport and an electron mediator. Reduction of XTT during the assay produces a water-soluble orange-colored formazan product. The amount of formazan was proportionate to the number of viable cells in the sample. Finally, absorbance (OD) was measured in a microplate reader (Biotek Synergy-HT, Winooski, VT, USA) at λ = 450 nm.
3.2.6. FRET-Based Z′-Lyte Assay
3.2.7. Western Blot
3.3. Docking Studies
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kurzrock, R.; Gutterman, J.U.; Talpaz, M. The molecular genetics of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J.; Talpaz, M.; Resta, D.J.; Peng, B.; Buchdunger, E.; Ford, J.M.; Lydon, N.B.; Kantarjian, H.; Capdeville, R.; Ohno-Jones, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hochhaus, A.; O’Brien, S.G.; Guilhot, F.; Druker, B.J.; Branford, S.; Foroni, L.; Goldman, J.M.; Muller, M.C.; Radich, J.P.; Rudoltz, M.; et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breccia, M.; Alimena, G. Second-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (Tki) as Salvage Therapy for Resistant or Intolerant Patients to Prior TKIs. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, e2014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.E.; Basak, G.W.; Kim, D.W.; Olavarria, E.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Apperley, J.F.; Hughes, T.; Niederwieser, D.; Mauro, M.J.; Chuah, C.; et al. Overall survival with ponatinib versus allogeneic stem cell transplantation in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias with the T315I mutation. Cancer 2017, 123, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.D.; Etienne, G.; Dorlhiac-Llacer, P.E.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs. imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Yang, C.; Fang, Q.; Wei, S.X.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Hu, X.Y.; Ma, D. K562 cell line resistance to nilotinib induced in vitro and preliminary investigation of its mechanisms. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2012, 33, 906–910. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, M.S.; Reddy, M.M.; Gonneville, J.R.; DeRoo, S.C.; Podar, K.; Griffin, J.D.; Weinstock, D.M.; Sattler, M. BCR-ABL promotes the frequency of mutagenic single-strand annealing DNA repair. Blood 2009, 114, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eadie, L.N.; Dang, P.; Goyne, J.M.; Hughes, T.P.; White, D.L. ABCC6 plays a significant role in the transport of nilotinib and dasatinib, and contributes to TKI resistance in vitro, in both cell lines and primary patient mononuclear cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maines, M.D.; Gibbs, P.E. 30 some years of heme oxygenase: From a “molecular wrecking ball” to a “mesmerizing” trigger of cellular events. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 338, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, L.; Floresta, G.; Ciaffaglione, V.; Gentile, D.; Margani, F.; Turnaturi, R.; Rescifina, A.; Pittala, V. Progress in the development of selective heme oxygenase-1 inhibitors and their potential therapeutic application. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intagliata, S.; Salerno, L.; Ciaffaglione, V.; Leonardi, C.; Fallica, A.N.; Carota, G.; Amata, E.; Marrazzo, A.; Pittala, V.; Romeo, G. Heme Oxygenase-2 (HO-2) as a therapeutic target: Activators and inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waza, A.A.; Hamid, Z.; Ali, S.; Bhat, S.A.; Bhat, M.A. A review on heme oxygenase-1 induction: Is it a necessary evil. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, L.Y. Heme oxygenase-1: Emerging target of cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chang, L.C. A Dual Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salerno, L.; Pittala, V.; Romeo, G.; Modica, M.N.; Siracusa, M.A.; Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Barbagallo, I.; Tibullo, D.; Sorrenti, V. Evaluation of novel aryloxyalkyl derivatives of imidazole and 1,2,4-triazole as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) inhibitors and their antitumor properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, L.; Vanella, L.; Sorrenti, V.; Consoli, V.; Ciaffaglione, V.; Fallica, A.N.; Canale, V.; Zajdel, P.; Pignatello, R.; Intagliata, S. Novel mutual prodrug of 5-fluorouracil and heme oxygenase-1 inhibitor (5-FU/HO-1 hybrid): Design and preliminary in vitro evaluation. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaffaglione, V.; Intagliata, S.; Pittala, V.; Marrazzo, A.; Sorrenti, V.; Vanella, L.; Rescifina, A.; Floresta, G.; Sultan, A.; Greish, K.; et al. New Arylethanolimidazole Derivatives as HO-1 Inhibitors with Cytotoxicity against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallica, A.N.; Sorrenti, V.; D’Amico, A.G.; Salerno, L.; Romeo, G.; Intagliata, S.; Consoli, V.; Floresta, G.; Rescifina, A.; D’Agata, V.; et al. Discovery of Novel Acetamide-Based Heme Oxygenase-1 Inhibitors with Potent In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13373–13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floresta, G.; Carotti, A.; Ianni, F.; Sorrenti, V.; Intagliata, S.; Rescifina, A.; Salerno, L.; Di Michele, A.; Sardella, R.; Pittala, V. Chromatograpic resolution of phenylethanolic-azole racemic compounds highlighted stereoselective inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 by (R)-enantiomers. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greish, K.F.; Salerno, L.; Al Zahrani, R.; Amata, E.; Modica, M.N.; Romeo, G.; Marrazzo, A.; Prezzavento, O.; Sorrenti, V.; Rescifina, A.; et al. Novel Structural Insight into Inhibitors of Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) by New Imidazole-Based Compounds: Biochemical and In Vitro Anticancer Activity Evaluation. Molecules 2018, 23, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irwin, M.E.; Rivera-Del Valle, N.; Chandra, J. Redox control of leukemia: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1349–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayerhofer, M.; Florian, S.; Krauth, M.T.; Aichberger, K.J.; Bilban, M.; Marculescu, R.; Printz, D.; Fritsch, G.; Wagner, O.; Selzer, E.; et al. Identification of heme oxygenase-1 as a novel BCR/ABL-dependent survival factor in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3148–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayerhofer, M.; Gleixner, K.V.; Mayerhofer, J.; Hoermann, G.; Jaeger, E.; Aichberger, K.J.; Ott, R.G.; Greish, K.; Nakamura, H.; Derdak, S.; et al. Targeting of heat shock protein 32 (Hsp32)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in leukemic cells in chronic myeloid leukemia: A novel approach to overcome resistance against imatinib. Blood 2008, 111, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibullo, D.; Barbagallo, I.; Giallongo, C.; La Cava, P.; Parrinello, N.; Vanella, L.; Stagno, F.; Palumbo, G.A.; Li Volti, G.; Di Raimondo, F. Nuclear translocation of heme oxygenase-1 confers resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 2765–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerny-Reiterer, S.; Meyer, R.A.; Herrmann, H.; Peter, B.; Gleixner, K.V.; Stefanzl, G.; Hadzijusufovic, E.; Pickl, W.F.; Sperr, W.R.; Melo, J.V.; et al. Identification of heat shock protein 32 (Hsp32) as a novel target in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorrenti, V.; Pittala, V.; Romeo, G.; Amata, E.; Dichiara, M.; Marrazzo, A.; Turnaturi, R.; Prezzavento, O.; Barbagallo, I.; Vanella, L.; et al. Targeting heme Oxygenase-1 with hybrid compounds to overcome Imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasarao, M.; Galliford, C.V.; Low, P.S. Principles in the design of ligand-targeted cancer therapeutics and imaging agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepali, K.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, M.; Bedi, P.M.; Dhar, K.L. Rational approaches, design strategies, structure activity relationship and mechanistic insights for anticancer hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 422–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Feng, Y.; Luo, K.; Gan, J.; Yingxue, L.; Wan, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Hybrid compounds as new Bcr/Abl inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, B.; Bornmann, W.G.; Pellicena, P.; Schindler, T.; Veach, D.R.; Miller, W.T.; Clarkson, B.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal structures of the kinase domain of c-Abl in complex with the small molecule inhibitors PD173955 and imatinib (STI-571). Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.N.; Vukomanovic, D.; Vlahakis, J.Z.; Szarek, W.A.; Nakatsu, K.; Jia, Z. Structural insights into human heme oxygenase-1 inhibition by potent and selective azole-based compounds. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Roux, B. Explaining why Gleevec is a specific and potent inhibitor of Abl kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floresta, G.; Pittala, V.; Sorrenti, V.; Romeo, G.; Salerno, L.; Rescifina, A. Development of new HO-1 inhibitors by a thorough scaffold-hopping analysis. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floresta, G.; Amata, E.; Gentile, D.; Romeo, G.; Marrazzo, A.; Pittala, V.; Salerno, L.; Rescifina, A. Fourfold Filtered Statistical/Computational Approach for the Identification of Imidazole Compounds as HO-1 Inhibitors from Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Floresta, G.; Amata, E.; Dichiara, M.; Marrazzo, A.; Salerno, L.; Romeo, G.; Prezzavento, O.; Pittala, V.; Rescifina, A. Identification of Potentially Potent Heme Oxygenase 1 Inhibitors through 3D-QSAR Coupled to Scaffold-Hopping Analysis. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahakis, J.Z.; Lazar, C.; Roman, G.; Vukomanovic, D.; Nakatsu, K.; Szarek, W.A. Heme oxygenase inhibition by alpha-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-omega-phenylalkanes: Effect of introduction of heteroatoms in the alkyl linker. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, E. Chagas disease research and development: Is there light at the end of the tunnel? Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.J. Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods IV: Extension of MNDO, AM1, and PM3 to more main group elements. J. Mol. Model. 2004, 10, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. YASARA View-molecular graphics for all devices-from smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponder, J.W.; Case, D.A. Force fields for protein simulations. Adv. Protein Chem. 2003, 66, 27–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melo, J.V.; Chuah, C. Resistance to imatinib mesylate in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Cancer Lett. 2007, 249, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Bi, L.; Ren, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.S. Advances in studies of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their acquired resistance. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.J.; Xie, R.L.; Zhao, Q.F.; Mei, X.D.; Ning, J. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of novel carbamate derivatives as potential dual-binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12817–12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Compound | BCR-ABL IC50 (μM) ± SD | HO-1 IC50 (μM) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| 1a | 0.109 ± 0.0016 | 44.79 ± 2.58 |
| 1b | 4.19 ± 0.16 | 64.56 ± 0.69 |
| 1c | 14.65 ± 0.283 | 149.38 ± 8.1 |
| 1d | 16.16 ± 0.208 | 116.00 ± 5.24 |
| 1e | 0.037 ± 0.0012 | 55.14 ± 0.71 |
| 1f | 5.21 ± 0.224 | 100.24 ± 3.29 |
| 1g | 0.077 ± 0.0036 | 50.95 ± 0.99 |
| 1h | 0.77 ± 0.042 | 65.36 ± 1.39 |
| 1i | 13.67 ± 0.139 | 83.44 ± 2.3 |
| 1j | 5.45 ± 0.223 | 3059 ± 201 |
| NIL | 0.039 a | – |
| IM | 0.309 a | – |
| LS/0 | – | 2.10 ± 0.3 b |
| LS1/71 | – | 1.00 ± 0.05 b |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | Calc.△GB (kcal/mol) | Calc. Ki (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 0.109 | −9.59 | 0.092 |
| 1b | 4.19 | −7.74 | 2.10 |
| 1c | 14.65 | −6.33 | 22.78 |
| 1d | 16.16 | −6.45 | 18.67 |
| 1e | 0.037 | −10.29 | 0.028 |
| 1f | 5.21 | −7.15 | 5.68 |
| 1g | 0.077 | −9.26 | 0.161 |
| 1h | 0.77 | −7.64 | 2.48 |
| 1i | 13.67 | −6.19 | 28.94 |
| 1j | 5.45 | −7.05 | 6.75 |
| NIL | 0.039 | −10.01 | 0.045 |
| IM | 0.309 | −8.99 | 0.255 |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | Calc.△GB (kcal/mol) | Calc. Ki (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 44.79 | −5.99 | 40.46 |
| 1b | 64.56 | −5.76 | 59.34 |
| 1c | 149.38 | −5.18 | 158.89 |
| 1d | 116.00 | −5.26 | 138.00 |
| 1e | 55.14 | −5.69 | 67.15 |
| 1f | 100.24 | −5.46 | 98.37 |
| 1g | 50.95 | −5.94 | 44.03 |
| 1h | 65.36 | −5.61 | 76.40 |
| 1i | 83.44 | −5.46 | 98.64 |
| 1j | 3059 | −4.05 | 1071.09 |
| QC-80a | 2.1 | −7.55 | 2.904 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciaffaglione, V.; Consoli, V.; Intagliata, S.; Marrazzo, A.; Romeo, G.; Pittalà, V.; Greish, K.; Vanella, L.; Floresta, G.; Rescifina, A.; et al. Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Target Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Molecules 2022, 27, 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103220
Ciaffaglione V, Consoli V, Intagliata S, Marrazzo A, Romeo G, Pittalà V, Greish K, Vanella L, Floresta G, Rescifina A, et al. Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Target Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Molecules. 2022; 27(10):3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103220
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiaffaglione, Valeria, Valeria Consoli, Sebastiano Intagliata, Agostino Marrazzo, Giuseppe Romeo, Valeria Pittalà, Khaled Greish, Luca Vanella, Giuseppe Floresta, Antonio Rescifina, and et al. 2022. "Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Target Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" Molecules 27, no. 10: 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103220
APA StyleCiaffaglione, V., Consoli, V., Intagliata, S., Marrazzo, A., Romeo, G., Pittalà, V., Greish, K., Vanella, L., Floresta, G., Rescifina, A., Salerno, L., & Sorrenti, V. (2022). Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Target Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Molecules, 27(10), 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103220