(+)-Catechin Stereoisomer and Gallate Induce Oxidative Stress in Rat Aorta
Abstract
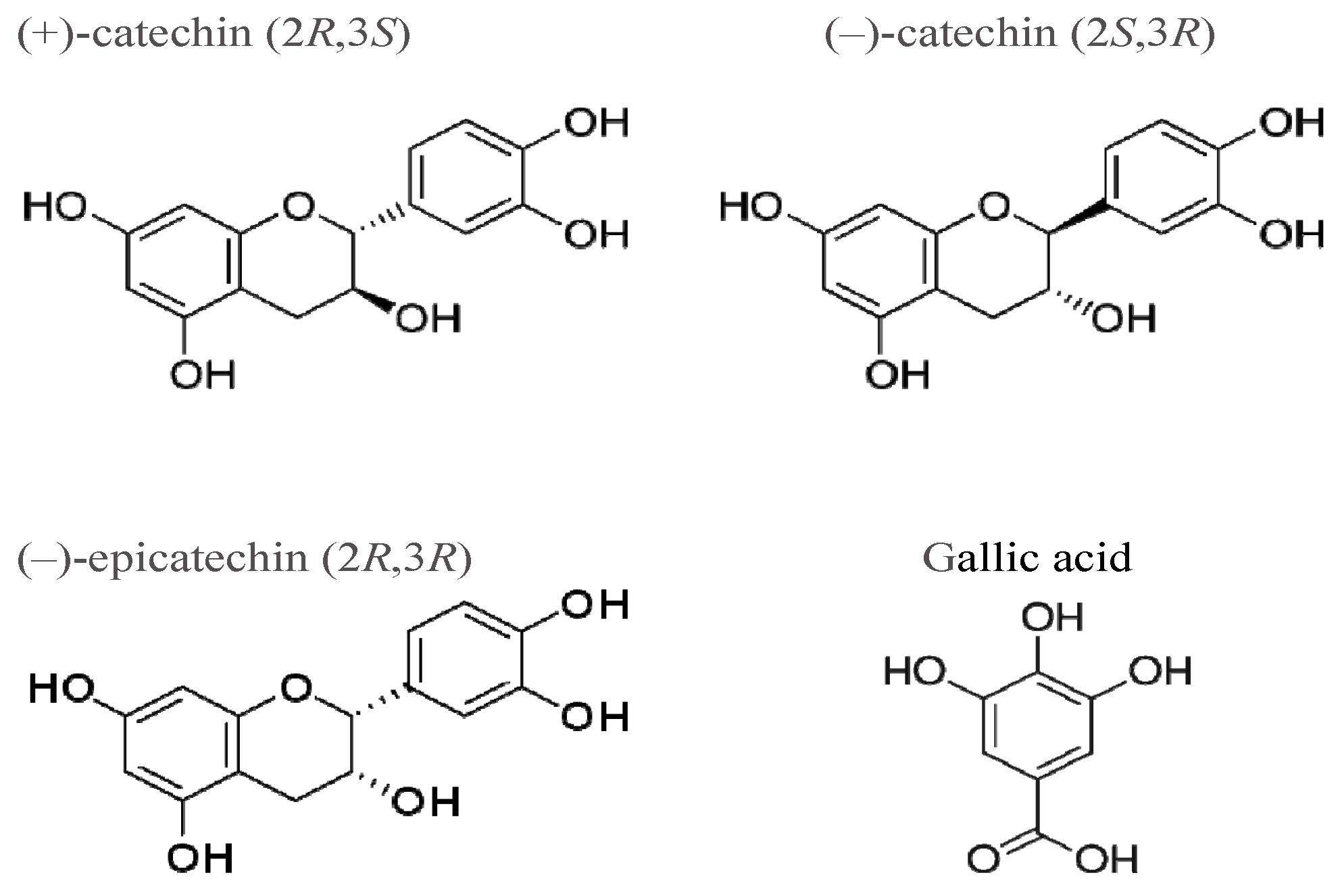
:1. Introduction
2. Results
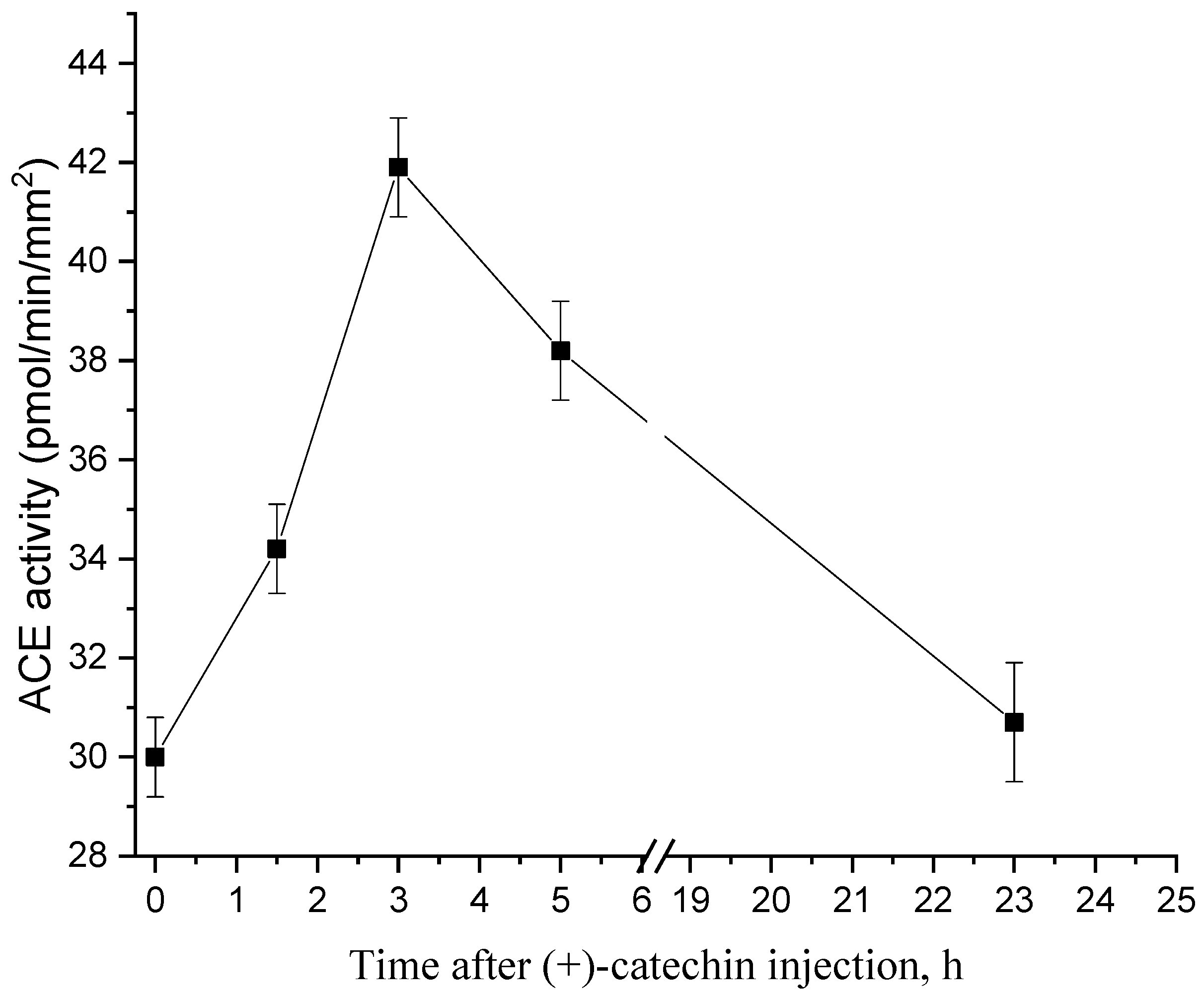
2.1. Dynamics of Changes in the Activity of ACE after Injection of (+)-Catechin
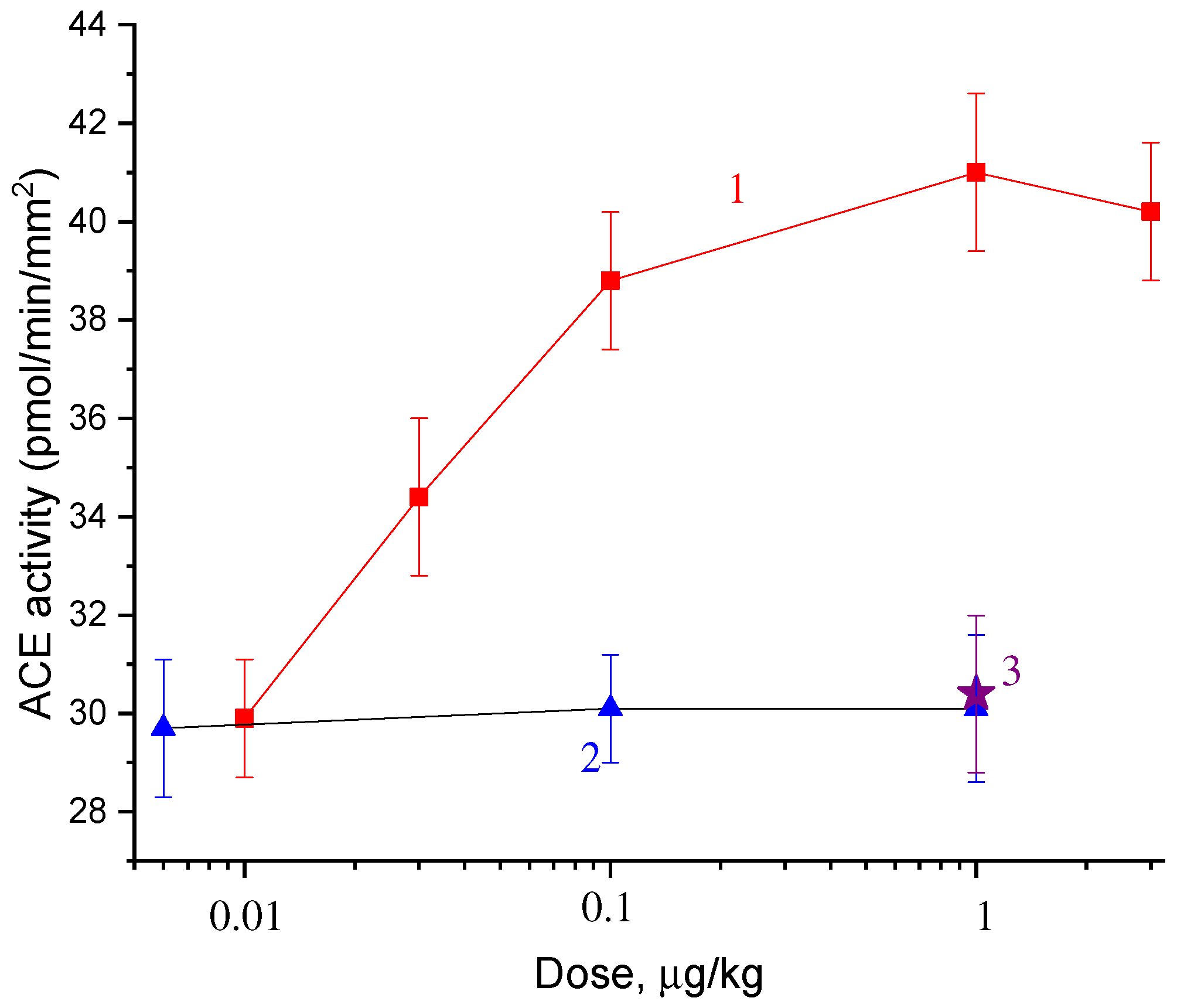
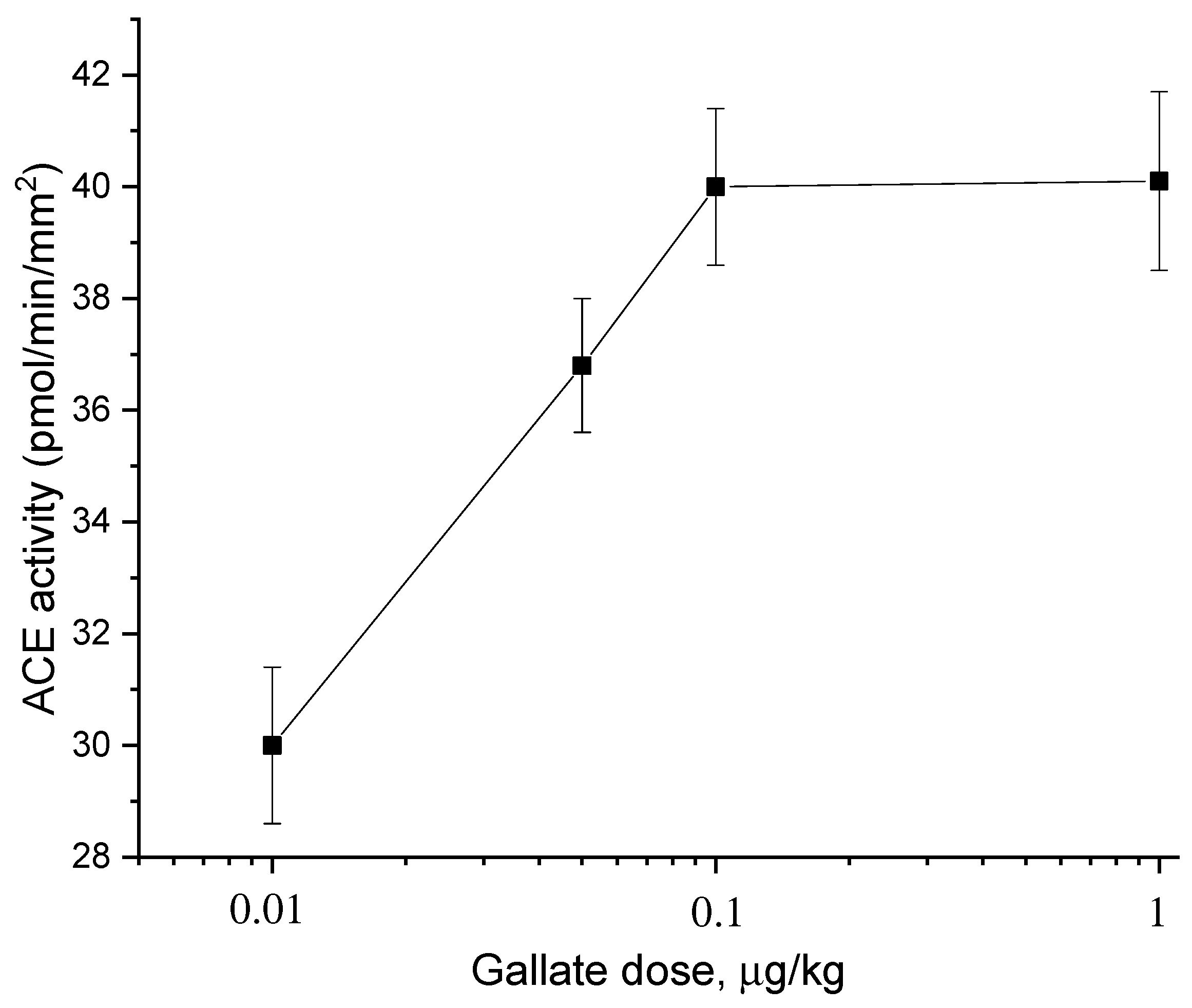
2.2. Dose Dependences of the Effect of Catechins and Gallate on ACE Activity
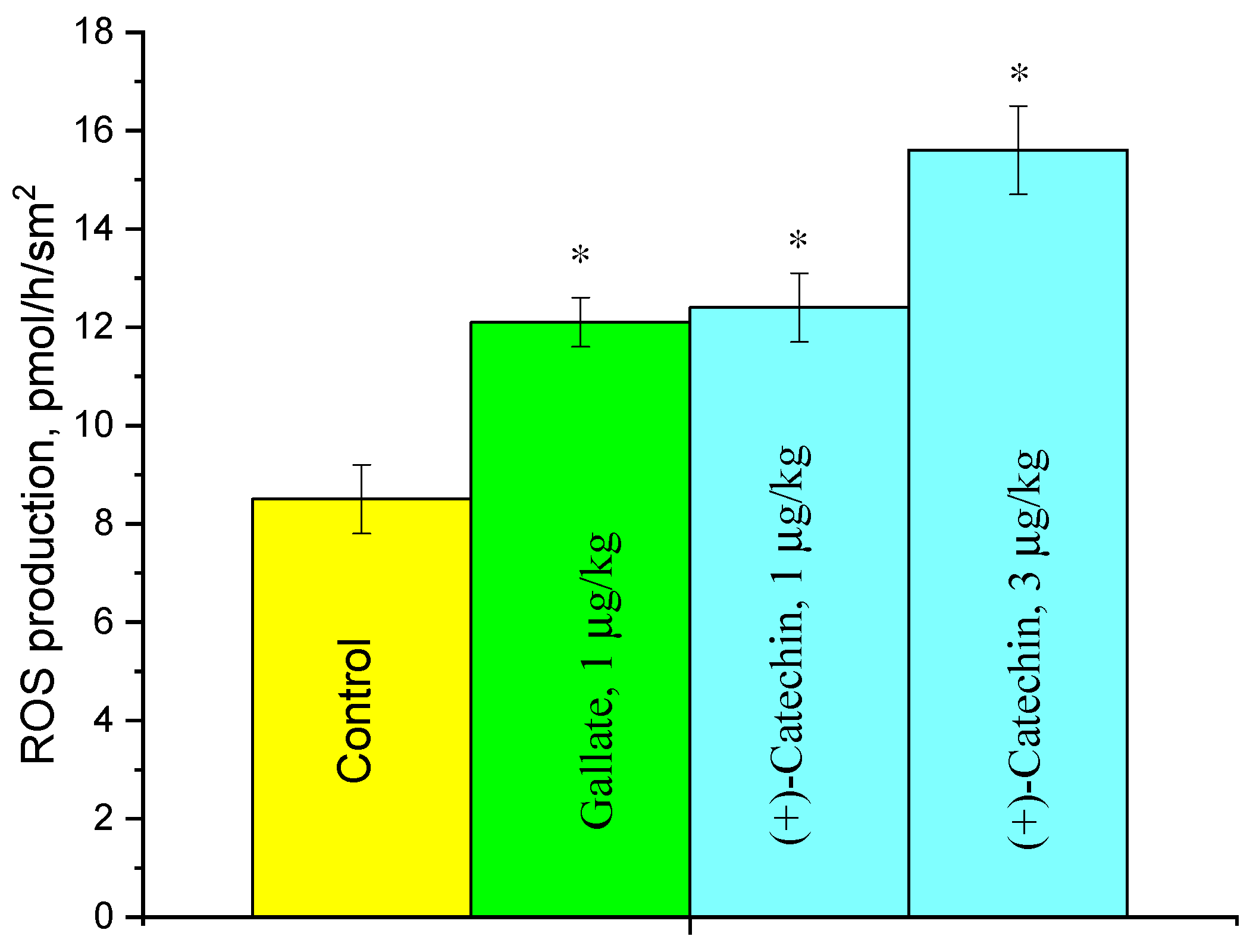
2.3. Effect of (+)-Catechin and Gallate on ROS Production in the Aorta
2.4. Effect of Fucoidin on the Increase in ACE Activity in Rat Aortas by the Actions of (+)-Catechin and Gallate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals, Mode of Introduction of Catechins and Gallate, and Aorta Preparation
4.2. Measurements of ACE Activity in the Aorta
4.3. Measurement of ROS in the Aorta
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, D.; Desideri, G.; Ferri, C. Flavonoids: Antioxidants against atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2010, 2, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dzau, V.J. Tissue angiotensin and pathobiology of vascular disease: A unifying hypothesis. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munzel, T.; Keaney, J.F. Are ACE inhibitors a “magic bullet” against oxidative stress? Circulation 2001, 104, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griendling, K.K.; Minieri, C.A.; Ollerenshaw, J.D.; Alexander, R.W. Angiotensin II stimulates NADH and NADPH oxidase activity in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landmesser, U.; Cai, H.; Dikalov, S.; McCann, L.; Hwang, J.; Jo, H.; Holland, S.M.; Harrison, D. GRole of p47phox in vascular oxidative stress and hypertension caused by angiotensin II. Hypertension 2002, 40, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heeneman, S.; Sluimer, J.C.; Daemen, M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and vascular remodeling. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Leto, T.L.; Hunyady, L.; Cat, K.J.; Bae, Y.S.; Rhee, S.G. Mechanism of angiotensin II-induced superoxide production in cells reconstituted with angiotensin type 1 receptor and the components of NADPH oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodgson, J.M.; Croft, K.D. Tea flavonoids and cardiovascular health. Mol. Aspects Med. 2010, 31, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van het Hof, K.H.; Kivits, G.A.A.; Weststrate, J.A.; Tijburg, L.B.M. Bioavailability of catechins from tea: The effect of milk. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartosikova, L.; Necas, J. Epigallocatechin gallate: A review. Vet. Med. 2018, 63, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Kim, N.; Shin, Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J. Activity of catechins and their applications. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.-T.; Kang, L.; Wang, C.-Z.; Huang, P.-J.; Huang, H.-T.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chou, S.-H.; Lu, C.-C.; Shen, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Decreases Osteoclastogenesis via Modulation of RANKL and Osteoprotegrin. Molecules 2019, 24, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korystova, A.F.; Kublik, L.N.; Samokhvaljva, T.V.; Shaposhnikova, V.V.; Korystov, Y.N. Black tea is more effective than green tea in prevention of radiation-induced oxidative stress in the aorta of rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, S.; Haytowitz, D.B. USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods. Release 3.2; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Anikina, V.A.; Kim, Y.A.; Korystova, A.F.; Levitman, M.K.; Shaposhnikova, V.V.; Korystov, Y.N. Effects of catechin on activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme and generation of reactive oxygen species in rat aorta. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 168, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.W. Chiral Toxicology: It’s the Same Thing.Only Different. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Liu, S.; Qu, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ni, D. Effect of Stereochemical Configuration on the Transport and Metabolism of Catechins from Green Tea across Caco-2 Monolayers. Molecules 2019, 24, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baba, S.; Osakabe, N.; Natsume, M.; Muto, Y.; Takizawa, T.; Terao, J. In Vivo Comparison of the Bioavailability of (+)-Catechin, (-)-Epicatechin and Their Mixture in Orally Administered Rats. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2885–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyfeler, F.; Moser, U.K.; Walter, P. Stereospecific effects of (+) and (−)-catechin on glycogen metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 763, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, M.B.G.; Manjolin, L.C.; Maquiaveli, C.C.; Santos-Filho, O.A.; da Silva, E.R. Inhibition of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis and Rat Arginases by Green Tea EGCG, (+)-Catechin and (2)-Epicatechin: A Comparative Structural Analysis of Enzyme-Inhibitor Interactions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanae, F.; Miyaichi, Y.; Kizu, H.; Hayashi, H. Effects of catechins on vascular tone in rat thoracic aorta with endothelium. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, D.J. Flavonoids for Reduction of Atherosclerotic Risk. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2004, 6, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuru, R.Y.; Roy, A.; Das, S.K.; Bera, S. Gallic Acid and Gallates in Human Health and Disease: Do Mitochondria Hold the Key to Success? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.A.; Korystova, A.F.; Kublik, L.N.; Levitman, M.K.; Shaposhnikova, V.V.; Korystov, Y.N. Flavonoids decrease the radiation-induced increase in the activity of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 837, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Ikeda, U.; Masuyama, J.-I.; Kitagawa, S.-I.; Kasahara, T.; Shimpo, M.; Kano, S.; Shimada, K. Monocyte-endothelial cell interaction induces expression of adhesion molecules on human umbilical cord endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 1996, 32, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjarne, Ø.; Bjørklid, E. Role of monocytes in atherogenesis. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 1069–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata, K.; Tanaka, N.; Suzuki, K. Epigallocatechin 3-gallate inhibits 7-ketocholesterol-induced monocyte–endothelial cell adhesion. Microvasc. Res. 2013, 88, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Perkins, J.T.; Hennig, B. EGCG prevents PCB-126-induced endothelial cell inflammation via epigenetic modifications of NF-κB target genes in human endothelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 28, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babu, P.V.A.; Si, H.; Liu, D. Epigallocatechin gallate reduces vascular inflammation in db/dbmice possibly through an NF-κB-mediated mechanism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, M.A.; Marasciulo, F.L.; Tarquinio, M.; Tiravanti, E.; Colantuono, G.; Federici, A.; Kim, J.; Quon, M.J.; Montagnani, M. EGCG, a green tea polyphenol, improves endothelial function and insulin sensitivity, reduces blood pressure, and protects against myocardial I/R injury in SHR. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1378–E1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiana, B.-J.; Tiana, C.-C.; Linga, X.-H.; Yua, L.-L.; Dinga, F.-Y.; Huoa, J.-H.; Zhuc, L.-C.; Wend, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-H.; Jing, P. miRNA-150-5p associate with antihypertensive effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate revealed by aorta miRNome analysis of spontaneously hypertensive rat. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases atherosclerotic plaque stability in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice fed a high-fat diet. Kardiol. Pol. 2018, 76, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanga, N.; Leea, J.-H.; Leea, W.W.; Koa, J.-Y.; Kima, E.-A.; Kim, J.-S.; Heuc, M.-S.; Kim, G.H.; Jeona, Y.-J. Gallic acid isolated from Spirogyra sp. Improves cardiovascular disease through a vasorelaxant and antihypertensive effect. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Piao, Z.H.; Sun, S.; Liu, B.; Kim, G.R.; Seok, Y.M.; Lin, M.Q.; Ryu, Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Kee, H.J.; et al. Gallic Acid Reduces Blood Pressure and Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Cardiac Hypertrophy in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korystov, Y.N.; Emel’yanov, M.O.; Korystova, A.F.; Levitman, M.K.; Shaposhnikova, V.V. Determination of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in rat aorta using the dichlorofluorescein assay. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, A.; Fernandez-Alfonso, M.S.; Sanchez-de-Rojas, R.; Ortega, T.; Paul, M.; González, C. Modulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme by nitric oxide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 124, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, A.; Murata, S.; Nishio, A. Role of ACE and NEP in bradykinin-induced relaxation and contraction response of isolated porcine basilar artery. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 365, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samokhvalova, T.V.; Kim, Y.A.; Korystova, A.F.; Kublik, L.N.; Shaposhnikova, V.V.; Korystov, Y.N. (+)-Catechin Stereoisomer and Gallate Induce Oxidative Stress in Rat Aorta. Molecules 2022, 27, 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113379
Samokhvalova TV, Kim YA, Korystova AF, Kublik LN, Shaposhnikova VV, Korystov YN. (+)-Catechin Stereoisomer and Gallate Induce Oxidative Stress in Rat Aorta. Molecules. 2022; 27(11):3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113379
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamokhvalova, Tamara V., Yuri A. Kim, Antonia F. Korystova, Ludmila N. Kublik, Vera V. Shaposhnikova, and Yuri N. Korystov. 2022. "(+)-Catechin Stereoisomer and Gallate Induce Oxidative Stress in Rat Aorta" Molecules 27, no. 11: 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113379
APA StyleSamokhvalova, T. V., Kim, Y. A., Korystova, A. F., Kublik, L. N., Shaposhnikova, V. V., & Korystov, Y. N. (2022). (+)-Catechin Stereoisomer and Gallate Induce Oxidative Stress in Rat Aorta. Molecules, 27(11), 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113379





