Focus on the Protein Fraction of Sports Nutrition Supplements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Samples Analysed
2.2. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis of the Protein Fraction
2.3. Amino Acid Composition
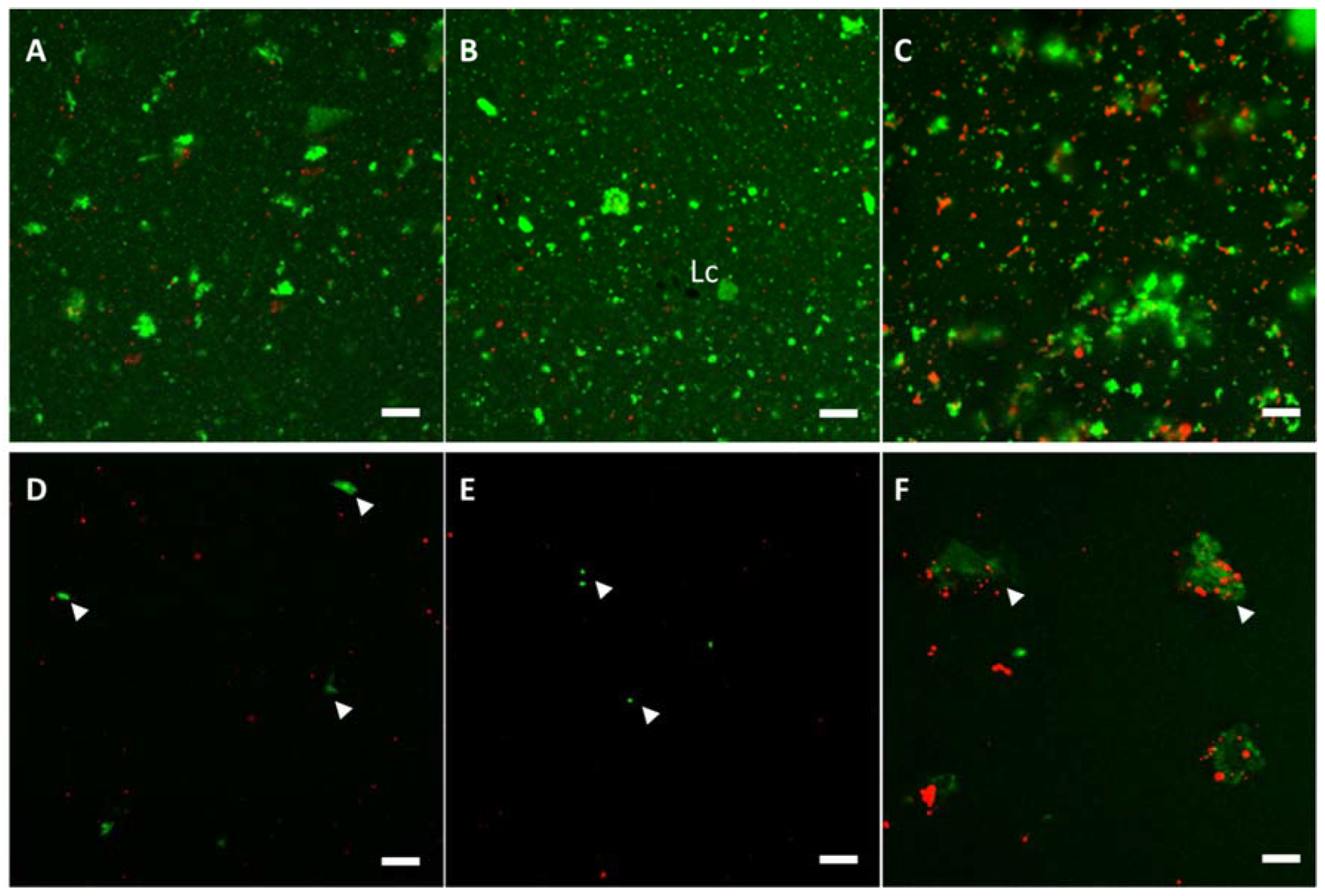
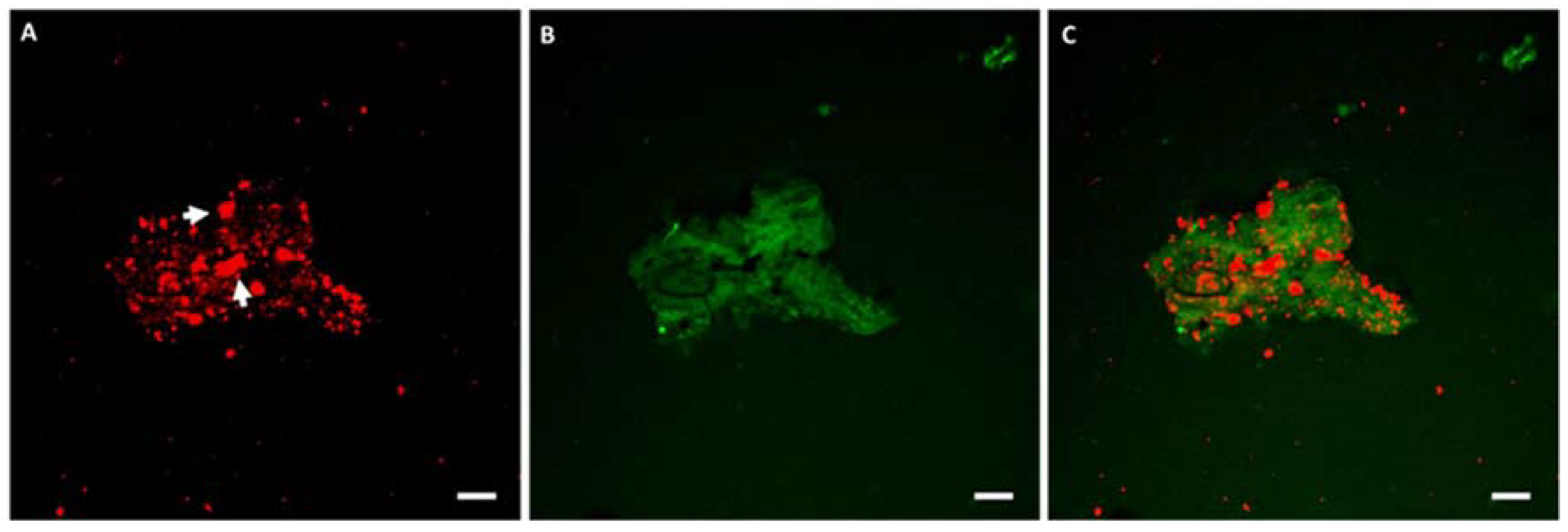
2.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Composition of Samples
3.3. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE)
3.4. Amino Acid Composition
3.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Arenas-Jal, M.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; García-Montoya, E. Trends in the food and sports nutrition industry: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2405–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerksick, C.M.; Wilborn, C.D.; Roberts, M.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.; Kleiner, S.M.; Jäger, R.; Kreider, R.B. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: Research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, K.; Getzin, A. Nutrition and supplement update for the endurance athlete: Review and recommendations. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Costa, B.R.B.; Roiffé, R.R.; de la Cruz, M.N. Quality Control of Protein Supplements: A Review. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exercise Metab. 2021, 31, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanov, P.; Sakač, M.; Jurdana, M.; Pražnikar, Z.J.; Kenig, S.; Hadnađev, M.; Jakus, T.; Petelin, A.; Škrobot, D.; Marić, A. High-Protein Bar as a Meal Replacement in Elite Sports Nutrition: A Pilot Study. Foods 2021, 10, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, L.M.; Pushmina, I.N.; Pushmina, V.V.; Kudriavtsev, M.D.; Sitnichuk, S.S. Fermented milk product for sports nutrition. Hum. Sport Med. 2019, 19, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Beausire, R.L.; Patel, S.; Patel, H. Innovative uses of milk protein concentrates in product development. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, A23–A29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrange, V.; Whitsett, D.; Burris, C. Global market for dairy proteins. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, A16–A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, P.B.Z.; Macedo, R.C.O. Effects of dietary supplementation in sport and exercise: A review of evidence on milk proteins and amino acids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 1225–12395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, S.; Masotti, F.; Pellegrino, L. Chemical modifications of casein occurring during industrial manufacturing of milk protein powders. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, A.; Van Gool, M.P.; Bultsma, M.; Cutroneo, S.; Sforza, S.; Tedeschi, T. Modifications induced by controlled storage conditions on whey protein concentrates: Effects on whey protein lactosylation and solubility. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 109, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, L.; D’Incecco, P. Impact of Processing on Nutritional Quality of Milk Proteins. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; McSweeney, P.L.H., McNamara, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 5, pp. 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- Guyomarc’h, F.; Law, A.J.; Dalgleish, D.G. Formation of soluble and micelle-bound protein aggregates in heated milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4652–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzone, G.; Arena, S.; Scaloni, A. Cross-linking reactions in food proteins and proteomic approaches for their detection. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishanthi, M.; Chandrapala, J.; Vasiljevic, T. Impact of storage conditions on solubility, heat stability and emulsifying properties of selected spray dried whey protein concentrates. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantuono, A.; D’Incecco, P.; Fortina, M.G.; Rosi, V.; Ricci, G.; Pellegrino, L. Milk substrates influence proteolytic activity of Pseudomonas fluorescens strains. Food Control 2020, 111, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, P.; Rosi, V.; Cabassi, G.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Pellegrino, L. Microfiltration and ultra-high-pressure homogenization for extending the shelf-storage stability of UHT milk. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulios, A.; Georgakouli, K.; Draganidis, D.; Deli, C.K.; Tsimeas, P.D.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Fatouros, I.G. Protein-based supplementation to enhance recovery in team sports: What is the evidence? J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 18, 523. [Google Scholar]
- Corgneau, M.; Gaiani, C.; Petit, J.; Nikolova, Y.; Banon, S.; Ritié-Pertusa, L.; Scher, J. Nutritional quality evaluation of commercial protein supplements. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeldt, H.C.; Hall, N.; Pretorius, B. 12th IFDC 2017 Special Issue–High protein sports supplements: Protein quality and label compliance. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 83, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswari, M.; Gifari, N.; Nuzrina, R.; Justickarin, S.; Fathiya, A.; Hutasuhut, F. Analysis of Protein Content on Commercial Protein Supplement in Indonesia. JUARA J. Olahraga 2021, 6, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.; Robertson, A.; Ofman, D. Dairy glycoconjugate emulsifiers: Casein–maltodextrins. Food Hydrocolloids 2000, 14, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasilova, N.; Gassner, A.L.; Girault, H.H. Analysis of major milk whey proteins by immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis coupled with MALDI-MS. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leiva, G.E.; Naranjo, G.B.; Malec, L.S. A study of different indicators of Maillard reaction with whey proteins and different carbohydrates under adverse storage conditions. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Fuerer, C.; McMahon, A. Quantification of Whey Protein Content in Milk-Based Infant Formula Powders by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-CGE): Multilaboratory Testing Study, Final Action 2016.15. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, C.M.; Roberts, M.D.; Dalbo, V.J.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Kendall, K.L.; Moon, J.R.; Stout, J.R. Effects of hydrolyzed whey versus other whey protein supplements on the physiological response to 8 weeks of resistance exercise in college-aged males. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, B.C.; Souza, G.H.; Lourenço, D.C.; Fasciotti, M. Proteomics in quality control: Whey protein-based supplements. J. Proteomics 2016, 147, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raak, N.; Abbate, R.A.; Lederer, A.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Size separation techniques for the characterisation of cross-linked casein: A review of methods and their applications. Separations 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, R.; Rajput, Y.S.; Mann, B.; Singh, R.; Gandhi, K. Separation methods for milk proteins on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: Critical analysis and options for better resolution. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 114, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, I.; Amigo, L.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Miralles, B. Peptides. In Handbook of Dairy Foods Analysis; Toldrà, F., Nollet, L.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 33–64. [Google Scholar]
- Masci, M.; Zoani, C.; Nevigato, T.; Turrini, A.; Jasionowska, R.; Caproni, R.; Ratini, P. Authenticity assessment of dairy products by Capillary Electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2021, 43, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, C.; Mathis, D.; Neuhaus, P.; Dürr, D.; Bisig, W.; Egger, L.; Portmann, R. Protein profile of dairy products: Simultaneous quantification of twenty bovine milk proteins. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 97, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Fu, L.; Shao, L.; Chen, Q.; Dorus, B.; Cao, X.; Fang, F. Quantification of major milk proteins using ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry and its application in milk authenticity analysis. Food Control 2022, 131, 108455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueiro, A.Y.; Rogero, M.M.; Tirapegui, J. Glutamine as an anti-fatigue amino acid in sports nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pellegrino, L.; Masotti, F.; Cattaneo, S.; Hogenboom, J.A.; De Noni, I. Nutritional quality of milk proteins. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry, 4th ed.; Paul, L.H., McSweeney, P., Fox, F., Eds.; Proteins: Basic Aspects; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1A, pp. 515–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, E.A.; Bazer, F.W.; Wu, G. Amino acids and their metabolites for improving human exercising performance. Amino Acids Hum. Nutr. Health 2021, 1332, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, H.B.; Wierenga, P.A.; Gruppen, H.; Schols, H.A. Maillard induced aggregation of individual milk proteins and interactions involved. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmierski, M.; Corredig, M. Characterization of soluble aggregates from whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocolloids 2003, 17, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, E.A.; Chevallier, M.; Le Floch-Fouéré, C.; Schuck, P.; Jeantet, R.; Croguennec, T. Heat-induced aggregation properties of whey proteins as affected by storage conditions of whey protein isolate powders. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lucey, J.A. Use of multi-angle laser light scattering and size-exclusion chromatography to characterize the molecular weight and types of aggregates present in commercial whey protein products. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3090–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8968-1: 2014; Milk and Milk Products: Determination of Nitrogen Content-Part 1: Kjeldahl Principle and Crude Protein Calculation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 5543:2004; Caseins and Caseinates—Determination of Fat Content—Gravimetric Method (Reference Method). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- ISO 22662:2009; Milk and Milk Products—Determination of Lactose Content by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (Reference Method). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 5545:2008; Rennet Caseins and Caseinates—Determination of Ash (Reference Method). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 5537:2004; Dried Milk–Determination of Moisture Content. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- D’Incecco, P.; Limbo, S.; Hogenboom, J.; Rosi, V.; Gobbi, S.; Pellegrino, L. Impact of extending hard-cheese ripening: A multiparameter characterization of Parmigiano Reggiano cheese ripened up to 50 months. Foods 2020, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogenboom, J.A.; D’Incecco, P.; Fuselli, F.; Pellegrino, L. Ion-exchange chromatographic method for the determination of the free amino acid composition of cheese and other dairy products: An interlaboratory validation study. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Incecco, P.; Bancalari, E.; Gatti, M.; Ranghetti, A.; Pellegrino, L. Low-temperature centrifugation of milk for manufacture of raw milk cheeses: Impact on milk debacterization and cheese yield. LWT 2020, 118, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, P.; Limbo, S.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Pellegrino, L. Novel technologies for extending the shelf life of drinking milk: Concepts, research trends and current applications. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 148, 111746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | PSS * | REF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A47 | C64 | Y08 | S15 | L03 | WPI | WPC | WP | |
| Protein | 84.1 ± 0.2 a | 76.7 ± 0.1 b | 66.5 ± 0.1 c | 95.8 ± 0.1 d | 86.1 ± 0.1 a | 88.3 ± 9.8 a | 35.1 ± 4.2 e | 13.5 ± 2.4 f |
| Lipids | 1.7 ± 0.2 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 b | 3.3 ± 0.4 c | 0.0 d | 0.0 d | 0.0 d | 3.1 ± 0.4 c | 1.2 ± 0.1 b |
| Lactose | 0.5 ± 0.1 a | 0.0 **a | 6.7 ± 0.2 b | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | 51.2 ± 1.3 c | 73.3 ± 1.2 d |
| Ash | 5.7 ± 0.0 a | 5.3 ± 0.2 a | 5.0 ± 0.1 a | 1.2 ± 0.0 b | 5.8 ± 0.0 a | 5.1 ± 0.9 a | 7.3 ± 1.1 c | 8.0 ± 1.2 c |
| Moisture | 7.1 ± 0.1 a | 6.8 ± 0.0 a | 7.3 ± 0.1 a | 3.1 ± 0.0 c | 6.9 ± 0.1 a | 3.4 ± 0.6 bc | 4.1 ± 0.6 b | 3.2 ± 0.5 c |
| Sample | PSS | Reference | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A47 | C64 | Y08 | S15 | L03 | WPI | WPC35 | WP | |||||||||
| TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | TAA | FAA | |
| Asp | 9.9 ± 0.4 | ---- | 8.9 ± 0.3 | ---- | 3.7 ± 0.1 | ---- | 7.8 ± 0.2 | ---- | 7.7 ± 0.2 | ---- | 9.8 ± 1.1 | ---- | 2.4 ± 0.4 | ---- | 0.8 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Thr | 6.6 ± 0.4 | ---- | 5.8 ± 0.3 | ---- | 2.3 ± 0.1 | ---- | 5.3 ± 0.5 | ---- | 5.0 ± 0.2 | ---- | 6.7 ± 0.4 | ---- | 2.2 ± 0.3 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Ser | 4.7 ± 0.1 | ---- | 4.1 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.9 ± 0.0 | ---- | 3.6 ± 0.2 | ---- | 4.3 ± 0.1 | ---- | 4.3 ± 0.3 | ---- | 1.9 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.6 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Glu | 15.6 ± 0.7 | ---- | 13.8 ± 0.8 | ---- | 6.4 ± 0.3 | ---- | 21.6 ± 1.9 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 15.2 ± 0.5 | ---- | 20.4 ± 1.5 | ---- | 5.4 ± 0.5 | ---- | 1.7 ± 0.2 | ---- |
| Gln | 0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0 ± 0 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 5.1 ± 0.5 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.0 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Gly | 1.6 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.4 ± 0.1 | ---- | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 9.3 ± 1 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.4 ± 0.2 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.2 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Ala | 4.7 ± 0.1 | ---- | 4.3 ± 0.1 | ---- | 2.1 ± 0.1 | ---- | 7.1 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | ---- | 4.4 ± 0.4 | ---- | 1.8 ± 0.2 | ---- | 0.6 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Val | 5.8 ± 0.3 | ---- | 5.1 ± 0.3 | ---- | 2.0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 4.2 ± 0.6 | ---- | 4.9 ± 0.2 | ---- | 5.2 ± 0.4 | ---- | 2.1 ± 0.3 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Cys2 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | ---- | 1.9 ± 0.1 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.5 ± 0.2 | ---- | 1.3 ± 0.0 | ---- | 2.1 ± 0.3 | ---- | 0.6 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.1 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Met | 1.9 ± 0.3 | ---- | 1.6 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.6 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1 ± 0.8 | ---- | 1.7 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.8 ± 0.2 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.2 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Ile | 6.4 ± 0.1 | ---- | 5.5 ± 0.0 | ---- | 2.1 ± 0.1 | ---- | 4.3 ± 0.2 | ---- | 4.8 ± 0.2 | ---- | 6.0 ± 0.6 | ---- | 2.2 ± 0.1 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Leu | 9.7 ± 0.2 | ---- | 8.9 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | ---- | 7.7 ± 0.4 | ---- | 8.3 ± 0.3 | ---- | 9.2 ± 0.9 | ---- | 3.6 ± 0.4 | ---- | 1.1 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Tyr | 2.5 ± 0.1 | ---- | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.9 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 2.4 ± 0.2 | ---- | 0.8 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.2 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Phe | 2.7 ± 0.1 | ---- | 2.5 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.3 ± 0.0 | ---- | 2.1 ± 0.2 | ---- | 3.0 ± 0.1 | ---- | 2.5 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.1 ± 0.1 | ---- | 0.3 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Lys | 9.2 ± 0.5 | ---- | 8.3 ± 0.3 | ---- | 3.1 ± 0.1 | ---- | 10.4 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | ---- | 8.2 ± 0.9 | ---- | 3.2 ± 0.2 | ---- | 1.0 ± 0.1 | ---- |
| His | 1.5 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.3 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.1 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.6 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.3 ± 0.2 | ---- | 0.8 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.2 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Arg | 1.9 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.7 ± 0.0 | ---- | 1.3 ± 0.1 | ---- | 1.4 ± 0.0 | ---- | 2.4 ± 0.1 | ---- | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 1 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | ---- | 0.3 ± 0.0 | ---- |
| Pro | 6.0 ± 0.1 | ---- | 5.0 ± 0.2 | ---- | 2.7 ± 0.1 | ---- | 4.2 ± 0.2 | ---- | 6.5 ± 0.2 | ---- | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | ---- | 0.7 ± 0.0 | ---- | |
| Total | 92.6 ± 0.8 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 82.5 ± 1 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 43.0 ± 2.2 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 94.6 ± 1 | 21.2 ± 0.8 | 79.6 ± 3.2 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 94.0 ± 6.2 | 6.1 ± 0.8 | 32.5 ± 3.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 10.0 ± 1.3 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellegrino, L.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Rosi, V.; Sindaco, M.; Gerna, S.; D’Incecco, P. Focus on the Protein Fraction of Sports Nutrition Supplements. Molecules 2022, 27, 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113487
Pellegrino L, Hogenboom JA, Rosi V, Sindaco M, Gerna S, D’Incecco P. Focus on the Protein Fraction of Sports Nutrition Supplements. Molecules. 2022; 27(11):3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113487
Chicago/Turabian StylePellegrino, Luisa, Johannes A. Hogenboom, Veronica Rosi, Marta Sindaco, Stefano Gerna, and Paolo D’Incecco. 2022. "Focus on the Protein Fraction of Sports Nutrition Supplements" Molecules 27, no. 11: 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113487
APA StylePellegrino, L., Hogenboom, J. A., Rosi, V., Sindaco, M., Gerna, S., & D’Incecco, P. (2022). Focus on the Protein Fraction of Sports Nutrition Supplements. Molecules, 27(11), 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113487







