Risk Assessment in Monitoring of Water Analysis of a Brazilian River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochemical Parameters
2.1.1. pH
2.1.2. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
2.1.3. Manganese molar concentration
2.1.4. Escherichia coli
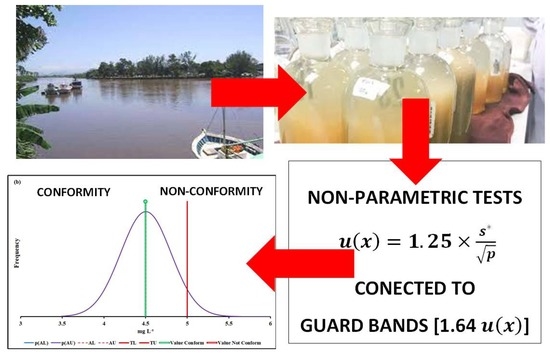
2.2. Robust Statistical Methods
2.3. Use of Uncertainty Information in Compliance Assessment
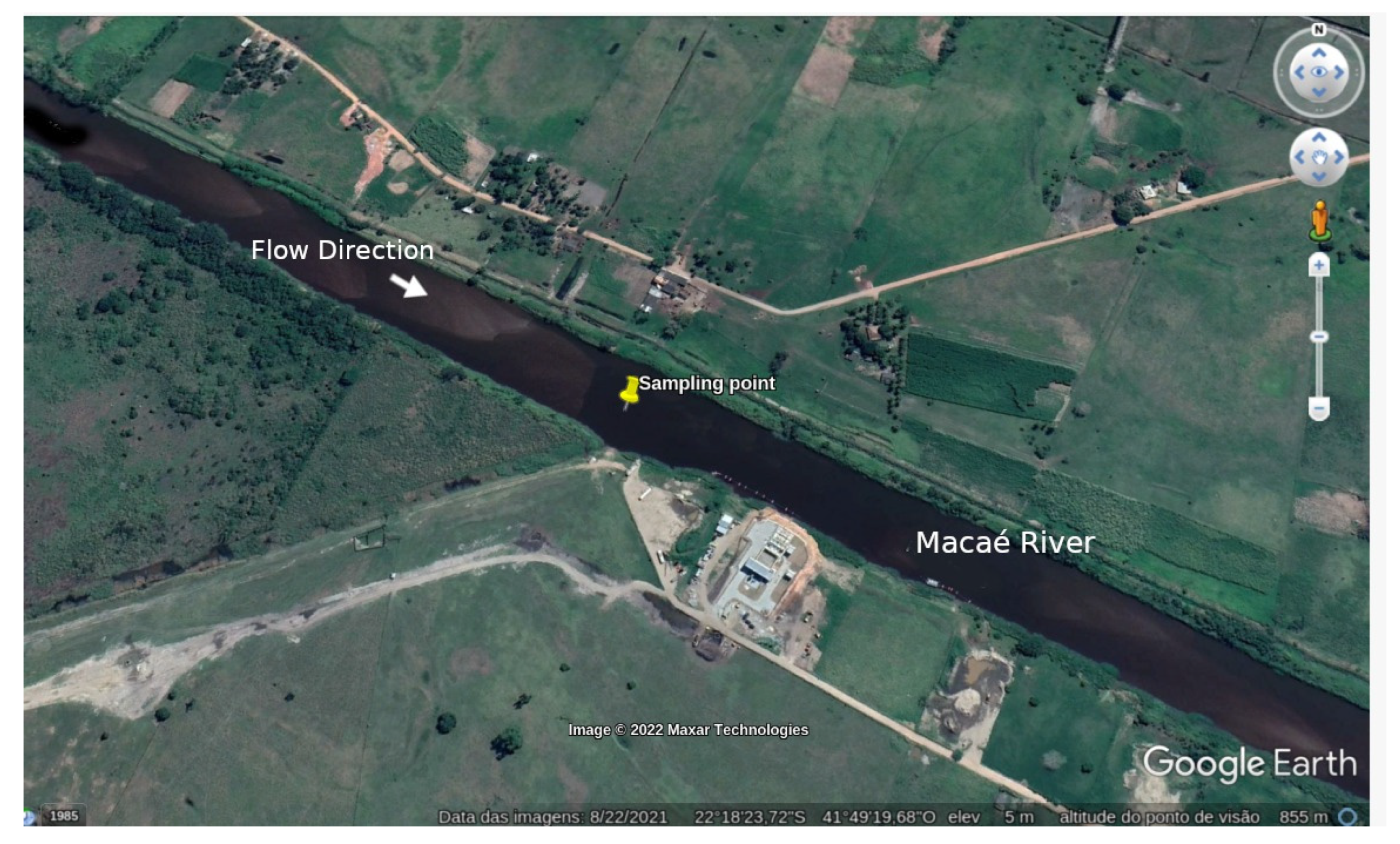
3. Experimental
4. Results
4.1. Preliminary Statistical Evaluation
4.2. Statistical Treatment
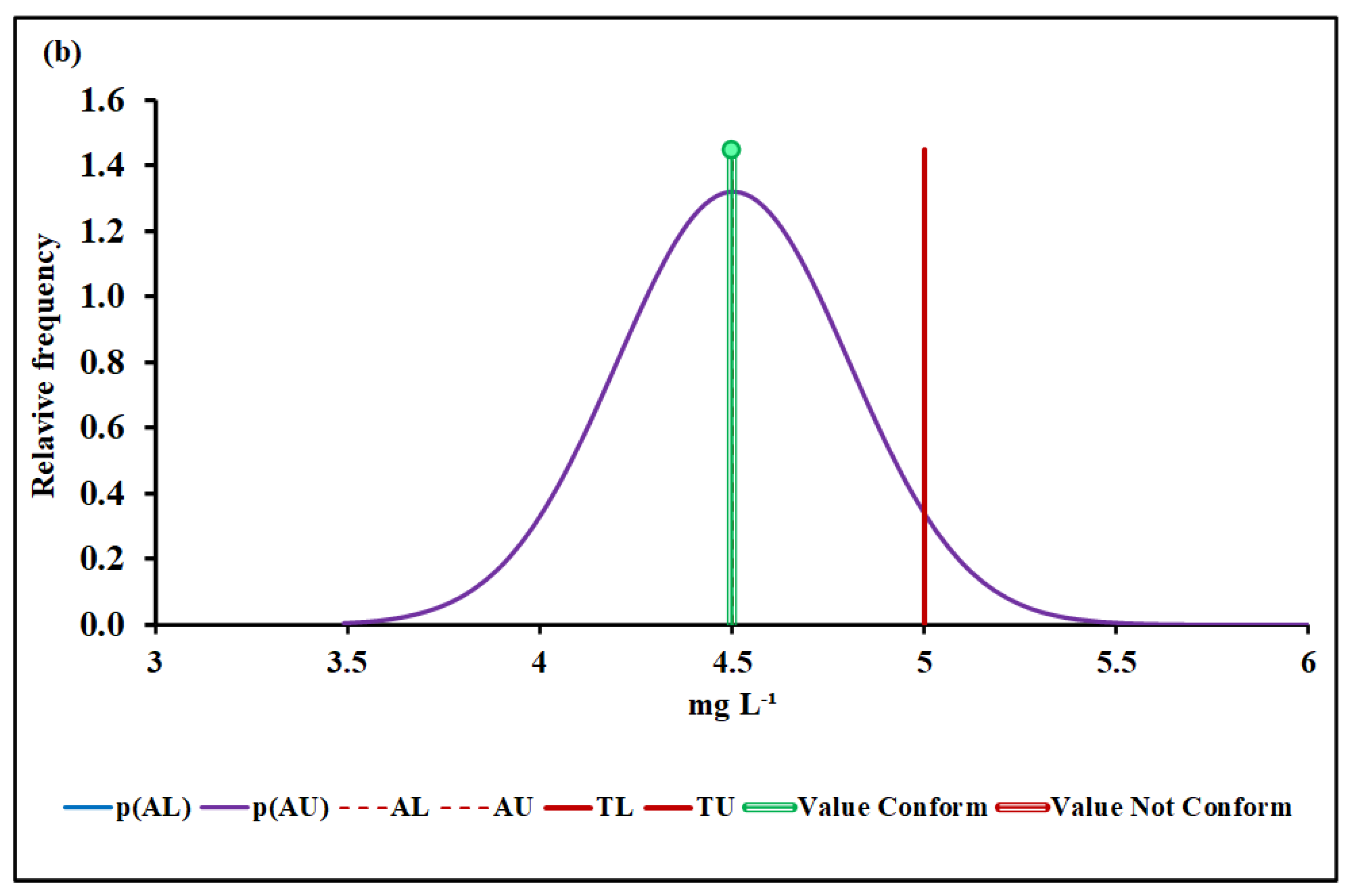
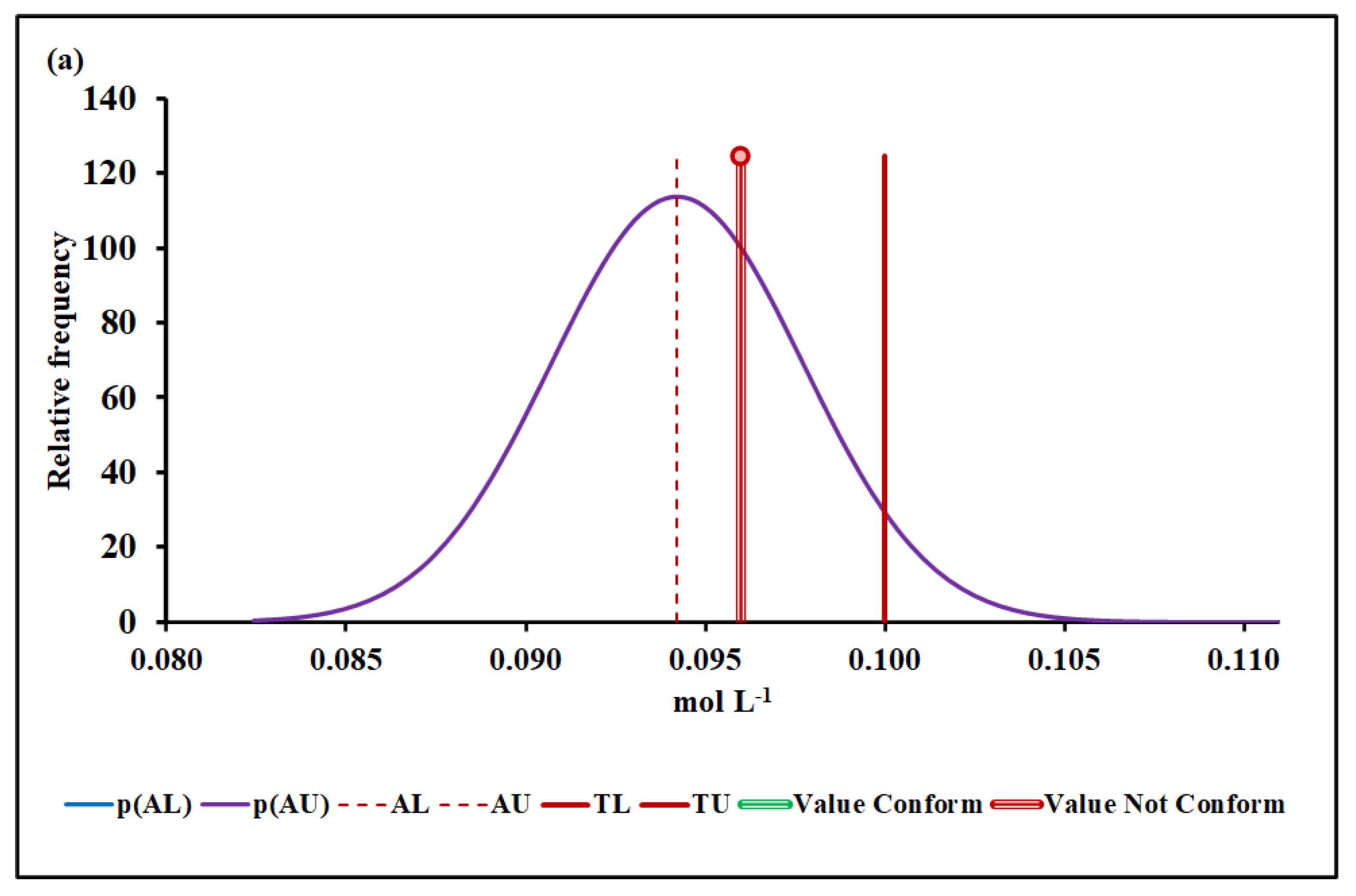
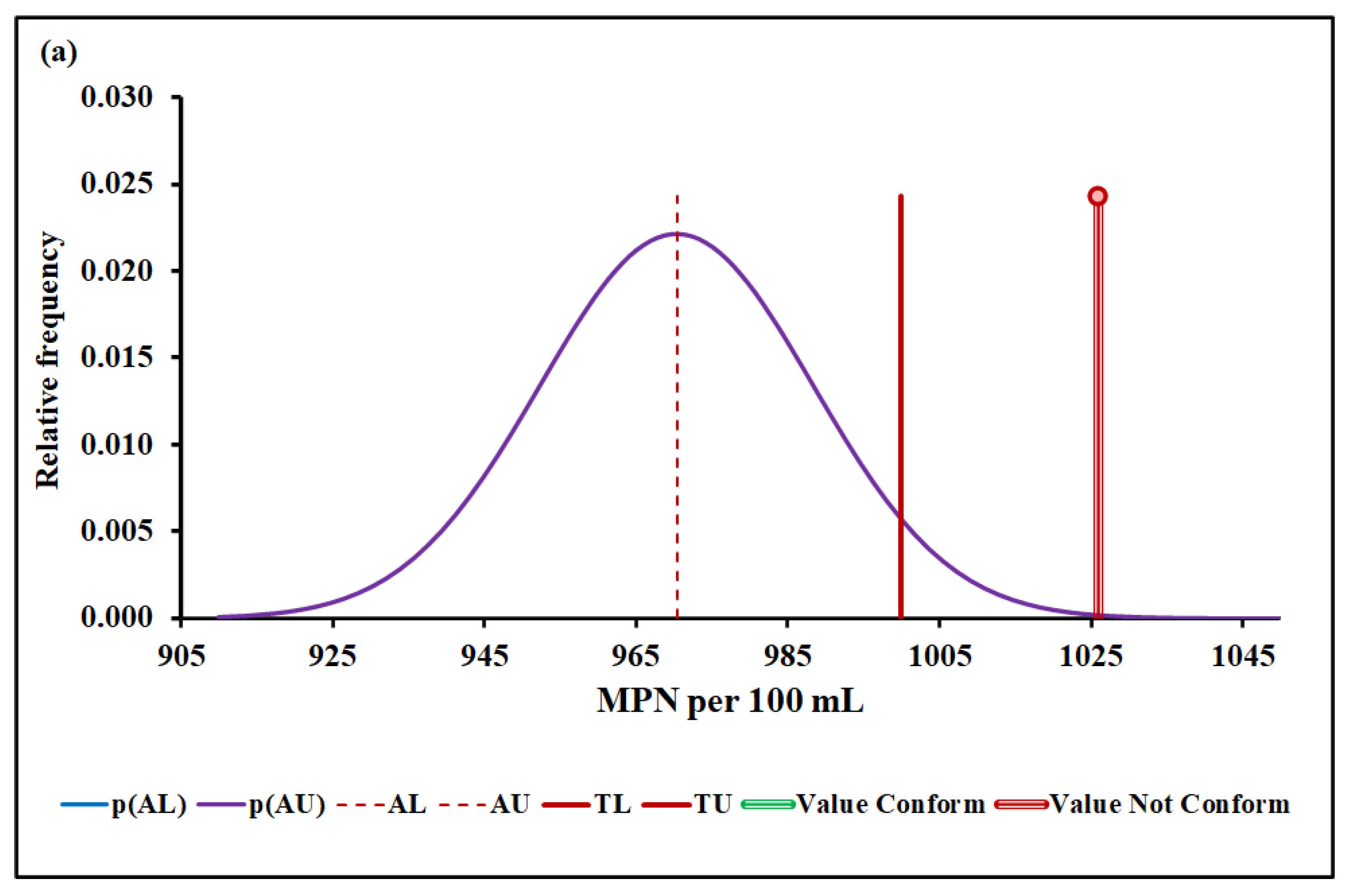
4.3. Compliance Assessment
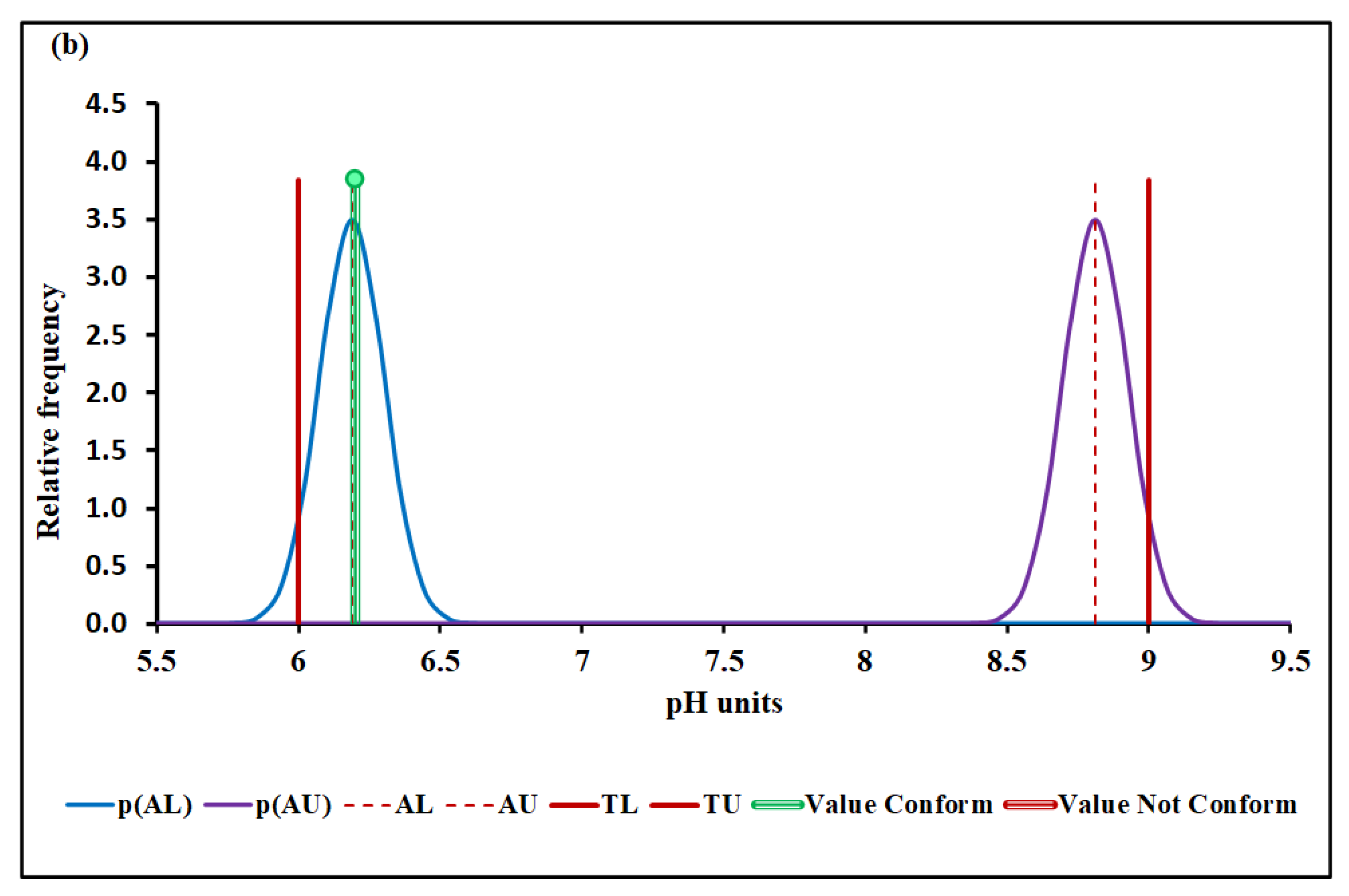
4.3.1. pH
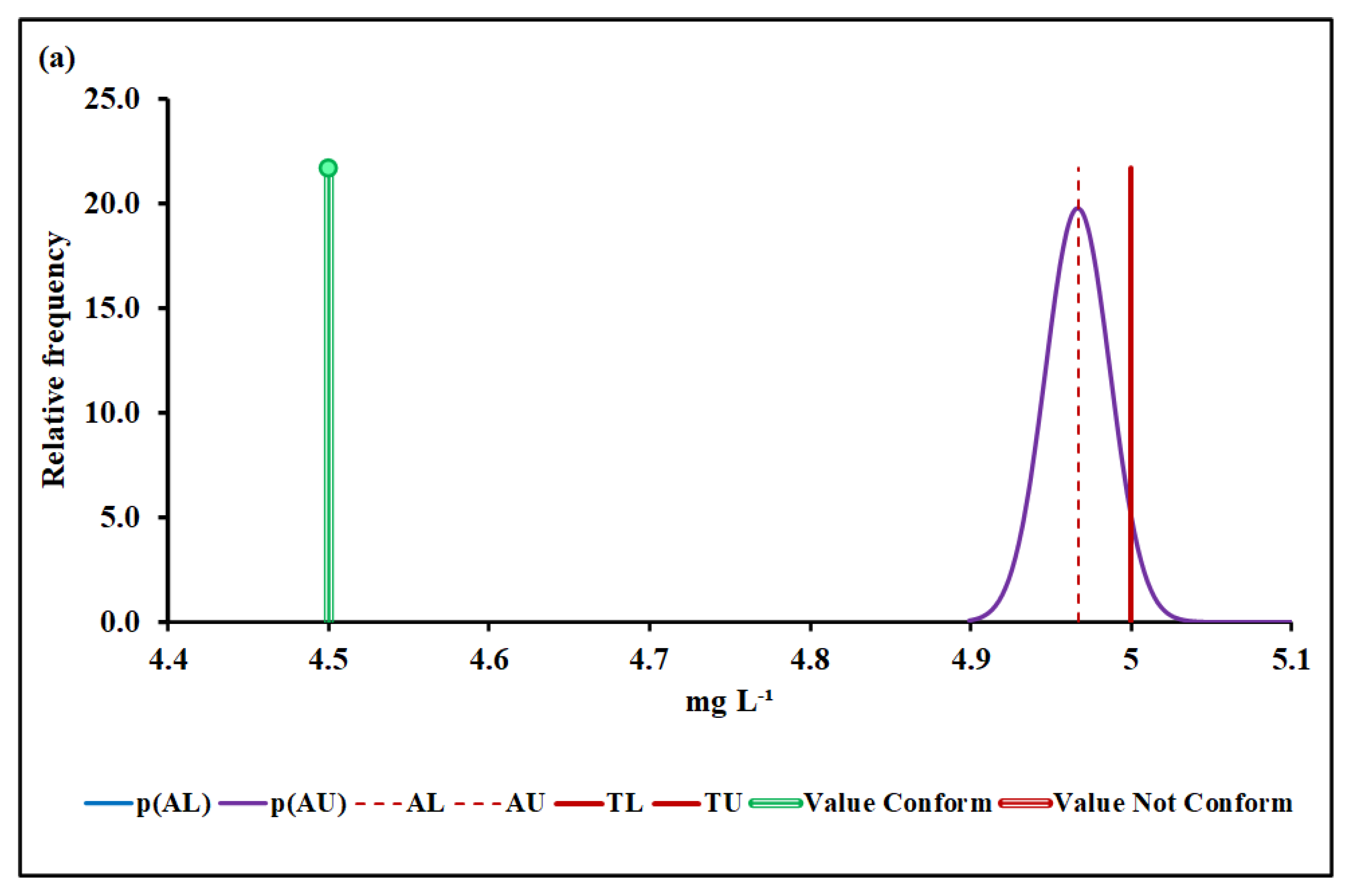
4.3.2. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
4.3.3. Manganese Molar Concentration
4.3.4. Escherichia coli
4.3.5. Summarizing Different Approaches
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Zadeh, S.M.; Turral, H.; Burke, J. Water Pollution from Agriculture: A Global Review. Executive Summary; FAO: Rome, Italy; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2017; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, R.A.; Lobo, E.A.; da Costa, A.B.; Delevati, D.M. Evaluation of water resource preservation areas in the Hydrographical Basin of Andreas Stream, RS, Brazil, using environmental monitoring programs. Rev. Ambiente Água 2019, 14, e2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A.; Harding, W.R.; Slawski, T.M.; Lin, H. Monitoring and Evaluation: The Foundation for Lake and Reservoir Management. Earth 2022, 3, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Abdyzhapar Uulu, S.; Abuduwaili, J. Exploration of the driving factors and distribution of fecal coliform in rivers under a traditional agro-pastoral economy in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollah, S.B.H.S.; Sharafati, A.; Mott, D.; Yaseen, Z.M. River water quality index prediction and uncertainty analysis: A comparative study of machine learning models. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.B.; Mohammadpour, R.; Linh, N.T.T.; Mohajane, M.; Pourjasem, A.; Sammen, S.S.; Anh, D.T.; Nam, V.T. Application of soft computing to predict water quality in wetland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howladar, M.F.; Chakma, E.; Koley, N.J.; Islam, S.; Numanbakth, M.A.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Chowdhury, T.R.; Akter, S. The water quality and pollution sources assessment of Surma river, Bangladesh using, hydrochemical, multivariate statistical and water quality index methods. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, J.Y.; An, K.-G. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Water Quality and Trophic State in an Artificial Dam Reservoir. Water 2021, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, G.; Kothari, R.; Dhar, S.; Pathania, D.; Tyagi, V.V. Impact assessment on water quality in the polluted stretch using a cluster analysis during pre- and COVID-19 lockdown of Tawi river basin, Jammu, North India: An environment resiliency. Energ. Ecol. Environ. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarek, S.; Kiedrzynska, E.; Kiedrzynski, M.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Mitsch, W.J.; Zalewski, M. Comparing ecotoxicological and physicochemical indicators of municipal wastewater effluent and river water quality in a Baltic Sea catchment in Poland. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babamiri, O.; Marofi, S. A multi-objective simulation–optimization approach for water resource planning of reservoir–river systems based on a coupled quantity–quality model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giao, N.T.; Nhien, H.T.H.; Anh, P.K.; Ni, D.V. Use of Complex Network Modelling to Assess the Influence of the Parameters on Water Quality of Rivers. Environ. Monit. Assess 2021, 193, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwacu, R.A.; Habanabakize, E.; Adamowski, J.; Schwinghamer, T.D. Using radical terraces for erosion control and water quality improvement in Rwanda: A case study in Sebeya catchment. Environ. Dev. 2021, 39, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Sun, C. Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Drop Combined with High Performance Liquid Chromatography for Analysis of 15 Phthalates in Water. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Othman, A.A. Evaluation of the suitability of surface water from Riyadh Mainstream Saudi Arabia for a variety of uses. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gayer, F.A.M.; de Angelis, D.F.; de Angelis, A.F.; Poletti, E.C.C. Use of Complex Network Modelling to Assess the Influence of the Parameters on Water Quality of Rivers. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, R.F.B.; Crisiogiovanni, E.L.; Trevisan, E.; Radomski, F.A.D. Spatial and temporal variation of water quality in a watershed in center-west Paraná, Brazil. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1734–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.A.; Silva Junior, L.C.S.; Azevedo, J.P.S.; Santos, M.A.; Assumpção, R.S.F.V. From Monitoring and Modeling to Management: How to Improve Water Quality in Brazilian Rivers? A Case Study: Piabanha River Watershed. Water 2021, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, G.C.; Carreira, R.S.; Massone, C.G. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in water: Method development and application to river samples from a populated tropical urban area. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboim, I.L.; Gomes, D.F.; Junior, P.O.M. Phytoplankton response to water quality seasonality in a Brazilian neotropical river. Environ. Monit. Assess 2020, 192, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.A.S.; Gonçalves, A.A.; Aragão, R.; Amorim, J.R.A.; Mota, P.V.M.; Srinivasan, V.S.; Garcia, C.A.B.; Figueiredo, E.E. Spatial and seasonal variability of the water quality characteristics of a river in Northeast Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, A.M.S.; Oliveira, M.A.L.; Ciminelli, V.S.T.; Silva, J.C.J. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Cr, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb from Sediment, Followed by FAAS and GFAAS Analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazilian National Environment Council (CONAMA). Resolution no. 357. Provides the Classification of Water Bodies and Environmental Guidelines for Their Framework, as Well as Stablishes the Conditions and Standards for Effluents Discharge; Brazilian National Environment Council (CONAMA): Brasília, Brazil, 2005; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. 4500-h+ ph. In Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, A.; Al Raisi, A.; Thankamony, R.; Perumal, P.; Al Hosani, S. Eutrophication sources, impacts and management: A case study from Abu Dhabi. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2020, 23, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. 3500-mn manganese. In Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.F.; Ozaki, D.A.F.; Barbosa, E.; dos Santos, E.E.; Gomes, M.M.; Iida, P.H.; dos Santos, S.C.A.; de Sá, F.G.; de Oliveira, E.C. Validation of the performance of process stream analyzer systems with nonparametric behavior. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2014, 19, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13528:2015; Statistical Methods for Use in Proficiency Testing by Interlaboratory Comparisons. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Holleben, C.; Oliveira, E.C. Variations in the classification of laboratory performance due to different protocols for use in proficiency testing programs. Measurement 2020, 152, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCGM 106: 2012; Evaluation of Measurement Data—The Role of Measurement Uncertainty in Conformity Assessment. Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology: Sèvres, France, 2012. Available online: www.bipm.org/en/publications/guides/gum.html (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Ellison, S.L.R.; Williams, A. (Eds.) EURACHEM/CITAC Guide: Use of Uncertainty Information in Compliance Assessment, 2nd ed.; Construction Innovation and Technology Application Centre: Hong Kong, China, 2021; Available online: https://www.eurachem.org/index.php/publications/guides (accessed on 14 September 2021).
- De Oliveira, E.C.; Biazon, C.L.; Moreira, R.M.; Filho, P.L.S. Uncertainty evaluation in the determination of oil and grease content in produced water by colorimetric method using Monte Carlo Simulation. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toczek, W.; Smulko, J. Risk Analysis by a Probabilistic Model of the Measurement Process. Sensors 2021, 21, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, E.C.; Lourenço, F.R. Risk of false conformity assessment applied to automotive fuel analysis: A multiparameter approach. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, E.C.; Lourenço, F.R. Data reconciliation applied to the conformity assessment of fuel products. Fuel 2021, 300, 120936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuselman, I.; Pennecchi, F.; da Silva, R.J.N.B.; Hibbert, D.B. Conformity assessment of multicomponent materials or objects: Risk of false decisions due to measurement uncertainty—A case study of denatured alcohols. Talanta 2017, 164, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, E.C. Use of Measurement Uncertainty in Compliance Assessment with Regulatory Limits. Braz. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 7, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Separovic, L.; Simabukuro, R.S.; Couto, A.R.; Bertanha, M.L.G.; Dias, F.R.S.; Sano, A.Y.; Caffaro, A.M.; Lourenço, F.R. Measurement Uncertainty and Conformity Assessment Applied to Drug and Medicine Analyses—A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simabukuro, R.; Jeong, N.A.; Lourenço, F.R. Application of Measurement Uncertainty on Conformity Assessment in Pharmaceutical Drug Products. J. AOAC Int. 2021, 104, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennecchi, F.R.; Kuselman, I.; da Silva, R.J.N.B.; Hibbert, D.B. Risk of a false decision on conformity of an environmental compartment due to measurement uncertainty of concentrations of two or more pollutants. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, J.L.; Tavares, L.P.S.; Kalas, F.A.; Rodrigues, P.P.G.W.; Wasserman, J.C.A. Reservoir implantation for flood dampening in the Macaé River basin using the Mohid Land model. Ciência Nat. 2019, 41, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Oliveira, E.C.; Orlando, A.F.; Ferreira, A.L.S.; Chaves, C.E.O. Comparison of different approaches for detection and treatment of outliers in meter proving factors determination. Flow Meas Instrum. 2016, 48, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, C.; Palma, C.; Dadamos, T.; Bettencourt da Silva, R.J.N. Evaluation of seawater composition in a vast area from the Monte Carlo simulation of georeferenced information in a Bayesian framework. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| pH Results | BOD Results (mg L−1) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.20 | 5.10 | 5.23 | 6.30 | 6.23 | 5.90 | 4.40 | 18.00 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 3.97 |
| 5.99 | 6.01 | 6.00 | 6.10 | 5.80 | 6.10 | 4.40 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 101.00 | 4.50 | 3.97 |
| 5.86 | 5.86 | 5.91 | 5.93 | 5.96 | 6.00 | 91.91 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 6.23 | 4.18 |
| 6.12 | 6.19 | 6.20 | 6.21 | 6.24 | 6.29 | 4.20 | 92.30 | 77.85 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.18 |
| 6.09 | 6.19 | 6.02 | 6.73 | 6.12 | 6.86 | 4.60 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 39.18 | 4.50 | 5.72 |
| 6.97 | 7.05 | 7.08 | 7.23 | 7.30 | 7.53 | 4.80 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 5.72 |
| 6.30 | 7.50 | 6.30 | 6.30 | 6.57 | 6.34 | 4.40 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 5.91 | 5.91 |
| 5.90 | 8.10 | 6.06 | 6.11 | 6.10 | 6.20 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 |
| 6.93 | 6.94 | 7.66 | 7.65 | 7.80 | 4.50 | 83.25 | 22.37 | 2.33 | 6.23 | ||
| 8.90 | 101.00 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 2.33 | 4.50 | ||||||
| 10.00 | 4.50 | 98.97 | 4.50 | 3.48 | 6.92 | ||||||
| 3.00 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 3.48 | 6.92 | ||||||
| 6.98 | 83.25 | 8.76 | 91.91 | 4.50 | 4.50 | ||||||
| 6.98 | 4.50 | 9.17 | 4.50 | 22.37 | 98.87 | ||||||
| 8.76 | 4.10 | 9.17 | 92.30 | 4.50 | 4.50 | ||||||
| 39.18 | 4.50 | 77.85 | 4.50 | ||||||||
| Manganese results (mg L−1) | Escherichia coli results (MPN * per 100 mL) | ||||||||||
| 0.376 | 0.079 | 0.081 | 0.079 | 0.096 | 0.115 | 901 | 1138 | 914 | 500 | 1058 | 1043 |
| 0.091 | 0.270 | 0.092 | 0.030 | 0.096 | 0.115 | 1100 | 1131 | 1048 | 500 | 911 | 952 |
| 0.280 | 0.320 | 0.092 | 0.070 | 0.096 | 0.137 | 1126 | 1000 | 1042 | 970 | 1900 | 1019 |
| 0.081 | 0.290 | 0.099 | 0.210 | 0.096 | 0.137 | 1098 | 964 | 1023 | 1102 | 1034 | 1096 |
| 0.139 | 0.083 | 0.073 | 0.077 | 0.096 | 0.081 | 902 | 1220 | 1111 | 1042 | 1079 | 926 |
| 0.095 | 0.083 | 0.073 | 0.090 | 0.098 | 0.139 | 500 | 1220 | 1128 | 1056 | 983 | 950 |
| 0.310 | 0.083 | 0.300 | 0.230 | 0.100 | 0.140 | 901 | 800 | 998 | 1114 | 1110 | 1118 |
| 0.057 | 0.085 | 0.076 | 0.091 | 0.100 | 0.140 | 1000 | 1000 | 952 | 965 | 960 | 933 |
| 0.330 | 0.095 | 0.126 | 0.091 | 0.100 | 0.168 | 1028 | 1121 | 1036 | 991 | 1094 | 1030 |
| 0.012 | 0.091 | 0.078 | 0.092 | 0.100 | 0.168 | 1000 | 985 | 922 | 1100 | 1139 | 994 |
| 0.089 | 0.091 | 0.078 | 0.200 | 0.113 | 0.376 | ||||||
| 0.079 | 0.081 | 0.099 | 0.096 | 0.113 | 0.080 | ||||||
| pH | BOD (mg L−1) | Mn (mol L−1) | Escherichia coli (MPN per 100 mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specification limit ‡ | 6–9 | 5 † | 0.1 † | 1000† |
| Median | 6.20 | 4.5 | 0.0956 | 1026 |
| Mean | 6.40 | 17.2 | 0.128 | 1016 |
| Standard deviation (SD) | 0.62 | 29.1 | 0.081 | 184 |
| IQR | 0.870 | 3.095 | 0.0553 | 142 |
| 0.645 | 2.2943 | 0.0410 | 105 | |
| 0.334 | 0.1483 | 0.0248 | 109 | |
| p | 52 | 94 | 72 | 60 |
| SD | 0.18 | 6.1 | 0.019 | 48 |
| nIQR | 0.23 | 0.60 | 0.012 | 35 |
| MADe | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.007 | 36 |
| 0.18 | 0.48 | 0.010 | 28 | |
| 0.095 | 0.03 | 0.006 | 29 |
| pH | BOD (mg L−1) | Mn (mol L−1) | Escherichia coli (MPN per 100 mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result | Consumer’s Risk | Result | Consumer’s Risk | Result | Consumer’s Risk | Result | Consumer’s Risk | |
| Median and MADe | 0.04% | 4.50 ± 0.04 | 0.00% | 0.096 ± 0.007 | 12.7% | 1026 ± 36 | 7.4% | |
| Median and nIQR | 4.0% | 4.50 ± 0.60 | 4.9% | 0.096 ± 0.012 | 25.3% | 1026 ± 35 | 6.9% | |
| Mean and SD | 0.00% | 17.2 ± 6.1 | Without overlap | 0.128 ± 0.019 | Without overlap | 1016 ± 48 | 25.2% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandão, L.P.; Silva, V.F.; Bassi, M.; de Oliveira, E.C. Risk Assessment in Monitoring of Water Analysis of a Brazilian River. Molecules 2022, 27, 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113628
Brandão LP, Silva VF, Bassi M, de Oliveira EC. Risk Assessment in Monitoring of Water Analysis of a Brazilian River. Molecules. 2022; 27(11):3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113628
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandão, Luciene Pires, Vanilson Fragoso Silva, Marcelo Bassi, and Elcio Cruz de Oliveira. 2022. "Risk Assessment in Monitoring of Water Analysis of a Brazilian River" Molecules 27, no. 11: 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113628
APA StyleBrandão, L. P., Silva, V. F., Bassi, M., & de Oliveira, E. C. (2022). Risk Assessment in Monitoring of Water Analysis of a Brazilian River. Molecules, 27(11), 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113628