Neurotoxin (N-Oxalyl-L-α,β-Diamino Propionic Acid) Content in Different Plant Parts of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Spanning Seedling to Maturity Stage: Does It Increase over Time?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Plant Material Sampling and Data Recording
2.3. Determination of Total ODAP Content
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
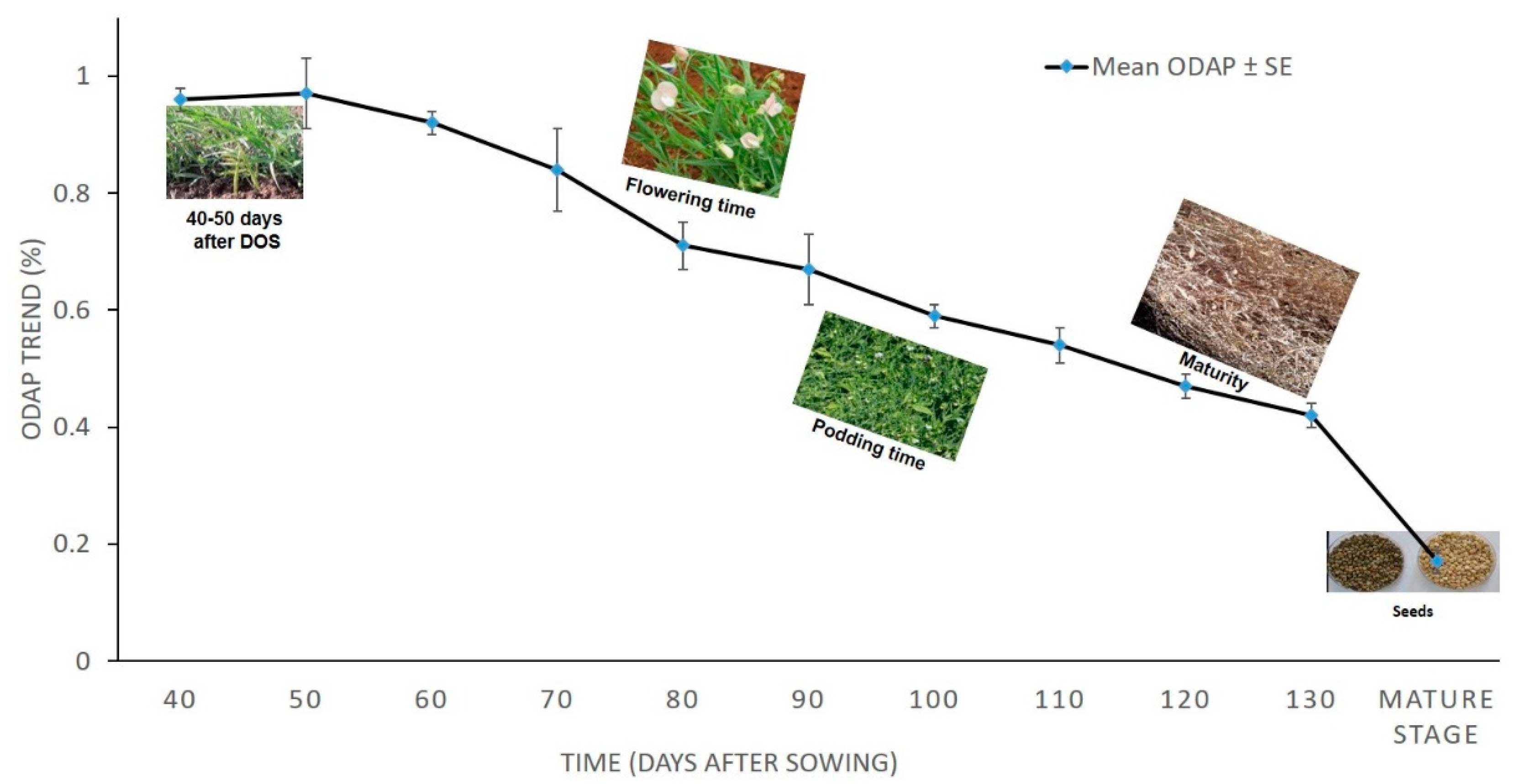
3.1. Total ODAP Content in Tested Grass Pea Accessions in 2010–2011
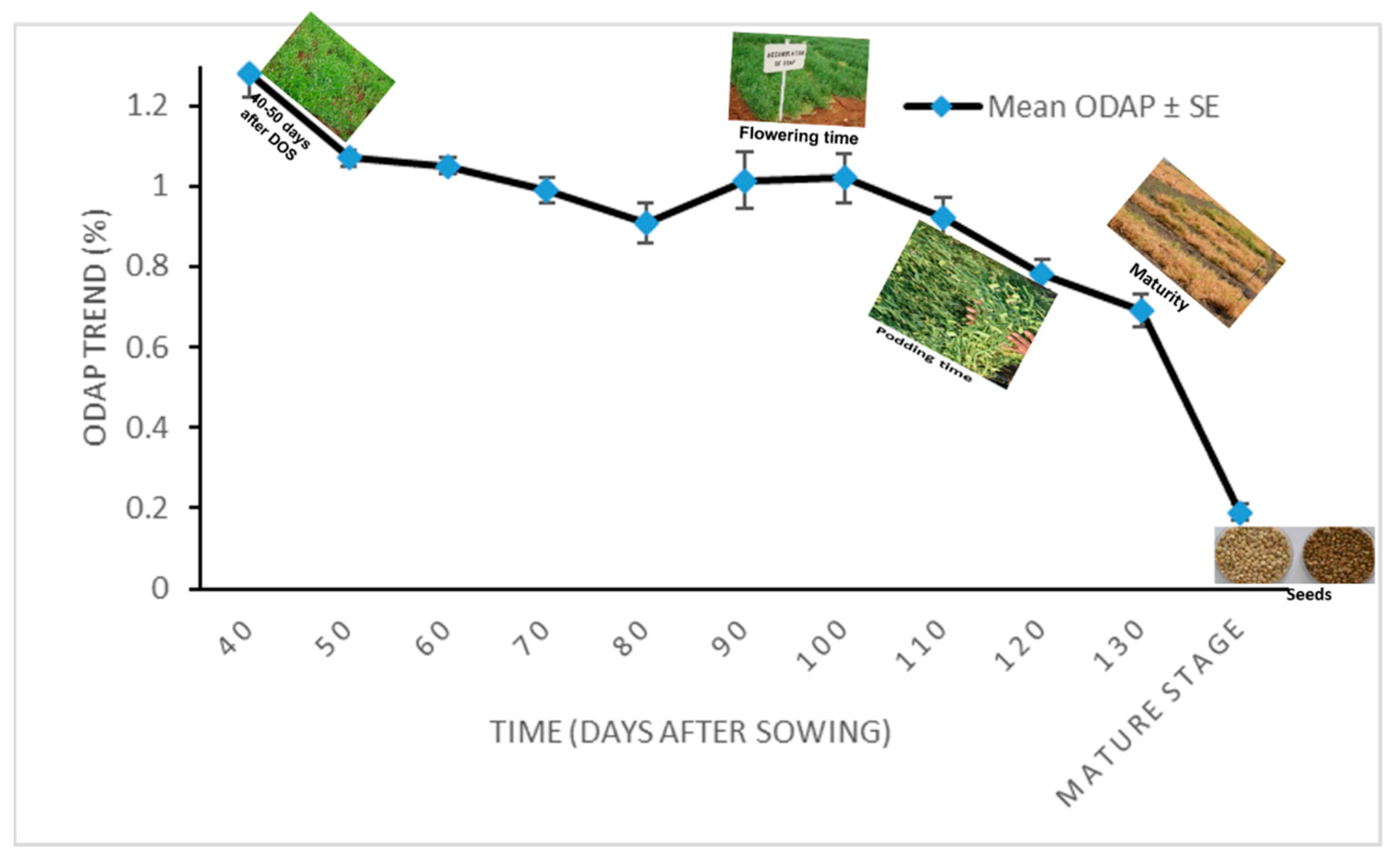
3.2. Total ODAP Content in Tested Grass Pea Accessions in 2011–2012
3.3. Distribution of Total ODAP in Different Plant Parts at Mature Stage
3.4. Yearly Variation in Total ODAP
4. Discussion
4.1. Total ODAP Content in Tested Grass Pea Accessions in 2010–2011 and 2011–2012
4.2. Changes in the Concentration of Total ODAP in Different Parts of Plants Depending on the Developmental Stage
4.3. Yearly Variation in Total ODAP
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ODAP | N-oxalyl-L-α, β-diaminopropionic acid |
| OPA | O-phthalaldehyde |
| DAS | Days after sowing |
References
- Kumar, S.; Bejiga, G.; Ahmed, S.; Nakkoul, H.; Sarkar, A. Genetic Improvement of grass pea for low neurotoxin (β-ODAP) content. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, P.; Barpete, S.; Sarker, A.; Amri, A.; Mathur, P.N.; Baum, M. Grass pea. In Genetic and Genomic Resources for Grain Legume Improvement; Singh, M., Upadhyaya, H.D., Bisht, I.S., Eds.; Elsevier: London, United Kingdom, 2013; pp. 269–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambein, F.; Travella, S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Montagu, M.V.; Heijde, M. Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.): Orphan crop, nutraceutical or just plain food? Planta 2019, 250, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.Y.; Spencer, P.S.; Li, Z.X.; Liang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, F.M. Lathyrus sativus (grass pea) and its neurotoxin ODAP. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, G.; Adriano, C. Disorders of upper and lower motor neurons. In Prognosis of Neurological Diseases; Springer: Milano, Italy, 2015; pp. 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Lambein, F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Kusama-Eguchi, K.; Ikegami, F. β-N-oxalyll-α,β-diaminopropionic acid, a multifunctional plant metabolite of toxic reputation. Arkivoc 2007, 9, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.S.; Rao, S.L.N. Lessons from neurolathyrism: A disease of the past & the future of Lathyrus sativus (Khesari dal). Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 32–37. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3767245/pdf/IJMR-138-32.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Hao, X.; Yang, T.; Liu, R.; Hu, J.; Yao, Y.; Burlyaeva, M.; Wang, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, H.; Zong, X.; et al. An RNA sequencing transcriptome analysis of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) and development of SSR and KASP markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, P.; Barpete, S.; Choukri, H.; Maalouf, F.; Sarkar, A. Grass Pea. In The Beans and the Peas; Pratap, A., Gupta, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, W. Stability of grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.) varieties for ODAP content and grain yield in Ethiopia. Lathyrus Lathyrism Newslett. 2003, 3, 32–34. Available online: https://www.clima.uwa.edu.au/data/assets/pdf_file/0005/919805/Tadesse.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Siddique, K.H.M.; Loss, S.P.; Herwig, S.P.; Wilson, J.M. Growth, yield and neurotoxin (ODAP) concentration of three Lathyrus species in Mediterranean type environments of Western Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1996, 36, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbury, C.D.; White, C.L.; Mullan, B.P.; Siddique, K.H.M. A review of the potential of Lathyrus sativus L. and L. cicera L. grain for use as animal feed. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2000, 87, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Khan, J.K.; Lambein, F. Biosynthesis of the neurotoxin â-ODAP in developing pods of Lathyrus sativus. Phytochemistry 1994, 35, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, W.; Bekele, E. Variation and association of morphological and biochemical characters in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). Euphytica 2003, 130, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.L.; Xiong, Y.; Bai, X.; Kong, H.; Tan, R.; Zhu, H.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wang, J.; Turner, N.C. Genotypic variation in the concentration of β-N-Oxalyl-l-α,β-diaminopropionic acid (β-ODAP) in grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.) seeds is associated with an accumulation of leaf and pod β-ODAP during vegetative and reproductive stages at three levels of water Stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6133–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf HK, M.; Hoque, K.; Uddin, A.; Roy, B.C.; Lambein, F. Homoarginine antagonizes the toxicity of Lathyrus toxin in one-day-chiks. Bangladesh J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1995, 10, 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Shamin, M.Z.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, K.; Yusuf, H.K.M.; Lambein, F. Mechanism of ODAP toxicity in one-day-old chicks. Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 11, 1–7. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1854/LU-271535 (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Fikre, A.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Ahmed, S.; Gheysen, G.; Lambein, F. Effect of Methionine Supplement on Physical Responses and Neurological Symptoms in Broiler Chicks Fed Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus) Based Starter Ration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.L.N. A sensitive and specific colorimetric method for the determination of α, β- diaminopropionic acid and the Lathyrus sativus neurotoxin. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.J.; Parreno, N.; Campbell, C.G. Phytochemical assessment of Lathyrus species for the neurotoxic agent, β-N-oxalyl-L-α, β-diaminopropionic acid. Planta Med. 1983, 47, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, G.; Narayan, R.K.J. Developmental variation of the neurotoxin, b-N-oxalyl-L-a, b-diaminopropionic acid (ODAP), in Lathyrus sativus. Ann. Bot. 1994, 74, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.J.; Xu, Q.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, F.M.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, Y.F. Accumulation pattern of toxin β-ODAP during lifespan and effect of nutrient elements on β-ODAP content in Lathyrus sativus seedlings. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergiovanni, A.R.; Lupo, F.; Zaccardelli, M. Environmental effect on yield, composition and technological seed traits of some Italian ecotypes of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergiovanni, A.R.; Damascelli, A. L-Homoarginine accumulation in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) dry seeds. A preliminary survey. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.D.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Loss, S.P. Cool season grain legumes for Mediterranean environments: Species × environment interaction in seed quality traits and anti-nutritional factors in the genus Vicia. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1999, 50, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urga, K.; Fufa, H.; Biratu, E.; Husain, A. Evaluation of Lathyrus sativus cultivated in Ethiopia for proximate composition, minerals, β-ODAP and anti-nutritional components. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Polignano, G.B.; Bisignano, V.; Tomaselli, V.; Uggenti, P.; Alba, V.; Gatta, C.D. Genotype × Environment interaction in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) lines. Int. J. Agron. 2009, 2009, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| S. No. | Day * | Mean ± SE (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B387 | B222 | B390 | Bio-520 | B587 | ||
| 1 | 40 | 0.89 ± 0.11 | 1.02 ± 0.08 | 0.96 ± 0.10 | 0.93 ± 0.22 | 1.00 ± 0.15 |
| 2 | 50 | 0.75 ± 0.09 | 1.06 ± 0.10 | 0.94 ± 0.11 | 1.09 ± 0.20 | 1.03 ± 0.06 |
| 3 | 60 | 0.88 ± 0.20 | 0.93 ± 0.22 | 0.95 ± 0.07 | 0.89 ± 0.30 | 0.95 ± 0.28 |
| 4 | 70 | 0.70 ± 0.23 | 1.00 ± 0.25 | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 0.64 ± 0.21 | 0.99 ± 0.12 |
| 5 | 80 | 0.64 ± 0.18 | 0.80 ± 0.20 | 0.70 ± 0.15 | 0.59 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.07 |
| 6 | 90 | 0.70 ± 0.05 | 0.89 ± 0.09 | 0.59 ± 0.06 | 0.49 ± 0.20 | 0.66 ± 0.04 |
| 7 | 100 | 0.62 ± 0.20 | 0.66 ± 0.10 | 0.56 ± 0.22 | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 0.61 ± 0.09 |
| 8 | 110 | 0.59 ± 0.07 | 0.61 ± 0.05 | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.42 ± 0.17 | 0.57 ± 0.18 |
| 9 | 120 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.54 ± 0.20 | 0.43 ± 0.23 | 0.39 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ± 0.09 |
| 10 | 130 | 0.48 ± 0.10 | 0.43 ± 0.20 | 0.39 ± 0.15 | 0.36 ± 0.15 | 0.43 ± 0.12 |
| 11 | Mature stage (seeds) | 0.17 ± 0.09 | 0.19 ± 0.10 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.17 ± 0.10 | 0.21 ± 0.04 |
| Source of Variation | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | Pr (>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 10 | 3.202 | 0.3202 | 56.43 | <2 × 1016 * |
| Error (Genotype × Time) | 40 | 0.227 | 0.0057 |
| * Days | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | Mature Stage (seeds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ** Mean ODAP% ± SE | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.97 ± 0.06 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 0.84 ± 0.07 | 0.71 ± 0.04 | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.02 |
| Sl. No | Day * | Mean ± SE (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B387 | B222 | B390 | Bio-520 | B587 | ||
| 1 | 40 | 1.47 ± 0.2 | 1.19 ± 0.06 | 1.27 ± 0.14 | 1.34 ± 0.19 | 1.13 ± 0.03 |
| 2 | 50 | 1.06 ± 0.04 | 1.02 ± 0.04 | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.10 ± 0.09 | 1.06 ± 0.07 |
| 3 | 60 | 1.04 ± 0.03 | 1.09 ± 0.04 | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.05 | 1.03 ± 0.02 |
| 4 | 70 | 0.93 ± 0.06 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 1.02 ± 0.02 | 1.10 ± 0.06 | 0.98 ± 0.02 |
| 5 | 80 | 0.80 ± 0.17 | 1.02 ± 0.24 | 0.81 ± 0.15 | 1.00 ± 0.20 | 0.91 ± 0.17 |
| 6 | 90 | 0.92 ± 0.21 | 1.08 ± 0.05 | 1.19 ± 0.10 | 1.37 ± 0.09 | 1.12 ± 0.08 |
| 7 | 100 | 1.22 ± 0.08 | 1.06 ± 0.11 | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 0.98 ± 0.16 | 0.98 ± 0.17 |
| 8 | 110 | 1.12 ± 0.27 | 0.92 ± 0.15 | 0.85 ± 0.12 | 0.89 ± 0.12 | 0.84 ± 0.14 |
| 9 | 120 | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 0.84 ± 0.13 | 0.76 ± 0.04 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.10 |
| 10 | 130 | 0.80 ± 0.20 | 0.58 ± 0.11 | 0.76 ± 0.06 | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 0.58 ± 0.10 |
| 11 | Mature stage (seeds) | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.20 ± 0.09 | 0.21 ± 0.22 |
| Source of Variation | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | Pr (>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 10 | 4.152 | 0.4152 | 39.59 | <2 × 1016 * |
| Error (Genotype × Time) | 40 | 0.419 | 0.0105 |
| Day * | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | Mature Stage (Seeds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ** ODAP% ± SE | 1.28 ± 0.06 | 1.07 ± 0.02 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 0.99 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 1.13 ± 0.07 | 1.02 ± 0.06 | 0.92 ± 0.05 | 0.78 ± 0.04 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.02 |
| Source | DF | Mean Square (Stem) | Mean Square (Leaf) | Mean Square (Pod Cover) | Mean Square (Seed) | Mean Square (Seed Coat) | Mean Square (Cotyledons) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rep | 2 | 0.060 | 0.007 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.009 |
| Genotypes | 4 | 0.026 | 0.157 * | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.017 * | 0.006 |
| Error | 8 | 0.032 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| Total | 14 |
| Plant Part | Total ODAP Content (%) (Mean ± SE) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B387 | B222 | B390 | Bio-520 | B587 | Total | |
| Stem | 0.342 ± 0.08 | 0.395 ± 0.02 | 0.266 ± 0.03 | 0.321 ± 0.03 | 0.514 ± 0.09 | 0.368 ± 0.05 |
| Leaf | 0.387 ± 0.05 | 1.009 ± 0.02 | 0.614 ± 0.06 | 0.663 ± 0.02 | 0.784 ± 0.01 | 0.691 ± 0.03 |
| Pod cover | 0.163 ± 0.01 | 0.285 ± 0.02 | 0.413 ± 0.08 | 0.219 ± 0.02 | 0.299 ± 0.02 | 0.276 ± 0.03 |
| Seed | 0.125 ± 0.02 | 0.200 ± 0.04 | 0.219 ± 0.04 | 0.211 ± 0.01 | 0.213 ± 0.03 | 0.193 ± 0.02 |
| Seed coat | 0.144 ± 0.03 | 0.260 ± 0.01 | 0.257 ± 0.06 | 0.354 ± 0.05 | 0.283 ± 0.03 | 0.260 ± 0.03 |
| Cotyledons | 0.181 ± 0.07 | 0.291 ± 0.02 | 0.249 ± 0.04 | 0.258 ± 0.02 | 0.379 ± 0.04 | 0.272 ± 0.04 |
| Days of Sampling after Sowing | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotypes | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | Mature Seed |
| Mean | 0.959 (2010) 1.278 (2011) | 0.972 (2010) 1.066 (2011) | 0.920 (2010) 1.048 (2011) | 0.839 (2010) 0.992 (2011) | 0.713 (2010) 0.907 (2011) | 0.667 (2010) 1.134 (2011) | 0.594 (2010) 1.021 (2011) | 0.536 (2010) 0.922 (2011) | 0.471 (2010) 0.782 (2011) | 0.418 (2010) 0.692 (2011) | 0.173 (2010) 0.193 (2011) |
| Variance | 0.003 (2010) 0.018 (2011) | 0.019 (2010) 0.001 (2011) | 0.001 (2010) 0.001 (2011) | 0.027 (2010) 0.005 (2011) | 0.010 (2010) 0.011 (2011) | 0.022 (2010) 0.027 (2011) | 0.003 (2010) 0.017 (2011) | 0.006 (2010) 0.013 (2011) | 0.004 (2010) 0.008 (2011) | 0.002 (2010) 0.010 (2011) | 0.001 (2010) 0.002 (2011) |
| t test (p value) | 0.004 | 0.173 | 0.000 | 0.107 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.364 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barpete, S.; Gupta, P.; Sen Gupta, D.; Kumar, J.; Bhowmik, A.; Kumar, S. Neurotoxin (N-Oxalyl-L-α,β-Diamino Propionic Acid) Content in Different Plant Parts of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Spanning Seedling to Maturity Stage: Does It Increase over Time? Molecules 2022, 27, 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123683
Barpete S, Gupta P, Sen Gupta D, Kumar J, Bhowmik A, Kumar S. Neurotoxin (N-Oxalyl-L-α,β-Diamino Propionic Acid) Content in Different Plant Parts of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Spanning Seedling to Maturity Stage: Does It Increase over Time? Molecules. 2022; 27(12):3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123683
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarpete, Surendra, Priyanka Gupta, Debjyoti Sen Gupta, Jitendra Kumar, Arpan Bhowmik, and Shiv Kumar. 2022. "Neurotoxin (N-Oxalyl-L-α,β-Diamino Propionic Acid) Content in Different Plant Parts of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Spanning Seedling to Maturity Stage: Does It Increase over Time?" Molecules 27, no. 12: 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123683
APA StyleBarpete, S., Gupta, P., Sen Gupta, D., Kumar, J., Bhowmik, A., & Kumar, S. (2022). Neurotoxin (N-Oxalyl-L-α,β-Diamino Propionic Acid) Content in Different Plant Parts of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Spanning Seedling to Maturity Stage: Does It Increase over Time? Molecules, 27(12), 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123683







