Yeast Strains and Wort Color as Factors Affecting Effects of the Ethanol Fermentation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Parameters, Carbohydrates and Glycerol Content
2.2. Phenolic Compound Content and Antioxidant Activity of Worts and Beers
2.3. Evaluation of the Morphological Characteristics of Yeast Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biological Material
3.2. Abbreviations
3.3. Brewing Technology
3.4. Basic Physico-Chemical Parameters
3.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Carbohydrates and Glycerol Content
3.6. Total Polyphenols Content
3.7. Ability of Iron Ion Reduction (FRAP)
3.8. Ability of Radical Cation ABTS•+ Reduction
3.9. Ability of Radical Cation DPPH• Reduction
3.10. Evaluation of the Morphological Characteristics of Yeast Cells
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Coghe, S.; D’Hollander, H.; Verachtert, H.; Delvaux, F.R. Impact of dark specialty malts on extract composition and wort fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 111, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopska, V.; Denkova-Kostova, R.; Dzhivoderova-Zarcheva, M.; Teneva, D.; Denev, P.; Kostov, G. Comparative Study on Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Different Malt Types. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, H.; Linforth, R.S.; Cook, D.J. Flavour generation during commercial barley and malt roasting operations: A time course study. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Adamenko, K.; Pietrzak, W.; Paszkot, J.; Głowacki, A.; Gasiński, A.; Leszczyński, P. The Potential of Traditional Norwegian KVEIK Yeast for Brewing Novel Beer on the Example of Foreign Extra Stout. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogerus, K.; Gibson, B. A re-evaluation of diastatic Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and their role in brewing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gąsior, J.; Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Kucharska, A.Z. Carbohydrates profile, polyphenols content and antioxidative properties of beer worts produced with different dark malts varieties or roasted barley grains. Molecules 2020, 25, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dack, R.E.; Black, G.W.; Koutsidis, G. The effect of Maillard reaction products and yeast strain on the synthesis of key higher alcohols and esters in beer fermentations. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.M.; Stewart, G.G. Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the production of fermented beverages. Beverages 2016, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.G. Yeast flocculation—Sedimentation and flotation. Fermentation 2018, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, D.O.; Guido, L.F. A review on the fate of phenolic compounds during malting and brewing: Technological strategies and beer styles. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszkot, J.; Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Anioł, M. Properties of Dry Hopped Dark Beers with High Xanthohumol Content. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.; Díaz, A.B.; Durán-Guerrero, E.; Lasanta, C. Influence of different fermentation conditions on the analytical and sensory properties of craft beers: Hopping, fermentation temperature and yeast strain. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.F.; Carvalho, J.; Pinto, E.; Cunha, S.; Almeida, A.A.; Ferreira, I.M. Nutritive value, antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds profile of brewer’s spent yeast extract. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 52, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbah, R.A.; Meledina, T.V.; Morozov, A.A. The effect of yeast growth stages on the absorption of polyphenols. Agron. Res. 2020, 18, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Fumi, M.D.; Galli, R.; Lambri, M.; Donadini, G.; De Faveri, D.M. Effect of full-scale brewing process on polyphenols in Italian all-malt and maize adjunct lager beers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawa-Rygielska, J. Oddziaływanie Jonów Cr (III) na Dynamikę i Efekty Fermentacji Zacierów Kukurydzianych VHG; Monografie; Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu: Wrocław, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Foszczyńska, B.; Dziuba, E.; Chmielewska, J. Ocena możliwości pomiaru średnicy komórek drożdży piwowarskich przy użyciu laserowego analizatora wielkości cząstek. Acta Sci. Pol. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yeast Data Sheet. Available online: https://fermentis.com/en/product/safale-s-04/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Yeast Data Sheet. Available online: https://fermentis.com/en/product/saflager-s-23/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Yeast Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.lallemandbrewing.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/TDS_LPS_BREWINGYEAST_VOSS_ENG_8.5x11.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Yeast Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.lallemandbrewing.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/TDS_LALBREW_PREM_BELLESAISON_ENGLISH_DIGITAL.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Prior, R.L.; Wu, X.; Schaich, K. Standardized methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.C.; Chen, H.Y. Antioxidant activity of various tea extracts in relation to their antimutagenicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
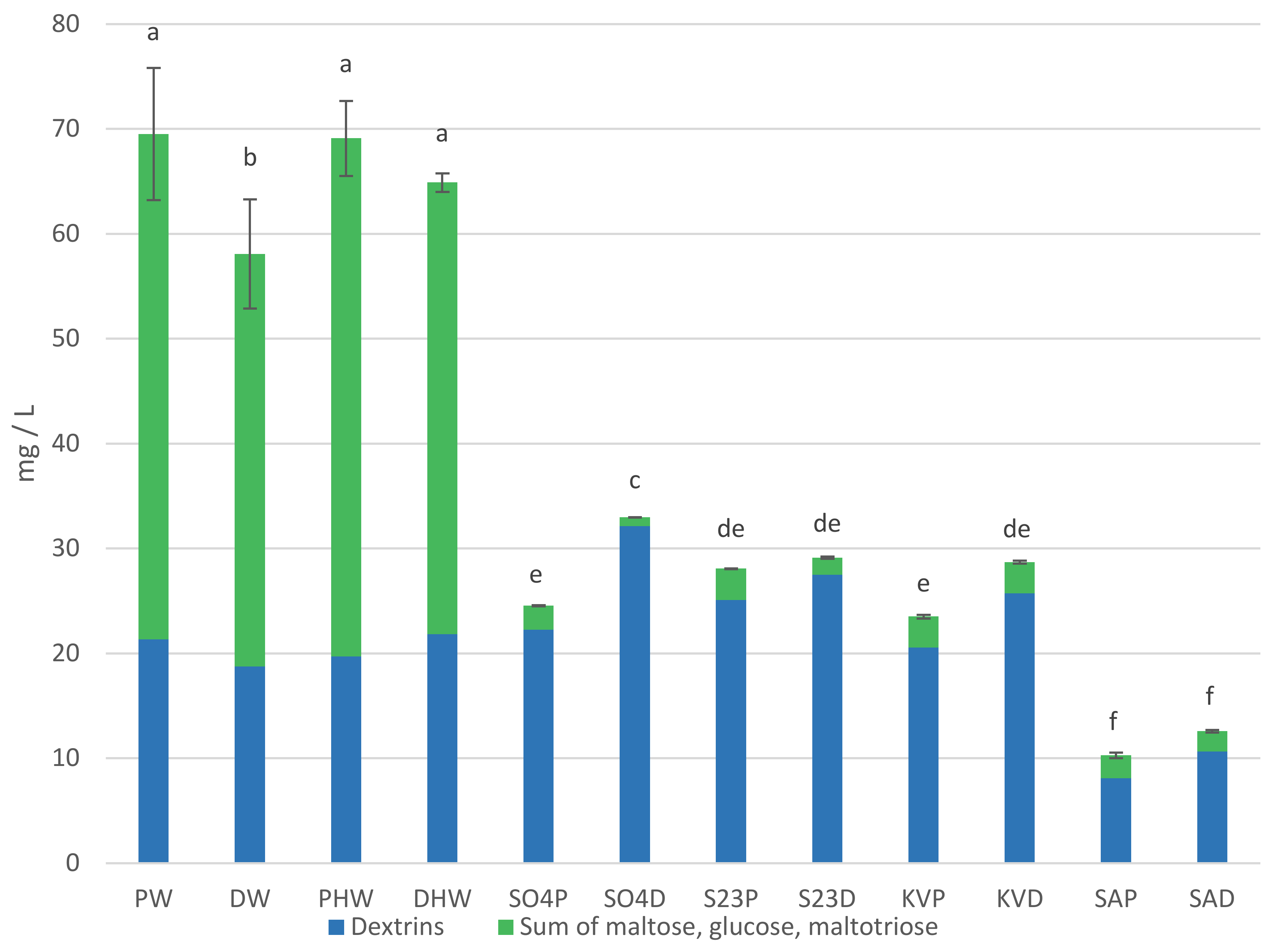


| Compound | Unit | PW | DW | HPW | HDW | S04P | S04D | S23P | S23D | KVP | KVD | SAP | SAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maltose | g/L | 32.24 ± 2.53 a 1 | 26.47 ± 1.36 c | 33.10 ± 1.45 a | 30.17 ± 0.40 b | 0.36 ± 0.01 d | nd 2 | 0.86 ± 0.00 d | 0.66 ± 0.00 d | 1.00 ± 0.01 d | 0.99 ± 0.02 d | 0.97 ± 0.06 d | 0.86 ± 0.05 d |
| Maltotriose | 9.61 ± 0.87 a | 8.70 ± 2.48 a | 9.78 ± 0.66 a | 8.17 ± 0.10 a | 1.71 ± 0.00 b | 0.85 ± 0.00 b | 1.84 ± 0.00 b | 0.97 ± 0.00 b | 1.37 ± 0.01 b | 1.51 ± 0.04 b | 1.00 ± 0.06 b | 0.91 ± 0.04 b | |
| Glucose | 6.34 ± 0.53 a | 4.16 ± 0.21 b | 6.54 ± 0.97 a | 4.73 ± 0.05 b | 0.23 ± 0.00 c | nd | 0.32 ± 0.00 c | nd | 0.60 ± 0.01 c | 0.48 ± 0.10 c | 0.23 ± 0.01 c | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | |
| Dextrins | 21.34 ± 2.37 de | 18.77 ± 1.15 f | 19.69 ± 0.51 ef | 21.84 ± 0.33 d | 22.25 ± 0.05 d | 32.13 ± 0.01 a | 25.07 ± 0.04 c | 27.50 ± 0.10 b | 20.55 ± 0.16 def | 25.73 ± 0.19 c | 8.08 ± 0.15 h | 10.66 ± 0.04 g | |
| Glicerol | nd | nd | nd | nd | 1.54 ± 0.00 cd | 1.92 ± 0.00 ab | 2.05 ± 0.00 a | 1.35 ± 0.01 d | 1.37 ± 0.01 d | 1.51 ± 0.15 cd | 1.82 ± 0.19 abc | 1.68 ± 0.33 bcd |
| Parameter | Unit | S04P | S04D | S23P | S23D | KVP | KVD | SAP | SAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | % v/v | 4.51 ± 0.02 h 1 | 4.71 ± 0.01 e | 4.73 ± 0.01 d | 4.66 ± 0.00 f | 4.80 ± 0.01 c | 4.58 ± 0.01 g | 5.60 ± 0.01 b | 5.79 ± 0.00 a |
| Density | g/cm3 | 1.006 ± 0.00 d | 1.009 ± 0.00 a | 1.006 ± 0.00 e | 1.009 ± 0.00 b | 1.004 ± 0.00 f | 1.008 ± 0.00 c | 0.999 ± 0.00 h | 1.002 ± 0.00 g |
| Real extract | % w/w | 3.75 ± 0.00 d | 4.38 ± 0.00 b | 3.70 ± 0.00 e | 4.56 ± 0.00 a | 3.34 ± 0.01 f | 4.20 ± 0.00 c | 2.23 ± 0.00 h | 2.58 ± 0.00 g |
| Apparent extract | % w/w | 2.11 ± 0.01 d | 2.68 ± 0.01 b | 1.98 ± 0.01 e | 2.87 ± 0.01 a | 1.58 ± 0.01 e | 2.54 ± 0.01 c | 0.19 ± 0.01 g | 0.47 ± 0.01 f |
| RDF | % w/w | 66.06 ± 0.11 e | 63.44 ± 0.02 g | 67.45 ± 0.06 d | 62.29 ± 0.01 h | 70.03 ± 0.01 c | 63.78 ± 0.06 f | 80.36 ± 0.04 a | 78.56 ± 0.01 b |
| ADF | % w/w | 80.25 ± 0.13 e | 76.81 ± 0.03 g | 81.94 ± 0.08 d | 75.37 ± 0.01 h | 85.23 ± 0.01 c | 77.31 ± 0.08 f | 98.26 ± 0.04 a | 95.89 ± 0.02 b |
| Calories | kcal/100 mL | 38.07 ± 0.12 g | 41.47 ± 0.02 b | 39.46 ± 0.35 e | 41.83 ± 0.01 a | 38.24 ± 0.05 g | 40.10 ± 0.07 d | 38.71 ± 0.06 f | 41.01 ± 0.04 c |
| pH | - | 4.21 ± 0.04 b | 4.12 ± 0.00 b | 4.44 ± 0.01 a | 4.42 ± 0.00 a | 4.13 ± 0.01 b | 4.00 ± 0.01 c | 4.04 ± 0.01 c | 3.99 ± 0.01 c |
| Parameter | Unit | PW | DW | HPW | HDW | S04P | S04D | S23P | S23D | KVP | KVD | SAP | SAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | mg GAE/L | 242.54 ± 2.55 h 1 | 316.99 ± 3.87 e | 278.65 ± 2.10 f | 402.55 ± 7.50 b | 286.99 ± 5.85 f | 346.16 ± 1.04 d | 260.32 ± 3.16 g | 365.88 ± 5.87 c | 233.09 ± 7.12 i | 333.66 ± 3.07 d | 244.48 ± 3.37 h | 547.56 ± 2.07 a |
| FRAP | mmol TE/L | 0.68 ± 0.02 g | 1.28 ± 0.02 c | 1.13 ± 0.04 d | 1.70 ± 0.02 a | 0.97 ± 0.05 f | 1.64 ± 0.04 ab | 1.03 ± 0.01 e | 1.65 ± 0.01 ab | 0.99 ± 0.02 ef | 1.62 ± 0.01 b | 1.01 ± 0.01 ef | 1.64 ± 0.01 ab |
| ABTS+• | 1.19 ± 0.02 h | 1.73 ± 0.01 d | 1.31 ± 0.02 f | 2.22 ± 0.01 a | 1.25 ± 0.02 g | 1.86 ± 0.03 c | 1.38 ± 0.01 e | 1.93 ± 0.04 b | 1.21 ± 0.01 g | 1.74 ± 0.02 d | 1.25 ± 0.04 g | 1.76 ± 0.01 d | |
| DPPH• | 0.31 ± 0.01 d | 0.58 ± 0.02 b | 0.20 ± 0.04 gh | 0.87 ± 0.01 a | 0.18 ± 0.02 h | 0.04 ± 0.02 i | 0.27 ± 0.01 ef | 0.30 ± 0.02 de | 0.23 ± 0.02 fg | 0.01 ± 0.01 i | 0.50 ± 0.01 c | 0.47 ± 0.01 c |
| Parameter | Unit | S04P | S04D | S23P | S23D | KVP | KVD | SAP | SAD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean cell diameter | µm | 5.88 | 6 | 5.86 | 5.89 | 5.43 | 4.54 | 4.15 | 4.13 | |
| Mean cell volume | pL | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | |
| Cell size class | M1 | % | 37.26 | 32.43 | 42.59 | 32.04 | 43.80 | 70.74 | 84.90 | 80.96 |
| M2 | 56.98 | 61.19 | 51.11 | 62.50 | 52.96 | 28.76 | 14.51 | 18.54 | ||
| M3 | 5.57 | 6.25 | 6.13 | 5.30 | 3.16 | 0.50 | 0.59 | 0.51 | ||
| M4 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paszkot, J.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Yeast Strains and Wort Color as Factors Affecting Effects of the Ethanol Fermentation Process. Molecules 2022, 27, 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27133971
Paszkot J, Kawa-Rygielska J. Yeast Strains and Wort Color as Factors Affecting Effects of the Ethanol Fermentation Process. Molecules. 2022; 27(13):3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27133971
Chicago/Turabian StylePaszkot, Justyna, and Joanna Kawa-Rygielska. 2022. "Yeast Strains and Wort Color as Factors Affecting Effects of the Ethanol Fermentation Process" Molecules 27, no. 13: 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27133971
APA StylePaszkot, J., & Kawa-Rygielska, J. (2022). Yeast Strains and Wort Color as Factors Affecting Effects of the Ethanol Fermentation Process. Molecules, 27(13), 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27133971






