HDAC Inhibitory and Anti-Cancer Activities of Curcumin and Curcumin Derivative CU17 against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
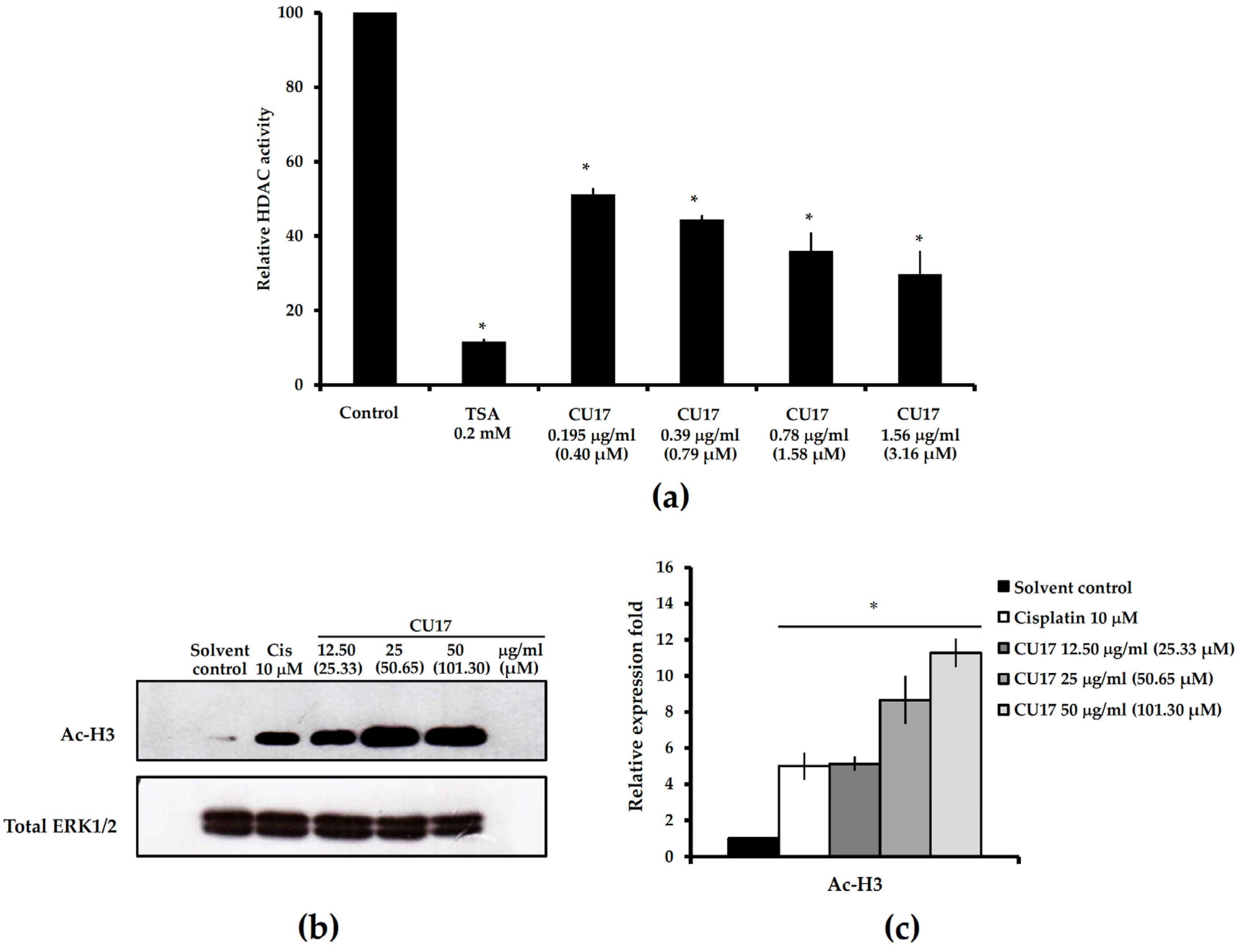
2.1. HDAC Inhibitory Activity of the Curcumin Derivative CU17
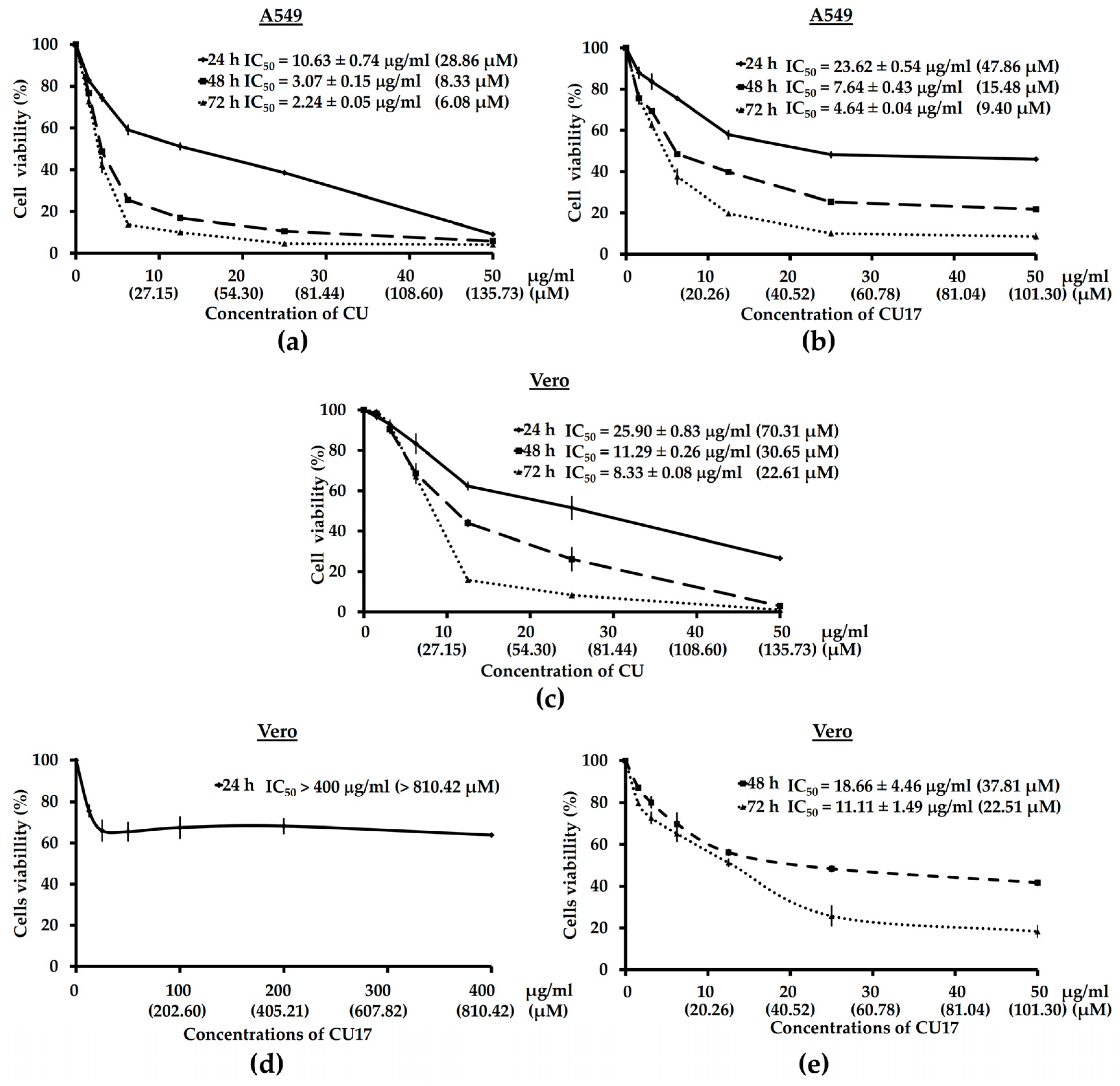
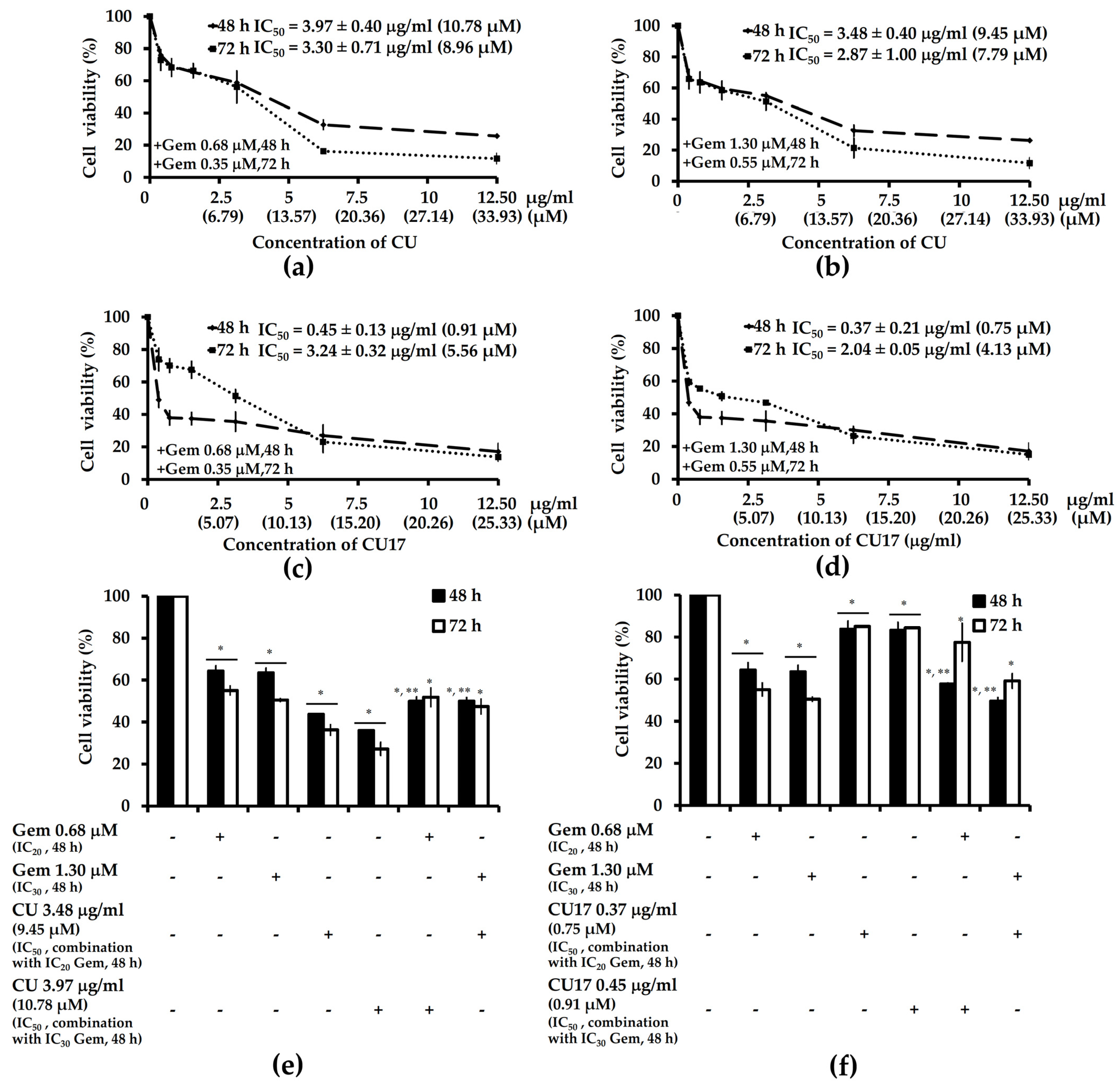
2.2. The Anti-Proliferative Activities of CU17 against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells
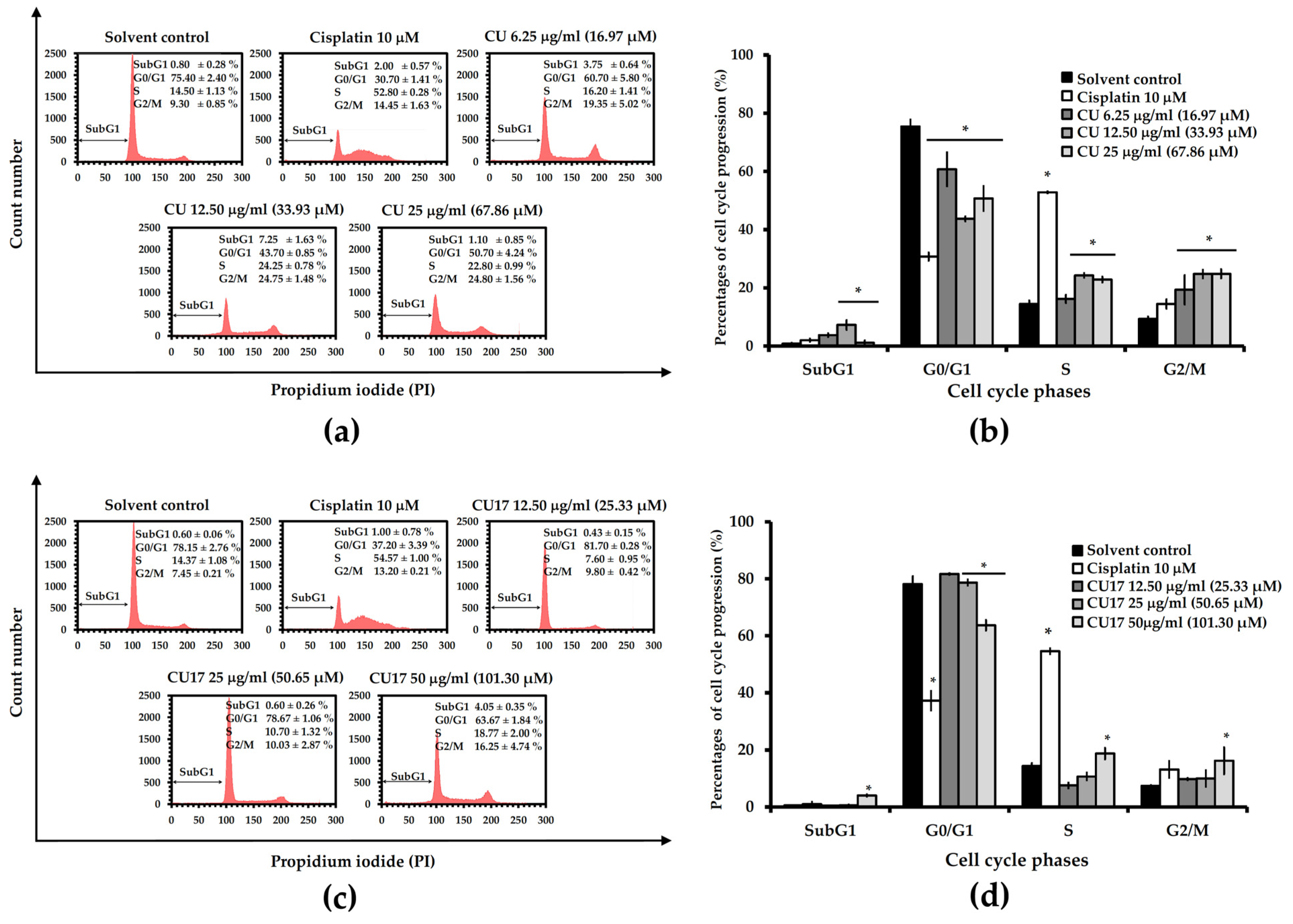
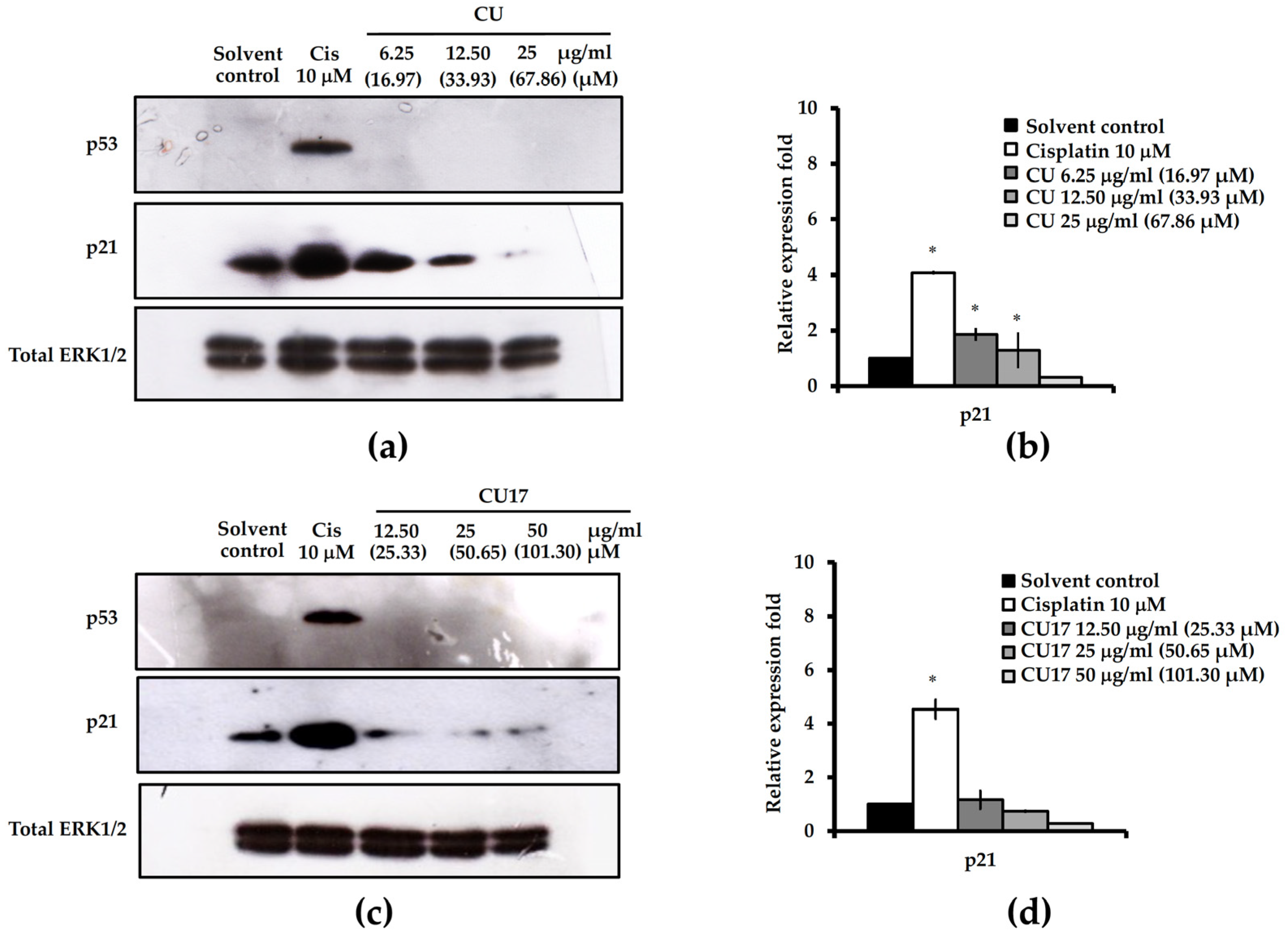
2.3. Effect of CU17 on the Cell Cycle Progression in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells
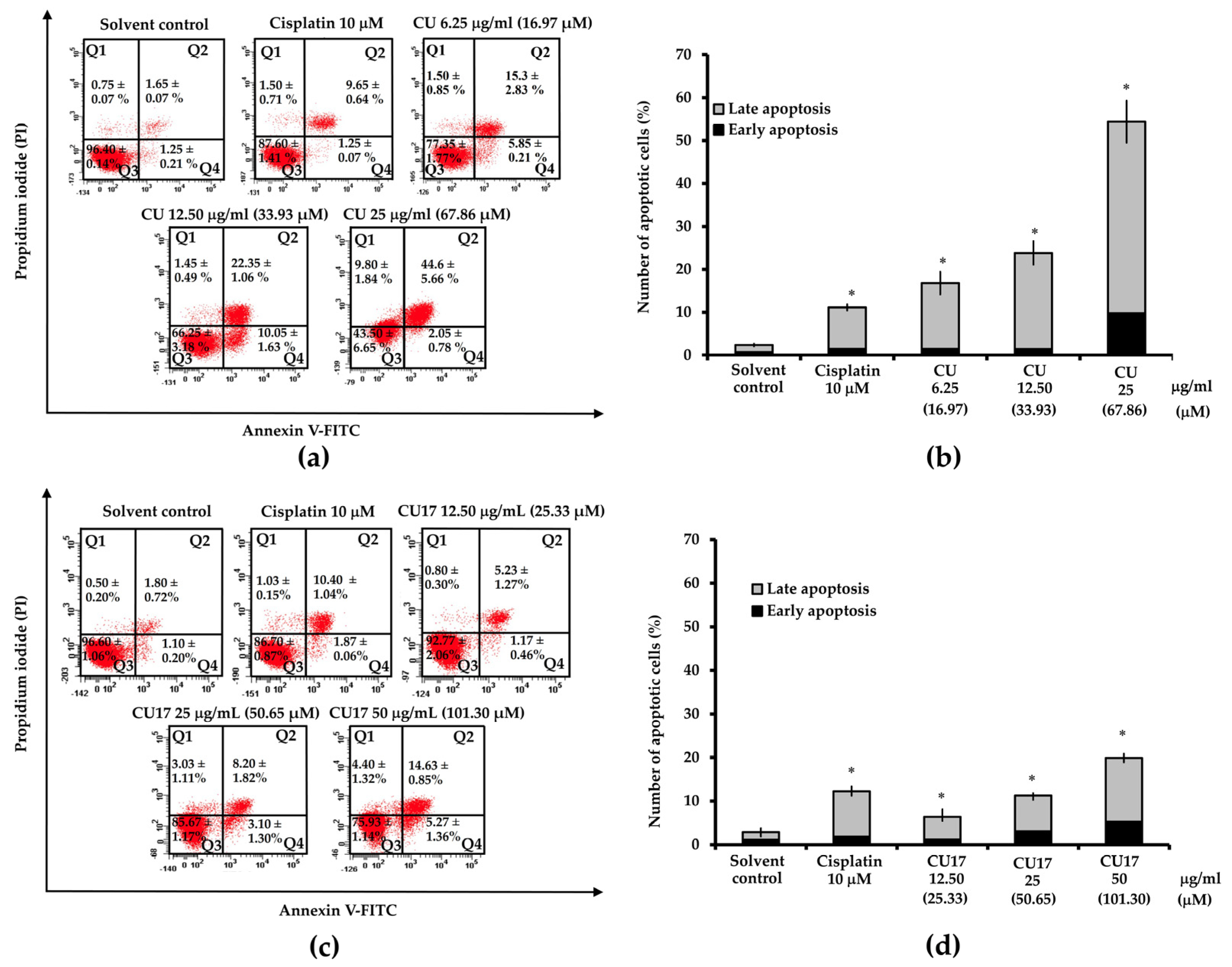
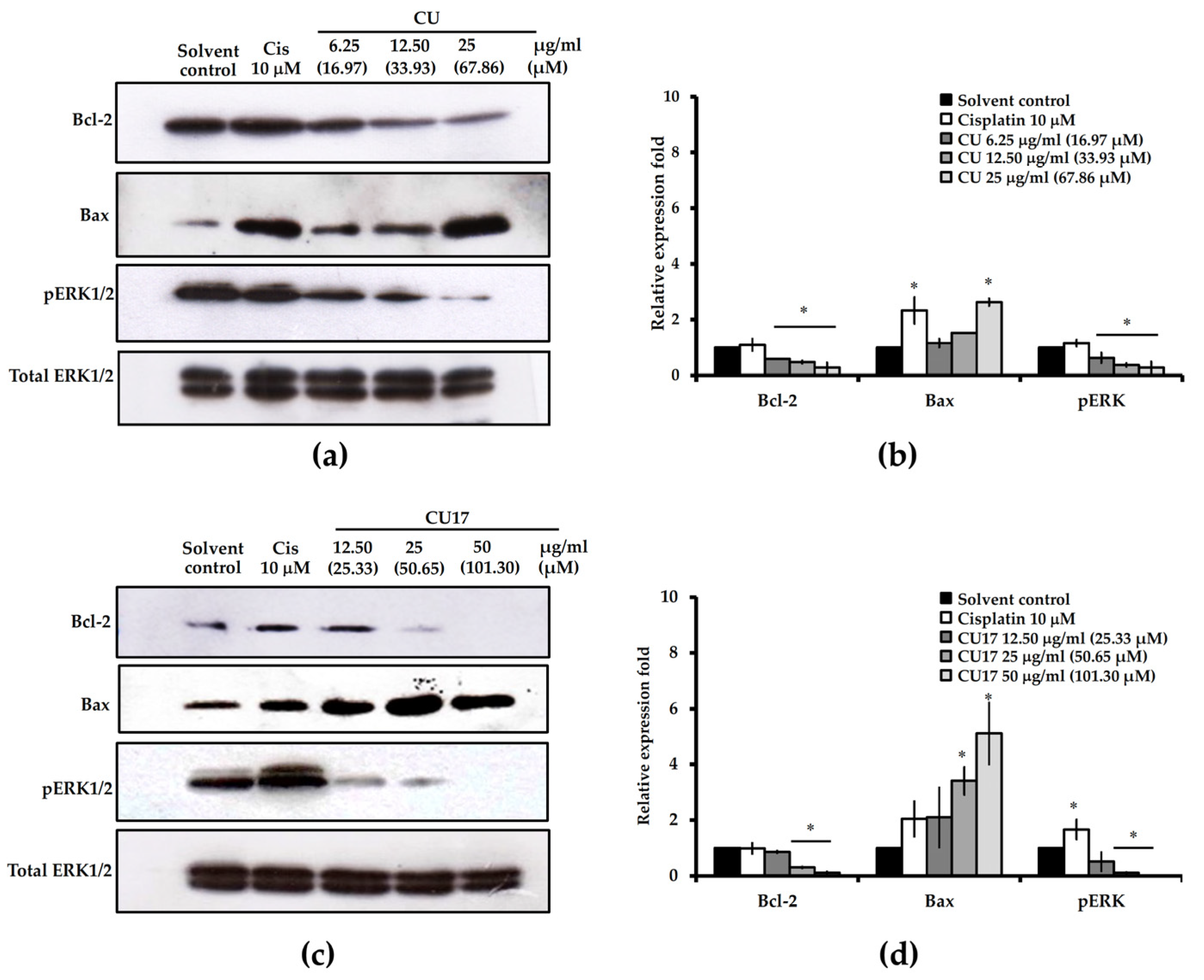
2.4. Effect of CU17 on Induction of Cellular Apoptosis against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells
2.5. CU17 Enhances the Antiproliferative Effect of Gemcitabine (Gem) on Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells
2.6. Combination Index and Dose Reduction Index of Gem and CU or CU17 in Combination Treatments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Condition
4.3. The Extraction and Isolation of Curcumin
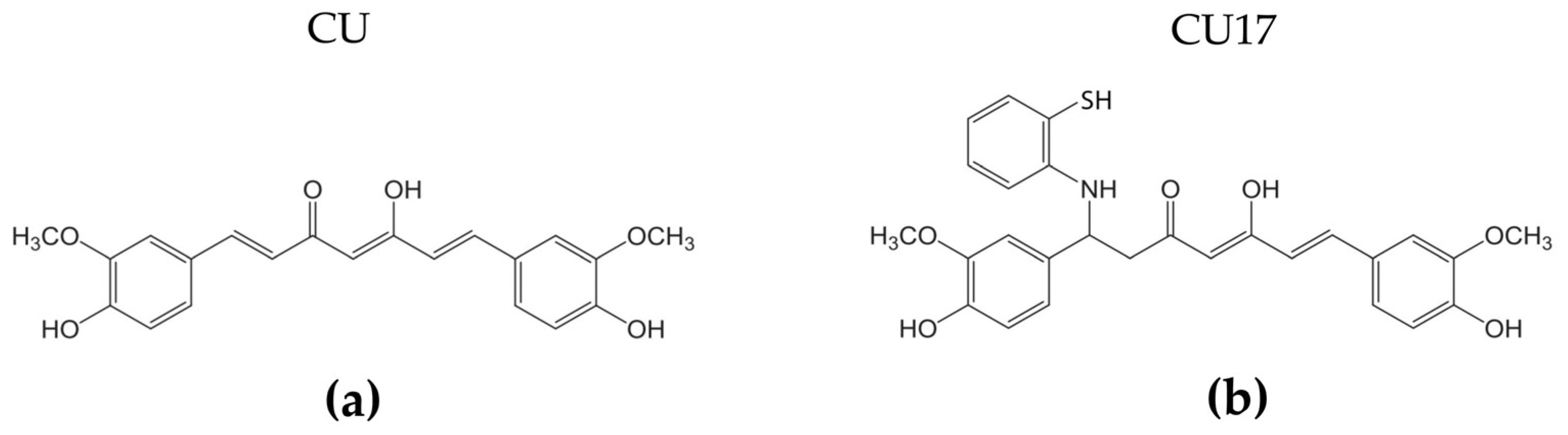
4.4. Curcumin Derivative CU17 Synthesis
4.5. In Vitro HDAC Inhibitory Activity
4.6. Docking of CU17 to HDAC Structural Model
4.7. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. Cell Cycle Progression
4.9. Cellular Apoptosis Detection
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/764-thailand-fact-sheets.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Hatami, E.; Nagesh, P.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.; Yallapu, M. Gambogic Acid Potentiates Gemcitabine Induced Anticancer Activity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 888, 173486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Jeon, J.; Sriplung, H.; Yeesoonsang, S.; Bilheem, S.; Rozek, L.; Chitapanarux, I.; Pongnikorn, D.; Daoprasert, K.; Vatanasapt, P.; et al. Temporal Trends and Geographic Patterns of Lung Cancer Incidence by Histology in Thailand, 1990 to 2014. J. Glob. Oncol. 2018, 4, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiarasi, A.; Sankar, R.; Anusha, C.; Saravanan, K.; Aarthy, K.; Karthic, S.; Mathuram, T.; Ravikumar, V. Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Anticancer Activity in A549 Lung Cancer Cells by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 40, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; Flores-Campos, R.; Silver, A.; de Álava, E.; Hajji, N.; García-Domínguez, D. Synergistic Enhancement of Cancer Therapy Using HDAC Inhibitors: Opportunity for Clinical Trials. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 578011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.; Johnstone, R. New and Emerging HDAC Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Marks, P.; Jiang, X. Apoptotic and Autophagic Cell Death Induced by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18030–18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, D.; Kato, Y.; Shabbeer, S.; Wei, Y.; Verheul, H.; Salumbides, B.; Sanni, T.; Atadja, P.; Pili, R. Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: The Hydroxamic Acid Derivative LBH589. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, B.; Johnson, J.; Cohen, M.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Vorinostat for Treatment of Advanced Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Oncologist 2007, 12, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsoni, S.; Damia, G.; Camboni, G. A Work in Progress: The Clinical Development of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zagni, C.; Floresta, G.; Monciino, G.; Rescifina, A. The Search for Potent, Small-Molecule Hdacis in Cancer Treatment: A Decade after Vorinostat. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 1373–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.T.; Li, H.Q.; Liu, F. Selective Histone Deacetylase Small Molecule Inhibitors: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cui, G.; Zhou, J. Curcumin, a Potent Anti-Tumor Reagent, Is a Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Regulating B-NHL Cell Line Raji Proliferation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bora-Tatar, G.; Dayangaç-Erden, D.; Demir, A.; Dalkara, S.; Yelekçi, K.; Erdem-Yurter, H. Molecular Modifications on Carboxylic Acid Derivatives as Potent Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Activity and Docking Studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5219–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoi, V.; Galani, V.; Lianos, G.; Voulgaris, S.; Kyritsis, A.; Alexiou, G. The Role of Curcumin in Cancer Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, A.; Sun, Y.; Sun, G. A Novel Synthetic Curcumin Derivative MHMM-41 Induces ROS-Mediated Apoptosis and Migration Blocking of Human Lung Cancer Cells A549. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cai, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, M.; Ying, S.; Shi, L.; Xu, R.; He, F.; Liang, G.; Zhang, X. Anti-Lung Cancer Activity of the Curcumin Analog JZ534 in vitro. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 504529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Tahir, A.; Bakht, M.; Salahuddin; Ahsan, M. Molecular Engineering of Curcumin, An Active Constituent of Curcuma Longa L. (Turmeric) of the Family Zingiberaceae with Improved Antiproliferative Activity. Plants 2021, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chainoglou, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Curcumin Analogues and Derivatives with Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity: Structural Characteristics and Molecular Targets. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.; Kumar, N.; Thakur, G. The Potency of Heterocyclic Curcumin Analogues: An Evidence-Based Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 166, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumboonma, P.; Senawong, T.; Saenglee, S.; Senawong, G.; Somsakeesit, L.; Yenjai, C.; Phaosiri, C. New Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors and Anticancer Agents From Curcuma Longa. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Badeli, R.; Karami, G.; Sahebkar, A. Investigation of the Efficacy of Adjunctive Therapy with Bioavailability-Boosted Curcuminoids in Major Depressive Disorder. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily, H.; Sahebkar, A.; Iranshahi, M.; Ganjali, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Ferns, G.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M. An Investigation of the Effects of Curcumin on Anxiety and Depression in Obese Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2015, 21, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.; Dahlin, J.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.; Walters, M. The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1620–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.; Newman, R.; Aggarwal, B. Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenglee, S.; Jogloy, S.; Patanothai, A.; Leid, M.; Senawong, T. Cytotoxic Effects of Peanut Phenolics Possessing Histone Deacetylase Inhibitory Activity in Breast and Cervical Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Yun, S.; Cha, E.; Choi, E.; Na, M.; Park, J.; Kang, J.; Son, J. Combining Microrna-449A/B with a HDAC Inhibitor Has a Synergistic Effect on Growth Arrest in Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Pili, R. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors and Epigenetic Modifications as a Novel Strategy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer J. 2013, 19, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xue, K.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Dong, W.; Song, J.; Sun, S.; Ma, T.; Li, W. C-Myc Regulates the CDK1/Cyclin B1 Dependent-G2/M Cell Cycle Progression by Histone H4 Acetylation in Raji Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 44, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, L.; Diao, H.; Dong, N.; Su, X.; Wang, B.; Mo, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces Cell Apoptosis and Cycle Arrest in Lung Cancer Cells via Mitochondrial Injury and P53 Up-Acetylation. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2016, 32, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Kurzrock, R.; Shankar, S. MS-275 sensitizes TRAIL-resistant breast cancer cells, inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis, and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3254–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Adachi, M.; Kawamura, R.; Imai, K. Bmf Is a Possible Mediator in Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors FK228 and CBHA-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 13, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rikiishi, H. Autophagic and Apoptotic Effects of HDAC Inhibitors on Cancer Cells. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 830260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhuang, L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, E.; Yu, Q. Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases Target the Rb-E2F1 Pathway for Apoptosis Induction through Activation of Proapoptotic Protein Bim. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16090–16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y. Regulation of P53 Responses by Post-Translational Modifications. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Kanchana, K.; Guo, G.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Liang, G. ROS Generation Mediates the Anti-Cancer Effects of WZ35 via Activating JNK and ER Stress Apoptotic Pathways in Gastric Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5860–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Song, X.; Shang, M.; Zou, W.; Zhang, M.; Wei, H.; Shao, H. Curcumin Exerts Cytotoxicity Dependent on Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, S.; Tian, Y.; Weiss, R.; Martin, D. Synergistic Inhibition of GP130 and ERK Signaling Blocks Chemoresistant Bladder Cancer Cell Growth. Cell. Signal. 2019, 63, 109381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Jue, W.; Huifen, S.; Ran, R.; Kai, X.; Xiangming, T.; Weiping, Z.; Li, F. Curcumin Co-Treatment Ameliorates Resistance to Gefitinib in Drug-Resistant NCI-H1975 Lung Cancer Cells. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 37, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenglee, S.; Senawong, G.; Jogloy, S.; Sripa, B.; Senawong, T. Peanut Testa Extracts Possessing Histone Deacetylase Inhibitory Activity Induce Apoptosis in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, A.; Nooter, K.; Burger, H.; Kortland, C.; Stoter, G. Bax Upregulation Is An Early Event in Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis in Human Testicular Germ-Cell Tumor Cell Line NT2, as Quantitated by Flow Cytometry. Cytometry 1997, 27, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijido, O.; Dejean, L. Upregulation of Bcl2 Inhibits Apoptosis-Driven BAX Insertion but Favors BAX Relocalization in Mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3305–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haldar, S.; Jena, N.; Croce, C. Inactivation of Bcl-2 by Phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4507–4511. [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro, E.; Simizu, S.; Takada, M.; Umezawa, K.; Imoto, M. Caspase-3 Activation Is Not Responsible for Vinblastine-Induced Bcl-2 Phosphorylation and G2/M Arrest in Human Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Ms-1 Cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Yokota, T.; Takaoka, Y.; Sakai, T. p15(INK4b) in HDAC inhibitor-induced growth arrest. FEBS Lett. 2003, 554, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, Y.; Shimada, M.; Harimoto, N.; Rikimaru, T.; Shirabe, K.; Tanaka, S.; Sugimachi, K. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Trichostatin a Induces Cell-Cycle Arrest/Apoptosis and Hepatocyte Differentiation in Human Hepatoma Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 103, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamble, D.; Lippard, S. Cisplatin and DNA Repair in Cancer Chemotherapy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of P53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHaan, R.; Yazlovitskaya, E.; Persons, D. Regulation of P53 Target Gene Expression by Cisplatin-Induced Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2001, 48, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, Y.; Maya, R.; Kazaz, A.; Oren, M. Mdm2 Promotes the Rapid Degradation of P53. Nature 1997, 387, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persons, D.; Yazlovitskaya, E.; Pelling, J. Effect of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase on P53 Accumulation in Response to Cisplatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35778–35785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shieh, S.; Ikeda, M.; Taya, Y.; Prives, C. DNA Damage-Induced Phosphorylation of P53 Alleviates Inhibition by MDM2. Cell 1997, 91, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.J.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschopf, K.; Haendeler, J.; Malchow, P.; Zeiher, A.; Dimmeler, S. Posttranslational Modification of Bcl-2 Facilitates Its Proteasome-Dependent Degradation: Molecular Characterization of the Involved Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Cui, D.; Huang, X.; Mao, S.; Ji, L.; Song, H.; Yi, C. Inhibitory Effect of Ginsenoside Rg3 Combined with Gemcitabine on Angiogenesis and Growth of Lung Cancer in Mice. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Ramachandra, M.; Subbaraju, G. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Polyhydroxycurcuminoids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 6374–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
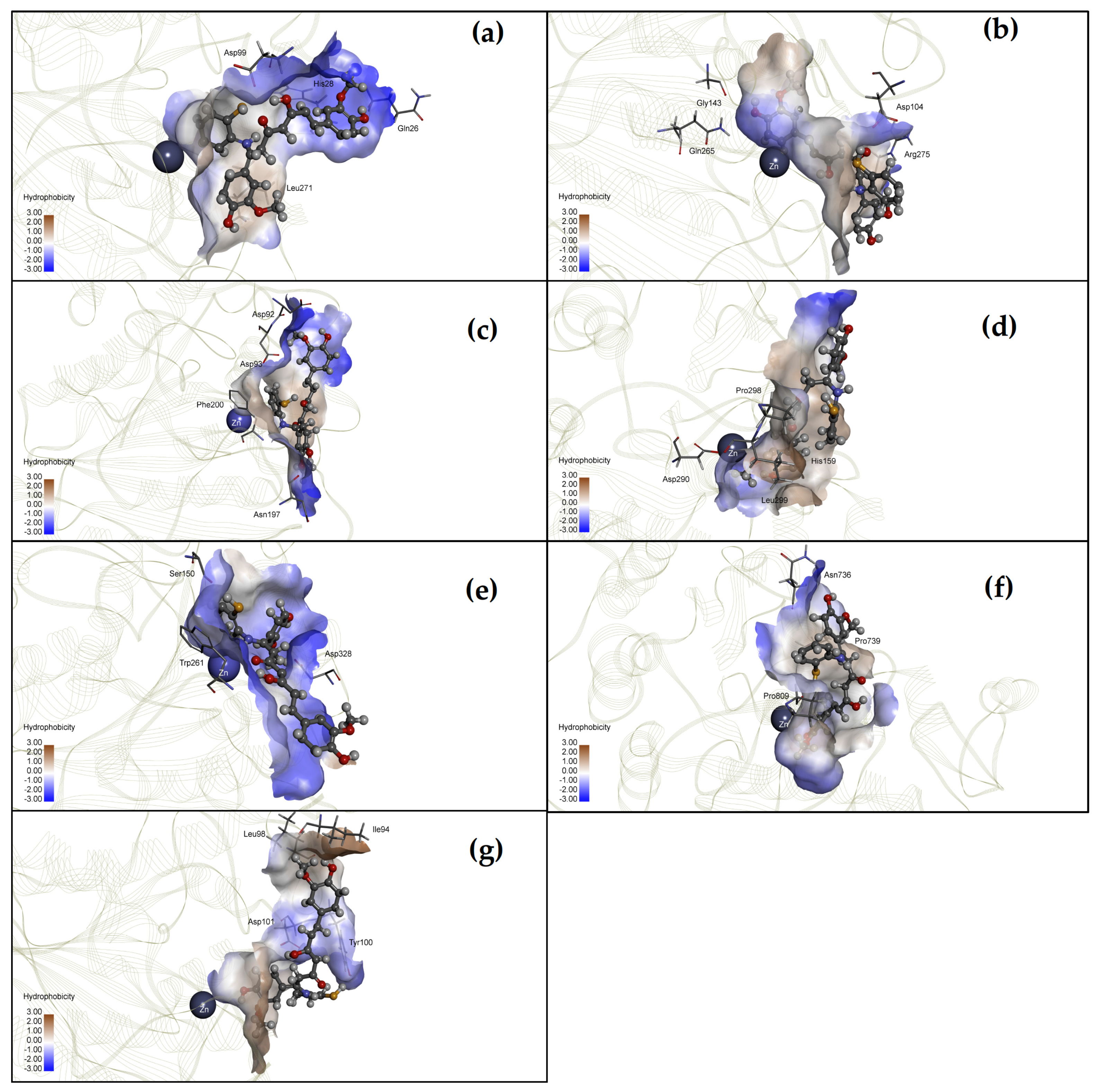
| Compound | Class I | Class II | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC1 | HDAC2 | HDAC3 | HDAC8 | HDAC4 | HDAC6 | HDAC7 | ||||||||
| ∆G | Ki | ∆G | Ki | ∆G | Ki | ∆G | Ki | ∆G | Ki | ∆G | Ki | ∆G | Ki | |
| CU | −6.96 | 7.88 | −8.04 | 1.27 | −9.82 | 0.06 | −7.22 | 5.13 | −9.11 | 0.21 | −7.82 | 1.85 | −8.12 | 1.11 |
| CU17 | −8.91 | 0.29 | −7.64 | 2.51 | −8.19 | 0.99 | −7.96 | 1.45 | −9.15 | 0.20 | −9.21 | 0.18 | −8.40 | 0.70 |
| Drug Combination | Exposure Time | A549 Cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | DRI | ||||
| Gem | CU | CU17 | |||
| Gem 0.68 μM (IC20) + CU | 48 h | 1.44 ± 0.14 | 15.94 | 0.77 | - |
| Gem 0.35 μM (IC20) + CU | 72 h | 2.11 ± 0.40 | 4.09 | 0.68 | - |
| Gem 1.30 μM (IC30) + CU | 48 h | 1.40 ± 0.15 | 7.91 | 0.88 | - |
| Gem 0.55 μM (IC30) + CU | 72 h | 2.20 ± 0.63 | 2.49 | 0.78 | - |
| Gem 0.68 μM (IC20) + CU17 | 48 h | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 15.94 | - | 56.25 |
| Gem 0.35 μM (IC20) + CU17 | 72 h | 1.18 ± 0.09 | 4.09 | - | 3.64 |
| Gem 1.30 μM (IC30) + CU17 | 48 h | 0.18 ± 0.00 | 7.91 | - | 38.93 |
| Gem 0.55 μM (IC30) + CU17 | 72 h | 1.07 ± 0.07 | 2.49 | - | 4.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Namwan, N.; Senawong, G.; Phaosiri, C.; Kumboonma, P.; Somsakeesit, L.-o.; Samankul, A.; Leerat, C.; Senawong, T. HDAC Inhibitory and Anti-Cancer Activities of Curcumin and Curcumin Derivative CU17 against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134014
Namwan N, Senawong G, Phaosiri C, Kumboonma P, Somsakeesit L-o, Samankul A, Leerat C, Senawong T. HDAC Inhibitory and Anti-Cancer Activities of Curcumin and Curcumin Derivative CU17 against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Molecules. 2022; 27(13):4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134014
Chicago/Turabian StyleNamwan, Narissara, Gulsiri Senawong, Chanokbhorn Phaosiri, Pakit Kumboonma, La-or Somsakeesit, Arunta Samankul, Chadaporn Leerat, and Thanaset Senawong. 2022. "HDAC Inhibitory and Anti-Cancer Activities of Curcumin and Curcumin Derivative CU17 against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells" Molecules 27, no. 13: 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134014
APA StyleNamwan, N., Senawong, G., Phaosiri, C., Kumboonma, P., Somsakeesit, L.-o., Samankul, A., Leerat, C., & Senawong, T. (2022). HDAC Inhibitory and Anti-Cancer Activities of Curcumin and Curcumin Derivative CU17 against Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Molecules, 27(13), 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134014






