Novel Design of RNA Aptamers as Cancer Inhibitors and Diagnosis Targeting the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of the NT-3 Growth Factor Receptor Using a Computational Sequence-Based Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virtual Screening to Identify Probable RNA Candidates
2.2. Generation of New Aptamer Sequences
2.3. Molecular Modeling and Docking of the New Aptamers
2.4. Aptamer Optimization and Final Interaction Profiling
3. Results
3.1. Virtual Screenings
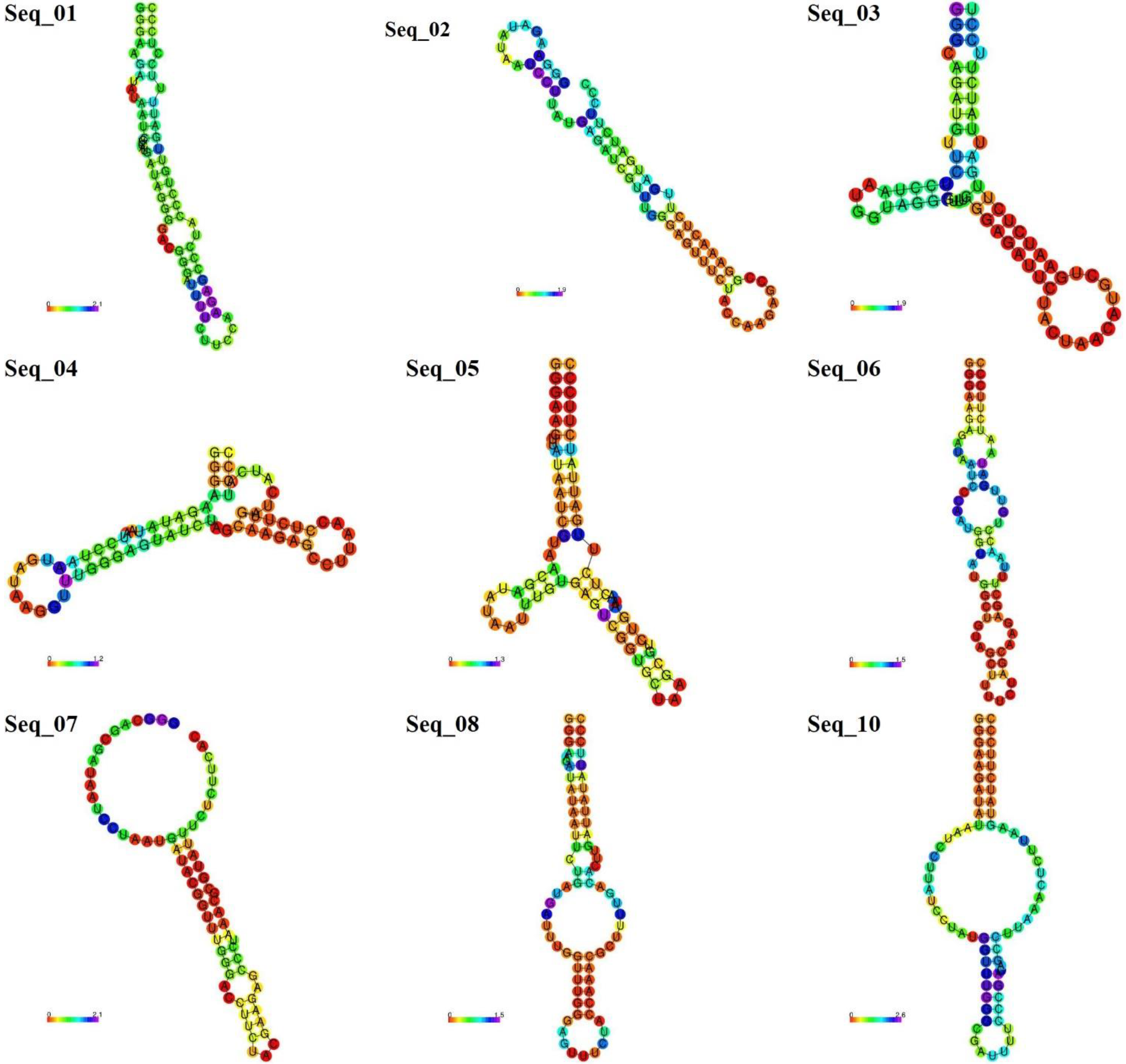
3.2. Novel Aptamers Generation
3.3. Docking Results
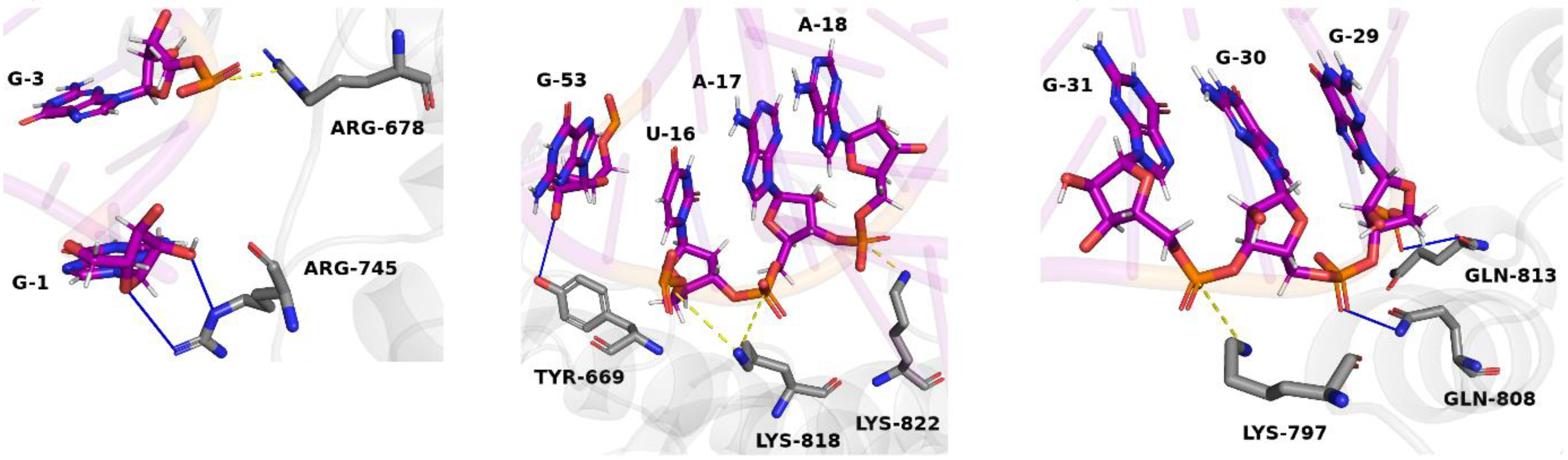
3.4. Optimization and Analysis of the Selected Aptamer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Aljohani, M.M.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Chinnappan, R.; Al-Kattan, K.; Zourob, M. Aptamers: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents for Blood Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiviyanathan, V.; Gorenstein, D.G. Aptamers and the next generation of diagnostic reagents. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Xia, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Song, Y.; et al. Homogeneous, Low-volume, Efficient, and Sensitive Quantitation of Circulating Exosomal PD-L1 for Cancer Diagnosis and Immunotherapy Response Prediction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4800–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Song, J.; Wei, X.; Huang, M.; Sun, M.; Zhu, L.; Lin, B.; Shen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Discovery of Aptamers Targeting the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9895–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Strom, M.; Hammond, D.S.; Shigdar, S. Anything You Can Do, I Can Do Better: Can Aptamers Replace Antibodies in Clinical Diagnostic Applications? Molecules 2019, 24, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Yan, J.; Xiong, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, D.; Liu, Z. Investigations on the interface of nucleic acid aptamers and binding targets. Anal. 2018, 143, 5317–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Nakamura, Y. Aptamers: A Review of Their Chemical Properties and Modifications for Therapeutic Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Göringer, H.U.; Adler, A.; Forster, N.; Homann, M. Post-SELEX Chemical Optimization of a Trypanosome-Specific RNA Aptamer. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2008, 11, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, P.; Nosrati, R.; Alibolandi, M.; Rafatpanah, H.; Abnous, K.; Khedri, M.; Ramezani, M. SELEX methods on the road to protein targeting with nucleic acid aptamers. Biochimie 2018, 154, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buglak, A.A.; Samokhvalov, A.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Methods and Applications of In Silico Aptamer Design and Modeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L. Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escamilla-Gutiérrez, A.; Ribas-Aparicio, R.M.; Córdova-Espinoza, M.G.; Castelán-Vega, J.A. In silico strategies for modeling RNA aptamers and predicting binding sites of their molecular targets. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2021, 40, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoleru, B.; Popescu, A.M.; Tache, D.E.; Neamtu, O.M.; Emami, G.; Tataranu, L.G.; Buteica, A.S.; Dricu, A.; Purcaru, S.O. Tropomyosin-receptor-kinases signaling in the nervous system. Maedica 2013, 8, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W. Roles of TrkC Signaling in the Regulation of Tumorigenicity and Metastasis of Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawn, S.; Krishna, N.; Pisklakova, A.; Qu, X.; Fenstermacher, D.A.; Fournier, M.; Vrionis, F.D.; Tran, N.; Chan, J.A.; Kenchappa, R.S.; et al. Neurotrophin Signaling via TrkB and TrkC Receptors Promotes the Growth of Brain Tumor-initiating Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3814–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cocco, E.; Scaltriti, M.; Drilon, A. NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, B.C.; Westbrook, J.; Ghosh, S.; Petrov, A.; Sweeney, B.; Zirbel, C.L.; Leontis, N.B.; Berman, H.M. The Nucleic Acid Database: New features and capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D114–D122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PyMOL. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 1.8; Schrodinger: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Lu, X.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-ylethynyl)-2-methylbenzamides as potent and selective pan-tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.-Y. Addressing recent docking challenges: A hybrid strategy to integrate template-based and free protein-protein docking. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2017, 85, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.-Y. HDOCK: A web server for protein–protein and protein–DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YYan, Y.; Tao, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.-Y. The HDOCK server for integrated protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Honer Zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, A.; Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.F.; Neuböck, R.; Hofacker, I.L. The Vienna RNA Websuite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W70–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biesiada, M.; Purzycka, K.J.; Szachniuk, M.; Blazewicz, J.; Adamiak, R.W. Automated RNA 3D Structure Prediction with RNAComposer. In RNA Structure Determination: Methods and Protocols; Turner, D.H., Mathews, D.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- PPopenda, M.; Szachniuk, M.; Antczak, M.; Purzycka, K.J.; Lukasiak, P.; Bartol, N.; Blazewicz, J.; Adamiak, R.W. Automated 3D structure composition for large RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: Expanding the scope of the protein–ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W530–W534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokobayashi, Y. Aptamer-based and aptazyme-based riboswitches in mammalian cells. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 52, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tickner, Z.; Farzan, M. Riboswitches for Controlled Expression of Therapeutic Transgenes Delivered by Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Jang, G.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Song, G. Predicting aptamer sequences that interact with target proteins using an aptamer-protein interaction classifier and a Monte Carlo tree search approach. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.Z.; Hamid, A.A.A.; Hitam, S.M.S.; Rahim, M.Z.A. In-silico selection of aptamer: A review on the revolutionary approach to understand the aptamer design and interaction through computational chemistry. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chushak, Y.; Stone, M.O. In silico selection of RNA aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.; Izzo, J.A.; Elmetwaly, S.; Gan, H.H.; Schlick, T. Computational generation and screening of RNA motifs in large nucleotide sequence pools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warfield, B.M.; Anderson, P.C. Molecular simulations and Markov state modeling reveal the structural diversity and dynamics of a theophylline-binding RNA aptamer in its unbound state. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soon, S.; Nordin, N.A. In silico predictions and optimization of aptamers against Streptococcus agalactiae surface protein using computational docking. Mater. Today: Proc. 2019, 16, 2096–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ID | ID | ID | ID | ID | ID | ID | ID | ID | ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ddy | 1nta | 2l1v | 2rn1 | 4fe5 | 5bjo | 6c63 | 6gzk | 6ubu | 7eog |
| 1et4 | 1ntb | 2lun | 2rqj | 4frg | 5kpy | 6c64 | 6k84 | 6up0 | 7kd1 |
| 1f1t | 1q8n | 2oom | 2rrc | 4l81 | 5lwj | 6e80 | 6p2h | 6v9d | 7kvt |
| 1nbk | 2au4 | 2pn9 | 3gca | 4lvv | 5ob3 | 6e8s | 6pq7 | 6vwt | 7l0z |
| 1nem | 2jwv | 2qbz | 3q50 | 4oqu | 5uza | 6e8t | 6q57 | 6wjr | 7oa3 |
| Aptamer | Docking Score |
|---|---|
| 5uza | −590.1 |
| 6gzk | −576.3 |
| 5lwj | −532.8 |
| 2qbz | −512.5 |
| 2au4 | −504.1 |
| 1q8n | −490.1 |
| 1nbk | −475.2 |
| 4lvv | −473.9 |
| 2lun | −465.9 |
| 2l1v | −463.4 |
| Identifier | Sequence | Predicted MFE (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 5uza | gggaagauauaauccuaaugauaugguuugggaguuucuaccaagagccuuaaacucuugauuaucuuccc | −21.5 |
| seq_01 | gggaagauauaaucGuCaugauaGggGACgggaUuuucuUccaagagccCuaCCcuGuugauuUucCuccc | −21.1 |
| seq_02 | gggaagauauaauccuUaugaGauCguuugggaguuucuaccaagagccGGaaacucuugauGaucuuccc | −21.7 |
| seq_03 | gggCagauGuUCuccuaaugGuaGgguuugggagAuucuacUaaCaUGcuGaaUcucuugauuaucuuccU | −19.9 |
| seq_04 | gggaagauauaauccuaaugauaAgguuugggaguAucuaGcaagagccuuaaCcucuugauCaucAuccc | −17.8 |
| seq_05 | gggaagUuauaaucGuaaCgauauAAuuugUgaguCGGuGcUaagCgUcuGaaacucuugauuaucuuccc | −18.1 |
| seq_06 | gggaagaGauaauccCaaugGuauggCuGUAgCUuuucuaGcaagagcUuuaaCcuGuugauAaucuuccc | −21.5 |
| seq_07 | gggCagCGauaauccuaaugauaCgguuugggaCCuucuacGaagagccCuaaacGcGuAUuuCucuucAc | −17.2 |
| seq_08 | gggaagauauaauUcuGaugauUugguuugggaguuucuaccaaACgcUuuUGacAcuugauuauAuuccc | −15.2 |
| seq_09 | gggaagauaCUaAcGuaaGgauaugUuuGgggaguuucuaccaagagccuuaaaGucuugauuGucuuUcc | −16.4 |
| seq_10 | gggaagauauaauccuUauCCuaugguuugggCgAuuUuCccGagagccuuaaacucuuAaGuaucuuccc | −19.2 |
| Identifier | Docking Score |
|---|---|
| seq_09 | −673.4 |
| seq_10 | −615.6 |
| seq_06 | −612.1 |
| seq_02 | −611.9 |
| seq_08 | −571 |
| seq_04 | −567.3 |
| seq_01 | −563.7 |
| seq_03 | −559.2 |
| seq_05 | −519.5 |
| seq_07 | −498.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhammad, A.M.; Zari, A.; Alsubhi, N.H.; Al-Zahrani, M.H.; Alghamdi, R.A.; Labib, M.M. Novel Design of RNA Aptamers as Cancer Inhibitors and Diagnosis Targeting the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of the NT-3 Growth Factor Receptor Using a Computational Sequence-Based Approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144518
Muhammad AM, Zari A, Alsubhi NH, Al-Zahrani MH, Alghamdi RA, Labib MM. Novel Design of RNA Aptamers as Cancer Inhibitors and Diagnosis Targeting the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of the NT-3 Growth Factor Receptor Using a Computational Sequence-Based Approach. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144518
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhammad, Ashraf M., Ali Zari, Nouf H. Alsubhi, Maryam H. Al-Zahrani, Rana Abdullah Alghamdi, and Mai M. Labib. 2022. "Novel Design of RNA Aptamers as Cancer Inhibitors and Diagnosis Targeting the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of the NT-3 Growth Factor Receptor Using a Computational Sequence-Based Approach" Molecules 27, no. 14: 4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144518
APA StyleMuhammad, A. M., Zari, A., Alsubhi, N. H., Al-Zahrani, M. H., Alghamdi, R. A., & Labib, M. M. (2022). Novel Design of RNA Aptamers as Cancer Inhibitors and Diagnosis Targeting the Tyrosine Kinase Domain of the NT-3 Growth Factor Receptor Using a Computational Sequence-Based Approach. Molecules, 27(14), 4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144518







