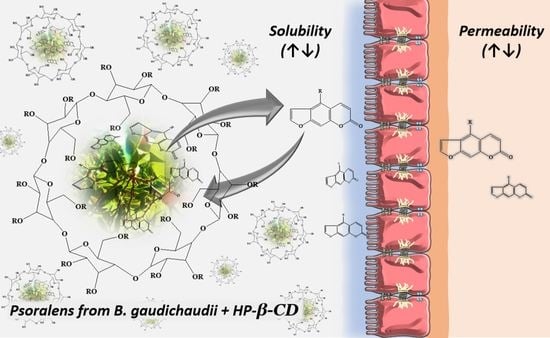
Improvement in Solubility–Permeability Interplay of Psoralens from Brosimum gaudichaudii Plant Extract upon Complexation with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
Abstract
Share and Cite
Machado, R.D.; Silva, J.C.G.; Silva, L.A.D.; Oliveira, G.d.A.R.; Lião, L.M.; Lima, E.M.; de Morais, M.C.; da Conceição, E.C.; Rezende, K.R. Improvement in Solubility–Permeability Interplay of Psoralens from Brosimum gaudichaudii Plant Extract upon Complexation with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Molecules 2022, 27, 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144580
Machado RD, Silva JCG, Silva LAD, Oliveira GdAR, Lião LM, Lima EM, de Morais MC, da Conceição EC, Rezende KR. Improvement in Solubility–Permeability Interplay of Psoralens from Brosimum gaudichaudii Plant Extract upon Complexation with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144580
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachado, Rúbia Darc, Júlio C. G. Silva, Luís A. D. Silva, Gerlon de A. R. Oliveira, Luciano M. Lião, Eliana M. Lima, Mariana C. de Morais, Edemilson C. da Conceição, and Kênnia R. Rezende. 2022. "Improvement in Solubility–Permeability Interplay of Psoralens from Brosimum gaudichaudii Plant Extract upon Complexation with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin" Molecules 27, no. 14: 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144580
APA StyleMachado, R. D., Silva, J. C. G., Silva, L. A. D., Oliveira, G. d. A. R., Lião, L. M., Lima, E. M., de Morais, M. C., da Conceição, E. C., & Rezende, K. R. (2022). Improvement in Solubility–Permeability Interplay of Psoralens from Brosimum gaudichaudii Plant Extract upon Complexation with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Molecules, 27(14), 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144580