Application of Orange Peel Waste as Adsorbent for Methylene Blue and Cd2+ Simultaneous Remediation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Adsorbent
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
2.3. Optimal Contact Time and Isotherms in Monocomponent Systems
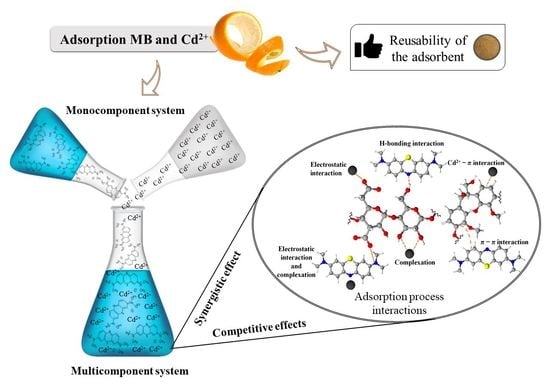
2.4. Adsorption in Multicomponent Systems
2.5. Adsorbent Reusability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Isotherms in Monocomponent Systems
3.2. Effect of Pollutant Equilibrium Concentration in Multicomponent Systems
3.3. Effect of Pollutant Equilibrium Concentration in Multicomponent Systems
3.4. Reusability of the Adsorbent
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awad, F.S.; Abouzied, K.M.; El-maaty, W.M.A.; El-wakil, A.M.; El-shall, M.S. Effective Removal of Mercury (II) from Aqueous Solutions by Chemically Modified Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Arab. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, M.; Gu, Y.; Han, R. Study of Methylene Blue Adsorption from Solution by Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composites. Desalin. Water Treat 2019, 147, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godt, J.; Scheidig, F.; Grosse-Siestrup, C.; Esche, V.; Brandenburg, P.; Reich, A.; Groneberg, D.A. The Toxicity of Cadmium and Resulting Hazards for Human Health. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2006, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Jing, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z. Applied Surface Science Enhanced Removal of Aqueous Cd (II) by a Biochar Derived from Salt-Sealing Pyrolysis Coupled with NaOH Treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 511, 145619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Biochar Prepared from Co-Pyrolysis of Municipal Sewage Sludge and Tea Waste for the Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions: Kinetics, Isotherm, Thermodynamic and Mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; North, M.; Wu, X. Rapid and Efficient Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solution by Hierarchically Porous, Activated Starbons®: Mechanism and Porosity Dependence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G.; Cai, W.; Hu, W. Adsorption of Cadmium(II) in Wastewater by Magnesium Oxide Modified Biochar. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, S.; Robles, I.; Ramirez, A.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N. Mercury Removal from Wastewater Using Agroindustrial Waste Adsorbents. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, E.; Ediati, R.; Kusumawati, Y.; Bahruji, H.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Prasetyoko, D. Review on Recent Advances of Carbon Based Adsorbent for Methylene Blue Removal from Waste Water. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 16, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareq, R.; Akter, N.; Azam, S. Chapter 10 - Biochars and Biochar Composites: Low-Cost Adsorbents for Environmental Remediation. In Biochar from Biomass and Waste; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 169–210. ISBN 9780128117293. [Google Scholar]
- Terzioğlu, P.; Güney, F.; Parın, F.N.; Şen, İ.; Tuna, S. Biowaste Orange Peel Incorporated Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Films for Food Packaging Applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Singhbabu, Y.N.; Didwal, P.N.; Nguyen, A.; Kim, J.; Park, C. Biowaste Orange Peel-Derived Mesoporous Carbon as a Cost-Effective Anode Material with Ultra-Stable Cyclability for Potassium-Ion Batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2020, 3, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ihsanullah, I.; Younas, M.; Ul Hassan Shah, M. Recent Advances in Applications of Low-Cost Adsorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Water: A Critical Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 278, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushra, R.; Mohamad, S.; Alias, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ahmad, M. Current Approaches and Methodologies to Explore the Perceptive Adsorption Mechanism of Dyes on Low-Cost Agricultural Waste: A Review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 319, 111040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.; Flora, J.R.V.; Min, C.; Yoon, Y. Removal of Heavy Metals from Water Sources in the Developing World Using Low-Cost Materials: A Review. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bediako, J.K.; Lin, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Zhao, Y.; Choi, J.; Song, M.; Cho, C.; Yun, Y. Evaluation of Orange Peel-Derived Activated Carbons for Treatment of Dye-Contaminated Wastewater Tailings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, S.; Ramirez, A.P.; Ulloa, M.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N.Y. Dyes Removal from Water Using Low Cost Absorbents. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez Muñoz, A.P.; Giraldo, S.; Flórez Yepes, E.; Acelas Soto, N.Y. Preparación de Carbón Activado a Partir de Residuos de Palma de Aceite y Su Aplicación Para La Remoción de Colorantes. Rev. Colomb. Química 2017, 46, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Hong, M.; Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Tan, Z. Contributions and Mechanisms of Components in Modi Fi Ed Biochar to Adsorb Cadmium in Aqueous Solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhafez, A.A.; Li, J. Removal of Pb (II) from Aqueous Solution by Using Biochars Derived from Sugar Cane Bagasse and Orange Peel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.L.; Kumar, M.R.; Narsaiah, T.B. Materials Today: Proceedings Removal of Heavy Metals (Cu & Ni) from Wastewater Using Rice Husk and Orange Peel as Adsorbents. Mater. Today Proc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumediene, M.; Benaïssa, H.; George, B.; Molina, S.; Merlin, A. Characterization of Two Cellulosic Waste Materials (Orange and Almond Peels) and Their Use for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Maderas. Cienc. Tecnol. 2015, 17, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A. Cadmium Removal and Recovery from Aqueous Solutions by Novel Adsorbents Prepared from Orange Peel and Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.E.; Nunell, G.V.; Bonelli, P.R.; Cukierman, A.L. Activated Carbon Developed from Orange Peels: Batch and Dynamic Competitive Adsorption of Basic Dyes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; You, S.; Chao, H. Thermodynamic Parameters of Cadmium Adsorption onto Orange Peel Calculated from Various Methods: A Comparison Study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2671–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, S. Turning Waste into Adsorbent: Modification of Discarded Orange Peel for Highly Efficient Removal of Cd(II) from Aqueous Solution. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 185, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.A.; Vishesh, Y.; Sarvshrestha, N.; Bhardwaj, A.S.; Kumar, P.A.; Topare, N.S.; Raut-Jadhav, S.; Bokil, S.A.; Khan, A. Adsorption Isotherm Studies of Methylene Blue Using Activated Carbon of Waste Fruit Peel as an Adsorbent. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visa, M.; Bogatu, C.; Duta, A. Simultaneous Adsorption of Dyes and Heavy Metals from Multicomponent Solutions Using Fly Ash. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5486–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, D.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Citric Acid-Crosslinked β-Cyclodextrin for Simultaneous Removal of Bisphenol A, Methylene Blue and Copper: The Roles of Cavity and Surface Functional Groups. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yin, J.; Ma, Q.; Baihetiyaer, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, X. Montmorillonite-Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Aerogel (M−rGO): A Green Adsorbent for the Dynamic Removal of Cadmium and Methylene Blue from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, S.; Robles, I.; Godínez, L.A.; Acelas, N.; Elizabeth, F. Experimental and Theoretical Insights on Methylene Blue Removal from Wastewater Using an Adsorbent Obtained from the Residues of the Orange Industry. Molecules 2021, 26, 4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Liu, F.Q.; Long, C.; Chen, T.P.; Wu, Q.Y.; Li, A.M. Synergic Removal and Sequential Recovery of Acid Black 1 and Copper (II) with Hyper-Crosslinked Resin and inside Mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Duan, Z.; Qin, R.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Song, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. Simultaneous Adsorption of Cd2+ and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Xanthate-Modified Baker ’ s Yeast. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Ramos, S.N.; Xavier, A.L.P.; Teodoro, F.S.; Gil, L.F.; Gurgel, L.V.A. Removal of Cobalt(II), Copper(II), and Nickel(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Phthalate-Functionalized Sugarcane Bagasse: Mono- and Multicomponent Adsorption in Batch Mode. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A.N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y.H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies in Adsorption of Heavy Metals Using Biosorbent: A Summary of Recent Studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 616–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgionny, A.; Acelas, N.Y.; Ocampo-pérez, R.; Padilla-ortega, E.; Leyva-ramos, R.; Flórez, E. Understanding Mechanisms in the Adsorption of Lead and Copper Ions on Chili Seed Waste in Single and Multicomponent Systems: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of Cadmium and Lead Ions by Phosphoric Acid-Modi Fi Ed Biochar Generated from Chicken Feather: Selective Adsorption and in Fl Uence of Dissolved Organic Matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Baharinikoo, L.; Farahani, M.D.; Mahdizadeh, B.; Farizhandi, A.A.K. Experimental Modelling Studies on the Removal of Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions Using ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, G.T.; Gok, X.Y.; Yong, W.F. Adsorption of Pollutants in Wastewater via Biosorbents, Nanoparticles and Magnetic Biosorbents: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Han, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Hao, C. Efficient Capture of Lead Ion and Methylene Blue by Functionalized Biomass Carbon-Based Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lv, J.; Guo, J.; Fu, S.; Guo, M.; Yang, P. The Polyaminocarboxylated Modifed Hydrochar for Efficient Capturing Methylene Blue and Cu (II) from Water. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Leng, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Zeng, G. Insight into Highly Efficient Removal of Cadmium and Methylene Blue by Eco-Friendly Magnesium Silicate-Hydrothermal Carbon Composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Alazba, A.A.; Shafiq, M. Comparative Study for Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye on Biochar Derived from Orange Peel and Banana Biomass in Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, T.A.; Ali, M.I. Potential Application of Natural and Modified Orange Peel as an Eco–Friendly Adsorbent for Methylene Blue Dye. Iraqi J. Sci. 2016, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Guediri, A.; Bouguettoucha, A.; Chebli, D.; Chafai, N.; Amrane, A. Molecular Dynamic Simulation and DFT Computational Studies on the Adsorption Performances of Methylene Blue in Aqueous Solutions by Orange Peel-Modified Phosphoric Acid. J. Mol. Struct. J. 2020, 1202, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-rabago, J.J.; Leyva-ramos, R.; Rivera-utrilla, J.; Ocampo-perez, R.; Cerino-cordova, F.J. Biosorption Mechanism of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution onto White Pine (Pinus Durangensis) Sawdust: Effect of Operating Conditions. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Ramos, R.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R.; Mendoza-Barron, J.; Fuentes-Rubio, L.; Guerrero-Coronado, R.M. Adsorption of Cadmium(II) from Aqueous Solution onto Activated Carbon. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Yu, H.; Ren, J.; Zhang, L.; Meng, P. Solution PH Affects Single, Sequential and Binary Systems of Sulfamethoxazole and Cadmium Adsorption by Self-Assembled Cellulose: Promotion or Inhibition? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J.; Niu, Q.; Liang, J. Simultaneous Removal of Cd (II) and Ionic Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite as an Adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über Die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chemie 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treybal, R.E. Mass-Transfer Operations, 3rd ed.; Carberry, J.J., Fair, J.R., Peters, M.S., Schowalter, W.R., Wei, J., Eds.; Mc Graw Hill International Book Company: Singapore, 1981; ISBN 0-07-066615-6. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Agarwal, M.; Sharma, S.; Singh, N. Competitive Removal of Cadmium and Lead Ions from Synthetic Wastewater Using Kappaphycus Striatum. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Chao, H.P. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperatures and Times on the Adsorption of Cadmium onto Orange Peel Derived Biochar. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; El-Halwany, M.M. Adsorption of Cadmium onto Orange Peels: Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 2014, 5, 1000238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuvaraja, G.; Krishnaiah, N.; Venkata, M. Biosorption of Pb (II) from Aqueous Solution by Solanum Melongena Leaf Powder as a Low-Cost Biosorbent Prepared from Agricultural Waste. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 114, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zeng, G.; Wu, Y. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue by Rhamnolipid-Functionalized Graphene Oxide from Wastewater. Water Res. 2014, 67, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathri, K.; Palanisamy, N. Methylene Blue Adsorption onto an Eco-Friendly Modified Polyacrylamide/Graphite Composites: Investigation of Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Zohra, F.; Chaudhry, S.A. Nigella Sativa Seed Based Nanohybrid Composite-Fe2O3–SnO2/BC: A Novel Material for Enhanced Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Water. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Yao, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Zhong, M. Effect of Pyrolysis Condition on the Adsorption Mechanism of Lead, Cadmium and Copper on Tobacco Stem Biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, Z.; Gao, M.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z. Properties and Adsorption Mechanism of Magnetic Biochar Modified with Molybdenum Disulfide for Cadmium in Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Gou, S.; He, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, S.; Duan, W.; Liu, T. An Efficient Chitosan-Based Adsorption Material Containing Phosphoric Acid and Amidoxime Groups for the Enrichment of Cu(II) and Ni(II) from Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Tankpa, V.; Bai, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, X. Mechanisms and Reutilization of Modi Fi Ed Biochar Used for Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Wang, J.J.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.; Yoon, C.; Jeon, J.; Hun, K.; Cho, J.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D. Cadmium Adsorption Characteristics of Biochars Derived Using Various Pine Tree Residues and Pyrolysis Temperatures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 553, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, Z.; Gao, M.; Qiu, W.; Islam, M.S.; Song, Z. Mechanisms for Cadmium Adsorption by Magnetic Biochar Composites in an Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusa, U.; Abdullahi, Y.; Garba, M.; Bello, G.N.; Aji, M.A.; Kubo, A.I. Selective and Simultaneous Removal of Methylene Blue and Cadmium (II) from Wastewater Using Waste Biomass Derived Porous Carbon. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2021, 12, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar]








| Langmuir | |
| Freundlich |
| Adsorbent | MB | Cd2+ |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | ||
| Qm (mmol g−1, mg g−1) | 0.7824, 250.6 | 0.2884, 32.4 |
| KL (L mmol−1) | 5.44 | 2.18 |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| RMSE | 0.023 | 0.021 |
| SSE | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| Freundlich | ||
| KF (mmol g−1) | 1.029 | 0.19 |
| n | 1.71 | 2.81 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.90 |
| RMSE | 0.027 | 0.020 |
| SSE | 0.006 | 0.003 |
| Treatment | Contaminant | Qm (mg g−1) | pH | Adsorption Isotherm | Adsorption Mechanisms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP washed | MB | 250.58 | 7 | Langmuir, Freundlich | Electrostatic interaction, H-bonding interaction, π–π interactions | This study |
| OP thermochemical activation using ZnCl2 (800 °C in N2 atmosphere) | MB | 339.82 | 8 | Sips y Langmuir | Electrostatic interaction, H-bonding interaction, π–π interactions | [16] |
| OP washed | MB | 192.31 | 4.5 | Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin | Electrostatic interaction, H-bonding interaction, π–π interactions | [31] |
| OP washed (OP) and chemical activation using NaOH (SOP) | MB | 14.16 OP 18.28 SOP | OP 4 SOP 9 | Freundlich | Electrostatic attraction | [44] |
| OP chemical activation using H3PO4 | MB | 307.63 | 6.2 | Langmuir | Electrostatic interaction, π–π interactions | [45] |
| OP washed | Cd2+ | 32.42 | 7 | Langmuir, Freundlich | Electrostatic interaction, complexation, Cd-π interactions | This study |
| OP washed | Cd2+ | 59.5 | 7 | Langmuir, Freundlich | Electrostatic interaction, complexation | [25] |
| OP washed and pyrolyzed at 700 °C | Cd2+ | 114.69 | 7 | Langmuir | Cd-π interactions, surface precipitation | [55] |
| OP Washed | Cd2+ | 4.90 | 5 | Langmuir | Not reported | [56] |
| OP modified with Fe2O3 | Cd2+ | 76.92 | 7 | Langmuir | Complexation, ion exchange | [23] |
| OP Bands (cm−1) | Bands after Adsorption (cm−1) | Functional Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-MB | OP-Cd2+ | OP-Cd (100 mg L−1)-MB (200 mg L−1) | OP-Cd (200 mg L−1)-MB (100 mg L−1) | ||
| 3314 | 3296 | 3290 | 3305 | 3308 | -OH |
| 1734 | 1732 | 1734 | 1732 | 1732 | -C=O |
| 1605 | 1598 | 1602 | 1597 | 1599 | C=N |
| 1519 | 1517 | 1517 | 1517 | 1517 | C=C |
| 1330 | 1329 | 1326 | 1331 | 1329 | -CH3 |
| 1013 | 1012 | 1010 | 1012 | 1012 | C-O-H |
| 891 | 882 | 889 | 882 | 886 | C-H aromatic |
| Adsorbent | Monocomponent Adsorption Qm (mg g−1) | Multicomponent Adsorption Qm (mg g−1) | Effect | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP washed | Cd2+ 32.42 | MB 250.58 | Cd2+ 34.8 | MB 86.79 | Synergistic (Cd2+ adsorption capacity increases in the presence of MB). Antagonistic (MB adsorption capacity is affected by the presence of Cd2+). | This study |
| Magnesium silicate biocomposite and subsequent hydrothermal carbonization | Cd (II) 104 | MB 325 | Cd (II) 108 | MB 200 | Synergistic (Cd (II) adsorption capacity showed a slight increase in the presence of MB). Antagonistic (MB adsorption capacity was affected by the presence of Cd (II) in the multicomponent system). | [42] |
| Xanthate-modified baker’s yeast | Cd2+ 224.5 | MB 56.25 | Cd2+ 267 | MB 57.88 | Synergistic (Cd2+ adsorption capacity increases in the presence of MB). MB adsorption capacity is almost unaffected by the presence of Cd2+. | [33] |
| Albizia lebbeck pods carbon (ALPC) | Cd2+ 185.19 | MB 80.01 | Cd2+ 181.8 | MB 91.74 | Antagonistic effect | [67] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giraldo, S.; Acelas, N.Y.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Padilla-Ortega, E.; Flórez, E.; Franco, C.A.; Cortés, F.B.; Forgionny, A. Application of Orange Peel Waste as Adsorbent for Methylene Blue and Cd2+ Simultaneous Remediation. Molecules 2022, 27, 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165105
Giraldo S, Acelas NY, Ocampo-Pérez R, Padilla-Ortega E, Flórez E, Franco CA, Cortés FB, Forgionny A. Application of Orange Peel Waste as Adsorbent for Methylene Blue and Cd2+ Simultaneous Remediation. Molecules. 2022; 27(16):5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165105
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiraldo, Stephanie, Nancy Y. Acelas, Raúl Ocampo-Pérez, Erika Padilla-Ortega, Elizabeth Flórez, Camilo A. Franco, Farid B. Cortés, and Angélica Forgionny. 2022. "Application of Orange Peel Waste as Adsorbent for Methylene Blue and Cd2+ Simultaneous Remediation" Molecules 27, no. 16: 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165105
APA StyleGiraldo, S., Acelas, N. Y., Ocampo-Pérez, R., Padilla-Ortega, E., Flórez, E., Franco, C. A., Cortés, F. B., & Forgionny, A. (2022). Application of Orange Peel Waste as Adsorbent for Methylene Blue and Cd2+ Simultaneous Remediation. Molecules, 27(16), 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165105