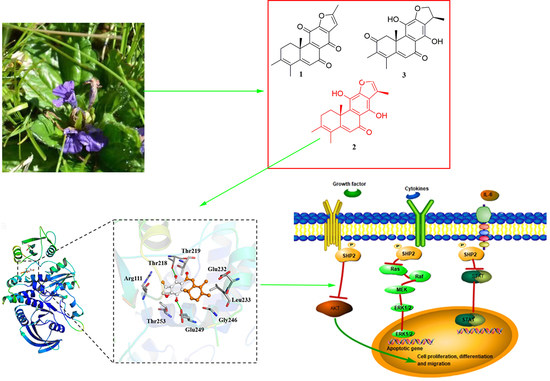
Ajuforrestin A, an Abietane Diterpenoid from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calanthe, Induces A549 Cell Apoptosis by Targeting SHP2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
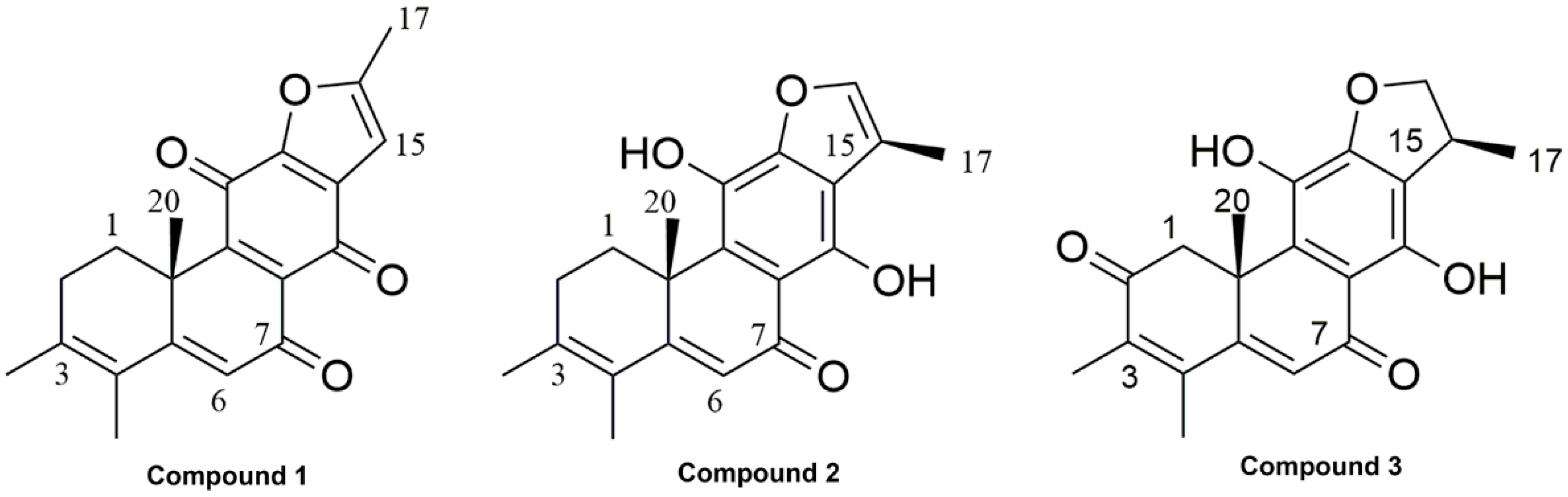
2.1. Phytochemical Investigation
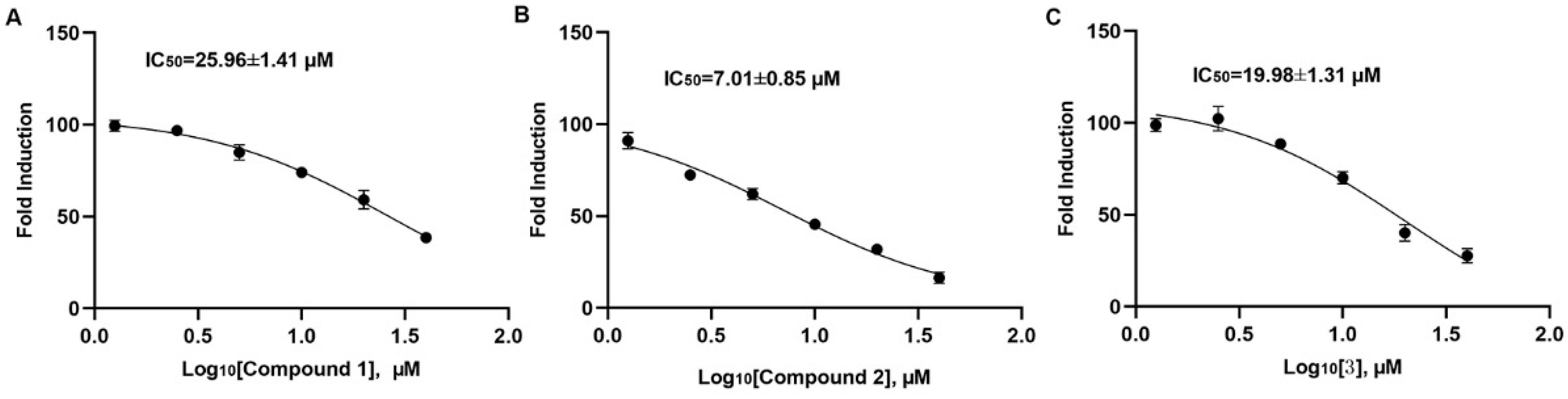
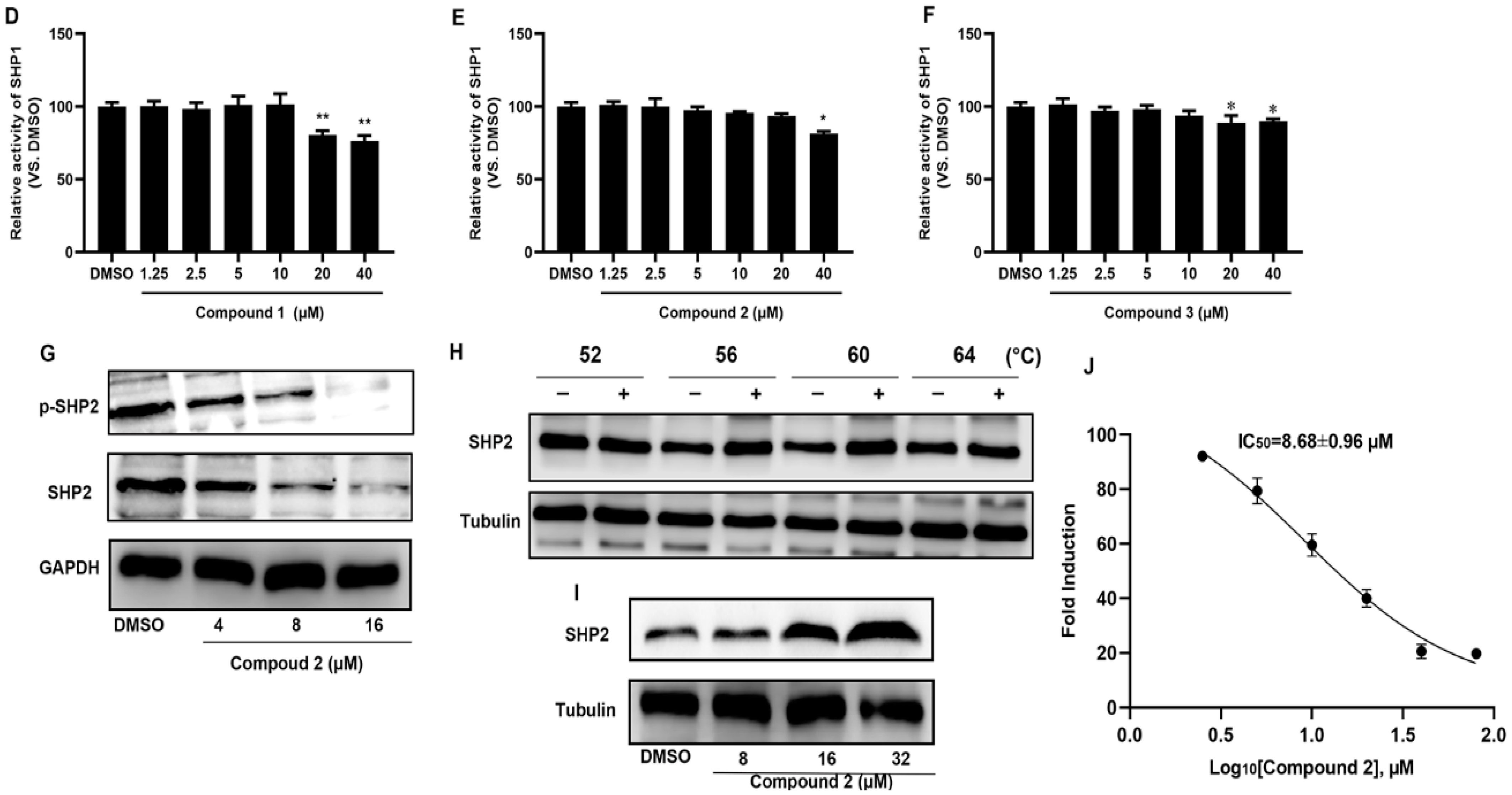
2.2. Compound 2 Inhibits A549 Cell Proliferation Targeting SHP2
2.3. Molecular Docking of Compound 2 with SHP2
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Properties Prediction of Compound 2
2.5. Compound 2 Attenuates A549 Invasion and Migration by the Inhibition of the ERK, AKT Pathway
2.6. Compound 2 Causes A549 Cell Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Cell Culture and Regents
4.4. Extraction and Isolation
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. The Activity of SHP1 and SHP2 In Vitro
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay
4.9. Molecular Docking
4.10. Pharmacokinetic Properties Prediction
4.11. A549 Cell Wound-Healing Assay
4.12. A549 Cell Invasion Assay
4.13. Apoptosis Flow Cytometry
4.14. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Liu, Q.; Qu, J.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y. Targeting SHP2 as a promising strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.Q.; Lin, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Cai, L.L.; Ruan, R.S.; Lu, Z.X.; Tzeng, C.M. Structure, function, and pathogenesis of SHP2 in developmental disorders and tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2014, 14, 567–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewa, T.; Sahu, K.K.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Kuban-Jankowska, A. Synthesis of small peptide compounds, molecular docking, and inhibitory activity evaluation against phosphatases PTP1B and SHP2. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 4139–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddraraju, K.V.; Aggarwal, D.; Zhang, Z.Y. Therapeutic Targeting of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, J.S.; McQueeney, K.E.; Burnett, J.C.; Wipf, P.; Sharlow, E.R. Small molecule targeting of PTPs in cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Jo, S.; Park, S.B.; Chae, C.H.; Lee, K.; Koh, B.; Shin, I. Development and structure-activity relationship study of SHP2 inhibitor containing 3,4,6-trihydroxy-5-oxo-5H-benzo[7]annulene. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Saxena, M.; Kapur, R. Role of SHP2 in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazhappilly, C.G.; Saleh, E.; Ramadan, W.; Menon, V.; Al-Azawi, A.M.; Tarazi, H.; Abdu-Allah, H.; El-Shorbagi, A.N.; El-Awady, R. Inhibition of SHP2 by new compounds induces differential effects on RAS/RAF/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways in different cancer cell types. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Bu, H.; Zhou, J.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhang, H. Recent Advances of SHP2 Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Current Development and Clinical Application. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11368–11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Maiese, K. The Src homology 2 domain tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2: Diversified control of cell growth, inflammation, and injury. Histol. Histopathol. 2007, 22, 1251–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.P.; Shen, X.F.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhang, M.; Tan, Y.Z. A new abietane diterpenoid glycoside from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calantha. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2856–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.M.; Cao, Z.X.; Yan, H.L.; Li, W.; Yang, F.; Zhao, W.J.; Diao, Q.C.; Tan, Y.Z. A new abietane diterpenoid from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calantha induces human lung epithelial A549 cell apoptosis by inhibiting SHP2. Fitoterapia 2020, 141, 104484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.X.; Xiong, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, J.J.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.X.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.F. Rearranged abietane diterpenoids from the roots of Clerodendrum trichotomum and their cytotoxicities against human tumor cells. Phytochemistry 2013, 89, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Diao, Q.Y.; Yu, H.Z.; Jiao, C.L.; Ruan, J. Phytochemical, cytotoxic and chemotaxonomic study on Ajuga forrestii Diels (Labiatae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, X.N.; Shen, T.; Wang, S.Q.; Guo, D.X.; Lou, H.X. Rearranged abietane diterpenoid hydroquinones from aerial parts of Ajuga decumbens Thunb. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunda, S.; Burrell, K.; Heir, P.; Zeng, L.; Alamsahebpour, A.; Kano, Y.; Raught, B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zadeh, G.; Ohh, M. Inhibition of SHP2-mediated dephosphorylation of Ras suppresses oncogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.L.; Haderk, F.; Bivona, T.G. Allosteric SHP2 inhibitors in cancer: Targeting the intersection of RAS, resistance, and the immune microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.J.; Haderk, F.; Stahlhut, C.; Schulze, C.J.; Hemmati, G.; Wildes, D.; Tzitzilonis, C.; Mordec, K.; Marquez, A.; Romero, J.; et al. RAS nucleotide cycling underlies the SHP2 phosphatase dependence of mutant BRAF-, NF1- and RAS-driven cancers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, T.; Ishihara, K.; Atsumi, T.; Nishida, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Miyata, T.; Itoh, S.; Narimatsu, M.; Maeda, H.; Fukada, T.; et al. Dissection of signaling cascades through gp130 in vivo: Reciprocal roles for STAT3- and SHP2-mediated signals in immune responses. Immunity 2000, 12, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajan, M.; de Rocca Serra, A.; Valet, P.; Edouard, T.; Yart, A. SHP2 sails from physiology to pathology. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 58, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Niu, R. Functions of Shp2 in cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Li, F.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, K.Z.; Yang, H.L.; Gao, Y.; Yu, J.R. Expression and clinical significance of SHP2 in gastric cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruess, D.A.; Heynen, G.J.; Ciecielski, K.J.; Ai, J.; Berninger, A.; Kabacaoglu, D.; Gorgulu, K.; Dantes, Z.; Wormann, S.M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; et al. Mutant KRAS-driven cancers depend on PTPN11/SHP2 phosphatase. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardi, S.; Mulero-Sanchez, A.; Prahallad, A.; Germano, G.; Bosma, A.; Krimpenfort, P.; Lieftink, C.; Steinberg, J.D.; de Wit, N.; Goncalves-Ribeiro, S.; et al. SHP2 is required for growth of KRAS-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer in vivo. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard-Chapeau, E.A.; Li, S.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhu, H.H.; Princen, F.; Fang, D.D.; Han, T.; Bailly-Maitre, B.; Poli, V.; et al. Ptpn11/Shp2 acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Xiang, D.M.; Sun, W.; Liu, N.; Sun, H.L.; Wen, W.; Shen, W.F.; Wang, R.Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; et al. PTPN11/Shp2 overexpression enhances liver cancer progression and predicts poor prognosis of patients. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ji, W.; Tian, R.; Zhang, F.; Niu, R. Shp2 Plays a Critical Role in IL-6-Induced EMT in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Cheng, H.; Ke, Y.; Wang, L. The prognostic significance of SHP2 and its binding protein Hook1 in non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 5897–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.S.Y.; Zhou, J.; Lim, J.S.L.; Hee, Y.T.; Chooi, J.Y.; Chung, T.H.; Tan, Z.T.; Zeng, Q.; Waller, D.D.; Sebag, M.; et al. IL6 Promotes a STAT3-PRL3 Feedforward Loop via SHP2 Repression in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Fernandez, A.; Lopez-Ruano, G.; Prieto-Bermejo, R.; Ijurko, C.; Diez-Campelo, M.; Sanchez-Guijo, F.; Hernandez-Hernandez, A. SHP1 and SHP2 inhibition enhances the pro-differentiative effect of phorbol esters: An alternative approach against acute myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Yang, X.; Yu, B. Strategies Targeting Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2 for Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3066–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, C.; Ye, Q.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Endothelial deletion of SHP2 suppresses tumor angiogenesis and promotes vascular normalization. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friman, T. Mass spectrometry-based Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA(R)) for target deconvolution in phenotypic drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, N.J.; Xi, R.Y.; Shi, X.K.; Li, R.Z.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, F. Hexachlorophene, a selective SHP2 inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and metastasis of KRAS-mutant NSCLC cells by inhibiting RAS/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 441, 115988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, J.K.; Valencia-Sama, I.; Osborn, A.J.; Propst, E.J.; Irwin, M.S.; Papsin, B.; Wolter, N.E. Combination mTOR and SHP2 inhibitor treatment of lymphatic malformation endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res. 2022, 143, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Xiao, M.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Bai, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, W.; Sun, K. SHP2 Inhibitors Show Anti-Myeloma Activity and Synergize With Bortezomib in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 841308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Jiang, M.; Yang, F.; Tang, X.; Lin, M.; Zhou, C.; Tan, Y.; Liu, D. Ajuforrestin A, an Abietane Diterpenoid from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calanthe, Induces A549 Cell Apoptosis by Targeting SHP2. Molecules 2022, 27, 5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175469
Yan H, Jiang M, Yang F, Tang X, Lin M, Zhou C, Tan Y, Liu D. Ajuforrestin A, an Abietane Diterpenoid from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calanthe, Induces A549 Cell Apoptosis by Targeting SHP2. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175469
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hongling, Miao Jiang, Fujin Yang, Xueyong Tang, Mao Lin, Chunyan Zhou, Yuzhu Tan, and Deming Liu. 2022. "Ajuforrestin A, an Abietane Diterpenoid from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calanthe, Induces A549 Cell Apoptosis by Targeting SHP2" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175469
APA StyleYan, H., Jiang, M., Yang, F., Tang, X., Lin, M., Zhou, C., Tan, Y., & Liu, D. (2022). Ajuforrestin A, an Abietane Diterpenoid from Ajuga ovalifolia var. calanthe, Induces A549 Cell Apoptosis by Targeting SHP2. Molecules, 27(17), 5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175469