Recent Trends in the Preparation of Nano-Starch Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
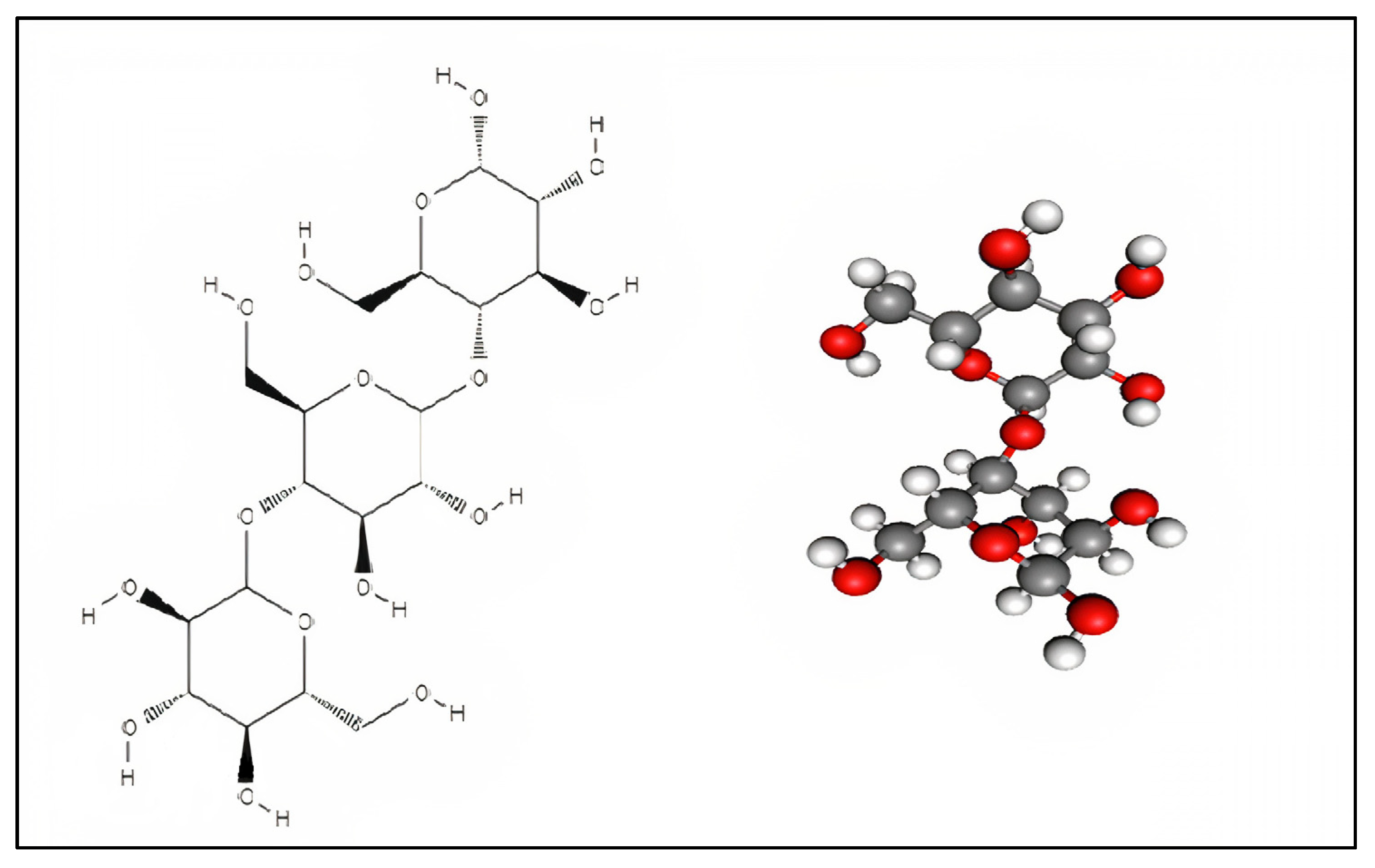
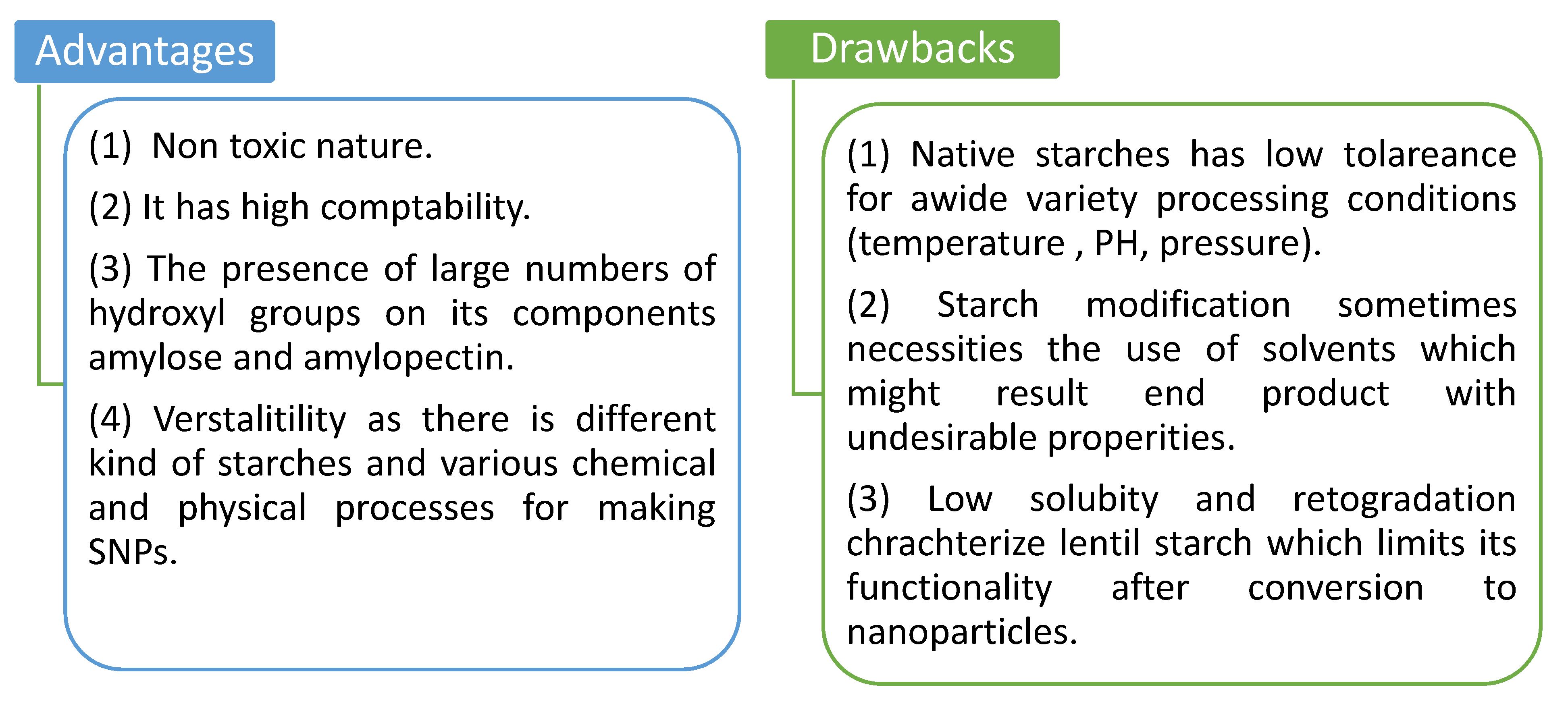
2. Starch Nanoparticles
3. The Classification Basis of the Preparation Method of Starch Nanoparticles
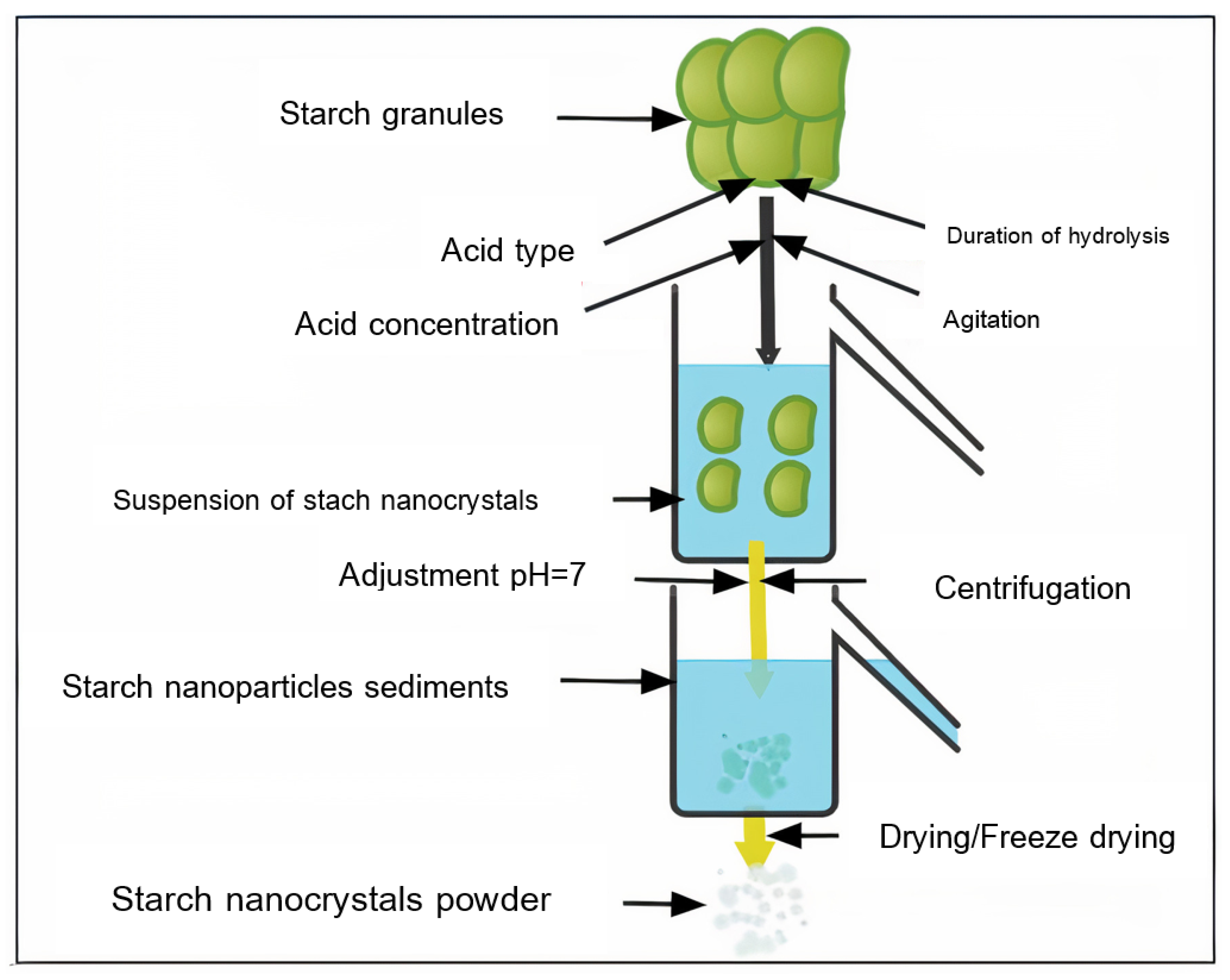
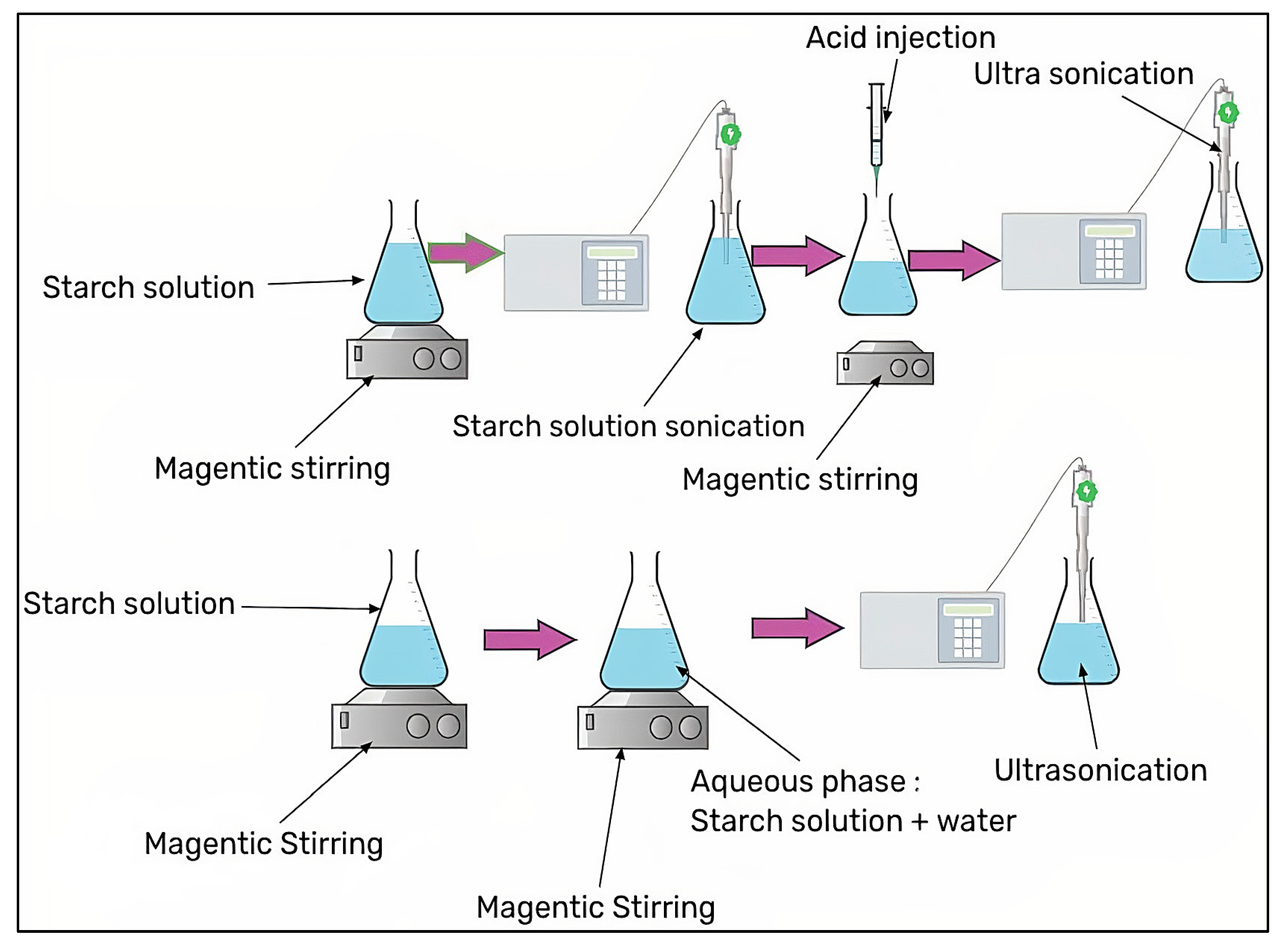
3.1. Acid Hydrolysis
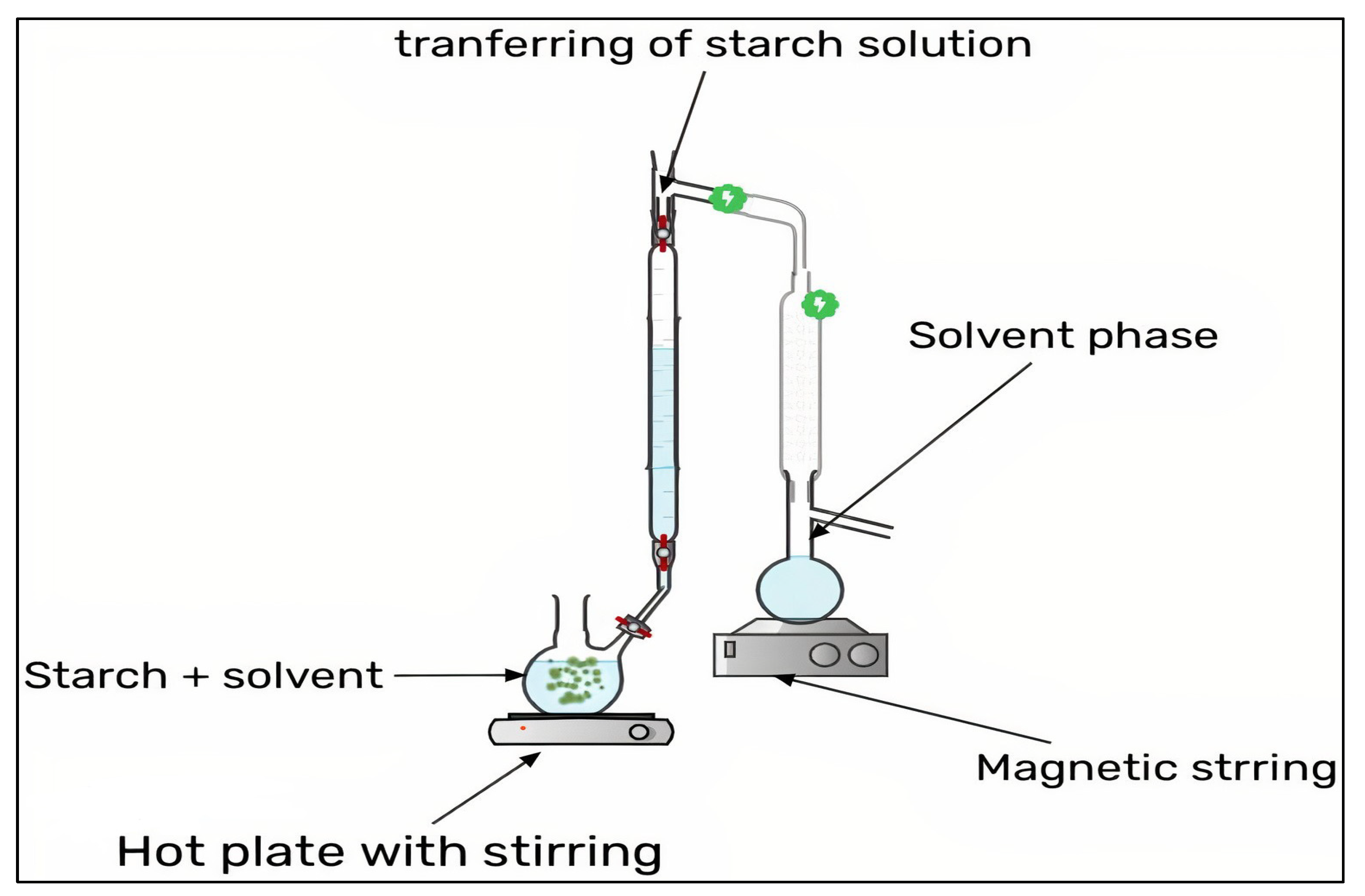
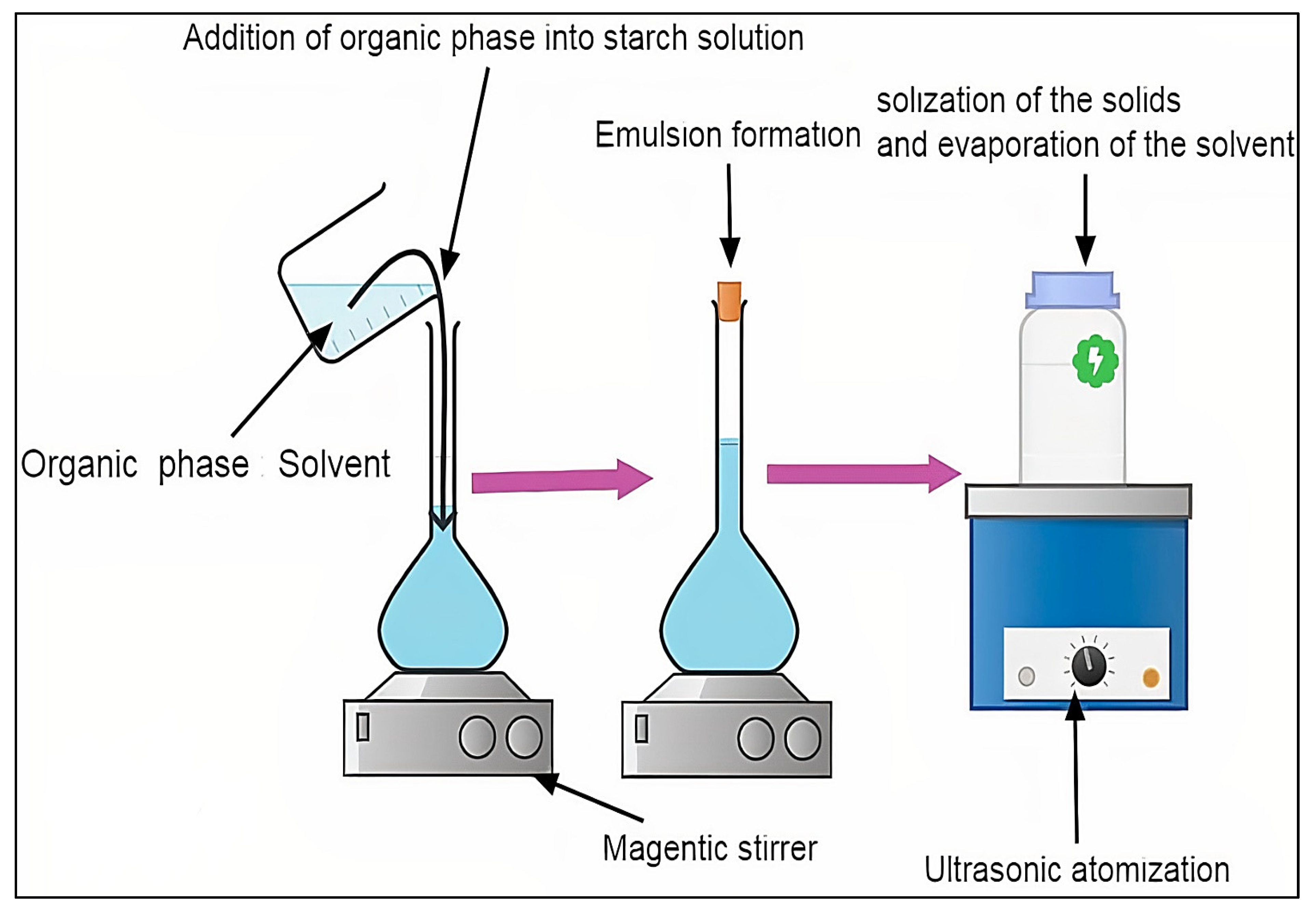
3.2. Nano-Precipitation
3.3. Milling
3.4. Gamma Radiation
3.5. Electro Spraying
3.6. High-Pressure Homogenization
3.7. Ultrasonication with/without Acid Hydrolysis
3.8. Enzymatic De-Branching with/without Acid Hydrolysis
4. Comparison of Production Rate of Starch Nanoparticles Preparation Methods
5. Techniques for Characterization of SNPs Properties
5.1. Thermal Properties
5.1.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
5.1.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
5.1.3. Differential Thermal Analysis
5.2. Mechanical Properties
5.2.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
5.2.2. Zeta Potential Analysis
5.3. Physiochemical Properties
5.3.1. Atomic Force Microscopy
5.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
5.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
5.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
5.4. Structural Properties
5.4.1. X-ray Diffraction
5.4.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Analysis
5.4.3. Dynamic Light Scattering
6. Applications of Starch Nano-Particles (SNPs)
6.1. SNPs in Non-Food Application
6.1.1. Carrier in Drug Delivery
6.1.2. Nano Starch in Food Packaging Industry
6.1.3. Adsorbents in Water Treatment
6.1.4. Emulsion Stabilizer
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Moran, D.; Gutiérrez, G.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Marefati, A.; Rayner, M.; Matos, M. Synthesis of starch nanoparticles and their applications for bioactive compound encapsulation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, C.P.; Cui, B.; Zhang, H.; Jayaraman, S.; Kodiveri Muthukaliannan, G. A comprehensive review on corn starch-based nanomaterials: Properties, simulations, and applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.B. Synthesis and modification approaches for starch nanoparticles for their emerging food industrial applications: A review. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 128, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.P.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yang, R.Y.; Yu, A.B. Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: Theoretical developments. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 3378–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoparticle and Microparticle–Based Delivery Systems: Encapsulation, Protection, and Release of Active Components; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Le Corre, D.; Bras, J.; Dufresne, A. Starch nanoparticles: A review. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remanan, M.K.; Zhu, F. Encapsulation of rutin using quinoa and maize starch nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 128534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.M.T.; Mondal, S.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Bui, N.T.; Oh, J. Rice starch coated iron oxide nanoparticles: A theranostic probe for photoacoustic imaging-guided photothermal cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Cai, W.; Ji, N.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, Q. Fabrication and characterization of hollow starch nanoparticles by heterogeneous crystallization of de-branched starch in a nano-emulsion system. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Gani, A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Rizvi, S.H. Influence of ball milling on the production of starch nanoparticles and its effect on structural, thermal and functionalproperties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Fang, D.; Wang, M.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Ji, N.; Dai, L.; Lu, H.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Preparation and characterization of waxy maize starch nanocrystals with a high yield via dry-heated oxalic acid hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelo, P.H.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Clerici, M.T.P.S. Starch nanoparticles: Production methods, structure, and properties for food applications. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 33, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, A. Cellulose-based composites and nanocomposites. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 401–418. [Google Scholar]
- Le Corre, D.; Bras, J.; Dufresne, A. Influence of native starch’s properties on starch nanocrystals thermal properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarti, C.; Sunarti, T.C.; Mangunwidjaja, D.; Richana, N. Preparation of arrowroot starch nanoparticles by butanol-complex precipitation, and its application as bioactive encapsulation matrix. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Truong, V.D.; Wang, L. Structures and rheological properties of corn starch as affected by acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 52, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Castillo, L.E.; Leite, M.A.; Ditchfield, C.; do Amaral, S.P.J.; Moraes, I.C.F. Quinoa starch nanocrystals production by acid hydrolysis: Kinetics and properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R. Characterization of acid hydrolysis based nano-converted mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) starch for morphological, rheological and thermal properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Du, C.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, W.; Yu, X.; Du, S.K. Preparation and characterization of quinoa starch nanoparticles as quercetin carriers. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Muñoz, O.I.; Ospina-Giraldo, L.F.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Nanoprecipitation: Applications for entrapping active molecules of interest in pharmaceutics. In Nano-and Microencapsulation-Techniques and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hedayati, S.; Niakousari, M.; Mohsenpour, Z. Production of tapioca starch nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation-sonication treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, I.J.; McClements, D.J. Production of nanoparticles by anti-solvent precipitation for use in food systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Guevara, L.; Nieto-Suaza, L.; Sanchez, L.T.; Pinzon, M.I.; Villa, C.C. Development of native and modified banana starch nanoparticles as vehicles for curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Characterization of starch nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation: Influence of amylose content and starch type. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 87, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, J.N.; Ismadji, S.; Gunarto, C.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ju, Y.H. A study of anionic, cationic, and nonionic surfactants modified starch nanoparticles for hydrophobic drug loading and release. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 112034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q. Pickering emulsions stabilized by media-milled starch particles. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 105, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, P.; Lau, M.; Breitung-Faes, S.; Kwade, A.; Barcikowski, S. Physical fabrication of colloidal ZnO nanoparticles combining wet-grinding and laser fragmentation. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 108, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, F.; Mende, S.; Schwedes, J.; Peukert, W. Nanomilling in stirred media mills. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 4557–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorfa, N.; Nlandu, H.; Belkacemi, K.; Hamoudi, S. Physical and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Modifications of Potato Starch Granules. Polymers 2022, 14, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Panmai, S.; Wu, Y. Nanosizing—oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, N.M.C.; de Lima, F.F.; Fialho, R.L.L.; Albuquerque, E.C.D.M.C.; Velasco, J.I.; Fakhouri, F.M. Production and characterization of starch nanoparticles. Appl. Modif. Starches 2018, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Haripriya, S. Physicochemical and structural evaluation of alkali extracted chickpea starch as affected by γ-irradiation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Jan, S.; Rani, S.; Jan, K.; Swer, T.L.; Prakash, K.S.; Dar, M.Z.; Bashir, K. Physicochemical and functional properties of gamma irradiated buckwheat and Potato starch. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 144, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Jabeen, M.; Geelani, H.; Masoodi, F.A.; Saba, I.; Muzaffar, S. Effect of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties of Indian Horse Chestnut (Aesculus indica Colebr.) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunder, M.; Mumbrekar, K.D.; Mazumder, N. Gamma radiation as a modifier of starch–Physicochemical perspective. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Hernandez, J.A.; Torres-Chavez, P.I.; Ramirez-Wong, B.; Rascon-Chu, A.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Rangel-Vázquez, N.A.; Rodríguez-Félix, F. Micro- and nanoparticles by electrospray: Advances and applications in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ji, N.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Green preparation of debranched starch nanoparticles with different crystalline structures by electrostatic spraying. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chen, X.D.; Mao, Z.H. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on the structure and thermal properties of maize starch. J. Food Eng. 2008, 87, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, B.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B. Physicochemical Properties and Digestion of LotusSeed Starch under High-Pressure Homogenization. Nutrients 2019, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, E.; Mandala, I. Modification of resistant starch nanoparticles using high-pressure homogenization treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, H.; Mahanta, C.L. Properties of starch nanoparticle obtained by ultrasonication and high pressure homogenization for developing carotenoids-enriched powder and Pickering nanoemulsion. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, N.M.C.; Correia, P.R.C.; Druzian, J.I.; Fakhouri, F.M.; Fialho, R.L.L.; de Albuquerque, E.C.M.C. PBAT/TPS composite films reinforced with starch nanoparticles produced by ultrasound. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 4308261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Mudgil, P.; Gani, A.; Hamed, F.; Masoodi, F.A.; Maqsood, S. Nano-encapsulation of catechin in starch nanoparticles: Characterization, release behavior and bioactivity retention during simulated in-vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Ren, L.; Tong, J.; Zhou, J. High efficiency and low cost preparation of size controlled starch nanoparticles through ultrasonic treatment and precipitation. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheikh, M.A. New technique in starch nanoparticles synthesis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, S.S.; Lim, S.T. Preparation, characterization, and utilization of starch nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreras, F.; Amaveda, H.; Lozano, A. Transient high-frequency ultrasonic water atomization. Exp. Fluids 2002, 33, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramisetty, K.A.; Pandit, A.B.; Gogate, P.R. Investigations into ultrasound induced atomization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahgholian, N.; Rajabzadeh, G. Preparation of BSA nanoparticles and its binary compounds via ultrasonic piezoelectric oscillator for curcumin encapsulation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, M.; Bertolini, A.C.; Teixeira, M.A.V.; Garcia, C.F. Biopolymers Technology; Bertolini, A.C., Ed.; Cultura Academia: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Allaith, S.A.; Abdel-aziz, M.E.; Thabit, Z.A.; Altemimi, A.B.; Abd El-Ghany, K.; Giuffrè, A.M.; Al-Manhel, A.J.A.; Ebrahim, H.S.; Mohamed, R.M.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G. Screening and Molecular Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria Producing-Glucan in Boza and Cider. Fermentation 2022, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldao, C.; Sarka, E.; Ulbrich, P.; Mensikova, E. Starch nanoparticles -two ways of their preparation. Czech J. Food Sci. 2018, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Zheng, B.; Guo, Z. Structural and physicochemical properties of lotus seed starch nanoparticles prepared using ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 68, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, T.; Zhuang, H.; Xu, Z.; Ye, R.; Sun, M. A review on patents of starch nanoparticles: Preparation, applications, and development. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2018, 9, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Polyoxometalates acid treatment for preparing starch nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, W.O.; Ray, S.S.; Emmambux, N.M. Isolation and characterisation of nanoparticles from tef and maize starch modified with stearic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel Haaj, S.; Magnin, A.; Petrier, C.; Boufi, S. Starch nanoparticles formation via high power ultrasonication. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, D.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, S.T. Preparation of crystalline starch nanoparticles using cold acid hydrolysis and ultrasonication. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.M.; Chakraborty, M.; Murthy, Z.V.P. Fast and scalable preparation of starch nanoparticles by stirred media milling. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebeish, A.; El-Rafie, M.H.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; El-Naggar, M.E. Ultra-fine characteristics of starch nanoparticles prepared using native starch with and without surfactant. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2013, 24, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanto, B.W.; Pranoto, Y.; Supriyanto, I.K. Breadfruit-Based Starch Nanoparticles Prepared Using Nanoprecipitation to Stabilize a Pickering Emulsion. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2021, 56, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufi, S.; Haaj, S.B.; Magnin, A.; Pignon, F.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Mortha, G. Ultrasonic assisted production of starch nanoparticles: Structural characterization and mechanism of disintegration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukare, A.S.; Arputharaj, A.; Bharimalla, A.K.; Saxena, S.; Vigneshwaran, N. Nanostarch production by enzymatic hydrolysis of cereal and tuber starches. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, X.; Ji, N.; Dai, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Q. Preparation and characterization of waxy maize starch nanoparticles via hydrochloric acid vapor hydrolysis combined with ultrasonication treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 80, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.; Moghadam, T.T.; Ranjbar, B. Differential scanning calorimetry techniques: Applications in biology and nanoscience. J. Biomol. Tech. 2010, 21, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Z. Preparation and characterization of starch nanoparticles via self-assembly at moderate temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, W.D.C.; dos Santos Lima, K.T.; Valencia, G.A.; Henao, A.C.A. Physicochemical Properties of Potato Starch Nanoparticles Produced by Anti-Solvent Precipitation. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2000086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, S.; Valapa, R.B.; Mishra, R.K.; Pugazhenthi, G.; Thomas, S. Thermogravimetric analysis for characterization of nanomaterials. In Thermal and Rheological Measurement Techniques for Nanomaterials Characterization; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 67–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shapi′i, R.A.; Othman, S.H.; Basha, R.K.; Naim, M.N. Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menczel, J.D.; Prime, R.B. (Eds.) Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, J.; Mohammed, A.P.; Kumar, M.A.; George, S.C.; Thomas, S. Thermoanalytical techniques of nanomaterials. In Characterization of Nanomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 213–236. [Google Scholar]
- Gardouh, A.R.; El-Din, A.S.S.; Mostafa, Y.; Gad, S. Starch Nanoparticles Preparation and Characterization by in situ combination of Sono-precipitation and Alkali hydrolysis under Ambient Temperature. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 14, 3543–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochigbo, S.S.; Luyt, A.S.; Mofokeng, J.P.; Antić, Ž.; Dramićanin, M.D.; Djoković, V. Dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of the composites of thermoplastic starch and lanthanum hydroxide nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Paridah, M.T. A review on dynamic mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced polymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parupudi, A.; Mulagapati, S.H.R.; Subramony, J.A. Nanoparticle technologies: Recent state of the art and emerging opportunities. In Nanoparticle Therapeutics; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 3–46. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, E.; Singhvi, G. Multifunctional nanocrystals for cancer therapy: A potential nanocarrier. In Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery and Therapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta potential measurement. In Characterization of Nanoparticles Intended for Drug Delivery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliapietra, B.L.; de Melo, B.G.; Sanches, E.A.; Plata-Oviedo, M.; Campelo, P.H.; Clerici, M.T.P.S. From Micro to Nanoscale: A Critical Review on the Concept, Production, Characterization, and Application of Starch Nanostructure. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Schoenenberger, M.; Gnecco, E.; Glatzel, T.; Meyer, E.; Brändlin, D.; Scandella, L. Characterization of nanoparticles using atomic force microscopy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 61, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiji, R.R.; Xu, X.; Reifenberger, R.; Raman, A.; Rudie, A.; Moon, R.J. Atomic force microscopy characterization of cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4480–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Ali, S.W. Characterization techniques for nanotechnology applications in textiles. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2008, 33, 304–317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F. Atomic force microscopy of starch systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3127–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, C.N.; Kling, I.C.S.; Ferreira, W.H.; Andrade, C.T.; Simao, R.A. Starch films containing starch nanoparticles as produced in a single step green route. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Biswas, K. Characterization of nanomaterials by physical methods. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 435–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, M.; Ji, N.; Liu, J.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Morphology and characteristics of starch nanoparticles self-assembled via a rapid ultrasonication method for peppermint oil encapsulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8363–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Effects of degree of polymerization on size, crystal structure, and digestibility of debranched starch nanoparticles and their enhanced antioxidant and antibacterial activities of curcumin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8499–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Putaux, J.L. Recent Advances in Electron Microscopy of Carbohydrate Nanoparticles. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 835663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prow, T.W.; Grice, J.E.; Lin, L.L.; Faye, R.; Butler, M.; Becker, W.; Roberts, M.S. Nanoparticles and microparticles for skin drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 470–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonde, S.; Badve, M.; Jain, B. Cavitation assisted novel method for synthesis of starch nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Process. 2022, 175, 108935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Anaya, N.M.; Schifman, L.A.; Oyanedel-Craver, V. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess molecular-level changes in microorganisms exposed to nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2016, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukaoluan, A.; Khantachawana, A.; Dechkunakorn, S.; Anuwongnukroh, N.; Tunthawiroon, P.; Srirussamee, K. Influence of Mouthwash Rinsing on the Mechanical Properties of Polymeric Ligature Ties Used for Dental Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Zhan, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, B.; Chen, P. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of capsaicin-loaded indica rice starch nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, P.; Mitchell, L. X-ray diffraction analysis of nanoparticles: Recent developments, potential problems and some solutions. Int. J. Nanosci. 2004, 3, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, W.J.; Lim, S.T. Characterization of nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis of various starches. Starch-Stärke 2012, 64, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, J.B.; Kampus, U.S.U. Modification and Characterization Starch Nanoparticles of Mangrove Fruit using Chemical-mechanical Method and Application as Basic Materials Making Hydrogel. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, Dallas, TX, USA, 7–9 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, N.; Nair, M.S.; Mazumder, A.; Poluri, K.M. Characterization of nanomaterials using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In Characterization of Nanomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 61–102. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Yarger, J.L. Characterizing gold nanoparticles by NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2018, 56, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, B.M.; Gidley, M.J.; Warren, F.J. Rapid quantification of starch molecular order through multivariate modelling of 13 C CP/MAS NMR spectra. Chem. Comm. 2015, 51, 14856–14858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.; Chudasama, D. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy NMR. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 11, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Tal, Y.; Boaler, P.J.; Dale, H.J.; Dooley, R.E.; Fohn, N.A.; Gao, Y.; Lloyd-Jones, G.C. Mechanistic analysis by NMR spectroscopy: A users guide. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2022, 129, 28–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.M.; Felício, M.R.; Santos, N.C.; Gonçalves, S.; Domingues, M.M. Application of light scattering techniques to nanoparticle characterization and development. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Yeap, S.P.; Che, H.X.; Low, S.C. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle by dynamic light scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, P.J. Differential light scattering and the measurement of molecules and nanoparticles: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 7–8, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyttlik, A.; Kuttich, B.; Kraus, T. Dynamic Light Scattering on Nanoparticles in Microgravity in a Drop Tower. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.F.A.; Gad, E.S. Investigation of an adsorbent based on novel starch/chitosan nanocomposite in extraction of indigo carmine dye from aqueous solutions. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 5556–5563. [Google Scholar]
- Kommareddy, S.; Tiwari, S.; Amiji, M. Long-circulating nano-vectors for tumor-selective gene delivery. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 4, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, S. Polyethylene glycol-conjugated copolymers for plasmid DNA delivery. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecher, M.E.; Owen, H.G.; Bandarenko, N. Alternatives to albumin: Starch replacement for plasma exchange. J. Clin. Apher. 1997, 12, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hielemans, W.; Belgacem, M.N.; Dufresne, A. Starch nanocrystals with large chain surface modifications. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4804–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, X.; Tong, C.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, A.; Cao, Y. Dialdehyde starch nanoparticles as antitumor drug delivery system: An in vitro, in vivo, and immunohistological evaluation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 3226–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Feky, G.S.; El-Rafie, M.H.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Hebeish, A.V. Utilization of crosslinked starch nanoparticles as a carrier for indomethacin and acyclovir drugs. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lan, Y. Preparation and Drug-Loading Properties of Amphoteric Cassava Starch Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, O.P.; Torres, F.G. Non-conventional starch nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Med. Devices Sens. 2020, 3, 10111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, Q.; Castle, L.; Watkins, R. Nanotechnologies in Food; Royal Society of Chemistry Publishers Cambridge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, Q.; Scotter, M.; Blackburn, J.; Ross, B.; Boxall, A.; Castle, L.; Watkins, R. Applications and implications of nanotechnologies for the food sector. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 25, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.S.; Chinnan, M.S. Biopolymer-based antimicrobial packaging: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Coste, A.; Schaich, K.M.; Zumbrunnen, D.; Yam, K.L. Advancing controlled release packaging through smart blending. Packag. Technol. Sci. Int. J. 2005, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Takhistov, P.; McClements, D.J. Functional materials in food nanotechnology. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristo, E.; Biliaderis, C.G. Physical properties of starch nanocrystal-reinforced pullulan films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumit, G. Nanotechnology in food packaging a critical review. Russ. J. Agric. Socio-Econ. Sci. 2012, 10, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Physicochemical properties of starch nanocomposite films enhanced by self-assembled potato starch nanoparticles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanin, M.; Al Abboud, M.A.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Hashem, A.H. Ecofriendly synthesis of biosynthesized copper nanoparticles with starch-based nanocomposite: Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer activities. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanin, M.S. Simple, Economic, Ecofriendly Method to Extract Starch Nanoparticles from Potato Peel Waste for Biological Applications. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Thory, R.; Sinhmar, A.; Pathera, A.K.; Nain, V. Development and characterization of nano starch-based composite films from mung bean (Vigna radiata). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, P.; Sinhmar, A.; Sharma, S.; Dufresne, A.; Thory, R.; Kaur, M.; Nain, V. Nanocomposite Starch Films: A New Approach for Biodegradable Packaging Materials. Starch-Stärke 2022, 74, 2100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Sarfaraz, S.; Sikandar, S.; Raza, A. Use of Nano-Sized Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2022, 13, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Alila, S.; Aloulou, F.; Thielemans, W.; Boufi, S. Sorption potential of modified nanocrystals for the removal of aromatic organic pollutant from aqueous solution. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, J.M.; Chien, Y.W. Competitive adsorption of benzoic acid and p-nitrophenol onto activated carbon: Isotherm and breakthrough curves. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, P.T.; Jones, G.J.; Hamilton, G.R. Removal of saxitoxins from drinking water by granular activated carbon, ozone and hydrogen peroxide-implications for compliance with the Australian drinking water guidelines. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4455–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, G.; Heath, L.; Thielemans, W. Cellulose nanocrystals grafted with polystyrene chains through surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP). Langmuir 2009, 25, 8280–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Sadegh, H.; Ghoshekandi, R.S.; Makhlouf, A.H. Nanoparticles as adsorbent; a positive approach for removal of noxious metal ions: A review. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2017, 34, 195–214. [Google Scholar]
- Younas, F.; Mustafa, A.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Wang, X.; Younas, S.; Mohy-Ud-Din, W.; Hussain, M.M. Current and emerging adsorbent technologies for wastewater treatment: Trends, limitations, and environmental implications. Water 2021, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, E.S.; Owda, M.; Mousa, R.Y. A novel starch nanoparticle citrate based adsorbent for removing of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 2075–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, M.; Stenius, P. Water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by hydrophobized microfibrillated cellulose. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2007, 28, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaj, S.B.; Magnin, A.; Boufi, S. Starch nanoparticles produced via ultrasonication as a sustainable stabilizer in Pickering emulsion polymerization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42638–42646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.B.; Kim, J.Y. Application of starch nanoparticles as a stabilizer for Pickering emulsions: Effect of environmental factors and approach for enhancing its storage stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamwilaisak, K.; Rittiwut, K.; Jutakridsada, P.; Iamamorphanth, W.; Pimsawat, N.; Knijnenburg, J.T.; Theerakulpisut, S. Rheology, stability, antioxidant properties, and curcumin release of oil-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by rice starch nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Preparation Methods | Sources | Morphology | Size (nm) | Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonication | Maize starch | platelet or granular | 30 to 100 | ≈100 | [57] |
| Acid hydrolysis and ultrasound | Maize starch | Globular shapes | 50 to 90 | 78 | [58] |
| Nanoprecipitation | Maize starch | Spherical | 135 to 155 | ND | [60] |
| Acid hydrolysis | Corn starch | Nanoplatelets | 107 | ND | [55] |
| Milling | Maize starch | Gel-like | 245 | ND | [59] |
| Enzymolysis | Maize starch | Irregular | 2.4 to 6.7 | 29.8 | [56] |
| Ultrasonication | Maize starch | platelet | 40 nm | - | [62] |
| Homogenization | Maize starch | Smaller starch Granules, pores | 540 | ND | [40] |
| Enzymolysis | Maize starch | Spherical | 162 ± 23, 301 | 18 | [63] |
| Acid hydrolysis and ultrasound | Maize starch | spherical and ellipsoidal | 20–250 | [64] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, N.A.; Darwesh, O.M.; Smuda, S.S.; Altemimi, A.B.; Hu, A.; Cacciola, F.; Haoujar, I.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G. Recent Trends in the Preparation of Nano-Starch Particles. Molecules 2022, 27, 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175497
Hassan NA, Darwesh OM, Smuda SS, Altemimi AB, Hu A, Cacciola F, Haoujar I, Abedelmaksoud TG. Recent Trends in the Preparation of Nano-Starch Particles. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175497
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Nora Ali, Osama M. Darwesh, Sayed Saad Smuda, Ammar B. Altemimi, Aijun Hu, Francesco Cacciola, Imane Haoujar, and Tarek Gamal Abedelmaksoud. 2022. "Recent Trends in the Preparation of Nano-Starch Particles" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175497
APA StyleHassan, N. A., Darwesh, O. M., Smuda, S. S., Altemimi, A. B., Hu, A., Cacciola, F., Haoujar, I., & Abedelmaksoud, T. G. (2022). Recent Trends in the Preparation of Nano-Starch Particles. Molecules, 27(17), 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175497









