Chronic Treatment with Melatonin Improves Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Aged Brain and Under Neurodegeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Markers of Neurodegeneration in SAMP8 Mice
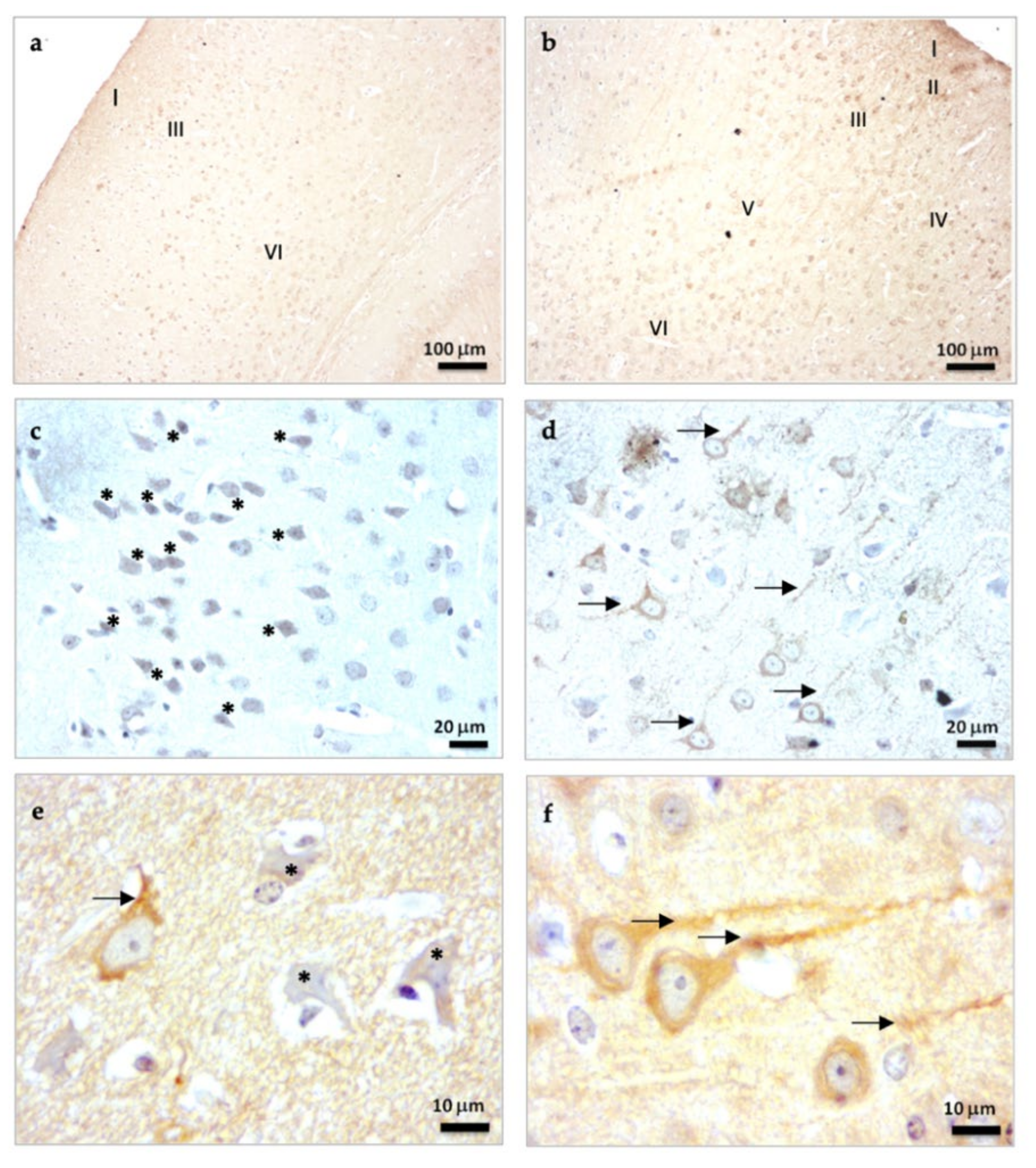
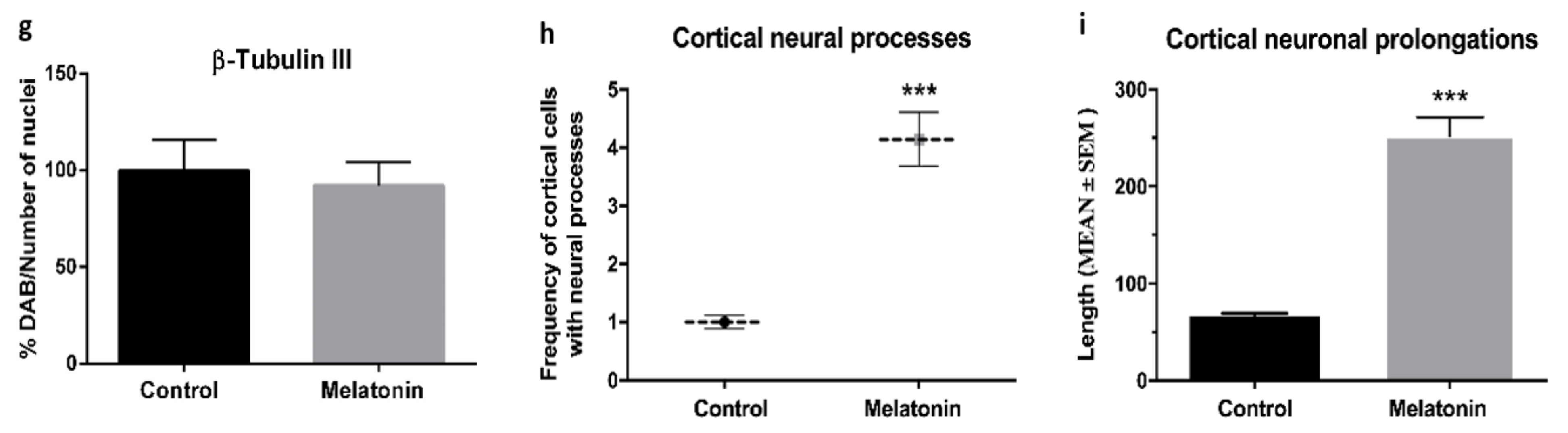
2.1.1. β-Tubulin III Immunostaining in the Brain Cortex of SAMP8 Mice
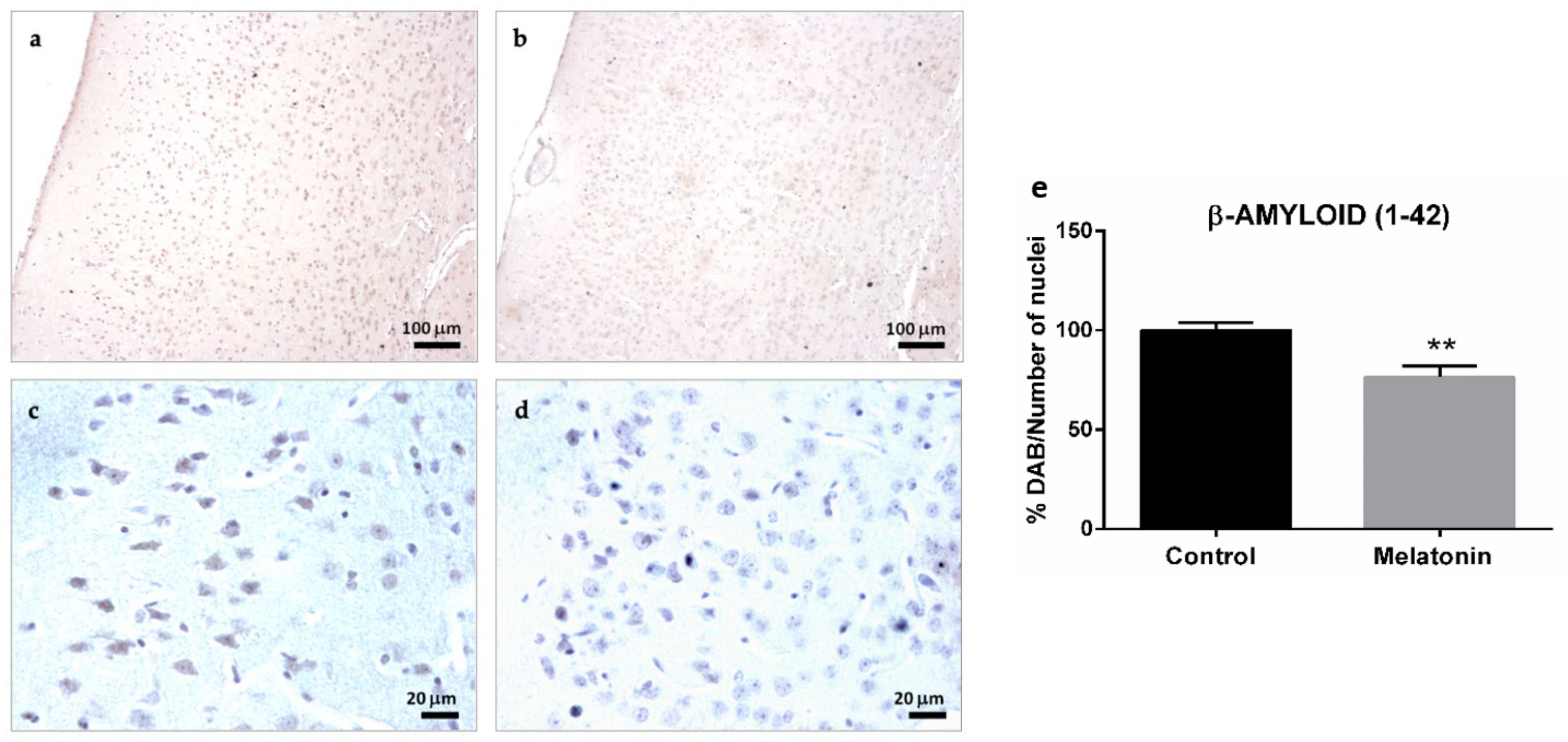
2.1.2. β-Amyloid (1-42) Immunostaining in the Brain Cortex of SAMP8 Mice
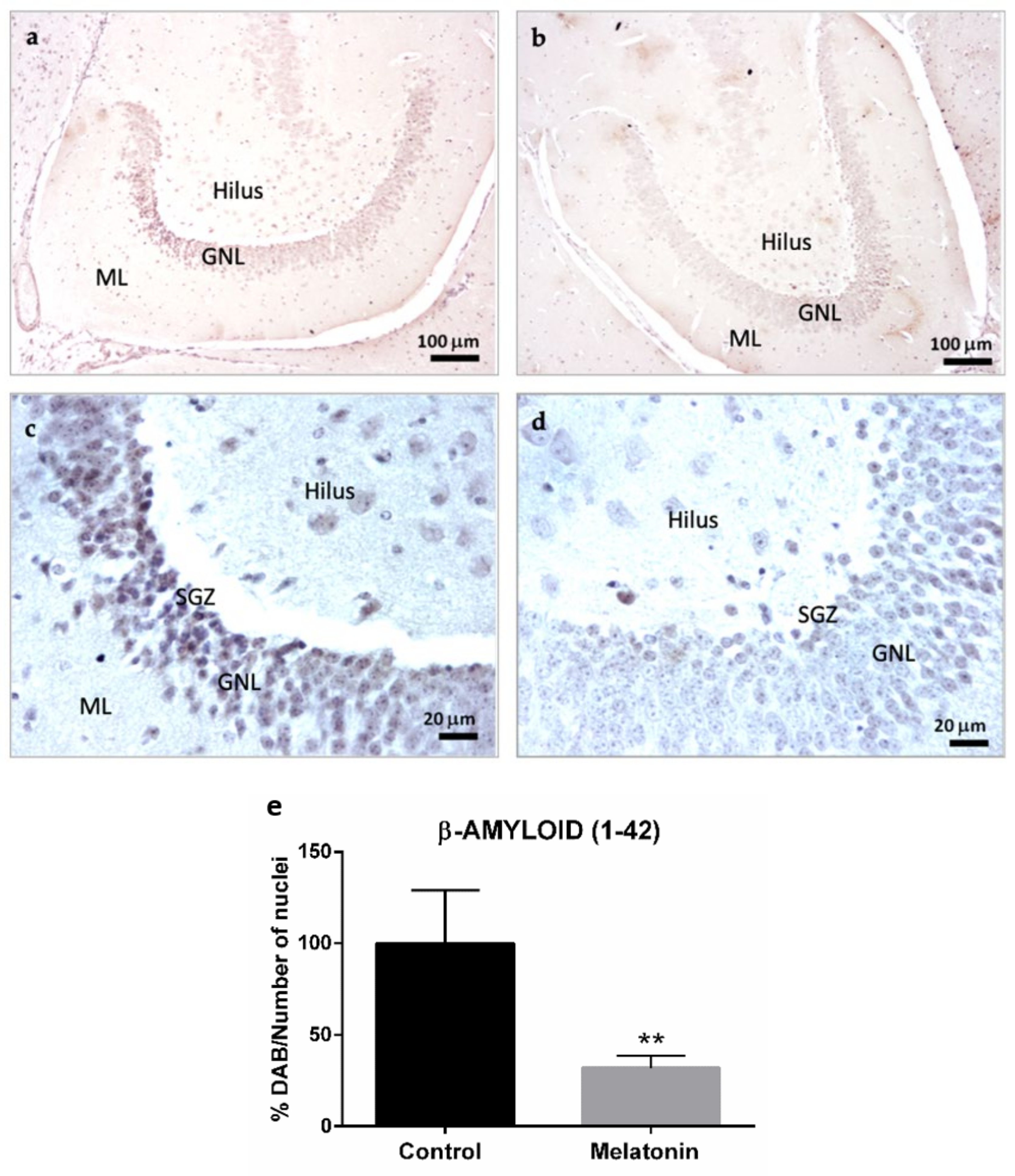
2.1.3. β-Amyloid (1-42) Immunostaining in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of SAMP8 Mice
2.2. Markers of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in SAMP8 Mice
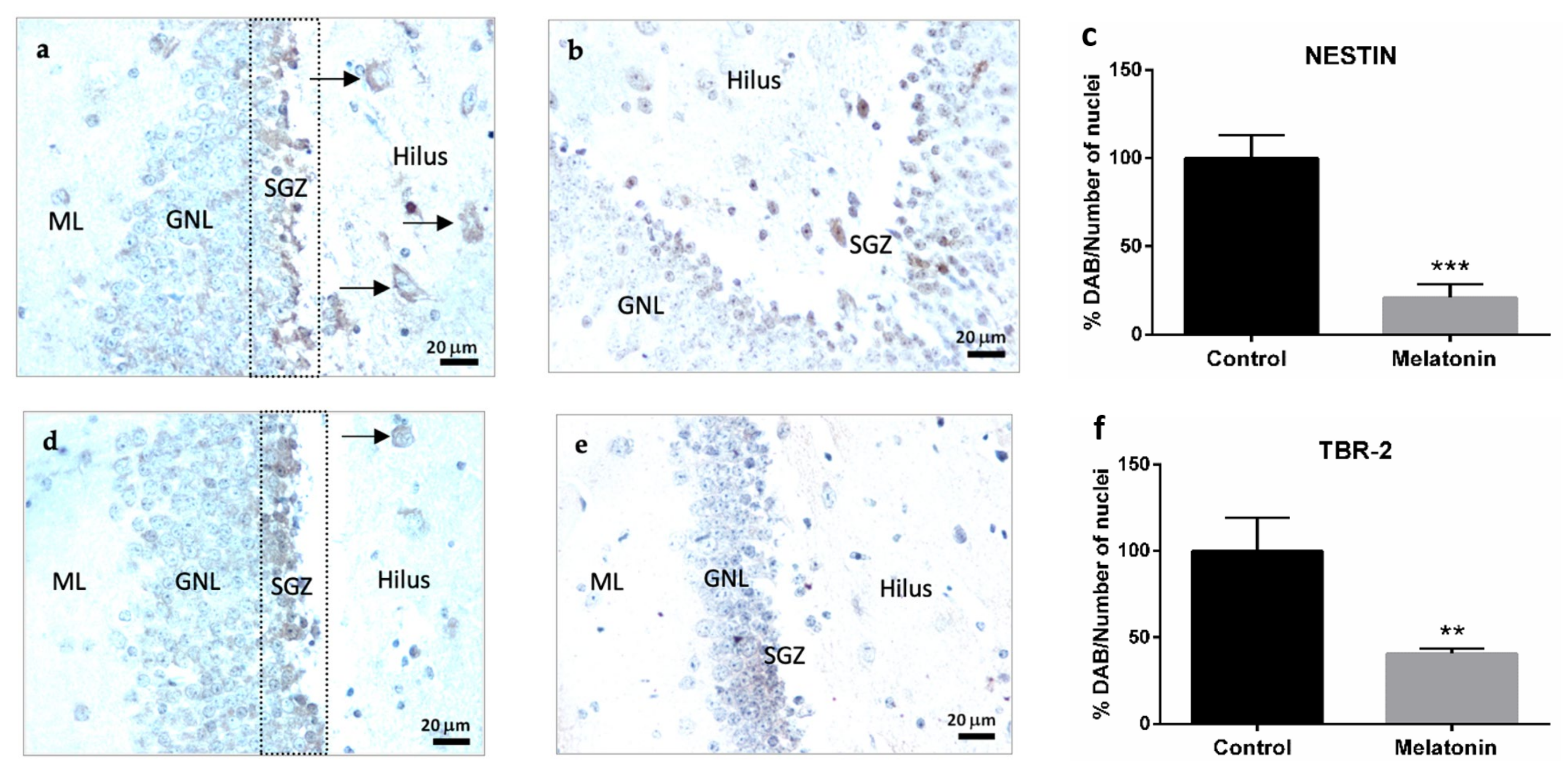
2.2.1. Nestin Immunostaining in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of SAMP8 Mice
2.2.2. TBR-2 Immunostaining in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of SAMP8 Mice
2.2.3. NeuroD1 Immunostaining in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of SAMP8 Mice
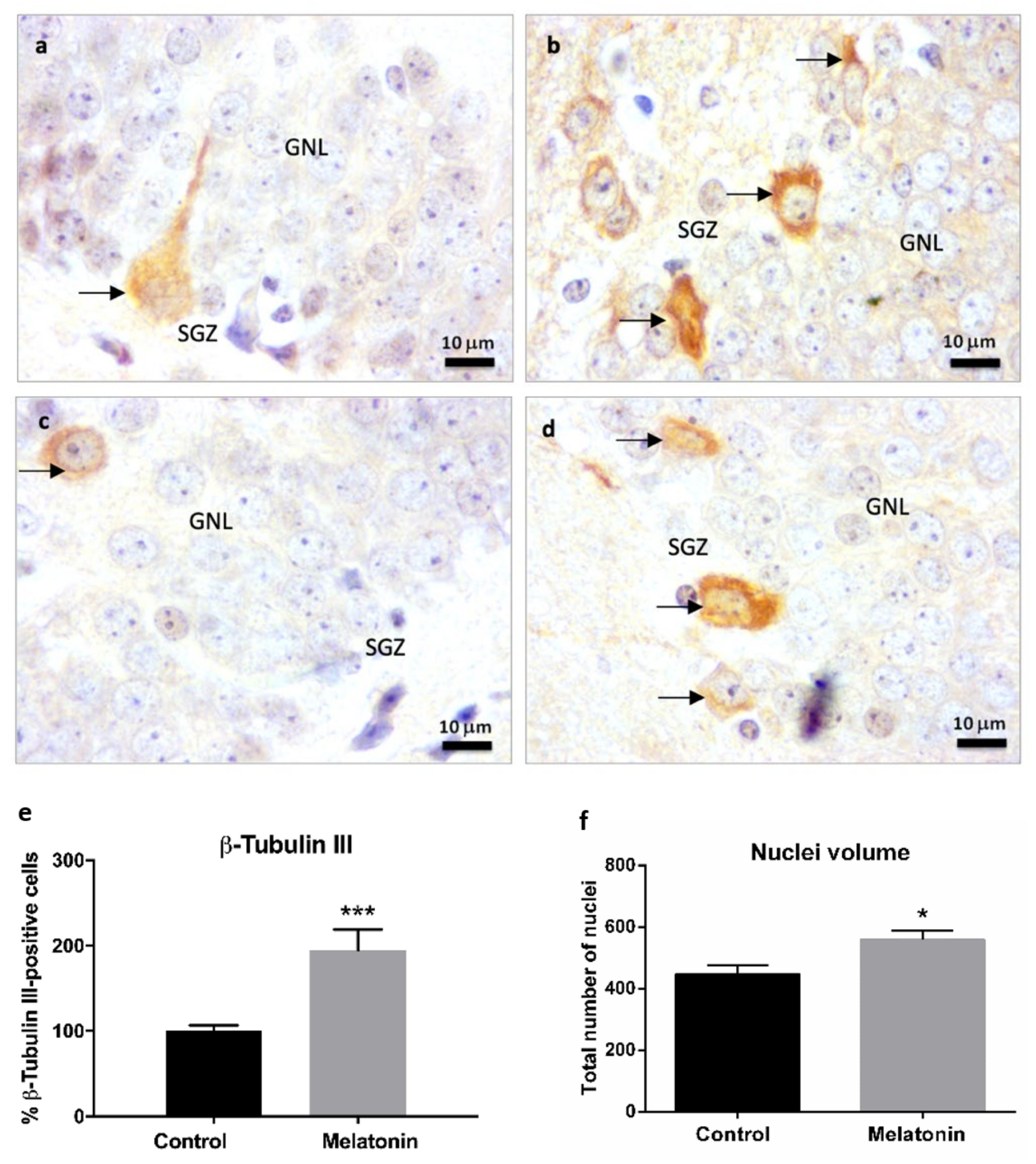
2.2.4. β-Tubulin III Immunostaining in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of SAMP8 Mice
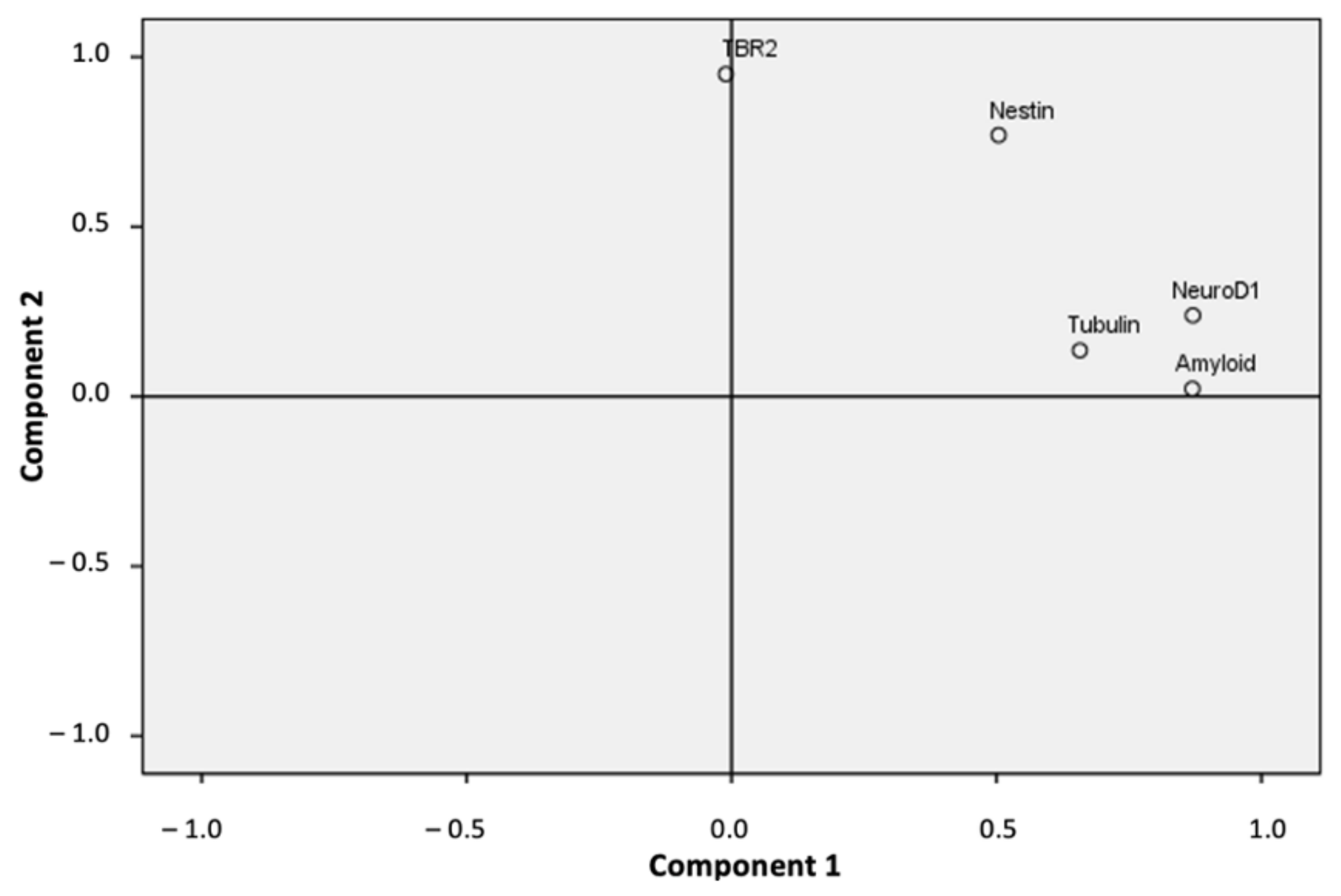
2.3. Principal Component Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Treatment
4.3. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
4.4. Image Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Abbott, L.C.; Nigussie, F. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian dentate gyrus. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2020, 49, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, C.G. Neurogenesis in the adult brain: Death of a dogma. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 1, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Toda, T.; Gage, F.H. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: A Coming-of-Age Story. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10401–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto-Oliveira, M.; Arrifano, G.P.F.; Malva, O.J.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Different Taxonomic Groups: Possible Functional Similarities and Striking Controversies. Cells 2019, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.K.; Musaraca, K.; Disouky, A.; Shetti, A.; Bheri, A.; Honer, W.G.; Kim, N.; Dawe, R.J.; Bennett, D.A.; Arfanakis, K.; et al. Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Persists in Aged Adults and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 974–982.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jimenez, E.P.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Flor-García, M.; Rábano, A.; Lorens-Martín, M. Evidences for Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Humans. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiao, J. Molecular Biomarkers for Embryonic and Adult Neural Stem Cell and Neurogenesis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 727542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.W.H.; Cheung, K.K.; Ngai, S.P.C.H.; Tsang, H.W.H.; Lau, B.W.M. Protective Effects of Melatonin on Neurogenesis Impairment in Neurological Disorders and Its Relevant Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disouky, A.; Lazarov, O. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 177, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Klempin, F.; Babu, H.; Benítez-King, G.; Kempermann, G. Melatonin modulates cell survival of new neurons in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2180–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Ortiz-Lopez, L.; Dominguez-Alonso, A.; Benitez-King, G.; Kempermann, G. Chronic treatment with melatonin stimulates dendrite maturation and complexity in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 50, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Alonso, A.; Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Benitez-King, G. Melatonin increases dendritogenesis in the hilus of hippocampal organotypic cultures. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresguerres, J.A.F.; Kireev, R.; Forman, K.; Cuesta, S.; Tresguerres, A.F.; Vara, E. Effect of chronic melatonin administration on several physiological parameters from old Wistar rats and SAMP8 mice. Curr. Aging Sci. 2012, 5, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Alonso, A.; Valdes-Tovar, M.; Solis-Chagoyán, H.; Benitez-King, G. Melatonin stimulates dendrite formation and complexity in the hilar zone of the rat hippocampus: Participation of the Ca++/Calmodulin complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1907–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Vega-Rivera, N.M.; Benitez-king, G.; Castro-Garcia, M.; Ortiz-Lopez, L. Melatonin supplementation delays the decline of adult hippocampal neurogenesis during normal aging of mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 530, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Vazquez, R.; Labastida-Lopez, C.; Romero-Castello, S.; Benitez-King, G.; Parra-Cervantes, P. Stimulation of dendrogenesis and neural maturation in adult mammals. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2016, 5, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennie, K.; De Butte, M.; Pappas, B.A. Melatonin promotes neurogenesis in dentate gyrus in the pinealectomized rat. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, B.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Sierra, V.; Huidobro-Fernandez, C.; Soria-Valles, C.; De Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Tolivia, D.; Gutierrez-Cuesta, J.; Pallas, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Favorable effects of a prolonged treatment with melatonin on the level of oxidative damage and neurodegeneration in senescence-accelerated mice. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 45, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, B.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Sierra, V.; Huidobro-Fernandez, C.; Soria-Valles, C.; De Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Tolivia, D.; Pallas, M.; Camins, A.; Rodriguez-Colunga, M.J.; et al. Melatonin alters cell death processes in response to age-related oxidative stress in the brain of senescence-accelerated mice. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Cuesta, J.; Sureda, F.X.; Romeu, M.; Canudas, A.M.; Caballero, B.; Coto-Montes, A.; Camins, A.; Pallas, M. Chronic administration of melatonin reduces cerebral injury biomarkers in SAMP8. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, J.A.; Caballero, B.; Potes, Y.; Perez-Martinez, Z.; Reiter, R.J.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Coto-Montes, A. Therapeutic potential of melatonin related to its role as an autophagy regulator: A review. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 66, e12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, M.; Kiyota, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Nagaoka, A.; Matsuo, T.; Nagawa, Y.; Takeda, T. Age-related changes in learning and memory in the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). Physiol. Behav. 1986, 38, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Kumar, V.B.; Bernardo, A.E.; Farr, S.A.; Uezu, K.; Tumosa, N.; Flood, J.F. Beta-amyloid precursor polypeptide in SAMP8 mice affects learning and memory. Peptides 2000, 21, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E. The SAMP8 mouse: A model of Alzheimer disease? Biogerontology 2002, 3, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, M.; Camins, A.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G.; Lee, H.-G.; Casadesus, G. From aging to Alzheimer’s disease: Unveiling “the switch” with the senescence-accelerated mouse model (SAMP8). J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 15, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Legido, A.; Perentes, E.; Mörk, S.J. Class III β-tubulin isotype: A key cytoskeletal protein at the crossroads of developmental neurobiology and tumor neuropathology. J. Child Neurol. 2003, 18, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Moreno, M.; Hortigüela, R.; Gonzalves, A.; Garcia-Carpio, I.; Manish, G.; Garcia-Bermudez, E.; Moreno-Estelles, M.; Eguiluz, C.; Vilaplana, J.; Pelegri, C.; et al. Aβ increases neural stem cell activity in senescence-accelerated SAMP8 mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 2623–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Vargas, J.A.; Castro-Alvarez, J.F.; Zapata-Berruecos, J.F.; Abdul-Rahim, K.; Arteaga-Noriega, A. Neurodegeneration and convergent factors contributing to the deterioration of the cytoskeleton in Alzheimer’s disease, cerebral ischemia and multiple sclerosis (Review). BioMed Rep. 2022, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okatani, Y.; Wakatsuki, A.; Reiter, R.J.; Miyahara, Y. Melatonin reduces oxidative damage of neural lipids and proteins in senescence-accelerated mouse. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.I.; Escames, G.; Lopez, L.C.; Lopez, A.; Garcia, J.A.; Ortiz, F.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Chronic melatonin treatment reduces the age-dependent inflammatory process in senescence-accelerated mice. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Cuesta, J.; Tajes, M.; Jimenez, A.; Coto-Montes, A.; Camins, A.; Pallas, M. Evaluation of potential pro-survival pathways regulated by melatonin in a murine senescence model. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 45, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.I.; Escames, G.; Lopez, L.C.; Lopez, A.; Garcia, J.A.; Ortiz, F.; Sanchez, V.; Romeu, M.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Improved mitochondrial function and increased life span after chronic melatonin treatment in senescent prone mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Ma, C.H.; Qu, H.; Fan, W.; Pang, J.; He, H. Differential effects of melatonin on hippocampal neurodegeneration in different aged accelerated senescence prone mouse-8. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 2008, 29, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carretero, M.; Escames, G.; Lopez, L.C.; Venegas, C.; Dayoub, J.C.; Garcia, L.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Long-term melatonin administration protects brain mitochondria from aging. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.J.; Piñol-Ripoll, G.; Martinez-Ballarin, E.; Fuentes-Broto, L.; Miana-Mena, F.J.; Venegas, C.; Caballero, B.; Escame, G.; Coto-Montes, A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin reduces membrane rigidity and oxidative damage in the brain of SAMP8 mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Cuesta, J.; Tajes, M.; Jimenez, A.; Camins, A.; Pallas, M. Effects of melatonin in the brain of the senescence-accelerated mice-prone 8 (SAMP8) model. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 52, 618–622. [Google Scholar]
- Cristofol, R.; Porquet, D.; Corpas, R.; Coto-Montes, A.; Serret, J.; Camins, A.; Pallas, M.; Sanfeliu, C. Neurons from senescence-accelerated SAMP8 mice are protected against frailty by the sirtuin 1 promoting agent melatonin and resveratrol. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlak, G.; Jenwitheesuk, A.; Chetsawang, B.; Govitrapong, P. Effects of melatonin on nervous system aging: Neurogenesis and neurodegeneration. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 123, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, R.D.; Kowalczyk, T.D.; Wolf, S.A.; Encinas, J.M.; Rippey, C.; Enikolopov, G.; Kempermann, G.; Hevner, R.F. Intermediate progenitors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Tbr2 expression and coordinate regulation of neuronal output. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3707–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Ocaña-Fernandez, M.A.; Vega-Rivera, N.M.; Torres-Perez, O.M.; Gomez-Sanchez, A.; Estrada-Camarena, E.; Ortiz-Lopez, L. Environmental enrichment induces neuroplastic changes in middle age female Balb/c mice and increases the hippocampal levels of BDNF, p-Akt and p-MAPK1/2. Neuroscience 2014, 260, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Tu, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, D.; Liu, X.; Pi, R. Effects of melatonin and its analogues on neural stem cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 420, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiro-Silva, J.; Antequera, D.; Pascual, C.; De la Fuente-Revenga, M.; Volt, H.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Rodriguez-Franco, M.I.; Carro, E. The Melatonin Analog IQM316 May Induce Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Preserve Recognition Memories in Mice. Cell Transpl. 2018, 27, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Gomez-Sanchez, A.; Ortiz-Lopez, L. Melatonin maintains calcium-binding calretinin-positive neurons in the dentate gyrus during aging of Balb/C mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.B.; Olvera-Hernandez, S.; Vega-Rivera, N.M.; Ortiz-Lopez, L. Melatonin Influences Structural Plasticity in the Axons of Granule Cells in the Dentate Gyrus of Balb/C Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, B.; Yue, C.; Xue, H.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q. Limited hippocampal neurogenesis in SAMP8 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2011, 1389, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Moreno, M.; Armenteros, T.; Gradari, S.; Hortigüela, R.; Garcia-Corzo, L.; Fontan-Lozano, A.; Trejo, J.L.; Mira, H. Noggin rescues age-related stem cell loss in the brain of senescent mice with neurodegenerative pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11625–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wen, S.-R.; Zhang, G.-W.; Wang, T.-G.; Hu, F.-X.; Li, X.-L.; Wang, D.-S. Effects of Chinese herbal medicine Fuzhisan on autologous neural stem cells in the brain of SAMP-8 mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tian, N.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Li, S.-H.; Zhou, Q.-Z.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.-Z. GSK-3β activation accelerates early-stage consumption of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in senescent mice. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9674–9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, H.-L.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Yin, Y.; Yue, L.; Ma, L.; Wan, Y.; Wang, J.-Z. Interneuron Accumulation of Phosphorylated tau Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis by Suppressing GABAergic Transmission. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 331–345.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, H.; Murano, Y.; Ohira, K.; Miwa, M.; Nakamura, K.; Miyakawa, T. Expression of progenitor cell/immature neuron markers does not present definitive evidence for adult neurogenesis. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, J.-C.; Han, J.-L.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, W. Different effects of mild and severe seizures on hippocampal neurogenesis in adult rats. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, A.R.; Yue, W. Semi-quantitative Determination of Protein Expression Using Immunohistochemistry Staining and Analysis: An Integrated Protocol. Bio-Protoc. 2019, 9, e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, B.; Rubio-Gonzalez, A.; Potes, Y.; Martinez-Reig, M.; Sanchez-Jurado, P.M.; Romero, L.; Solano, J.J.; Abizanda, P.; Coto-Montes, A. Associations of the antioxidant capacity and hemoglobin levels with functional physical performance of the upper and lower body limbs. Age 2014, 36, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Component 1 | Component 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| β-Amyloid (1-42) | 0.870 | 0.023 |
| Nestin | 0.504 | 0.770 |
| TBR-2 | −0.011 | 0.949 |
| NeuroD1 | 0.871 | 0.239 |
| β-Tubulin III | 0.657 | 0.136 |
| β-Amyloid (1-42) | Nestin | TBR-2 | NeuroD1 | β-Tubulin III | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation * | β-Amyloid (1-42) | 1 | 0.396 | 0.098 | 0.707 | 0.374 |
| Nestin | 0.396 | 1 | 0.607 | 0.635 | 0.379 | |
| TBR-2 | 0.098 | 0.607 | 1 | 0.188 | 0.140 | |
| NeuroD1 | 0.707 | 0.635 | 0.188 | 1 | 0.424 | |
| β-Tubulin III | 0.374 | 0.379 | 0.140 | 0.424 | 1 | |
| p-values * | β-Amyloid (1-42) | - | 0.034 | 0.333 | 0.000 | 0.043 |
| Nestin | 0.043 | - | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.041 | |
| TBR-2 | 0.333 | 0.001 | - | 0.201 | 0.268 | |
| NeuroD1 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.201 | - | 0.025 | |
| β-Tubulin III | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.268 | 0.025 | - |
| Name | Code | Company |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-β-Tubulin III (TUBB3) | T2200 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| β-Amyloid (1-42) (D9A3A) | #14974 | Cell Signaling |
| Anti-Nestin | N5413 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Anti-TBR-2 | #ABN1687 | Millipore |
| Anti-NeuroD1 | #ABE991 | Millipore |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cachán-Vega, C.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Potes, Y.; Bermejo-Millo, J.C.; Rubio-González, A.; García-González, C.; Antuña, E.; Bermúdez, M.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, J.; Boga, J.A.; et al. Chronic Treatment with Melatonin Improves Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Aged Brain and Under Neurodegeneration. Molecules 2022, 27, 5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175543
Cachán-Vega C, Vega-Naredo I, Potes Y, Bermejo-Millo JC, Rubio-González A, García-González C, Antuña E, Bermúdez M, Gutiérrez-Rodríguez J, Boga JA, et al. Chronic Treatment with Melatonin Improves Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Aged Brain and Under Neurodegeneration. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175543
Chicago/Turabian StyleCachán-Vega, Cristina, Ignacio Vega-Naredo, Yaiza Potes, Juan Carlos Bermejo-Millo, Adrian Rubio-González, Claudia García-González, Eduardo Antuña, Manuel Bermúdez, José Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, José Antonio Boga, and et al. 2022. "Chronic Treatment with Melatonin Improves Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Aged Brain and Under Neurodegeneration" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175543
APA StyleCachán-Vega, C., Vega-Naredo, I., Potes, Y., Bermejo-Millo, J. C., Rubio-González, A., García-González, C., Antuña, E., Bermúdez, M., Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, J., Boga, J. A., Coto-Montes, A., & Caballero, B. (2022). Chronic Treatment with Melatonin Improves Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Aged Brain and Under Neurodegeneration. Molecules, 27(17), 5543. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175543








