Influence of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Antioxidative Potential of Basil Varieties (Ocimum basilicum L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
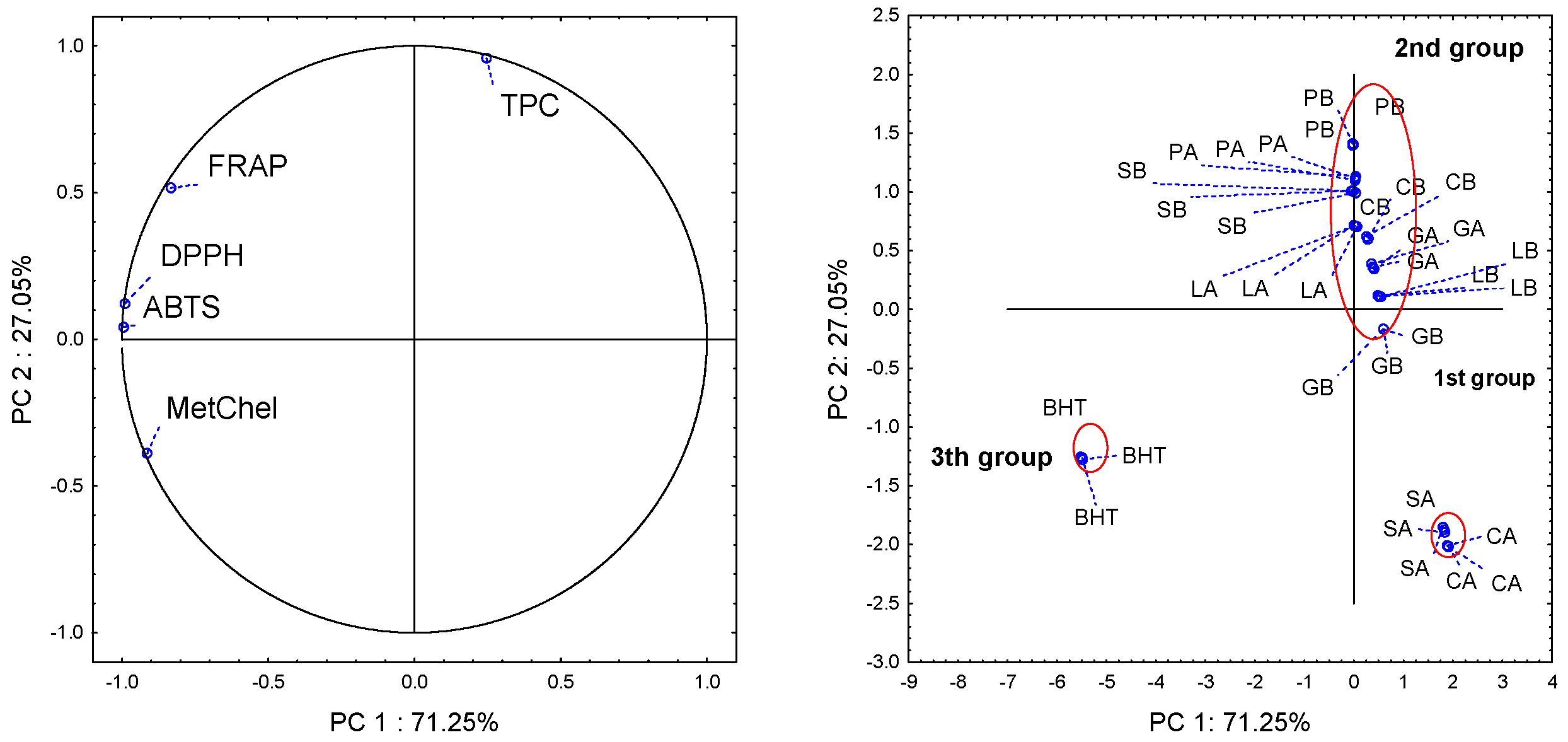
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tungmunnithum, D.; Thongboonyou, A.; Pholboon, A.; Yangsabai, A. Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants for Pharmaceutical and Medical Aspects: An Overview. Medicines 2018, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczak, N. Phenolic Compounds in Dried Herbs and Spices Commonly Used in The Kitchen. J. Educ. Health Sport 2018, 8, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Kong, L.Q.; Yee, K.Y.; Chua, W.Y.; Loo, T.Y. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Some Fresh and Dried Labiatae Herbs. Free Radic. Antioxid. 2012, 2, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, S. Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) a Source of Valuable Phytonutrients. Int. J. Clin. Nutr. Diet 2017, 3, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurav, T.P.; Jayaramaiah, R.H.; Punekar, S.A.; Dholakia, B.B.; Giri, A.P. Generation of Novelties in the Genus Ocimum as a Result of Natural Hybridization: A Morphological, Genetical and Chemical Appraisal. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 156, 112859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdina, I.; Priss, O. Effect of the Substrate Composition on Yield and Quality of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J. Hortic. Res. 2016, 24, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajomo, E.M.; Aing, M.S.; Ford, L.S.; Niemeyer, E.D. Chemotyping of Commercially Available Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Varieties: Cultivar and Morphotype Influence Phenolic Acid Composition and Antioxidant Properties. NFS J. 2022, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Chaudhuri, P.K. A Review on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Holy Basil (Ocimum sanctum L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.-S.; Shin, H.-S. Selected Commercial Plants: A Review of Extraction and Isolation of Bioactive Compounds and Their Pharmacological Market Value. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 82, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Monroe, A.; Day, M.R. Growth, Yield, Plant Quality and Nutrition of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) under Soilless Agricultural Systems. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, S.K.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M.; Stepulak, A. The biological and pharmacological activity of essential oils in the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases. Postępy Hig. Med. Dośw. 2013, 67, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil of Ocimum Basilicum L. (Sweet Basil) from Western Ghats of North West Karnataka, India. Ancient Sci. Life 2014, 33, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, A.S.; Antić, M.P.; Jelačić, S.C.; Šolević Knudsen, T.M. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils of Three Ocimum basilicum L. Cultivars from Serbia. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2018, 47, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokelmann, J.M. Holy Basil/Tulsi (Ocimum tenuiflorum/Sanctum). In Medicinal Herbs in Primary Care; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 437–440. ISBN 978-0-323-84676-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nurzyńska-Wierdak, R. Sweet Basil Essential Oil Composition: Relationship between Cultivar, Foliar Feeding with Nitrogen and Oil Content. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012, 24, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Dai, J.; Zhang, D. Addition of Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) in Tris-Based Extender Improves Post-Thaw Quality and Motion Dynamics of Dog Spermatozoa. Cryobiology 2020, 97, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtkunz, C.; Küpper, K.; Weber, T.; Leng, G.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. A Biomonitoring Study Assessing the Exposure of Young German Adults to Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 228, 113541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, J.; Veiga, J.; Karmali, A.; Nicolai, M.; Pinto Reis, C.; Nobre, B.; Palavra, A. Supercritical CO2 Extracts and Volatile Oil of Basil (Ocimum Basilicum L.) Comparison with Conventional Methods. Separations 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatian, M.; Peyvast, G.; Olfati, J.A.; Ramezani-Kharazi, P. Different Species of Basil Need Different Ammonium to Nitrate Ratio in Hydroponics’ System. Acta Agric. Slov. 2014, 103, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimler, D.; Romani, A.; Ieri, F. Plant Polyphenol Content, Soil Fertilization and Agricultural Management: A Review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.M.; Niemeyer, E.D. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilization on the Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8685–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinsi, B.; Negrini, N.; Morgutti, S.; Espen, L. Nitrogen Starvation and Nitrate or Ammonium Availability Differently Affect Phenolic Composition in Green and Purple Basil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.R.O.; Fernandes, Â.; Di Gioia, F.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Polyzos, N.; Dias, M.I.; Pinela, J.; Kostić, M.; Soković, M.D.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; et al. The Effect of Nitrogen Input on Chemical Profile and Bioactive Properties of Green- and Red-Colored Basil Cultivars. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, D.S.; Sundus, H.A.; Anaam, M.A.; Shatha, Z.S.; Nuha, N. Determination of Total Phenol, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Avena Sativa and Ocimum basilicum. Baghdad. Sci. J. 2014, 11, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, F.; Carović-Stanko, K.; Ristić, M.; Grdiša, M.; Liber, Z.; Šatović, Z. Morphological and Biochemical Intraspecific Characterization of Ocimum Basilicum L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Brunton, N.P. Effect of Drying Method on the Antioxidant Capacity of Six Lamiaceae Herbs. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cultivar | TPC (mg GADE/g.d.m) | DPPH (mg Trolox/g d.m.) | ABTS (mg Trolox/g d.m.) | FRAP (mmol Fe2+/L) | Metal Chelating (mg EDTA/g d.m.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | ||||||||||
| A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | |
| green leaf basil | ||||||||||
| Sweet | 26.75 a | 129.59 e | 33.94 a | 189.85 g | 2.16 a | 11.29 de | 4.35 a | 27.67 g | 23.80 f | 6.14 b |
| Greek | 102.56 e | 80.45 b | 153.02 d | 123.10 b | 9.39 c | 9.35 c | 23.42 cd | 20.00 b | 4.83 a | 5.80 ab |
| Cinnamon | 20.34 a | 112.02 d | 26.61 a | 161.47 e | 2.26 a | 9.36 c | 3.09 a | 25.47 e | 19.49 e | 6.36 b |
| Lemon | 108.92 d | 90.33 c | 158.44 de | 131.66 c | 10.65 d | 8.44 b | 29.50 g | 22.89 c | 7.64 c | 6.47 a |
| red leaf basil | ||||||||||
| Purple | 141.35 f | 165.44 g | 175.94 f | 192.17 g | 11.91 e | 13.40 f | 26.81 f | 24.52 de | 14.19 d | 19.49 e |
| BHT | 493.11 h | 36.45 g | 42.45 g | 260.72 g | ||||||
| Cultivar | Fertilization | |
| Sweet Basil (Ocimum basilicum) | NH4NO3 (variant A) | (NH4)2SO4 (variant B) |
| Greek Basil (Ocimum basilicum minimum) | ||
| Cinnamon Basil (Ocimum basilicum cinnamon) | ||
| Lemon Basil (Ocimum basilicum citriodora) | ||
| Purple Basil (Ocimum basilicum purpurescens) | ||
| Development phases | ||
| Sowing | 8 May 2017 | |
| Emerging | 17 May 2017 | |
| Harvest date | 17 July 2017 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hęś, M.; Golcz, A.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Jędrusek-Golińska, A.; Dziedzic, K.; Mildner-Szkudlarz, S. Influence of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Antioxidative Potential of Basil Varieties (Ocimum basilicum L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 5636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175636
Hęś M, Golcz A, Gramza-Michałowska A, Jędrusek-Golińska A, Dziedzic K, Mildner-Szkudlarz S. Influence of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Antioxidative Potential of Basil Varieties (Ocimum basilicum L.). Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175636
Chicago/Turabian StyleHęś, Marzanna, Anna Golcz, Anna Gramza-Michałowska, Anna Jędrusek-Golińska, Krzysztof Dziedzic, and Sylwia Mildner-Szkudlarz. 2022. "Influence of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Antioxidative Potential of Basil Varieties (Ocimum basilicum L.)" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175636
APA StyleHęś, M., Golcz, A., Gramza-Michałowska, A., Jędrusek-Golińska, A., Dziedzic, K., & Mildner-Szkudlarz, S. (2022). Influence of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Antioxidative Potential of Basil Varieties (Ocimum basilicum L.). Molecules, 27(17), 5636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175636








