Exploration of the Interrelationship within Biomass Pyrolysis Liquid Composition Based on Multivariate Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
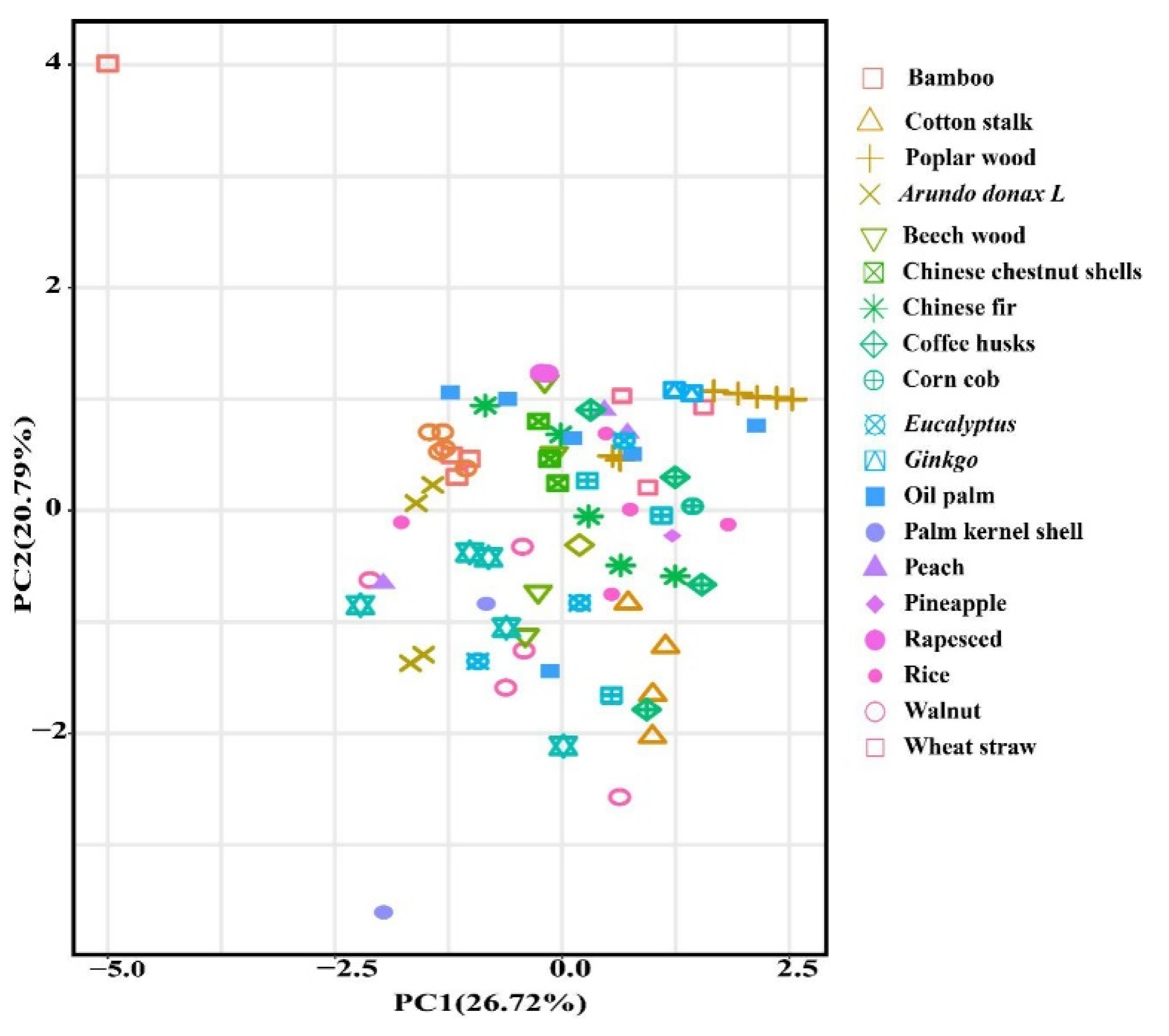
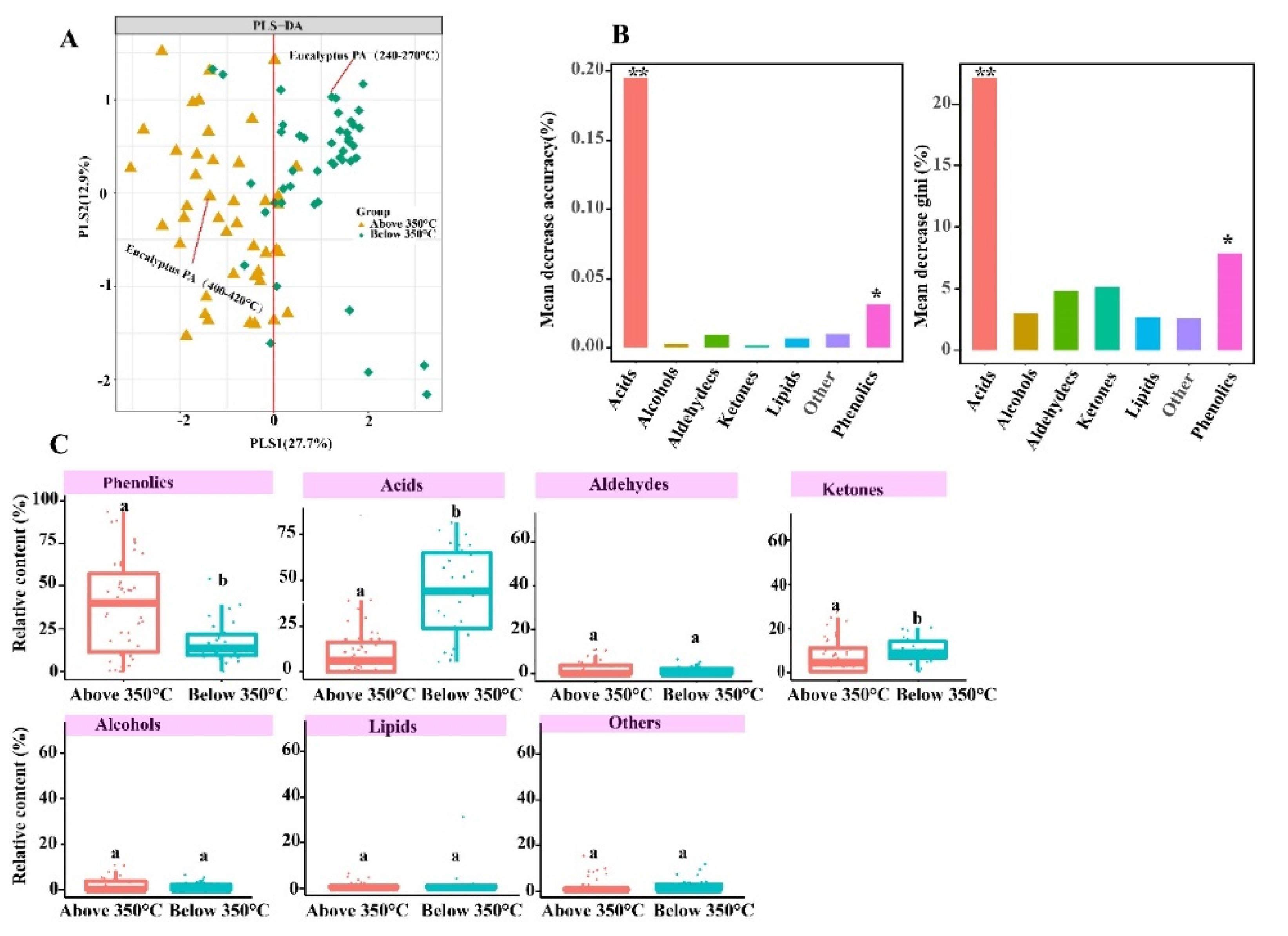
2.1. Effect of the Feedstock on PA Components
2.2. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperatures on PA Components
2.3. PA Compounds Generated during Pyrolysis
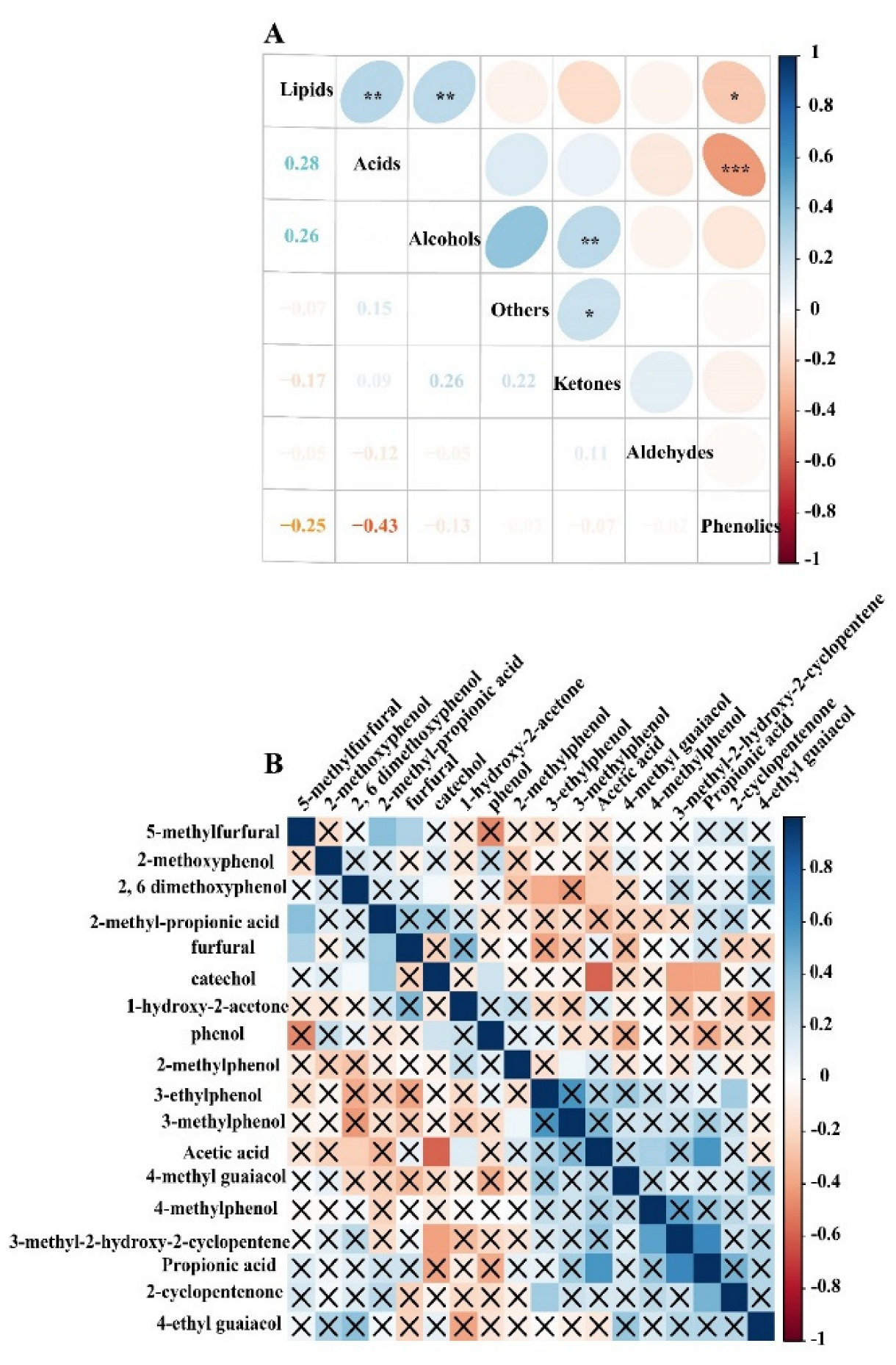
2.4. Correlation Relationship of PA Compositions
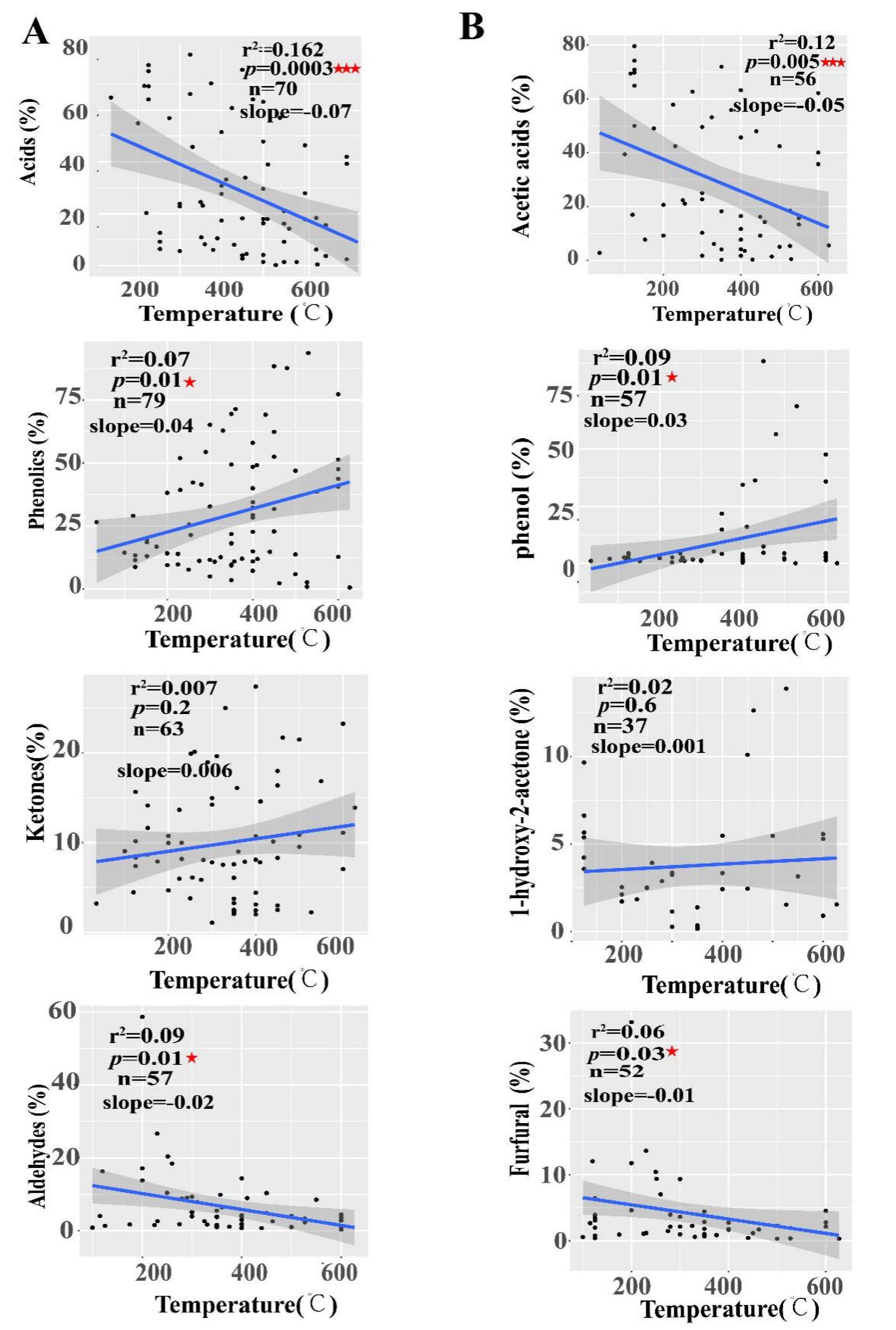
2.5. Linear Relationship between PA Compositions and Pyrolysis Temperatures
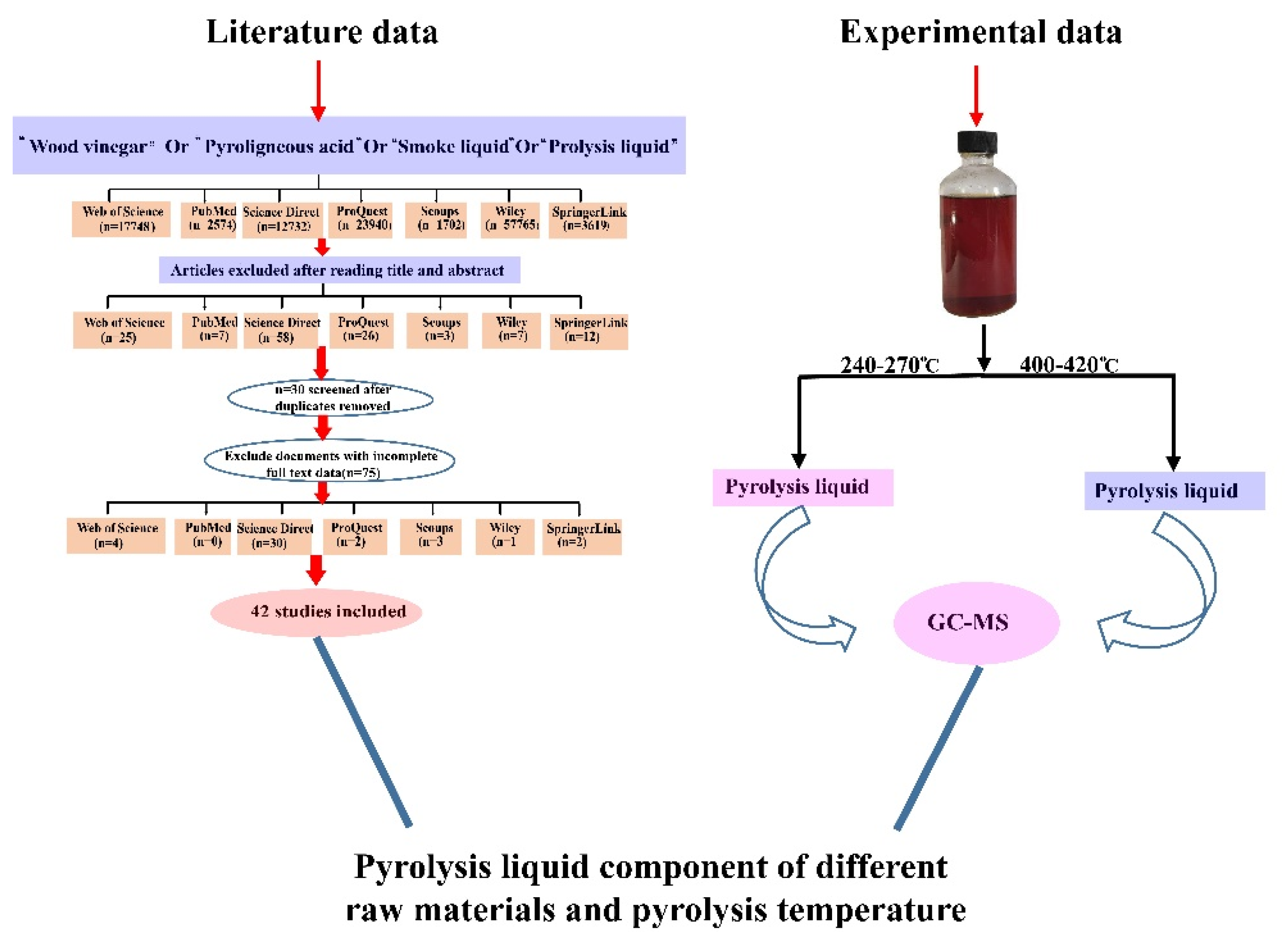
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Data Processing
3.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
3.3.2. Random Forest Model
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Lyu, J. Effect of hydrothermal treatment on biomass structure with evaluation of post-pyrolysis process for wood vinegar preparation. Fuel 2021, 305, 121513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Gu, S.; Bridgwater, A. Study on the pyrolytic behaviour of xylan-based hemicellulose using TG–FTIR and Py–GC–FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2010, 87, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Huang, Q.; Jin, F.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Separation of high added-value chemical compositions derived from biomass pyrolysis liquid via sequential multi-step pH adjustment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 230, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, J.; Mašek, O.; Wang, L.; et al. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the characterisation of dissolved organic matter from pyrolysis liquid. Molecules 2021, 26, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Yan, B.; Chen, G.; Cheng, Z.; Li, W.; Lin, F.; Hou, L. Multi-step separation of different chemical groups from the heavy fraction in biomass fast pyrolysis oil. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 202, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shao, J.; Yang, H.; Guo, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H. Effects of biomass pyrolysis derived wood vinegar on microbial activity and communities of activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, L.; Yao, Y.; Sun, G.; Guo, X. Anaerobic digestion of swine manure using aqueous pyrolysis liquid as an additive. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hu, S.; Kang, K.; Li, X.; Geng, Z.; Zhu, M. The effects of pyrolysis temperature and storage time on the compositions and properties of the pyroligneous acids generated from cotton stalk based on a polygeneration process. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 161, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, M.; Hu, Y. High-temperature CO2 capture by Li4SiO4 adsorbents: Effects of pyroligneous acid (PA) modification and existence of CO2 at desorption stage. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 197, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Sun, C.; Hou, X.; Wu, M.; Yao, Y.; Li, F. Pyrolysis of Arundo donax L. to produce pyrolytic vinegar and its effect on the growth of dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 247, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, X.; Dong, J. Preparation, chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of pyroligneous acids from walnut tree branches. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2010, 87, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, K.; Barwicki, J.; Hryniewicz, M.; Szadkowska, D.; Szadkowski, J. Production of electricity and heat from biomass wastes using a converted aircraft turbine AI-20. Processes 2021, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Characterization of five kinds of wood vinegar obtained from agricultural and forestry wastes and identification of major antioxidants in wood vinegar. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 35, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Preparation and characterization of two wood vinegars obtained from hull of spina date seed and shell of peanut. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2017, 33, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, L.; Xu, H.; Mu, X.; Wang, H. Multivariate data analysis applied in alkali-based pretreatment of corn stover. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wei, H.; Himmel, M.E.; Jameel, H.; Kelley, S.S. NIR and Py-mbms coupled with multivariate data analysis as a high-throughput biomass characterization technique: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, C.E.; Wolfrum, E.J. Rapid analysis of composition and reactivity in cellulosic biomass feedstocks with near-infrared spectroscopy. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Zakaria, Z. Pyroligneous acid—The smoky acidic liquid from plant biomass. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, H.; Lyu, J. Study on an alternative approach for the preparation of wood vinegar from the hydrothermolysis process of cotton stalk. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jiang, J.; He, J.; Sun, K.; Sun, Y. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the characteristics of wood vinegar derived from Chinese fir waste: A comprehensive study on its growth regulation performance and mechanism. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19054–19062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ningbo, G.; Baoling, L.; Aimin, L.; Juanjuan, L. Continuous pyrolysis of pine sawdust at different pyrolysis temperatures and solid residence times. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2015, 14, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Hou, B.; Zheng, H.; Deng, W.; Liu, D.; Tang, W. Study on the preparation of wood vinegar from biomass residues by carbonization process. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Ong, H.; Show, P.; Hsieh, T. Torrefaction, pyrolysis and two-stage thermodegradation of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin. Fuel 2019, 258, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H. Fates of chemical elements in biomass during its pyrolysis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6367–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Gao, C.; Xu, P. Efficient utilization of hemicellulose hydrolysate for propionic acid production using Propionibacterium acidipropionici. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Zhou, Z.; Kishita, A.; Enomoto, H.; Kishida, H.; Moriya, T. A new hydrothermal process for producing acetic acid from biomass waste. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2007, 85, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ru, B.; Lin, H.; Sun, W.; Luo, Z. Pyrolysis behaviors of four lignin polymers isolated from the same pine wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakzeski, J.; Bruijnincx, P.; Jongerius, A.; Weckhuysen, B. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmadi, M.; Kawamoto, H.; Saka, S. Thermal reactions of guaiacol and syringol as lignin model aromatic nuclei. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2011, 92, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.; Ha, J.; Kim, J.; Suh, D. Production of aromatic compounds from oil palm empty fruit bunches by hydro-and solvothermolysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Wu, S.; Mou, H.; Liang, J.; Lei, M. Study on the pyrolysis mechanism of three guaiacyl-type lignin monomeric model compounds. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2016, 118, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lyons-Hart, J.; Banyasz, J.; Shafer, K. Real-time evolved gas analysis by FTIR method: An experimental study of cellulose pyrolysis. Fuel 2001, 80, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, D.; Yoshikawa, T.; Norinaga, K.; Hayashi, J.; Tago, T.; Masuda, T. Production of ketones from pyroligneous acid of woody biomass pyrolysis over an iron-oxide catalyst. Fuel 2013, 103, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, N.; Chen, M.; Yi, W. Comparative study on the pyrolysis of cellulose and its model compounds. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 193, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, J.B., III; Pithawalla, Y.B.; Naworal, J.D. Carbohydrate pyrolysis mechanisms from isotopic labeling: Part 3. the pyrolysis of D-glucose: Formation of C3 and C4 carbonyl compounds and a cyclopentenedione isomer by electrocyclic fragmentation mechanisms. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2008, 82, 42–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh, F.; McGinnis, G. Chemical composition and thermal analysis of cottonwood. Carbohyd. Res. 1971, 16, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Partly chemical analysis of liquid fraction of flash pyrolysis products from biomass in the presence of sodium carbonate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Han, T.; Jiang, J.; Sun, K.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive insights into the influences of acid-base properties of chemical pretreatment reagents on biomass pyrolysis behavior and wood vinegar properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2020, 15, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X. Analysis of property variation and stability on the aging of bio-oil from fractional condensation. Renew. Energy 2020, 148, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Song, K.; Yu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Zu, G.; Zu, Y. Pyrolysis process and antioxidant activity of pyroligneous acid from Rosmarinus officinalis leaves. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2013, 104, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.; Wu, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. A new method for comprehensive utilization of wood vinegar by distillation and liquid− liquid extraction. Process. Biochem. 2018, 75, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, M.; Maggi, F.; Zengin, G.; Asghari, B.; Eskandani, M. Essential oils of hedgenettles (Stachys inflata, S. lavandulifolia, and S. byzantina) have antioxidant, anti-Alzheimer, antidiabetic, and anti-obesity potential: A comparative study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 112089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.; Arora, J.; Chew, J.; Dauenhauer, P.; Mushrif, S. Fast pyrolysis of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin: Effect of operating temperature on bio-oil yield and composition and insights into the intrinsic pyrolysis chemistry. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 15838–15852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, X. Coupling effect of condensing temperature and residence time on bio-oil component enrichment during the condensation of biomass pyrolysis vapors. Fuel 2020, 274, 117861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, H.; Ru, B.; Dai, G.; Wang, X.; Xiao, G.; Luo, Z. Kinetic modeling of biomass components pyrolysis using a sequential and coupling method. Fuel. 2016, 185, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, H.; Yang, W. Catalytic pyrolysis of demineralized lignocellulosic biomass. Fuel 2019, 252, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aït-Sahalia, Y.; Xiu, D. Principal component analysis of high-frequency data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2019, 114, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artoni, F.; Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. Applying dimension reduction to EEG data by principal component analysis reduces the quality of its subsequent independent component decomposition. NeuroImage 2019, 175, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.; Benediktsson, J.; Sveinsson, R. Random forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; An, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the impact of source water on tap water bacterial communities in 46 drinking water supply systems in China. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branca, C.; Giudicianni, P.; Di Blasi, C. GC/MS characterization of liquids generated from low-temperature pyrolysis of wood. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 3190–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, R.S.; Kataki, R.; Bhaskar, T. Characterization of liquid and solid product from pyrolysis of Pongamia glabra deoiled cake. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbas, A. Pyrolysis of ground beech wood in irregular heating rate conditions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2005, 73, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Q.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lu, Q.; Yang, Y.P. Characteristics and mechanism study of analytical fast pyrolysis of poplar wood. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2012, 57, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janairo, J.I.B.; Amalin, D.M. Volatile chemical profile of cacao liquid smoke. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.S.; Ly, H.V.; Choi, G.H.; Kim, J.; Woo, H.C. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of the alga Saccharina japonica. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, G.; Din, A.M.; Hameed, B.H. Pyrolysis of oil palm mesocarp fiber and palm frond in a slow-heating fixed-bed reactor: A comparative study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, E.; Arena, K.; Caramão, E.B.; Herrero, M. Quantitative analysis of aqueous phases of bio-oils resulting from pyrolysis of different biomasses by two-dimensional comprehensive liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1602, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Gao, P.; Liu, C.; Ding, X.; Huang, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, L. Antioxidant properties of compounds isolated from wood vinegar by activity-guided and pH-gradient extraction. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 38, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, A.Y.; Jain, K.; Darah, I. Antioxidant activity of compounds isolated from the pyroligneous acid, Rhizophora apiculata. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, W.; Zu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, J. Antioxidant properties of pyroligneous acid obtained by thermochemical conversion of Schisandra chinensis Baill. Molecules 2014, 19, 20821–20838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.; Zhao, Z. Isolation and bioactivities of organic acids and phenols from walnut shell pyroligneous acid. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2011, 91, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Musa, N.F. Antioxidant property and chemical profile of pyroligneous acid from pineapple plant waste biomass. Process. Biochem. 2015, 50, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Xu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zong, P.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, Y. Thermal degradation of food waste by TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS: Pyrolysis behaviors, products, kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Uehara, T.; Furuno, T. Effect of bamboo vinegar on regulation of germination and radicle growth of seed plants II: Composition of moso bamboo vinegar at different collection temperature and its effects. J. Wood Sci. 2004, 50, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.A.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.S. Fast pyrolysis of palm kernel cake using a fluidized bed reactor: Design of experiment and characteristics of bio-oil. J. In. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, J.S. Co-production of furfural and acetic acid from corncob using ZnCl2 through fast pyrolysis in a fluidized bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oramahi, H.A.; Yoshimura, T.; Diba, F.; Setyawati, D. Antifungal and antitermitic activities of wood vinegar from oil palm trunk. J. Wood Sci. 2018, 64, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.S.; Fasciotti, M.; Monteiro, T.V.; Lima, K.M. Chemical composition of pyroligneous acid obtained from Eucalyptus GG100 clone. Molecules 2018, 23, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pino, J.A. Characterisation of volatile compounds in a smoke flavouring from rice husk. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priharto, N.; Ronsse, F.; Yildiz, G.; Heeres, H.J.; Deuss, P.J.; Prins, W. Fast pyrolysis with fractional condensation of lignin-rich digested stillage from second-generation bioethanol production. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2020, 145, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setter, C.; Silva, F.T.M.; Assis, M.R.; Ataíde, C.H.; Trugilho, P.F.; Oliveira, T.J.P. Slow pyrolysis of coffee husk briquettes: Characterization of the solid and liquid fractions. Fuel 2020, 261, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, K.; Adriaensens, P.; Reggers, G.; Schreurs, S.; Carleer, R.; Yperman, J. Flash pyrolysis of rapeseed cake: Influence of temperature on the yield and the characteristics of the pyrolysis liquid. J. Appl. Pyrol. 2011, 90, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surboyo, M.D.C.; Arundina, I.; Rahayu, R.P.; Mansur, D.; Bramantoro, T. Potential of distilled liquid smoke derived from coconut (Cocos nucifera L) shell for Traumatic Ulcer Healing in Diabetic Rats. Eur. J. Dent. 2019, 13, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theapparat, Y.; Chandumpai, A.; Leelasuphakul, W.; Laemsak, N. Pyroligneous acids from carbonisation of wood and bamboo: Their components and antifungal activity. J. Trop. Fore. Sci. 2015, 27, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, F.; Lyu, J. Effect of oxidation processing on the preparation of post-hydrothermolysis acid from cotton stalk. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Yang, H.; Ma, F.; Yu, H. Comparative study of the fast pyrolysis behavior of ginkgo, poplar, and wheat straw lignin at different temperatures. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 122, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S. Antioxidant activities and chemical profiles of pyroligneous acids from walnut shell. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2010, 88, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Li, K.; Xiao, H.; Cai, N.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tu, X.; Chen, H. Pyrolysis of Chinese chestnut shells: Effects of temperature and Fe presence on product composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Yuan, H.; Qi, Y.; Lv, P.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, Y. Characterization of the decomposition behaviors of catalytic pyrolysis of wood using copper and potassium over thermogravimetric and Py-GC/MS analysis. Energy 2016, 114, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Yang, C.H.; Liang, M.T.; Gao, Z.J.; Wu, Y.W.; Chuang, L.Y. Chemical composition, antioxidant, and antibacterial activity of wood vinegar from Litchi chinensis. Molecules 2016, 21, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Huang, H.; Xiao, G. Comparison of non-catalytic and catalytic fast pyrolysis of corncob in a fluidized bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, G.; Huang, Q.; Jin, F.; Lin, L.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sajjad, M.; Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; et al. Exploration of the Interrelationship within Biomass Pyrolysis Liquid Composition Based on Multivariate Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 5656. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175656
Guo G, Huang Q, Jin F, Lin L, Wang Q, Fu Q, Liu Y, Sajjad M, Wang J, Liao Z, et al. Exploration of the Interrelationship within Biomass Pyrolysis Liquid Composition Based on Multivariate Analysis. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5656. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175656
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Genmao, Qing Huang, Fangming Jin, Linyi Lin, Qingqing Wang, Qionglin Fu, Yin Liu, Muhammad Sajjad, Junfeng Wang, Zhenni Liao, and et al. 2022. "Exploration of the Interrelationship within Biomass Pyrolysis Liquid Composition Based on Multivariate Analysis" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5656. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175656
APA StyleGuo, G., Huang, Q., Jin, F., Lin, L., Wang, Q., Fu, Q., Liu, Y., Sajjad, M., Wang, J., Liao, Z., & Cai, M. (2022). Exploration of the Interrelationship within Biomass Pyrolysis Liquid Composition Based on Multivariate Analysis. Molecules, 27(17), 5656. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175656






