High Thermal Resistance of Epoxy/Cyanate Ester Hybrids Incorporating an Inorganic Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Nanomaterial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
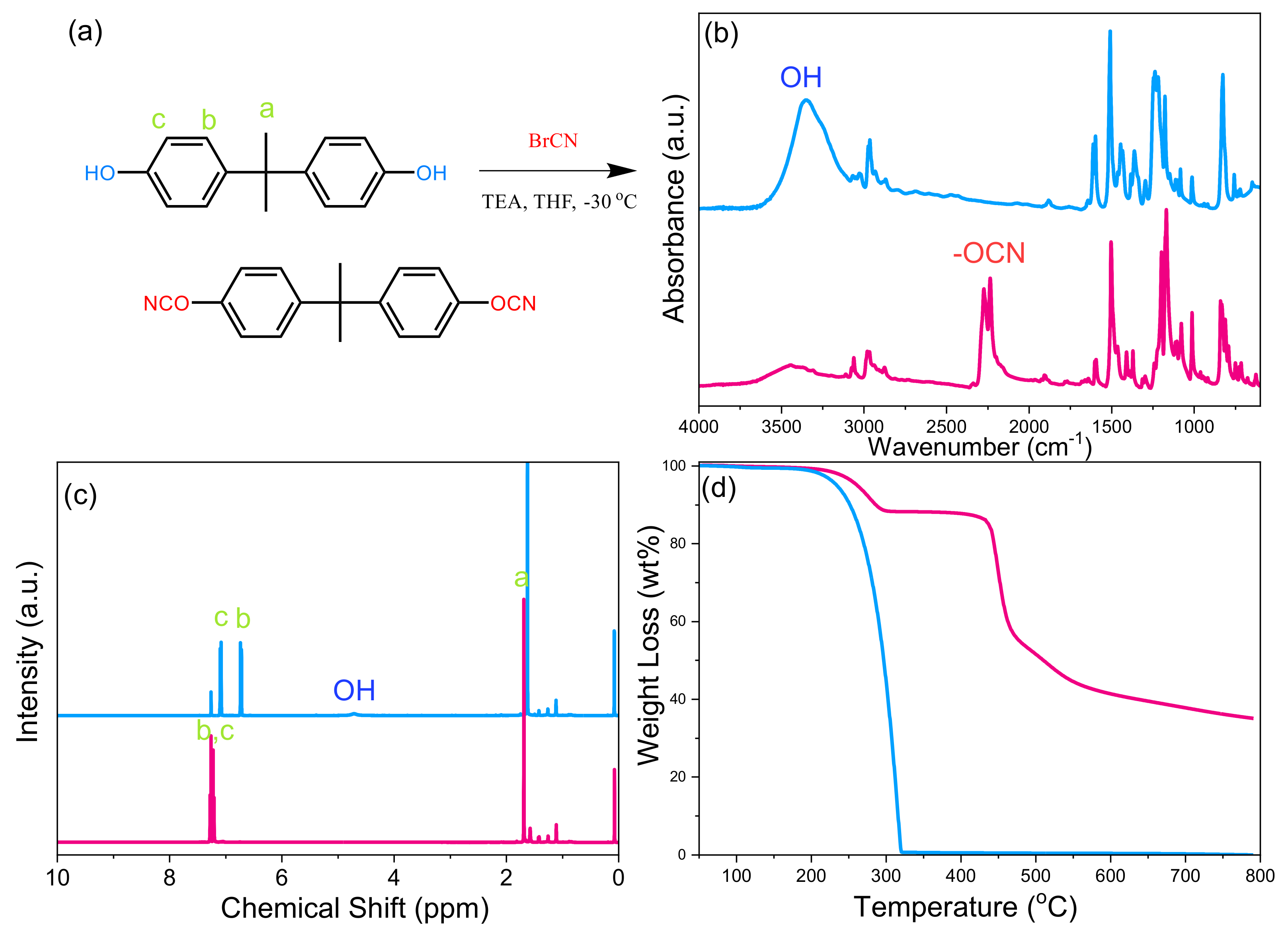
2.1. Preparation of the BADCy Monomer
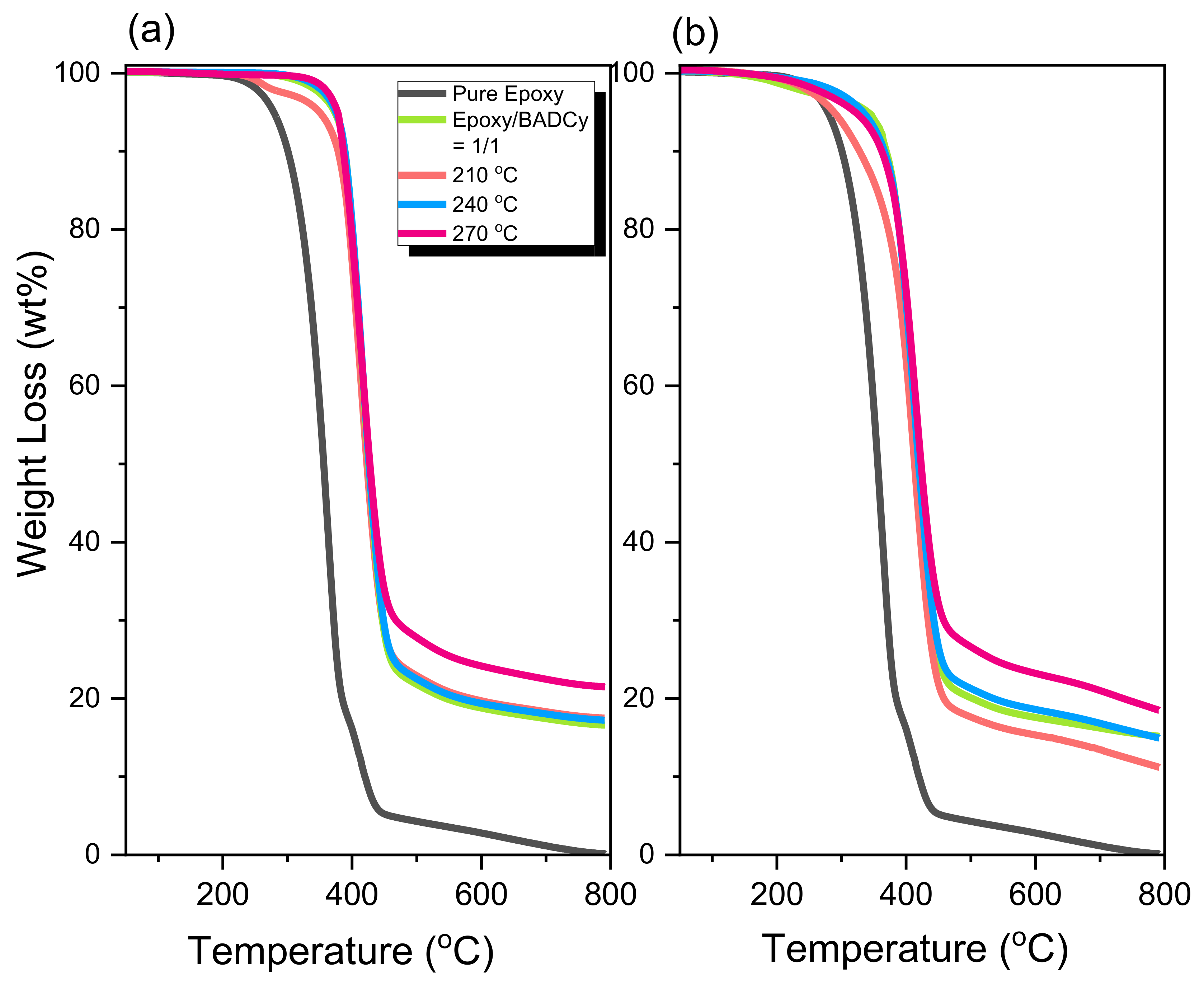
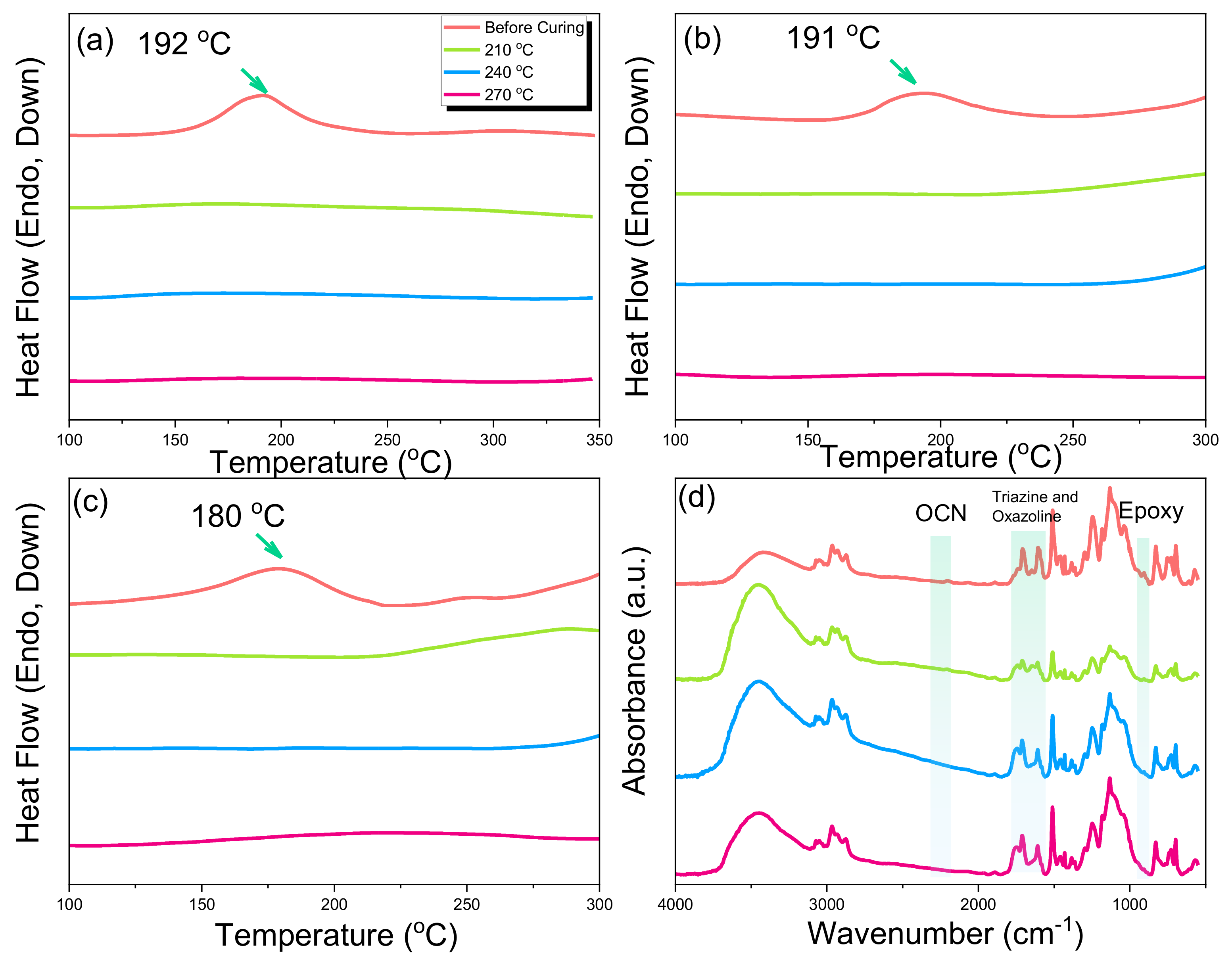
2.2. Thermal Polymerization of Epoxy/BADCy Hybrids
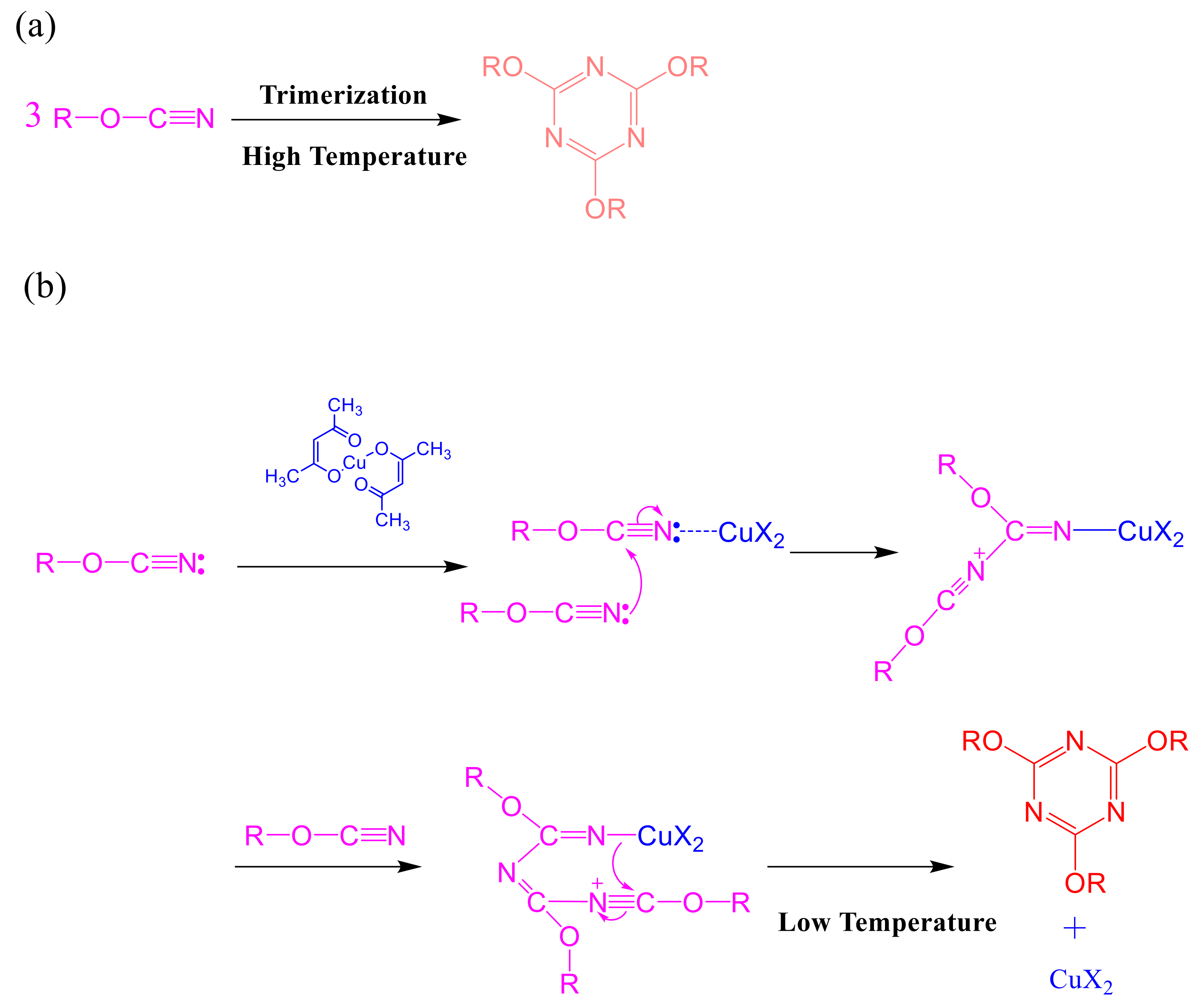
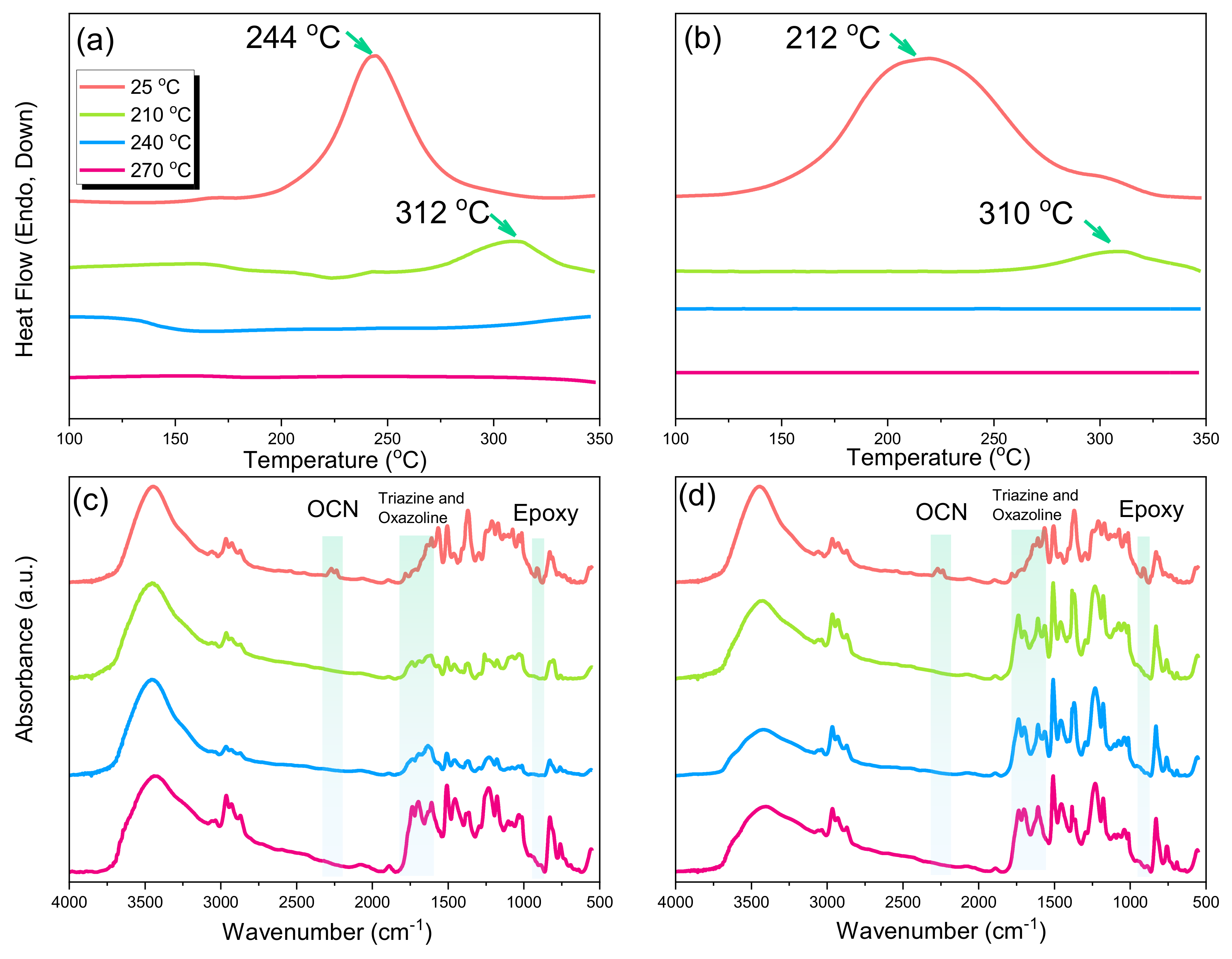
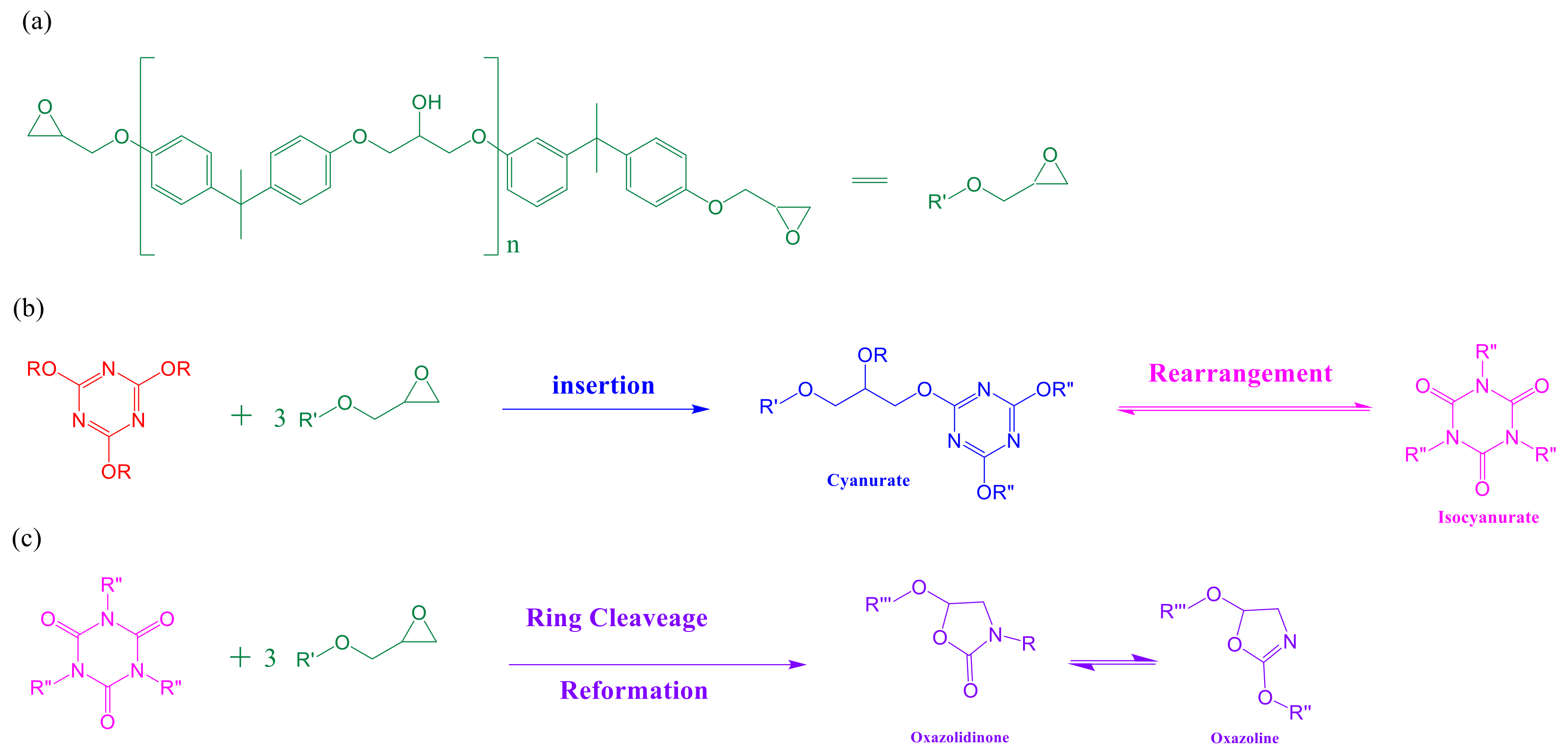
2.3. Thermal Polymerization of Epoxy/DDSQ-OCN Hybrids
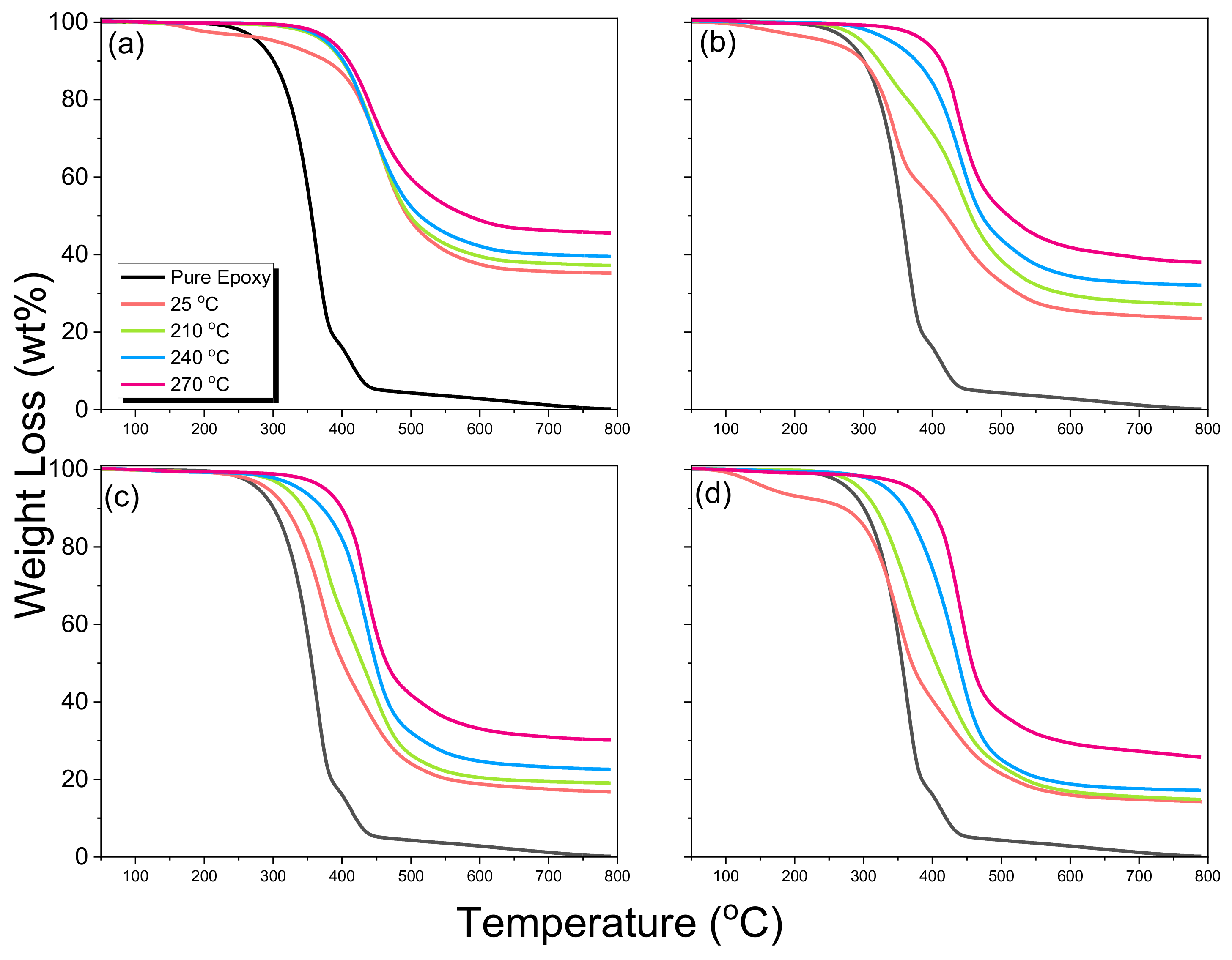
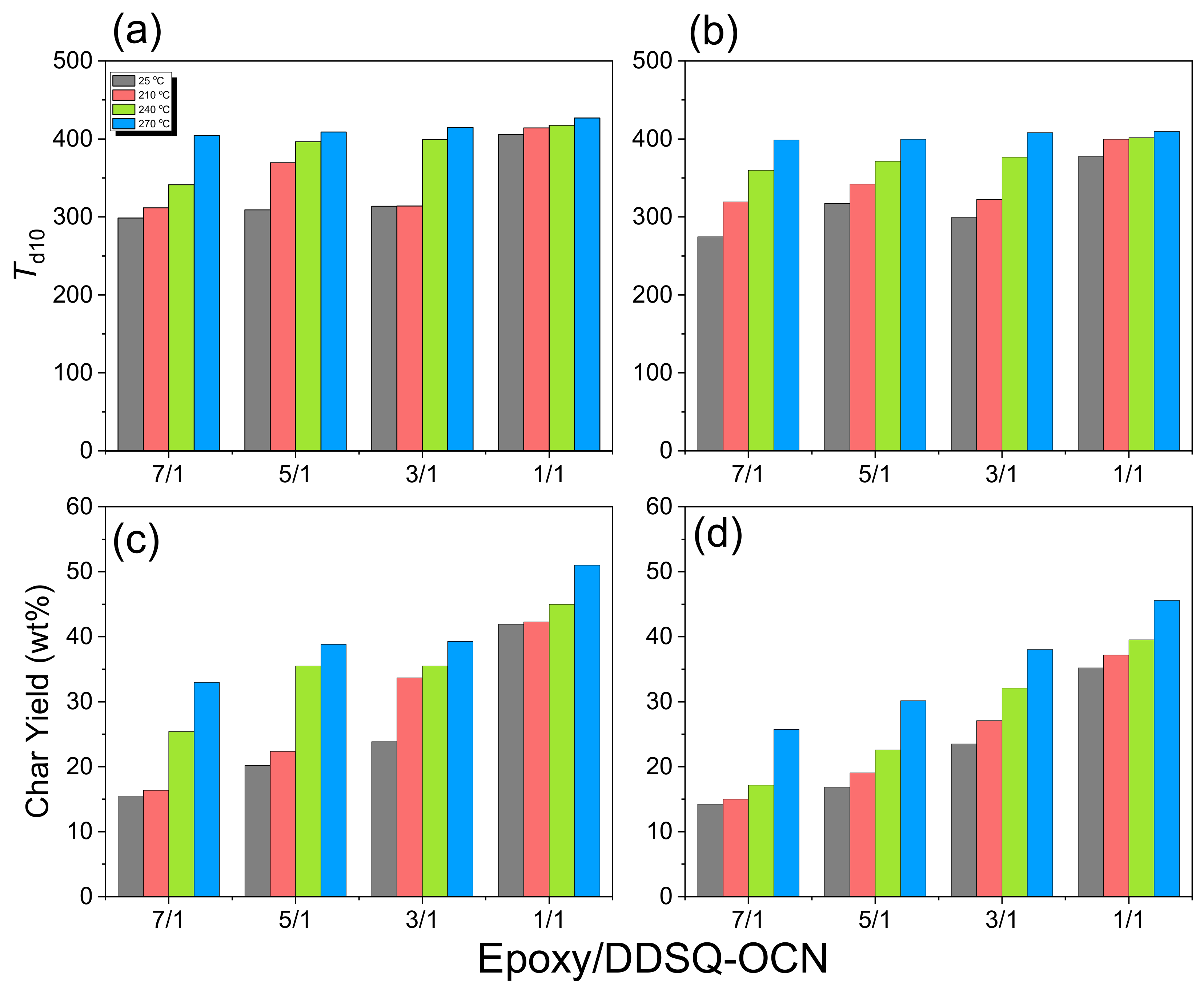
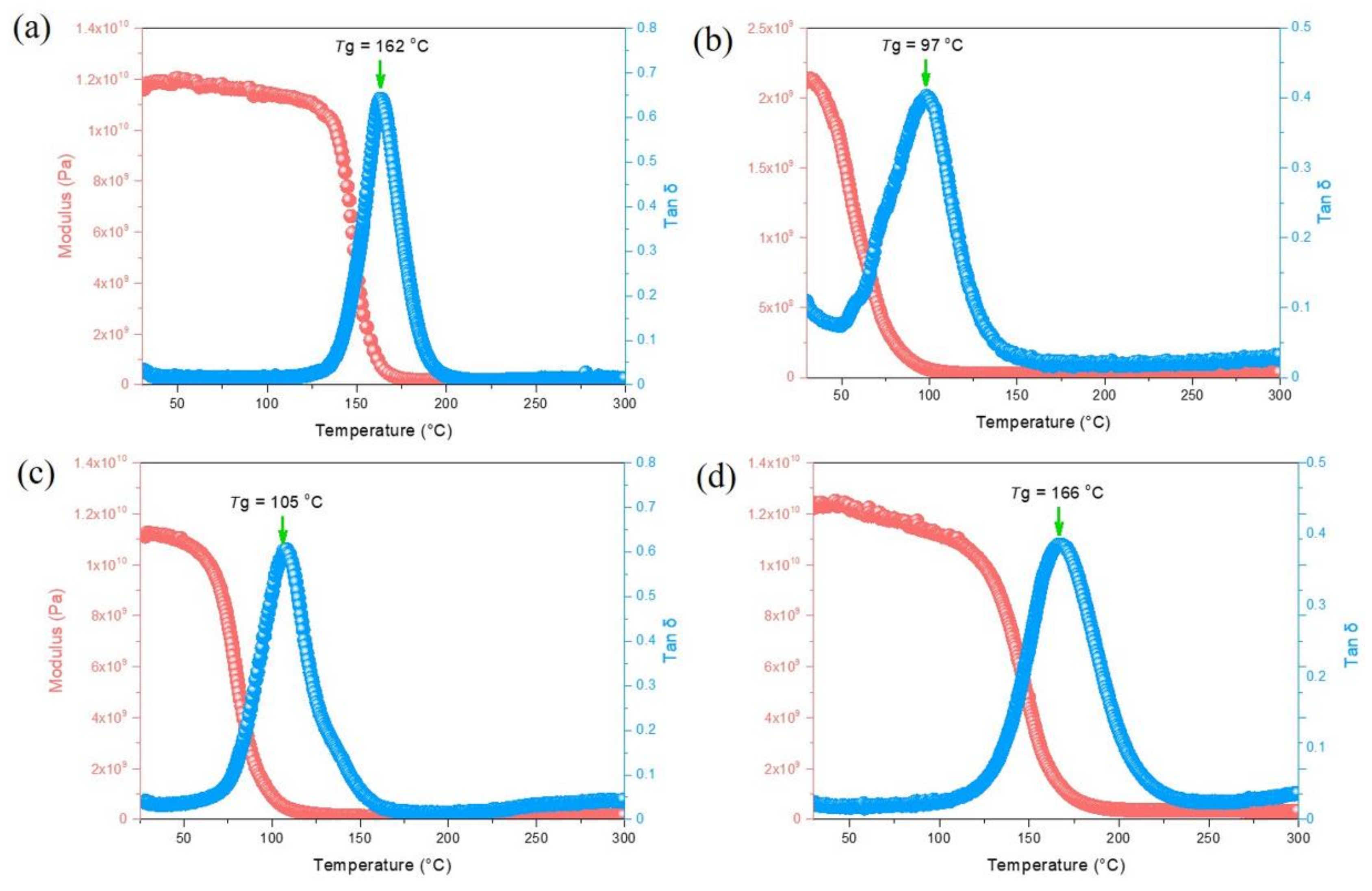
2.4. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/DDSQ-OCN Hybrids
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Bisphenol A Cyanate Ester (BADCy)
3.3. Epoxy/BADCy and Epoxy/DDSQ-OCN Hybrids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Huo, S.; Song, P.; Yu, B.; Ran, S.; Chevali, V.S.; Liu, L.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H. Phosphorus-containing flame retardant epoxy thermosets: Recent advances and future perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 114, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Novel Functionalized BN Nanosheets/Epoxy Composites with Advanced Thermal Conductivity and Mechanical Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2020, 12, 6503–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Tung, S.H.; Jeng, R.J.; Abu-Omar, M.M.; Lin, C.H. A facile strategy to achieve fully bio-based epoxy thermosets from eugenol. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4475–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Lin, J.; Shen, B.; He, S.; Bian, X. Analysis of the Electrical and Thermal Properties for Magnetic Fe3O4-Coated SiC-Filled Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Zhong, X.; Shi, X.; Dang, J.; Gu, J. Liquid crystal epoxy resins with high intrinsic thermal conductivities and their composites: A mini-review. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 20, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Lv, Y. Uniaxial Tensile Creep Behavior of Epoxy-Based Polymer Using Molecular Simulation. Polymers 2021, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junid, R.; Siregar, J.P.; Endot, N.A.; Razak, J.A.; Wilkinson, A.N. Optimization of Glass Transition Temperature and Pot Life of Epoxy Blends Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Polymers 2021, 13, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Liu, D. The Curing Kinetics Analysis of Four Epoxy Resins Using a Diamine Terminated Polyether as Curing Agent. Thermochim. Acta 2021, 702, 178987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, S.R.; Creighton, C.; Griffin, J.M.; Gashi, B.V.; Varley, R.J. Aromatic tetra-glycidyl ether versus tetra-glycidyl amine epoxy networks: Influence of monomer structure and epoxide conversion. Polymer 2022, 239, 124401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, S.R.; Creighton, C.; Griffin, J.M.; Gashi, B.V.; Varley, R.J. Cure Kinetics and Network Development of a Very High Tg Naphthalene-Based Epoxy Amine Network. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5717–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Krogsta, D.V. Self-Assembly and Phase Transformation of Block Copolymer Nanostructures in Ionic Liquid-Cured Epoxy. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, V.; Thompson, Z.J.; Joly, G.D.; Bates, F.S.; Francis, L.F. Adhesion Strength of Block Copolymer Toughened Epoxy on Aluminum. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Sun, Z.; Min, W.; Ou, H.; Qi, L.; Yu, M. Improving the toughness of thermosetting epoxy resins via blending triblock copolymers. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, R.; Sharif, S.; Nabiałek, M.; Zamree Abd Rahim, S.; Khushairi, M.T.M.; Suhaimi, M.A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Hanid, M.H.M.; Wysłocki, J.J.; Błoch, K. Hybrid Mold: Comparative Study of Rapid and Hard Tooling for Injection Molding Application Using Metal Epoxy Composite (MEC). Materials 2021, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Hou, X.; Shi, D.; Hu, G.H.; Xie, X. Novel micro-nano epoxy composites for electronic packaging application: Balance of thermal conductivity and processability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 209, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Xiao, Y.F.; Luo, X.; Liu, B.W.; Guo, D.M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.Z. Flame-Retardant multifunctional epoxy resin with high performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 132031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, L.; Brauner, C.; Teuwen, J.; Dransfeld, C. In Situ Characterization of the Reaction-Diffusion Behavior during the Gradient Interphase Formation of Polyetherimide with a High-Temperature Epoxy System. Polymers 2022, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kang, M.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Rhee, K.Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, S.-J. Roles of Small Polyetherimide Moieties on Thermal Stability and Fracture Toughness of Epoxy Blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Heuer, S.; Teuwen, J.; Dransfeld, C. Effect of a Dwell Stage in the Cure Cycle on the Interphase Formation in a Poly(ether imide)/High Tg Epoxy System. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6111–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosetti, Y.; Alcouffe, P.; Pascault, J.-P.; Gérard, J.-F.; Lortie, F. Polyether Sulfone-Based Epoxy Toughening: From Micro- to Nano-Phase Separation via PES End-Chain Modification and Process Engineering. Materials 2018, 11, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshmi, M.S.; Reddy, B.S.R. Synthesis and characterization of new epoxy and cyanate ester resins. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, C.; Sun, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lee, H.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. Melt Processable Novolac Cyanate Ester/Biphenyl Epoxy Copolymer Series with Ultrahigh Glass-Transition Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 15551–15562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Ba, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, G.; Fang, X.; Kuo, S.-W. Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxanes Reinforced Epoxy/Bismaleimide Hybrids Featuring High Thermal Stability. Polymers 2022, 14, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, G.; Lobato, Á.; Pandey, R.; Odegard, G.M. Mechanical Response of Polymer Epoxy/BMI Composites with Graphene and a Boron Nitride Monolayer from First Principles. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, A.; Kilian, R.; Sinapius, M.; Rager, K.; Dietzel, A. Tensile Strength and Structure of the Interface between a Room-Curing Epoxy Resin and Thermoplastic Films for the Purpose of Sensor Integration. Polymers 2021, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, J.; Ogawa, R.; Ota, K.; Mori, Y.; Tsuge, A.; Endo, T. Rapid Curing System of a Cyanate Ester Resin/Epoxy Resin with a Thermal Latent Polymeric Hardener Based on a Phenol–Amine Salt. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Cochran, E.W. Cyanate ester composites to improve thermal performance: A review. Polym. Inter. 2022, 71, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, B.; Hamerton, I. An automated in-situ polymerisation procedure for multi-functional cyanate ester resins via ring formation. Polymer 2021, 228, 123938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, S.; Dean, D.; Jordan, K.; Price, G.; Vaia, R. Chemorheology of cyanate ester—organically layered silicate nanocomposites. Polymer 2003, 44, 6901–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, A.; Sasidharan, S.; Gopinathapanicker, J.C.; Kandasubramanian, B.; Anand, A. Cyanate ester epoxy blends for structural and functional composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 3260–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Song, M. Cyanate ester resin/graphene nanocomposite: Curing dynamics and network formation. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yuan, L.; Guan, Q.; Liang, G.; Gu, A. Optimizing Ply Pattern and Composition of Layered Composites Based on Cyanate Ester, Carbon Nanotube, and Boron Nitride: Toward Ultralow Dielectric Loss and High Energy Storage. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 5238–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Qi, X.; Yang, D.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Grygoryeva, O.; Strizhak, P.; Fainleib, A.; Tang, J. Improved Mechanical, Anti-UV Irradiation, and Imparted Luminescence Properties of Cyanate Ester Resin/Unzipped Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Europium Nanocomposites. Materials 2021, 14, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Yakushev, P.; Kirllenko, D.; Egorova, L.; Grigoryeva, O.; Ryzhov, V.; Starostenko, O. High performance multi-functional cyanate ester oligomer-based network and epoxy-POSS containing nanocomposites: Structure, dynamics, and properties. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Li, G.; Toghiani, H.; Koo, J.H.; Pittman, C.U. Cyanate ester/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites: Synthesis and characterization. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Camino, G.; Yang, R. Polymer/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites: An overview of fire retardance. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 67, 77–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, A.; Dinkaran, K.; Kumar, A.A.; Alagar, M. Synthesis and characterization of epoxy modified cyanate ester POSS nanocomposites. High Perform. Polym. 2012, 24, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, G.; Wang, X. Epoxy-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/cyanate ester resin organic–inorganic hybrids with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yan, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Preparation and characterization of POSS-SiO2/cyanate ester composites with high performance. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Toghiani, H.; Pittman, C.U. Synthesis, Morphology and Viscoelastic Properties of Epoxy/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) and Epoxy/Cyanate Ester/POSS Nanocomposites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2011, 21, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W. Hydrogen bonding interactions in polymer/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanomaterials. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Highly Thermally Stable, Transparent, and Flexible Polybenzoxazine Nanocomposites by Combination of Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxanes and Polydimethylsiloxane. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 5739–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Kuo, S.W. Ortho-Imide and Allyl Groups Effect on Highly Thermally Stable Polybenzoxazine/Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Hybrids. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 9602–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Mei, H.; Liu, N.; Zheng, S. Organic–Inorganic Polycyclooctadienes with Double-Decker Silsesquioxanes in the Main Chains: Synthesis, Self-Healing, and Shape Memory Properties Regulated with Quadruple Hydrogen Bonds. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 7119–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Kikuchi, R.; Grunzinger, S.J.; Kakimoto, M.; Oikawa, H. Synthesis and characterization of semiaromatic polyimides containing POSS in main chain derived from double-decker-shaped silsesquioxane. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 5698–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Kakimoto, M.; Oikawa, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Organosoluble Aromatic Polyimides Containing POSS in Main Chain Derived from Double Decker Shaped Silsesquioxane. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Wang, C.F.; Huang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W. Highly thermally stable mesoporous Poly (cyanate ester) featuring double-decker–shaped polyhedral silsesquioxane framework. Polymer 2019, 185, 121940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Kuo, S.W. Mesoporous Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Materials with Frank-Kasper Phases Templated by an Unusual Linear Symmetry Diblock Copolymer. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kao, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; EL-Mahdy, A.F.M.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Kuo, S.-W. High Thermal Resistance of Epoxy/Cyanate Ester Hybrids Incorporating an Inorganic Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Nanomaterial. Molecules 2022, 27, 5938. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185938
Kao Y-C, Chen W-C, EL-Mahdy AFM, Hsu M-Y, Lin C-H, Kuo S-W. High Thermal Resistance of Epoxy/Cyanate Ester Hybrids Incorporating an Inorganic Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Nanomaterial. Molecules. 2022; 27(18):5938. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185938
Chicago/Turabian StyleKao, Yang-Chin, Wei-Cheng Chen, Ahmed F. M. EL-Mahdy, Meei-Yu Hsu, Chih-Hao Lin, and Shiao-Wei Kuo. 2022. "High Thermal Resistance of Epoxy/Cyanate Ester Hybrids Incorporating an Inorganic Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Nanomaterial" Molecules 27, no. 18: 5938. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185938
APA StyleKao, Y.-C., Chen, W.-C., EL-Mahdy, A. F. M., Hsu, M.-Y., Lin, C.-H., & Kuo, S.-W. (2022). High Thermal Resistance of Epoxy/Cyanate Ester Hybrids Incorporating an Inorganic Double-Decker-Shaped Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Nanomaterial. Molecules, 27(18), 5938. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27185938








