Distribution of Platinum and Palladium between Dissolved, Nanoparticulate, and Microparticulate Fractions of Road Dust
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Concentration of Pt and Pd in Bulk Road Dust Samples
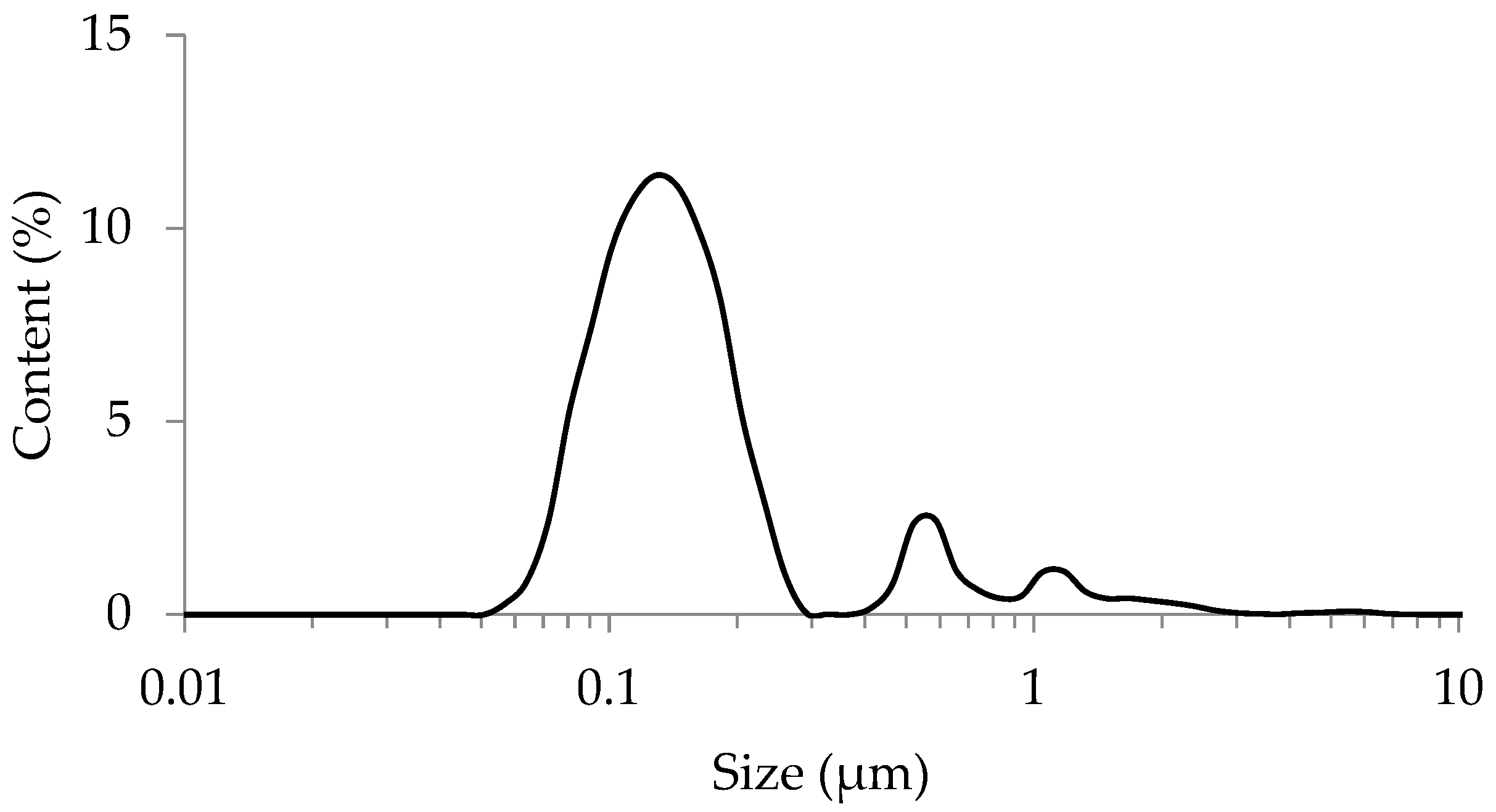
2.2. Particle Size Distribution of Separated Clay Fractions of Road Dust
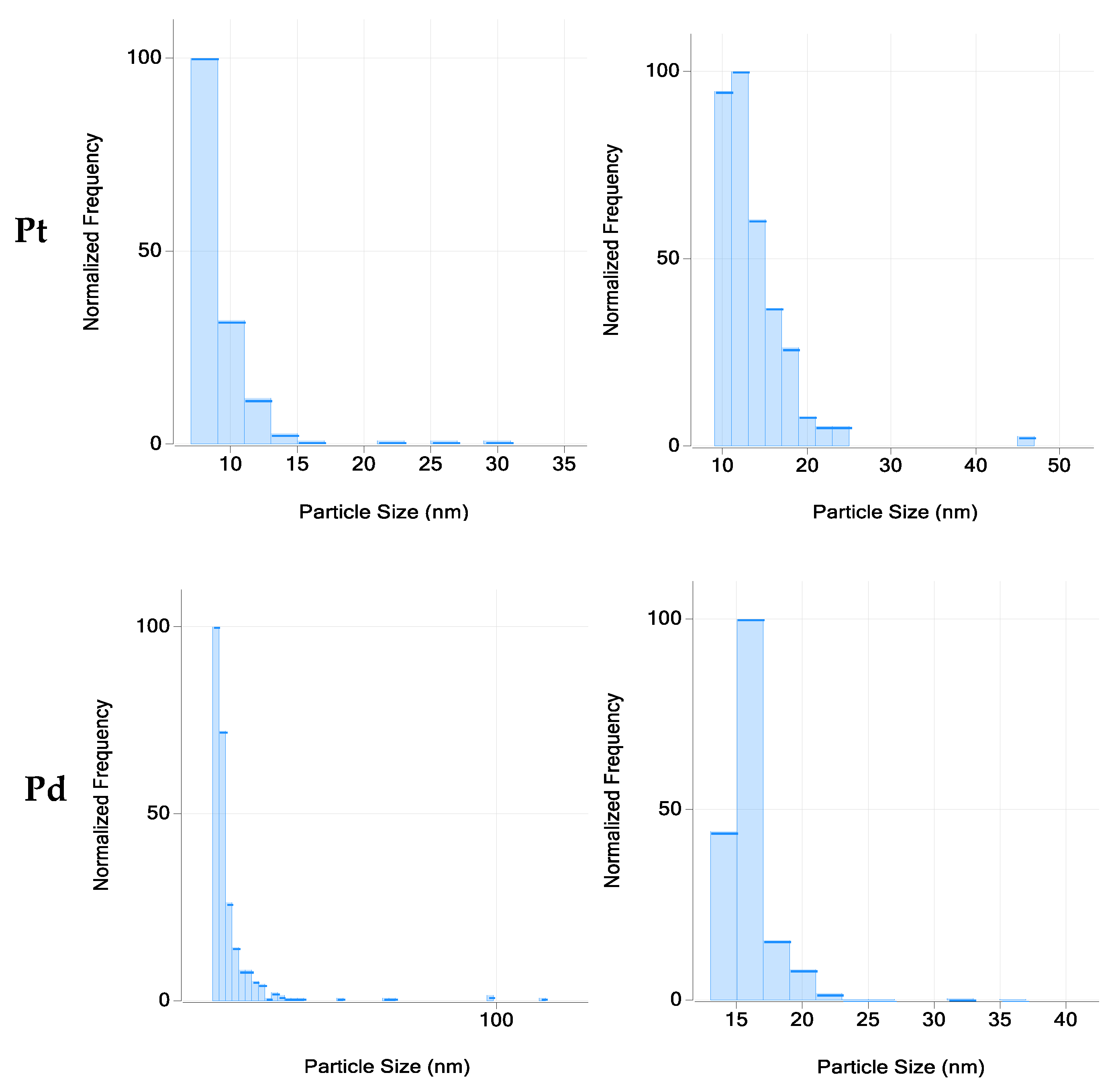
2.3. Concentration of Nanoparticulate Pt and Pd in Road Dust Samples
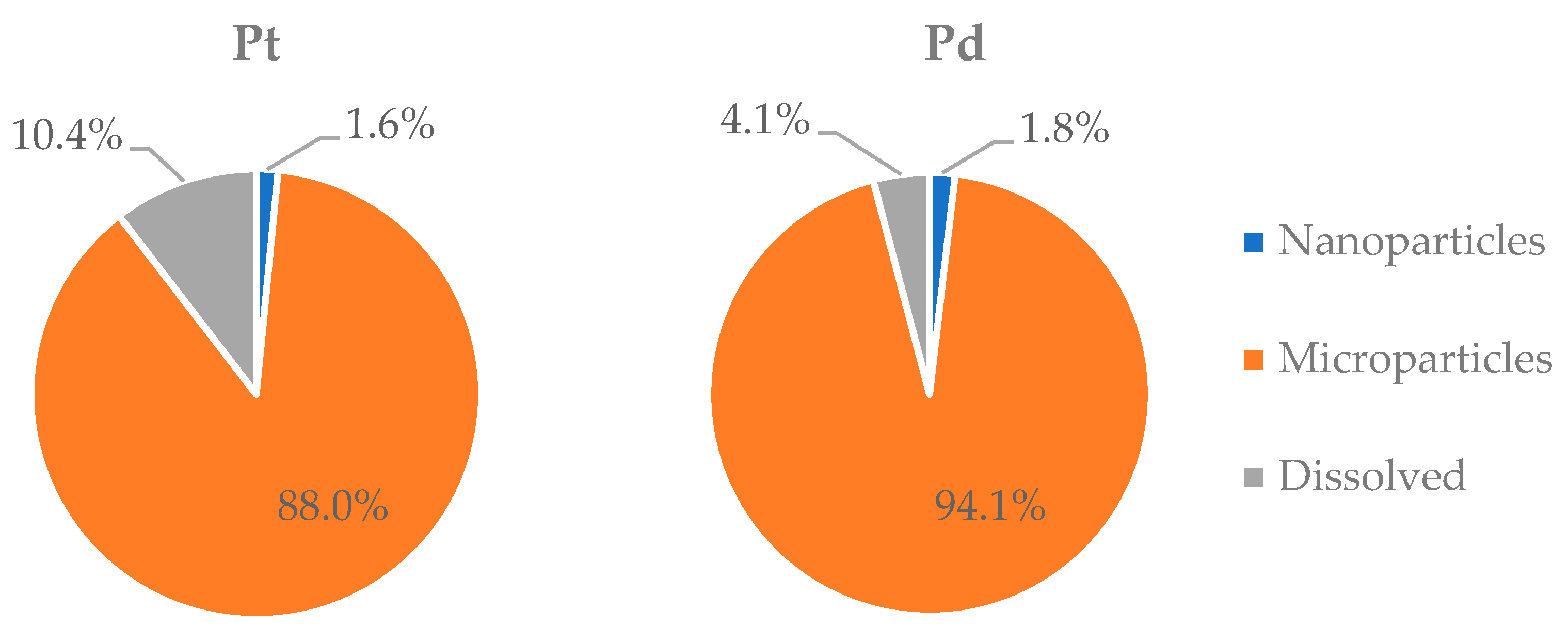
2.4. Association of Pt and Pd with Nanoparticulate, Microparticulate, and Dissolved Fractions of Road Dust
3. Materials and Methods
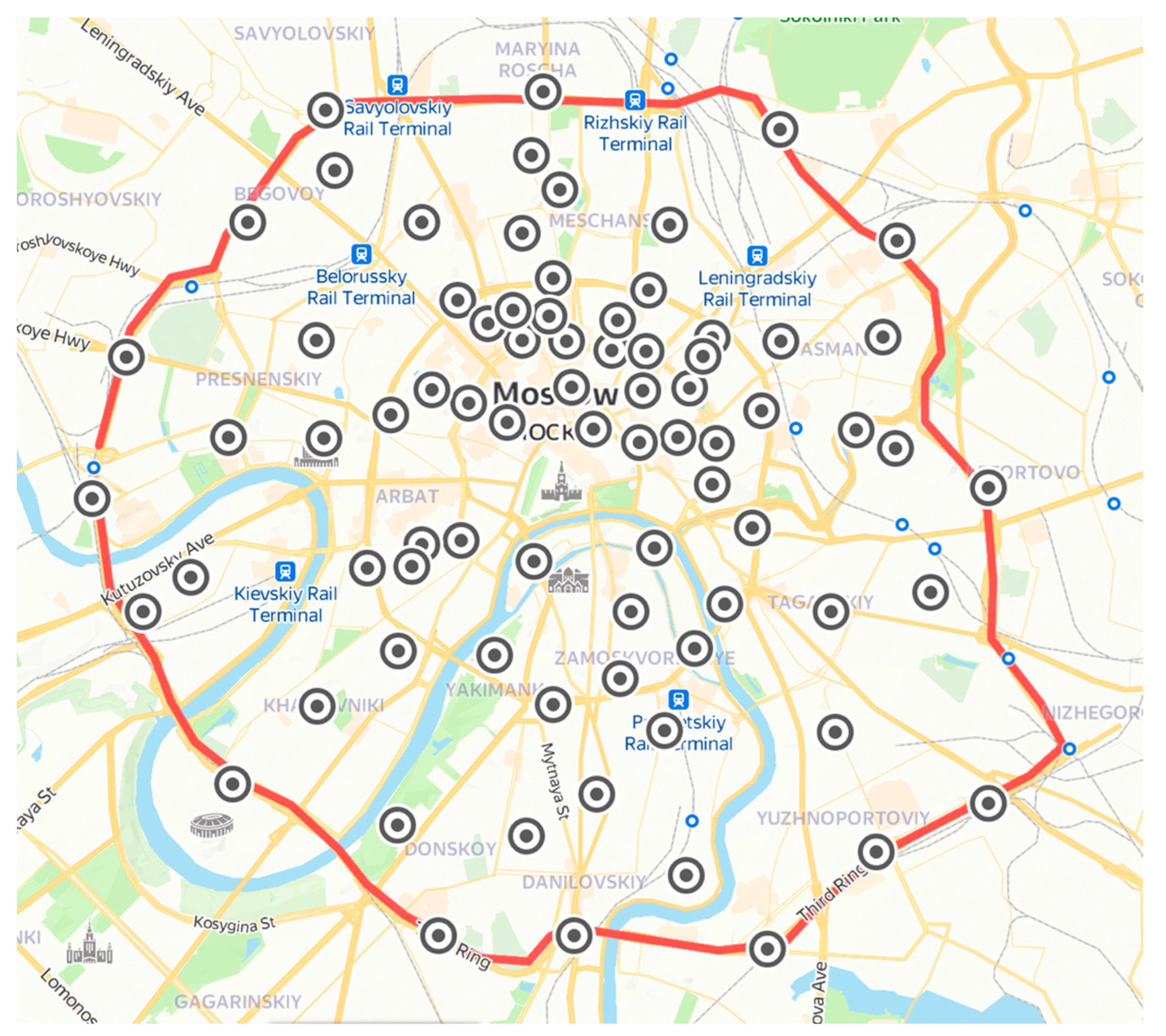
3.1. Road Dust Sampling
3.2. Determination of Platinum and Palladium in Road Dust Samples
3.3. Separation of Clay Fractions of Road Dust Samples
3.4. SpICP-MS Determination of Pt and Pd in the Clay Fraction of Road Dust
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rauch, S.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J.; Ramos, R.; Hemond, H.F. Platinum Group Elements in Airborne Particles in Mexico City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7554–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, M.; Palacios, M.A.; Gómez, M.M.; Morrison, G.; Rauch, S.; McLeod, C.; Ma, R.; Caroli, S.; Alimonti, A.; Petrucci, F.; et al. Environmental Risk of Particulate and Soluble Platinum Group Elements Released from Gasoline and Diesel Engine Catalytic Converters. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 296, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.A.; Gómez, M.M.; Moldovan, M.; Morrison, G.; Rauch, S.; McLeod, C.; Ma, R.; Laserna, J.; Lucena, P.; Caroli, S.; et al. Platinum-Group Elements: Quantification in Collected Exhaust Fumes and Studies of Catalyst Surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 257, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereini, F.; Alt, F.; Messerschmidt, J.; Von Bohlen, A.; Liebl, K.; Püttmann, W. Concentration and Distribution of Platinum Group Elements (Pt, Pd, Rh) in Airborne Particulate Matter in Frankfurt Am Main, Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereini, F.; Alt, F. Palladium Emissions in the Environment: Analytical Methods, Environmental Assessment and Health Effects, 1st ed.; Zereini, F., Alt, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; ISBN 3540292195. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindra, K.; Bencs, L.; Van Grieken, R. Platinum Group Elements in the Environment and Their Health Risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 318, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, M.; Veschambre, S.; Amouroux, D.; Bénech, B.; Donard, O.F.X. Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium in Fresh Snow from the Aspe Valley (Pyrenees Mountains, France). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.S. Platinum Group Element Pollution Is a Growing Concern in Countries with Developing Economy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13903–13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.S.; Mitra, A.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Rothenberg, S.E.; Tripathi, S.N.; Bizimis, M. Emerging Airborne Contaminants in India: Platinum Group Elements from Catalytic Converters in Motor Vehicles. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 75, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folens, K.; Van Acker, T.; Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Cornelis, G.; Vanhaecke, F.; Du Laing, G.; Rauch, S. Identification of Platinum Nanoparticles in Road Dust Leachate by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artelt, S.; Kock, H.; König, H.P.; Levsen, K.; Rosner, G. Engine Dynamometer Experiments: Platinum Emissions from Differently Aged Three-Way Catalytic Converters. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3559–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.; Hemond, H.F.; Barbante, C.; Owari, M.; Morrison, G.M.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Wass, U. Importance of Automobile Exhaust Catalyst Emissions for the Deposition of Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium in the Northern Hemisphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8156–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, B.; Palacios, M.A.; Gómez, M.; Sanchez, J.L.; Morrison, G.; Rauch, S.; McLeod, C.; Ma, R.; Caroli, S.; Alimonti, A.; et al. Levels and Risk Assessment for Humans and Ecosystems of Platinum-Group Elements in the Airborne Particles and Road Dust of Some European Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 299, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitsar, K.; Koellensperger, G.; Hann, S.; Limbeck, A.; Puxbaum, H.; Stingeder, G. Determination of Pt, Pd and Rh by Inductively Coupled Plasma Sector Field Mass Spectrometry (ICP-SFMS) in Size-Classified Urban Aerosol Samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2003, 18, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereini, F.; Wiseman, C.L.S. Platinum Metals in the Environment, 1st ed.; Zereini, F., Wiseman, C.L.S., Eds.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-662-44558-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, S.; Morrison, G.M. Environmental Relevance of the Platinum-Group Elements. Elements 2008, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschka, D.; Nachtwey, M. Traffic-Borne Platinum Pollution in Municipal Sewage Treatment Plants. In Anthropogenic Platinum-Group Element Emissions, 1st ed.; Zereini, F., Alt, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, S.; Hemond, H.F.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B. Recent Changes in Platinum Group Element Concentrations and Osmium Isotopic Composition in Sediments from an Urban Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewska, B.A.; Godlewska-Zyłkiewicz, B.; Bocca, B.; Caimi, S.; Caroli, S.; Hulanicki, A. Platinum, Palladium and Rhodium Content in Road Dust, Tunnel Dust and Common Grass in Białystok Area (Poland): A Pilot Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 321, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Shi, Y. Distribution of Platinum Group Elements in Road Dust in the Beijing Metropolitan Area, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladonin, D.V. Platinum-Group Elements in Soils and Street Dust of the Southeastern Administrative District of Moscow. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2018, 51, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zhou, M.F.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, J.; Huang, Y. The Characteristics of Automobile Catalyst-Derived Platinum Group Elements in Road Dusts and Roadside Soils: A Case Study in the Pearl River Delta Region, South China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J. Accumulation and Distribution Characteristics of Platinum Group Elements in Roadside Dusts in Beijing, China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, C.L.S.; Niu, J.; Levesque, C.; Chénier, M.; Rasmussen, P.E. An Assessment of the Inhalation Bioaccessibility of Platinum Group Elements in Road Dust Using a Simulated Lung Fluid. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, B.; Gómez, M.; Sanchez, J.L.; Fernández, R.; Palacios, M.A. Platinum and Rhodium Distribution in Airborne Particulate Matter and Road Dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 269, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Spectroscopic and Voltammetric Analysis of Platinum Group Metals in Road Dust and Roadside Soil. Environments 2018, 5, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chon, H.T.; Sager, M.; Marton, L. Platinum Pollution in Road Dusts, Roadside Soils, and Tree Barks in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Geochem. Health 2012, 34, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Balaram, V.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Sawant, S.S.; Ramesh, S.L. Anthropogenic Platinum, Palladium and Rhodium Concentrations in Road Dusts from Hyderabad City, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, N.; Bozlaker, A.; Chellam, S. Multi-Elemental Characterization of Tunnel and Road Dusts in Houston, Texas Using Dynamic Reaction Cell-Quadrupole-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry: Evidence for the Release of Platinum Group and Anthropogenic Metals from Motor Vehicles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 735, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.I.; Dudding, L.M. Platinum Emissions and Levels in Motorway Dust Samples: Influence of Traffic Characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 334–335, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, J.D.; Murray, F. Anthropogenic Platinum Group Element (Pt, Pd and Rh) Concentrations in Road Dusts and Roadside Soils from Perth, Western Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 317, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebek, O.; Mihaljevič, M.; Strnad, L.; Ettler, V.; Ježek, J.; Štědrý, R.; Drahota, P.; Ackerman, L.; Adamec, V. Dissolution Kinetics of Pd and Pt from Automobile Catalysts by Naturally Occurring Complexing Agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 198, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.; Morrison, G.M. Routes for Bioaccunmulation and Transormation of Platinum in the Urban Environment. In Anthropogenic Platinum-Group Element Emissions, 1st ed.; Zereini, F., Alt, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, C.; Monhemius, A.J.; Plant, J.A. The Estimation of the Bioavailabilities of Platinum, Palladium and Rhodium in Vehicle Exhaust Catalysts and Road Dusts Using a Physiologically Based Extraction Test. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Environmental Health Criteria 125 Platinum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Environmental Health Criteria 226 Palladium; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon, Z.E.; Newkirk, C.; Hicks, S. Impact of Platinum Group Metals on the Environment: A Toxicological, Genotoxic and Analytical Chemistry Study. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2006, 41, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, H.P.; Hertel, R.F.; Koch, W.; Rosner, G. Determination of Platinum Emissions from a Three-Way Catalyst-Equipped Gasoline Engine. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1992, 26, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hurt, R.H. Ion Release Kinetics and Particle Persistence in Aqueous Nano-Silver Colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Martin, G.; Sanz-Landaluze, J.; Madrid, Y. Nanospeciation Analysis Using Field Flow Fractionation. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolin, M.S.; Ivaneev, A.I.; Fedyunina, N.N.; Fedotov, P.S. Nanospeciation of Metals and Metalloids in Volcanic Ash Using Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.Y.; Wold, S. Gold Colloid Analysis by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry in a Single Particle Mode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 555, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.Y.; Rossé, R.; Wold, S. Uranium Colloid Analysis by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2006, 68, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.Y.; Bitea, C. Zirconia Colloid Analysis by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.Y. Thorium Colloid Analysis by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2004, 62, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.Y. Colloid Analysis by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy: A Feasibility Study. Proc. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 217, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Jiménez-Lamana, J. Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry for the Analysis of Inorganic Engineered Nanoparticles in Environmental Samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Jiménez-Lamana, J. Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: A Powerful Tool for Nanoanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, M.; Doi, Y.; Hellwich, K.-H.; Hess, M.; Hodge, P.; Kubisa, P.; Rinaudo, M.; Schué, F. Terminology for Biorelated Polymers and Applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 377–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubrakova, I.V.; Tyutyunnik, O.A.; Koshcheeva, I.Y.; Sadagov, A.Y.; Nabiullina, S.N. Migration Behavior of Platinum Group Elements in Natural and Technogeneous Systems. Geochem. Int. 2017, 55, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weather in Moscow in July 2021. Available online: https://world-weather.info/forecast/russia/moscow/july-2021/.
- Karandashev, V.K.; Khvostikov, V.A.; Nosenko, S.V.; Burmii, Z.P. Stable Highly Enriched Isotopes in Routine Analysis of Rocks, Soils, Grounds, and Sediments by ICP-MS. Inorg. Mater. 2017, 53, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Concentration, ng g−1 | Location | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | Pd | ||
| 317 | - | Madrid, Spain | [25] |
| 326 58 74 34 173 | 71 - - 203 - | Gothenburg, Sweden Sheffield, UK London, UK Rome, Italy Munich, Germany | [13] |
| 0.16–1.28 | 0.64–1.76 | Stellenbosch, South Africa | [26] |
| 5–79 | - | Ghent, Belgium Gothenburg, Sweden | [10] |
| 28 | 58 | Beijing, China | [23] |
| 12–357 (mean 71) | 8–225 (mean 158) | Moscow, Russia | [21] |
| 3.8–444 (mean 115) | - | Seoul, Korea | [27] |
| 34–111 | 33–42 | Białystok, Poland | [19] |
| 1.5–43 | 1.2–58 | Hyderabad, India | [28] |
| 12–187 14–178 5–48 | 12–287 34–514 13–554 | Hong Kong, China Shenzhen, China Guangzhou, China | [22] |
| 35–131 | 10–88 | Houston, USA | [29] |
| 4–356 (mean 97) | 0.1–125 (mean 20) | Beijing, China | [20] |
| 102–764 | - | London, UK | [30] |
| 54–419 | 58–440 | Perth, Australia | [31] |
| <5–151 | 10–516 | Toronto, Canada | [24] |
| Element | Concentration, ng g−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | |
| Pt | 7 | 35 | 9 | 142 |
| Pd | 50 | 235 | 155 | 456 |
| Size (nm) | Number Concentration (Particles L−1) | Mass Concentration (ng L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certified values | 29.4 ± 1.3 | 2.1 × 108 | 53 |
| Experimental results | 29.2 ± 0.1 | (2.0 ± 0.3) ×108 | 54 ± 8 |
| Particle Concentration (Particles L−1) | Mass Concentration (ng L−1) | Ionic Concentration (ng L−1) | Median Size (nm) | Size Detection Limit (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | |||||
| Mean | 2.8 × 108 | 1.6 | 12 | 7 | 3.5 |
| Minimum | 1.2 × 106 | 0.03 | 1 | 6 | 2.8 |
| Maximum | 3.4 × 109 | 18.2 | 34 | 11 | 5.1 |
| Pd | |||||
| Mean | 1.1 × 109 | 21 | 90 | 13 | 6.7 |
| Minimum | 5.7 × 107 | 3 | 13 | 10 | 4.4 |
| Maximum | 3.0 × 109 | 104 | 708 | 21 | 13.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ermolin, M.S.; Ivaneev, A.I.; Brzhezinskiy, A.S.; Fedyunina, N.N.; Karandashev, V.K.; Fedotov, P.S. Distribution of Platinum and Palladium between Dissolved, Nanoparticulate, and Microparticulate Fractions of Road Dust. Molecules 2022, 27, 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186107
Ermolin MS, Ivaneev AI, Brzhezinskiy AS, Fedyunina NN, Karandashev VK, Fedotov PS. Distribution of Platinum and Palladium between Dissolved, Nanoparticulate, and Microparticulate Fractions of Road Dust. Molecules. 2022; 27(18):6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186107
Chicago/Turabian StyleErmolin, Mikhail S., Alexandr I. Ivaneev, Anton S. Brzhezinskiy, Natalia N. Fedyunina, Vasily K. Karandashev, and Petr S. Fedotov. 2022. "Distribution of Platinum and Palladium between Dissolved, Nanoparticulate, and Microparticulate Fractions of Road Dust" Molecules 27, no. 18: 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186107
APA StyleErmolin, M. S., Ivaneev, A. I., Brzhezinskiy, A. S., Fedyunina, N. N., Karandashev, V. K., & Fedotov, P. S. (2022). Distribution of Platinum and Palladium between Dissolved, Nanoparticulate, and Microparticulate Fractions of Road Dust. Molecules, 27(18), 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186107






