Sequential Injection Amperometric System Coupling with Bioreactor for In-Line Glucose Monitoring in Cell Culture Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
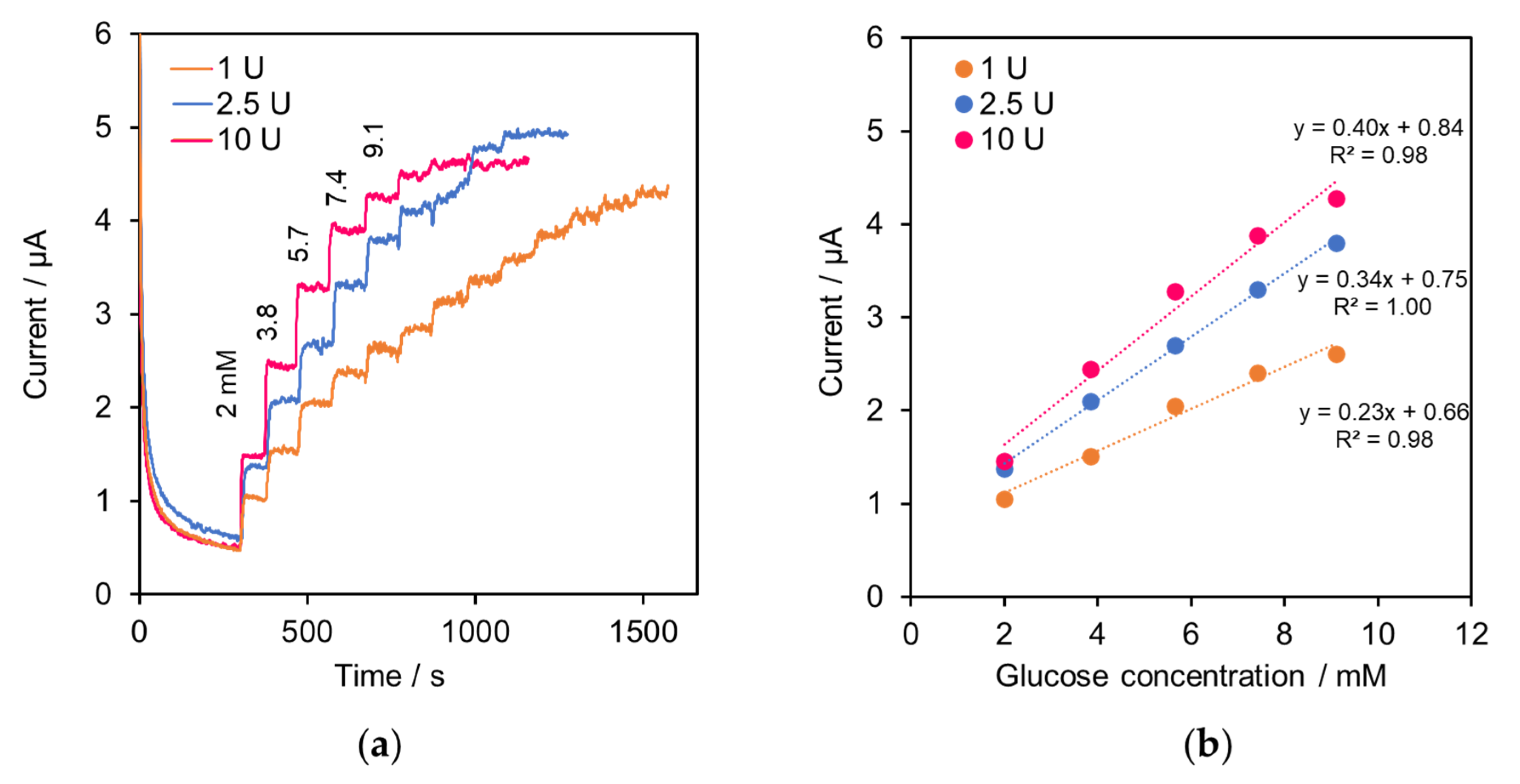
2.1. Performance of the Modified SPE
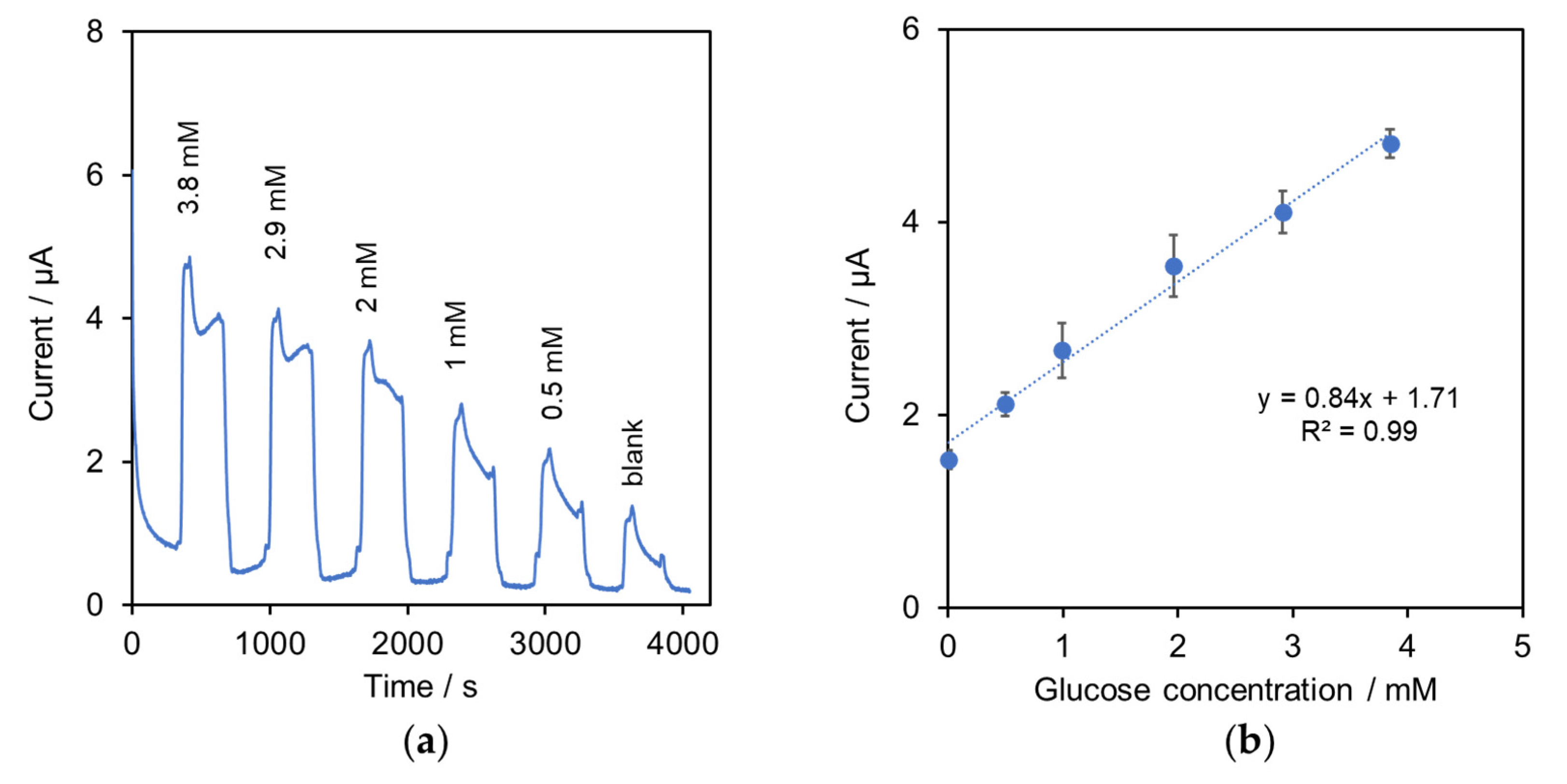
2.2. Characterization of the System for Determination of Glucose in Cell Culture Media
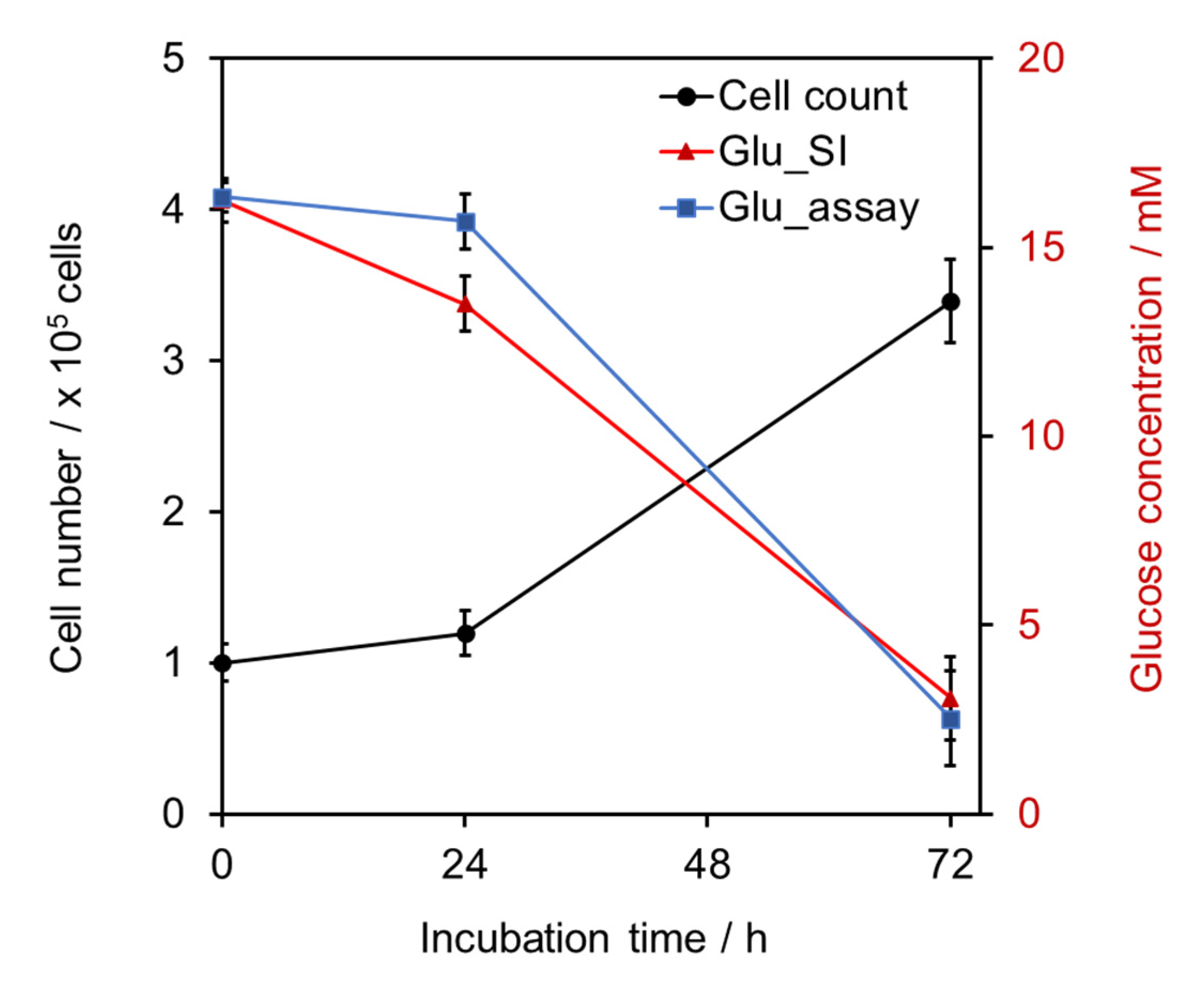
2.3. Application
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. System Design and Fabrication
3.1.1. The Design Concept
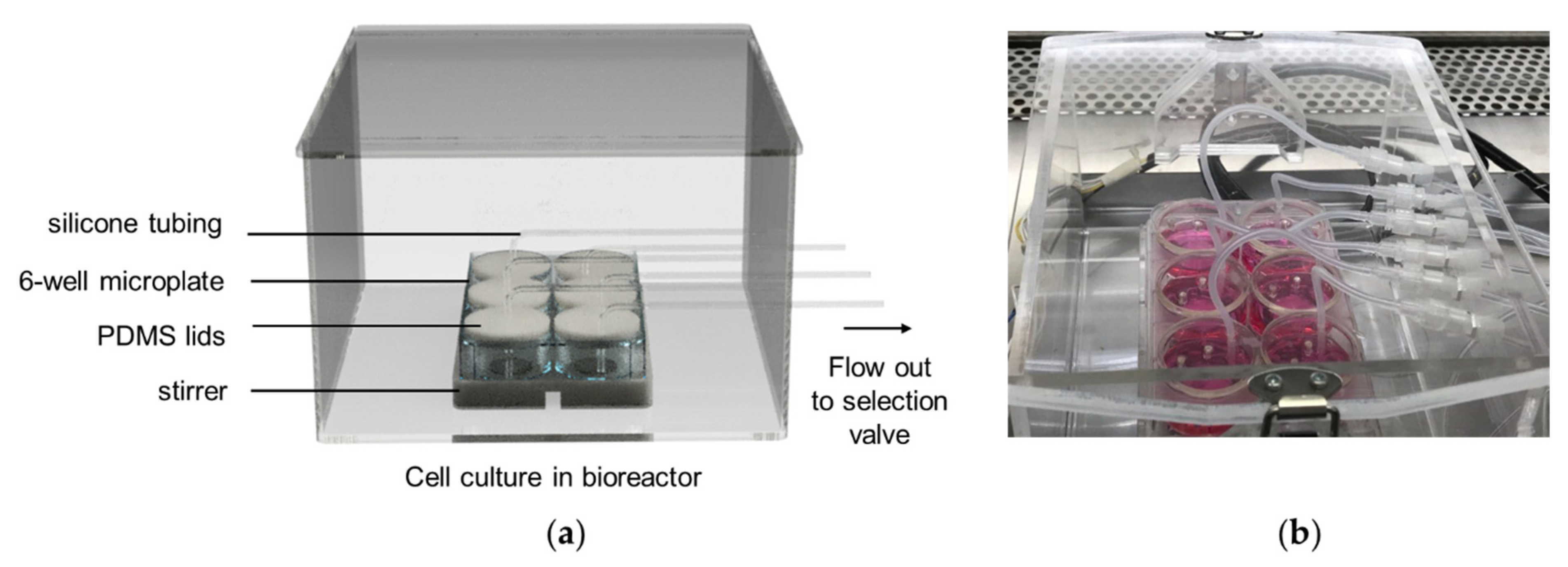
3.1.2. The Bioreactor
3.1.3. The SI System
3.1.4. The Electrochemical Detection Unit
3.2. Reagents and Chemicals
3.3. Modification of SPE
3.4. Electrochemical Measurement
3.5. Glucose Monitoring Using the System
3.6. Cell Culture of L929 Cell Line
3.7. Glucose Enzymatic Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruzicka, J.M.; Graham, D. Sequential injection: A new concept for chemical sensors, process analysis and laboratory assays. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 237, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, P.J.; Christian, G.D. Sequential Injection Analysis: A Versatile Technique for Bioprocess Monitoring. Acc. Chem. Res. 1996, 29, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solich, P.; Sklenářová, H.; Huclová, J.; Šatínský, D.; Schaefer, U.F. Fully automated drug liberation apparatus for semisolid preparations based on sequential injection analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 499, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklenarova, H.; Beran, M.; Novosvetska, L.; Smejkalova, D.; Solich, P. Sequential Injection Analysis for Automation and Evaluation of Drug Liberation Profiles: Clotrimazole Liberation Monitoring. Molecules 2021, 26, 5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimundova, J.; Satinsky, D.; Sklenarova, H.; Solich, P. Automation of simultaneous release tests of two substances by sequential injection chromatography coupled with Franz cell. Talanta 2006, 69, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguinaga Martinez, M.V.; Jozicova, N.; Dusek, J.; Horstkotte, B.; Pavek, P.; Miro, M.; Sklenarova, H. Real-time monitoring of Metridia luciferase release from cells upon interaction with model toxic substances by a fully automatic flow setup—A proof of concept. Talanta 2022, 245, 123465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Fernandez, J.; Vellala, P.; Kulkarni, T.A.; Aguilar, I.; Ritz, D.; Lan, K.; Patel, P.; et al. A Fully Integrated Online Platform for Real Time Monitoring of Multiple Product Quality Attributes in Biopharmaceutical Processes for Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hun-Chi, S.H.H.; Mattiasson, B. On-line monitoring of D-lactic acid during a fermentation process using immobilized D-lactate dehydrogenase in a sequential injection analysis system. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 300, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauser, H.; Busch, M.; Höbel, W.; Polster, J. Bioprocess monitoring by sequential injection analysis. Lat. Am. Appl. Res. 2001, 31, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Alhusban, A.A.; Gaudry, A.J.; Breadmore, M.C.; Gueven, N.; Guijt, R.M. On-line sequential injection-capillary electrophoresis for near-real-time monitoring of extracellular lactate in cell culture flasks. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1323, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharmalingam, T.; Wu, C.; Callahan, S.; Goudar, C.T. A framework for real-time glycosylation monitoring (RT-GM) in mammalian cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Wee, S. Micro sequential injection system as the interfacing device for process analytical applications. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabadaj, M.; Szuplewska, A.; Kalinowska, D.; Chudy, M.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P. Studying pharmacodynamic effects in cell cultures by chemical fingerprinting − SIA electronic tongue versus 2D fluorescence soft sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwfo, K.; Wongwilai, W.; Sakai, T.; Teshima, N.; Grudpan, K. Determination of Albumin, Glucose, and Creatinine Employing a Single Sequential Injection Lab-at-Valve with Mono-Segmented Flow System Enabling In-Line Dilution, In-Line Single-Standard Calibration, and In-Line Standard Addition. Molecules 2020, 25, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.H.; Lee, S.Y. Glucose biosensors: An overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Chen, J. Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase promoted by carbon nanotubes. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 332, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Mai, Z.; Zou, X.; Cai, P.; Mo, J. Glucose biosensors based on platinum nanoparticles-deposited carbon nanotubes in sol-gel chitosan/silica hybrid. Talanta 2008, 74, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S. One-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles/carbon nanotubes/chitosan film and its application in glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X. Carbon nanotube/chitosan/gold nanoparticles-based glucose biosensor prepared by a layer-by-layer technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.-J.; Wang, A.-N.; Peng, S.-Y. An Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Composed of Carbon-Coated Nano Tin Sulfide. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, C.; Casulli, M.A.; Olivo, J.; Foglia, L.; Orso, E.; Mazza, M.; Carrara, S.; De Micheli, G. Design, development, and validation of an in-situ biosensor array for metabolite monitoring of cell cultures. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fuentes, F.J.; Molina, G.A.; Silva, R.; Lopez-Miranda, J.L.; Esparza, R.; Hernandez-Martinez, A.R.; Estevez, M. Developing a CNT-SPE Sensing Platform Based on Green Synthesized AuNPs, Using Sargassum sp. Sensors 2020, 20, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tric, M.; Lederle, M.; Neuner, L.; Dolgowjasow, I.; Wiedemann, P.; Wolfl, S.; Werner, T. Optical biosensor optimized for continuous in-line glucose monitoring in animal cell culture. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5711–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacopo Olivo, L.F. Maria Antonietta Casulli, Cristina Boero, Sandro Carrara, and Giovanni De Micheli, Glucose and Lactate Monitoring in Cell Cultures with a Wireless Android Interface. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) Proceedings, Lausanne, Switzerland, 22–24 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton, R.M.; Cox, T.; Tuffin, R.; Drago, G.A.; Griffiths, J.; Pittson, R.; Johnson, G.; Xu, J.; Sage, I.C.; Davies, R.; et al. Fabrication and evaluation of a micro(bio)sensor array chip for multiple parallel measurements of important cell biomarkers. Sensors 2014, 14, 20519–20532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weltin, A.; Slotwinski, K.; Kieninger, J.; Moser, I.; Jobst, G.; Wego, M.; Ehret, R.; Urban, G.A. Cell culture monitoring for drug screening and cancer research: A transparent, microfluidic, multi-sensor microsystem. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Petropoulos, K.; Kurth, F.; Gao, H.; Migliorelli, D.; Guenat, O.; Generelli, S. Screen-Printed Glucose Sensors Modified with Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs) for Cell Culture Monitoring. Biosensors 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udomsom, S.; Budwong, A.; Wongsa, C.; Sangngam, P.; Baipaywad, P.; Manaspon, C.; Auephanwiriyakul, S.; Theera-Umpon, N.; Paengnakorn, P. Automatic Programmable Bioreactor with pH Monitoring System for Tissue Engineering Application. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.; Miller, J. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, M.; Makino, N.; Matsuda, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Kakizaki, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Kawata, S. High Glucose Accelerates Cell Proliferation and Increases the Secretion and mRNA Expression of Osteopontin in Human Pancreatic Duct Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbach, S.; Jansen, T.; Horke, S.; Heeren, T.; Scholz, A.; Coldewey, M.; Karpi, A.; Hausding, M.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Oelze, M.; et al. Hyperglycemia and oxidative stress in cultured endothelial cells—A comparison of primary endothelial cells with an immortalized endothelial cell line. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2012, 26, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorello, M.L.; Treweeke, A.T.; Macfarlane, D.P.; Megson, I.L. The impact of glucose exposure on bioenergetics and function in a cultured endothelial cell model and the implications for cardiovascular health in diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, T.M.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidics: Fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 77, 977–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.D.; Lin, X.-Y. Experimental Study on Microfluidic Mixing with Different Zigzag Angles. Micromachines 2019, 10, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, F.; Neves, A.; Lima, D.; Lourenço, S.; Silva, L.; Lima, K. Bioorganic Concepts Involved in the Determination of Glucose, Cholesterol and Triglycerides in Plasma via Enzymatic Colorimetric Method. Química Nova 2015, 38, 588–594. [Google Scholar]


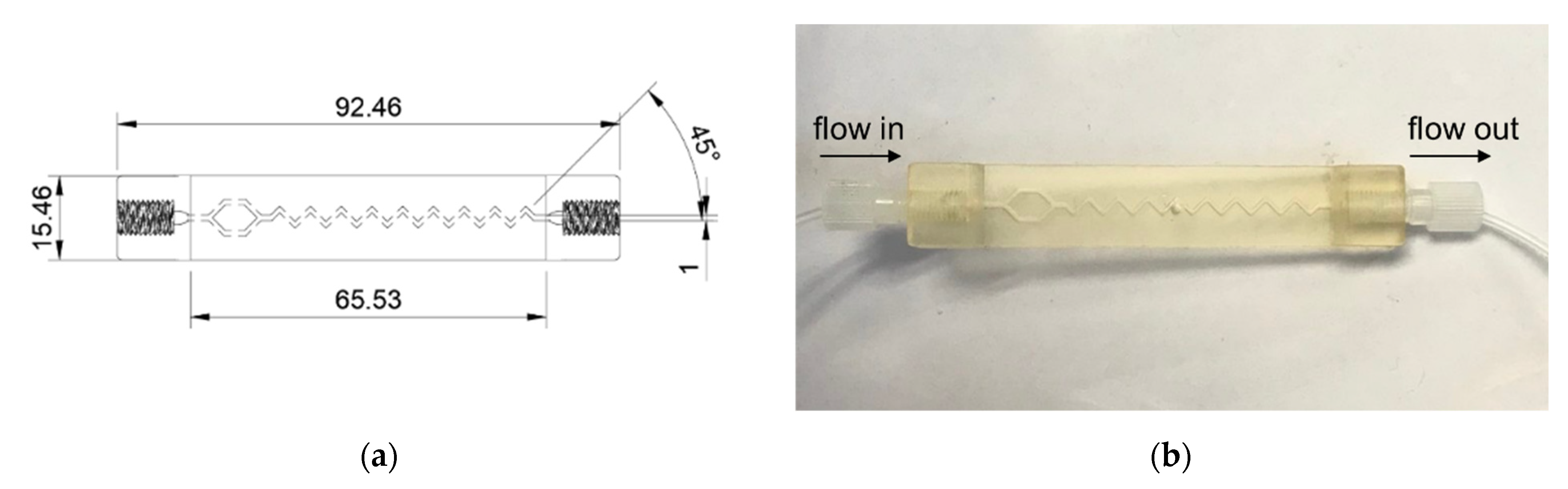
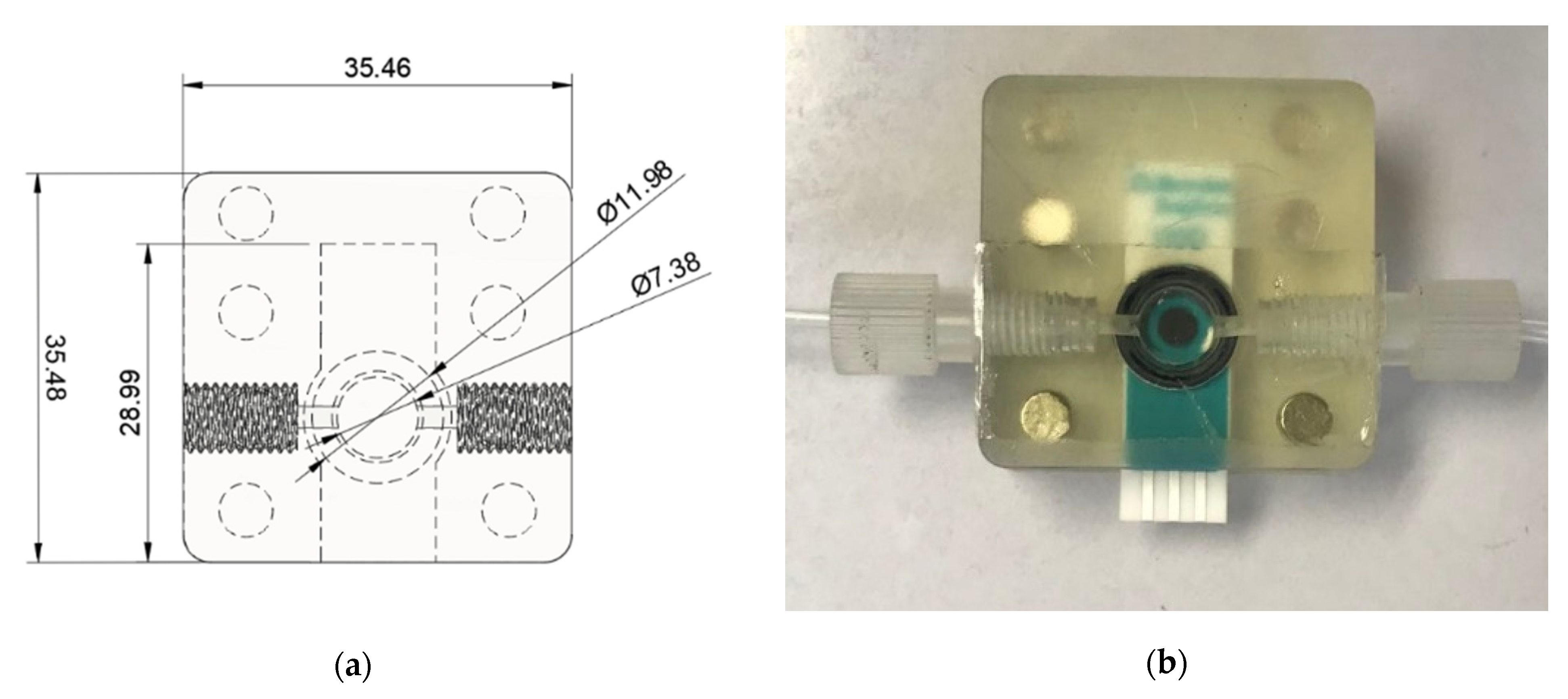
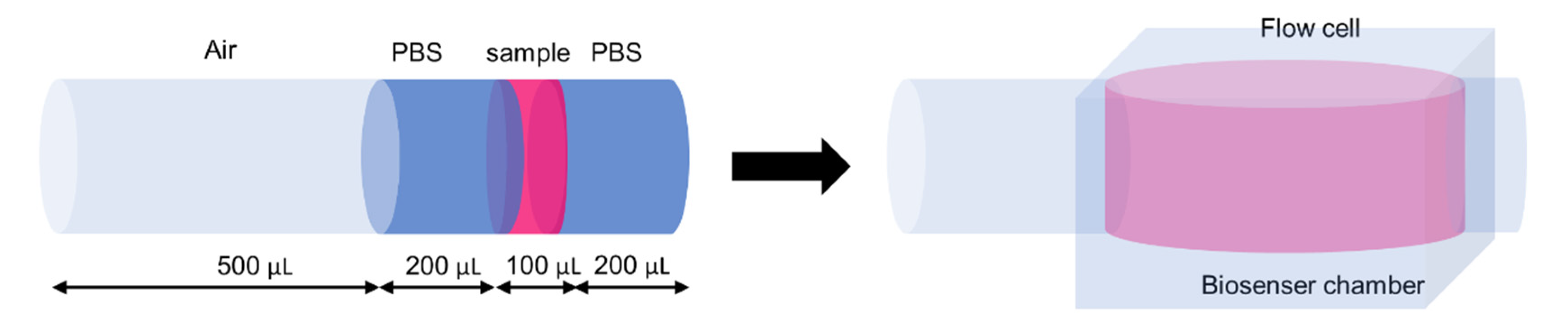
| Detection Technique | Sensor Components | Linear Range (mM) | Cell Type | In-Line Measurement | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical | Oxygen sensor covered with glucose oxidase enzyme, bovine serum albumin (BSA), glycerol, glutaraldehyde | 0–20 | Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) cells | Yes | [23] |
| Electrochemical | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes, chitosan, glucose oxidase enzyme | 5–25 | Human myeloid leukemia (U937) cells | Yes | [21,24] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometric) | Water-based carbon ink formulations containing cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPC), glucose oxidase enzyme | up to 5 | Human choriocarcinoma (BeWo) cells | Yes | [25] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometric) | pHEMA enzyme membrane containing glucose oxidase | up to 10 | Human glioblastoma multiforme (T98G) brain cancer cells | Yes | [26] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometric) | Carbon black–Prussian blue screen-printed electrode modified with Glucose oxidase and cellulose nanocrystals | 0.1–2 | NIH 3T3 fibroblast cells | No | [27] |
| Electrode | Sensitivity | Linear Range | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiwalled carbon nanotubes, chitosan, platinum nanoparticles, glucose oxidase enzyme, methyltrimethoxysilane (MTOS) | 2.8 µA mM−1 | 1.2 µM−6 mM | 0.3 µM | [17] |
| Silver nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, chitosan, glucose oxidase enzyme | 135.9 µA mM−1 | 0.5–50 µM | 0.1 µM | [18] |
| Carbon nanotubes, gold nanoparticles, chitosan, glucose oxidase enzyme | n/a | 6 µM–5 mM | 3 µM | [19] |
| Carbon-coated tin sulfide (C-SnS) nanoparticles, glucose oxidase enzyme | 439 nA mM−1 mm−2 | 0.03–0.7 mM | n/a | [20] |
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes, chitosan, glucose oxidase enzyme | 4.7 ± 1.3 nA mM−1 mm−2 | 5–25 mM * | 1.4 mM | [21] |
| Water-based carbon ink formulations containing cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPC), glucose oxidase enzyme | 6 nA mM−1 | Up to 5 mM * | n/a | [25] |
| pHEMA enzyme membrane containing glucose oxidase | 3.3 nA mM−1 mm−2 | Up to 10 mM * | 75 µM | [26] |
| Carbon black–Prussian blue screen-printed electrode modified with glucose oxidase and cellulose nanocrystals | 57 ± 3 nA mM−1mm−2 | 0.1–2 mM | 4 µM | [27] |
| This work | 66.8 nA mM−1 mm−2 | Up to 3.8 mM * | 0.3 mM |
| Command | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Loop | Number | Set number of scripts to repeat |
| Pump | Number | Set volume of syringe pump to aspirate or dispense (mL) |
| Goto | Number | Jump to a line number that set of the script |
| Wait | hh:mm:ss | Set delay time |
| Dir | F or B | Set syringe pump direction (forward or backward) |
| Ch | Selection valve (A or B or C or else) | Select selection valve position |
| Start | Starting syringe pump | |
| Msgbox | Text | Displays the specified text in the message box |
| Line Number | Command | Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Loop | 3 | Repeat all actions for 3 times |
| 2 | Pump | 0.5 | Aspirate air 500 μL into holding coil |
| 3 | Dir | B | |
| 4 | Ch | B | |
| 5 | Start | ||
| 6 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 7 | Pump | 0.2 | Aspirate PBS 200 μL into holding coil |
| 8 | Dir | B | |
| 9 | Ch | C | |
| 10 | Start | ||
| 11 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 12 | Pump | 0.1 | Aspirate sample 100 μL into holding coil |
| 13 | Dir | B | |
| 14 | Ch | E | |
| 15 | Start | ||
| 16 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 17 | Pump | 0.2 | Aspirate PBS 200 μL into holding coil |
| 18 | Dir | B | |
| 19 | Ch | C | |
| 20 | Start | ||
| 21 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 22 | Pump | 1 | Dispense all segment 1000 μL from holding coil to sensor |
| 23 | Dir | F | |
| 24 | Ch | A | |
| 25 | Start | ||
| 26 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 27 | Pump | 0.5 | Aspirate air 500 μL into holding coil (cleaning) |
| 28 | Dir | B | |
| 29 | Ch | B | |
| 30 | Start | ||
| 31 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 32 | Pump | 0.5 | Aspirate PBS 500 μL into holding coil (cleaning) |
| 33 | Dir | B | |
| 34 | Ch | C | |
| 35 | Start | ||
| 36 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 37 | Pump | 1 | Dispense all segment 1000 μL from holding coil to sensor (cleaning) |
| 38 | Dir | F | |
| 39 | Ch | A | |
| 40 | Start | ||
| 41 | Wait | 00:00:10 | |
| 42 | Goto | 2 | Repeat all actions for 3 times |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wongsa, C.; Udomsom, S.; Budwong, A.; Kiwfo, K.; Grudpan, K.; Paengnakorn, P. Sequential Injection Amperometric System Coupling with Bioreactor for In-Line Glucose Monitoring in Cell Culture Application. Molecules 2022, 27, 6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196665
Wongsa C, Udomsom S, Budwong A, Kiwfo K, Grudpan K, Paengnakorn P. Sequential Injection Amperometric System Coupling with Bioreactor for In-Line Glucose Monitoring in Cell Culture Application. Molecules. 2022; 27(19):6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196665
Chicago/Turabian StyleWongsa, Chanyanut, Suruk Udomsom, Apiwat Budwong, Kanokwan Kiwfo, Kate Grudpan, and Pathinan Paengnakorn. 2022. "Sequential Injection Amperometric System Coupling with Bioreactor for In-Line Glucose Monitoring in Cell Culture Application" Molecules 27, no. 19: 6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196665
APA StyleWongsa, C., Udomsom, S., Budwong, A., Kiwfo, K., Grudpan, K., & Paengnakorn, P. (2022). Sequential Injection Amperometric System Coupling with Bioreactor for In-Line Glucose Monitoring in Cell Culture Application. Molecules, 27(19), 6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196665








