A Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Histamine in Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
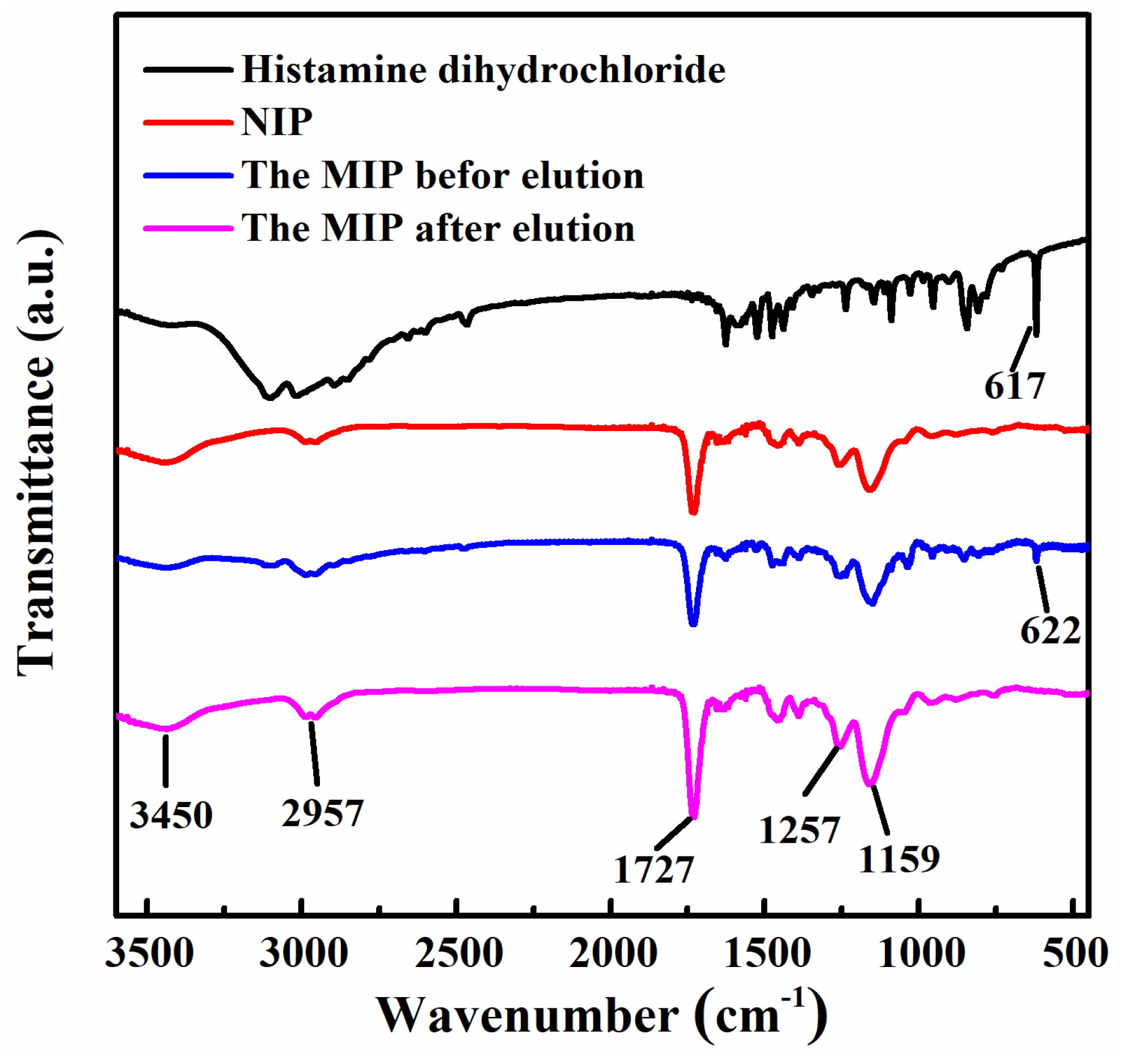
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the MIP
2.2. Optimization of the MISPE Procedures
2.3. Optimization of the CE Conditions
2.4. Analytical Parameters
2.5. Repeatability, Selectivity and Anti-Interference Capability of the MISPE-CE Method
2.6. Accuracy and Applicability of the MISPE-CE Method
2.7. Merits of the MISPE-CE Method
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Apparatus and CE Conditions
3.3. Synthesis of the MIP
3.4. The MISPE-CE Procedure
3.5. Sample Preparation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Biji, K.B.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Mohan, C.O.; Gopal, T.K.S. Biogenic amines in seafood: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamankesh, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Mollahosseini, A.; Seidi, S. Application of a novel electromembrane extraction and microextraction method followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine biogenic amines in canned fish. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Ye, W. Carbon Dots-modified nanoporous membrane and Fe3O4@Au magnet nanocomposites-based FRET assay for ultrasensitive histamine detection. Molecules 2019, 24, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, E.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z.; Irudayaraj, J. Bimodal counterpropagating-responsive sensing material for the detection of histamine. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 44933–44944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Zhuang, D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Fang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Rapid determination of histamine in fish by thin-layer chromatography-image analysis method using diazotized visualization reagent prepared with p-nitroaniline. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3386–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Scombrotoxin (histamine) formation. In Fish and Fisheries Products Hazards and Control Guidance; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 113–151. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Hong, C.; Huang, Z. Histamine detection in fish samples based on indirect competitive ELISA method using iron-cobalt co-doped carbon dots labeled histamine antibody. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kočar, D.; Köse, S.; Koral, S.; Tufan, B.; Ščavničar, A.; Pompe, M. Analysis of Biogenic Amines Using Immunoassays, HPLC, and a Newly Developed IC-MS/MS Technique in Fish Products-A Comparative Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounnoun, A.; El Maadoudi, M.; Cacciola, F.; Mondello, L.; Bougtaib, H.; Alahlah, N.; Amajoud, N.; El Baaboua, A.; Louajri, A. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of histamine in fish samples using fluorescence detection with pre-column derivatization. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Tayebee, R.; Abdar, A.; Sani, F.N. Synthesis of a zinc-based metal-organic framework with histamine as an organic linker for the dispersive solid-phase extraction of organophosphorus pesticides in water and fruit juice samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1597, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Phillippy, A.M.; Deng, K.; Rui, X.; Li, Z.; Tortorello, M.L.; Zhang, W. Transcriptomic responses of Salmonella enterica serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium to chlorine-based oxidative stress. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 5013–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, I.M.; Apetrei, C. Amperometric Biosensor Based on Diamine Oxidase/Platinum Nanoparticles/Graphene/Chitosan Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Histamine Detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voeten, R.L.C.; Ventouri, I.K.; Haselberg, R.; Somsen, G.W. Capillary electrophoresis: Trends and recent advances. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1464–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riasová, P.; Jenčo, J.; Moreno-González, D.; Heyden, Y.V.; Mangelings, D.; Polášek, M.; Jáč, P. Development of a capillary electrophoresis method for the separation of flavonolignans in silymarin complex. Electrophoresis 2022, 43, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Montero, L.; Llorens, L.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Cifuentes, A. Recent advances in the application of capillary electromigration methods for food analysis and Foodomics. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 136–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Perez-Cejuela, H.; Benavente, F.; Simo-Alfonso, E.F.; Herrero-Martinez, J.M. A hybrid nano-MOF/polymer material for trace analysis of fluoroquinolones in complex matrices at microscale by on-line solid-phase extraction capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 2021, 233, 122529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, L.; Marin, G.; Vergara-Barberan, M.; Gagliardi, L.G.; Sanz-Nebot, V.; Herrero-Martinez, J.M.; Benavente, F. Polymeric monolithic microcartridges with gold nanoparticles for the analysis of protein biomarkers by on-line solid-phase extraction capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Cui, Y.; Yang, C.; Yan, X. Synthesis of magnetic amino-functionalized microporous organic network composites for magnetic solid phase extraction of endocrine disrupting chemicals from water, beverage bottle and juice samples. Talanta 2020, 206, 120179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Fang, G.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. On-line SPE coupled with LC for analysis of traces of Sudan dyes in foods. Chromatographia 2010, 71, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Meng, C.; Li, J.; He, L. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the determination of ten macrolide drugs residues in animal muscles by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, T.; Zhou, H.; Yu, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid phase extraction. Chromatographia 2006, 64, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Yao, S. Synthesis and application of multiwalled carbon nanotubes-molecularly imprinted sol-gel composite material for on-line solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography determination of trace Sudan IV. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 661, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebnasagh, A.; Karimi, G.; Mohajeri, S.A. Preparation and evaluation of histamine imprinted polymer as a selective sorbent in molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography analysis in canned fish. Food Anal. Method. 2014, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Nazari, Z.; Noshirvani, N. Synthesis of chitosan based magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective separation and spectrophotometric determination of histamine in tuna fish. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, J.O.; Nolan, K.; Smyth, M.R.; Mizaikoff, B. Molecularly imprinted polymers-potential and challenges in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 534, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, H.; Ma, S.; Bo, C.; Ou, J.; Gong, B. Recent application of molecular imprinting technique in food safety. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1657, 462579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassana, A.H.A.; Sappia, L.; Moura, S.L.; Ali, F.H.M.; Moselhy, W.A.; Sotomayor, M.D.T.; Pividori, M.I. Biomimetic magnetic sensor for electrochemical determination of scombrotoxin in fish. Talanta 2019, 194, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourado, C.S.; Domingues, I.F.F.; Magalhães, L.O.; Casarin, F.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Braga, J.W.B.; Dias, A.C.B. Optimization of a saccharin molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction procedure and evaluation by MIR hyperspectral imaging for analysis of diet tea by HPLC. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, R.; Noroozian, E.; Jassbi, A.R. Molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the analysis of 1,8-cineole in thyme and sagebrush distillates. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabkhani, S.; Pourmoslemi, S.; Harchegani, A.L. Rapid determination of metanil yellow in turmeric using a molecularly imprinted polymer dispersive solid-phase extraction and visible light spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. Fluorescent sensing probe for the sensitive detection of histamine based on molecular imprinting ionic liquid-modified quantum dots. Food Anal. Method 2017, 10, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhao, L.; Chu, B.; Feng, Q.; Yan, W.; Lin, J. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the selective determination of 17 β-estradiol in fishery samples with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2009, 78, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, R.A.; Flores, D.H.Â.; da Silva, R.C.S.; Dutra, F.V.A.; Borges, K.B. Pipette-tip solid-phase extraction using poly(1-vinylimidazole-co-trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate) as a new molecularly imprinted polymer in the determination of avermectins and milbemycins in fruit juice and water samples. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numanoglu, E.; Boyaci, I.H.; Topcu, A. Simple determination of histamine in cheese by capillary electrophoresis with diode array detection. J. Food Drug Anal. 2008, 16, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasnicka, F.; Kavkova, S.; Honzlova, A. Electrophoretic determination of histamine. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Villar, N.; Saurina, J.; Hernandez-Cassou, S. Capillary electrophoresis determination of biogenic amines by field-amplified sample stacking and in-capillary derivatization. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginterova, P.; Marak, J.; Stanova, A.; Maier, V.; Sevcik, J.; Kaniansky, D. Determination of selected biogenic amines in red wines by automated on-line combination of capillary isotachophoresis-capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 904, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, L.; Valese, A.C.; Azevedo, M.S.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Piovezan, M.; Vistuba, J.P.; Micke, G.A. Development of a fast and selective separation method to determine histamine in tuna fish samples using capillary zone electrophoresis. Talanta 2013, 106, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. A surface-imprinted surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensor for histamine detection based on dual semiconductors and Ag nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Samples | Original Level (μg/L) | Added Level (μg/L) | Found Level (μg/L) | Recovery (±RSD, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.00 | 21.95 | 92.63 ± 3.13 | ||
| Rice vinegar | 14.54 | 10.00 | 25.13 | 105.90 ± 2.30 |
| 15.00 | 31.19 | 111.00 ± 2.03 | ||
| 8.00 | 17.10 | 93.38 ± 4.26 | ||
| Liquor | 9.63 | 10.00 | 20.03 | 104.00 ± 3.31 |
| 15.00 | 24.12 | 96.60 ± 3.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Xu, Z. A Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Histamine in Foods. Molecules 2022, 27, 6987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206987
Fan Y, Yu R, Chen Y, Sun Y, Waterhouse GIN, Xu Z. A Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Histamine in Foods. Molecules. 2022; 27(20):6987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206987
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yixuan, Runze Yu, Yongfeng Chen, Yufeng Sun, Geoffrey I. N. Waterhouse, and Zhixiang Xu. 2022. "A Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Histamine in Foods" Molecules 27, no. 20: 6987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206987
APA StyleFan, Y., Yu, R., Chen, Y., Sun, Y., Waterhouse, G. I. N., & Xu, Z. (2022). A Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Histamine in Foods. Molecules, 27(20), 6987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206987










