Thermal and Rheological Performances Evaluation of a Modified Biopolymer for Fracturing Fluid System
Abstract
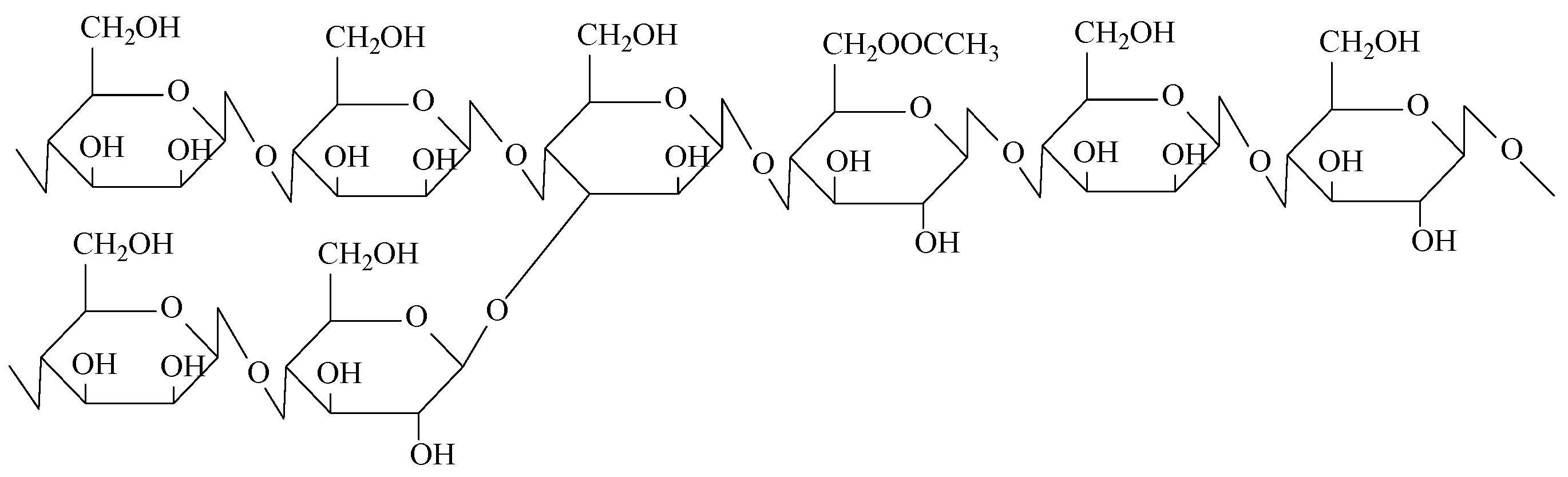
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
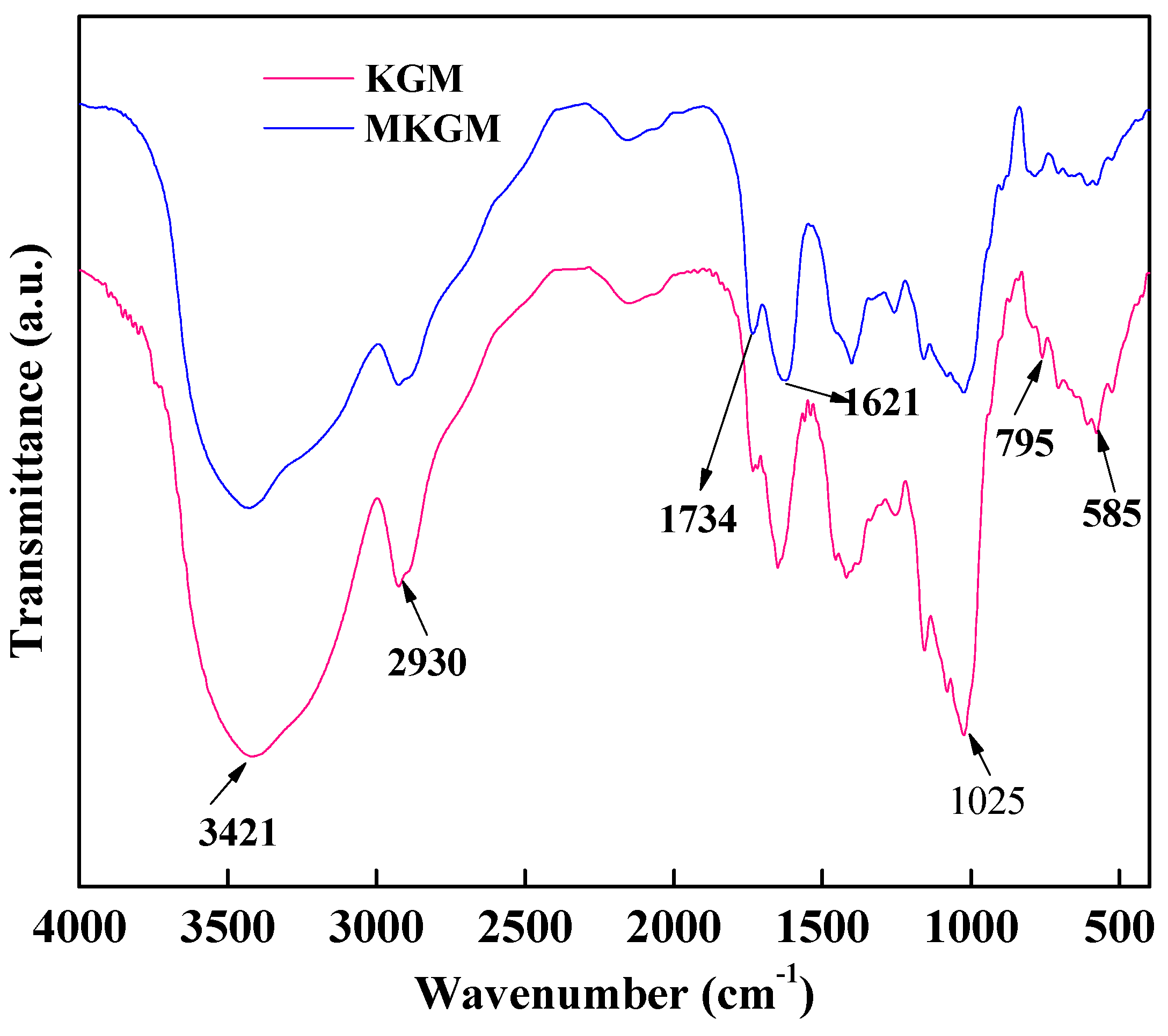
2.1. ATR-FTIR Analysis
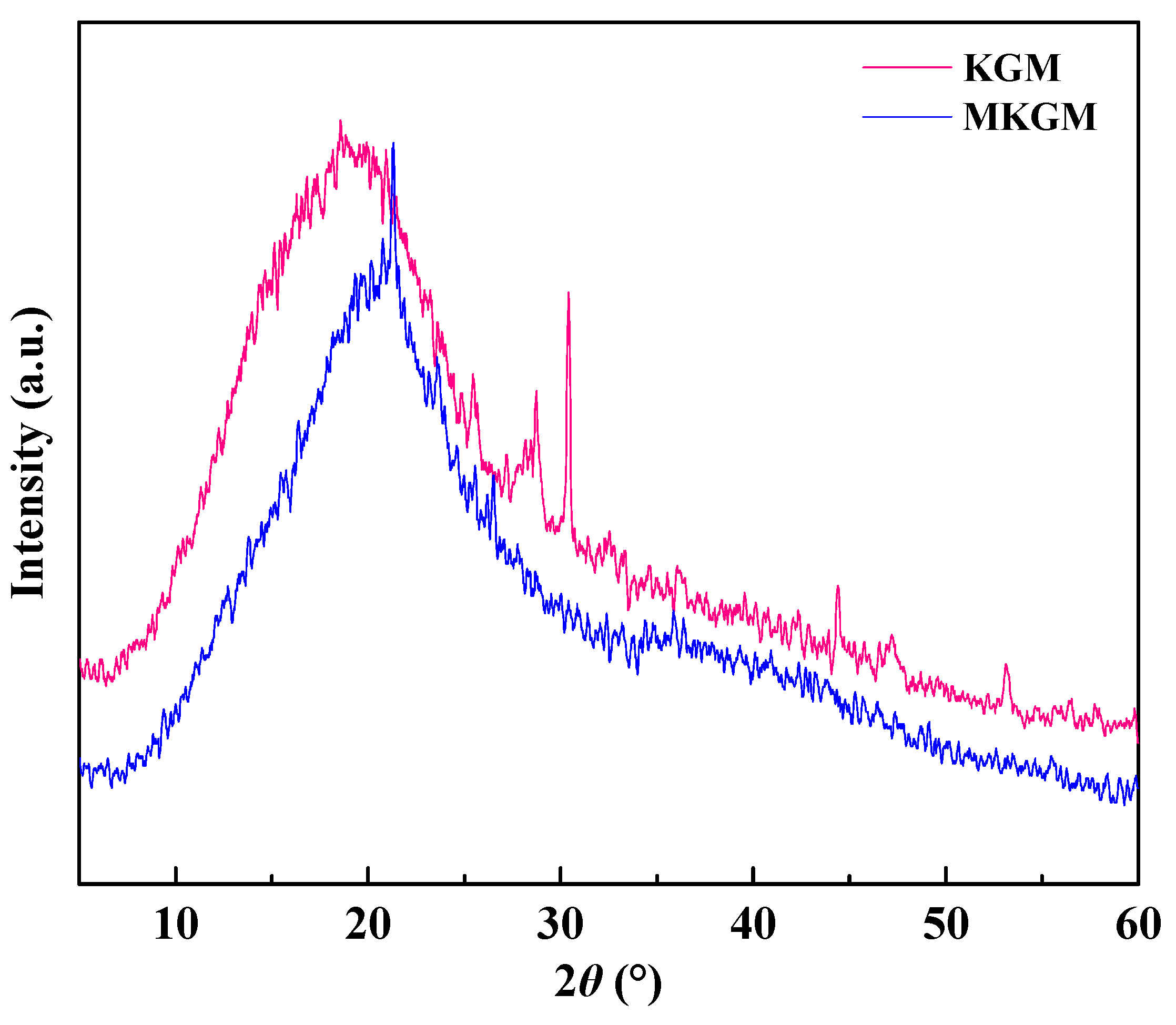
2.2. XRD Analysis
2.3. Thermal Analysis
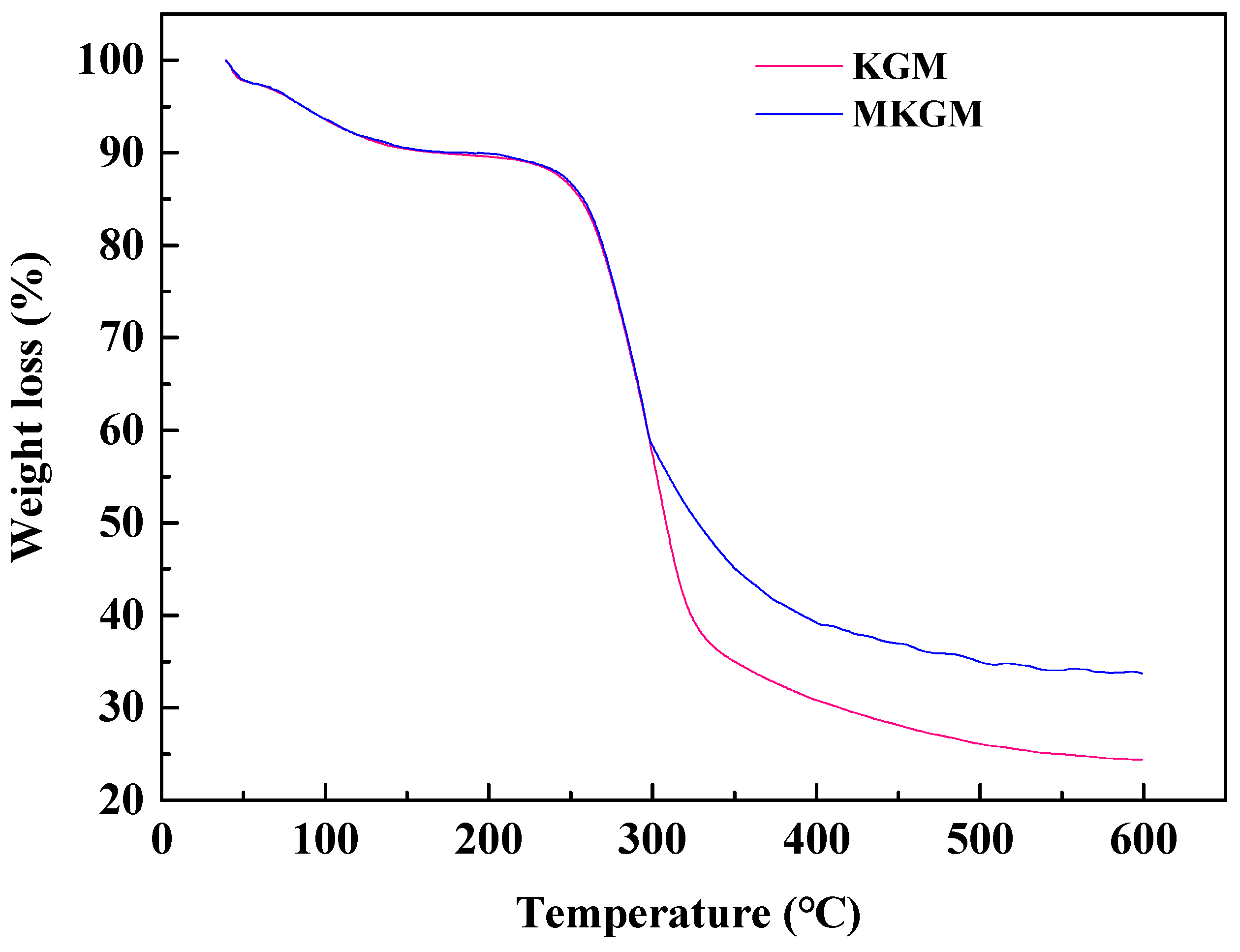
2.3.1. Thermal Stability Analysis
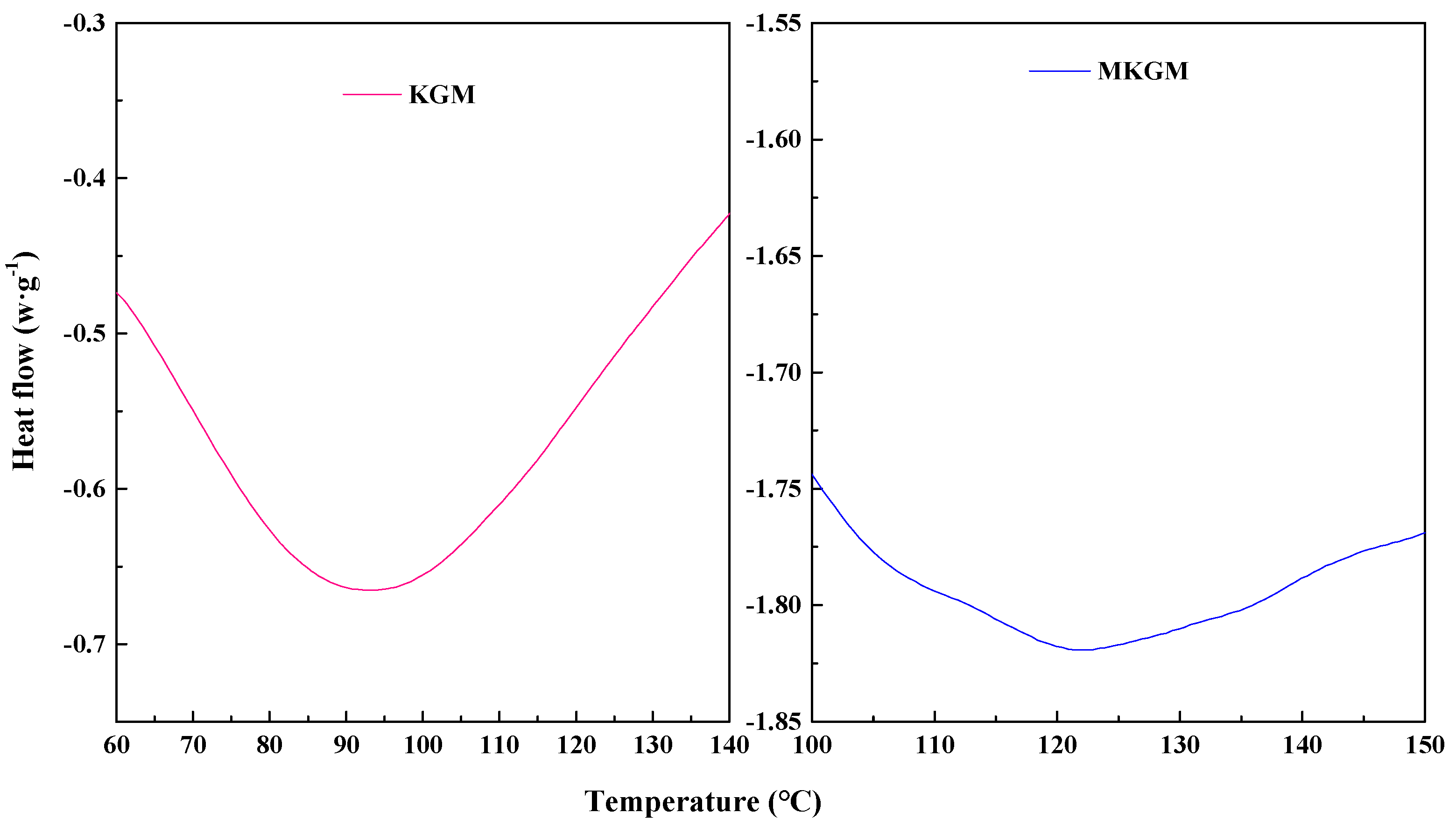
2.3.2. DSC Analysis
2.4. Rheological Performances Analysis
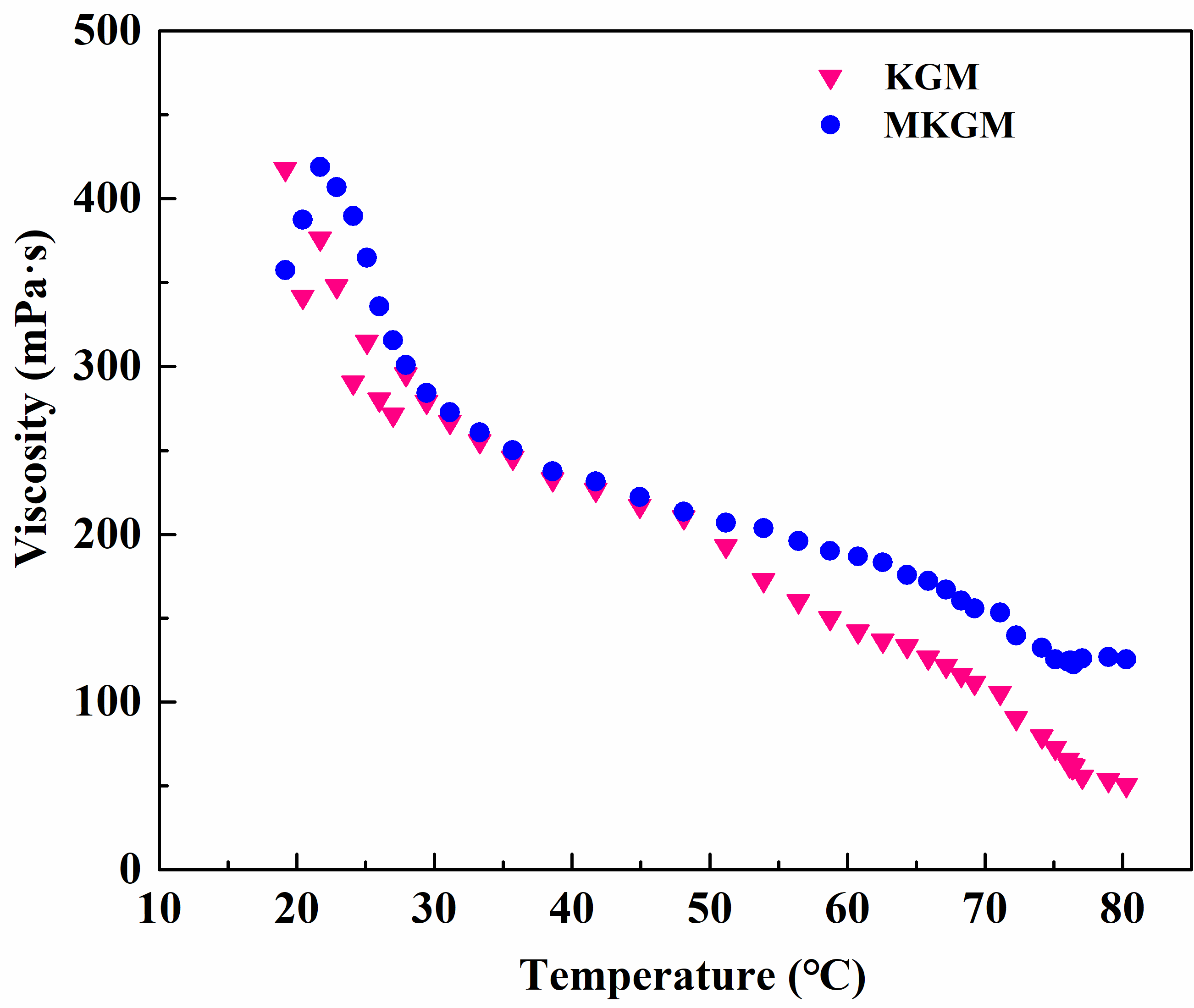
2.4.1. Temperature Resistance Test
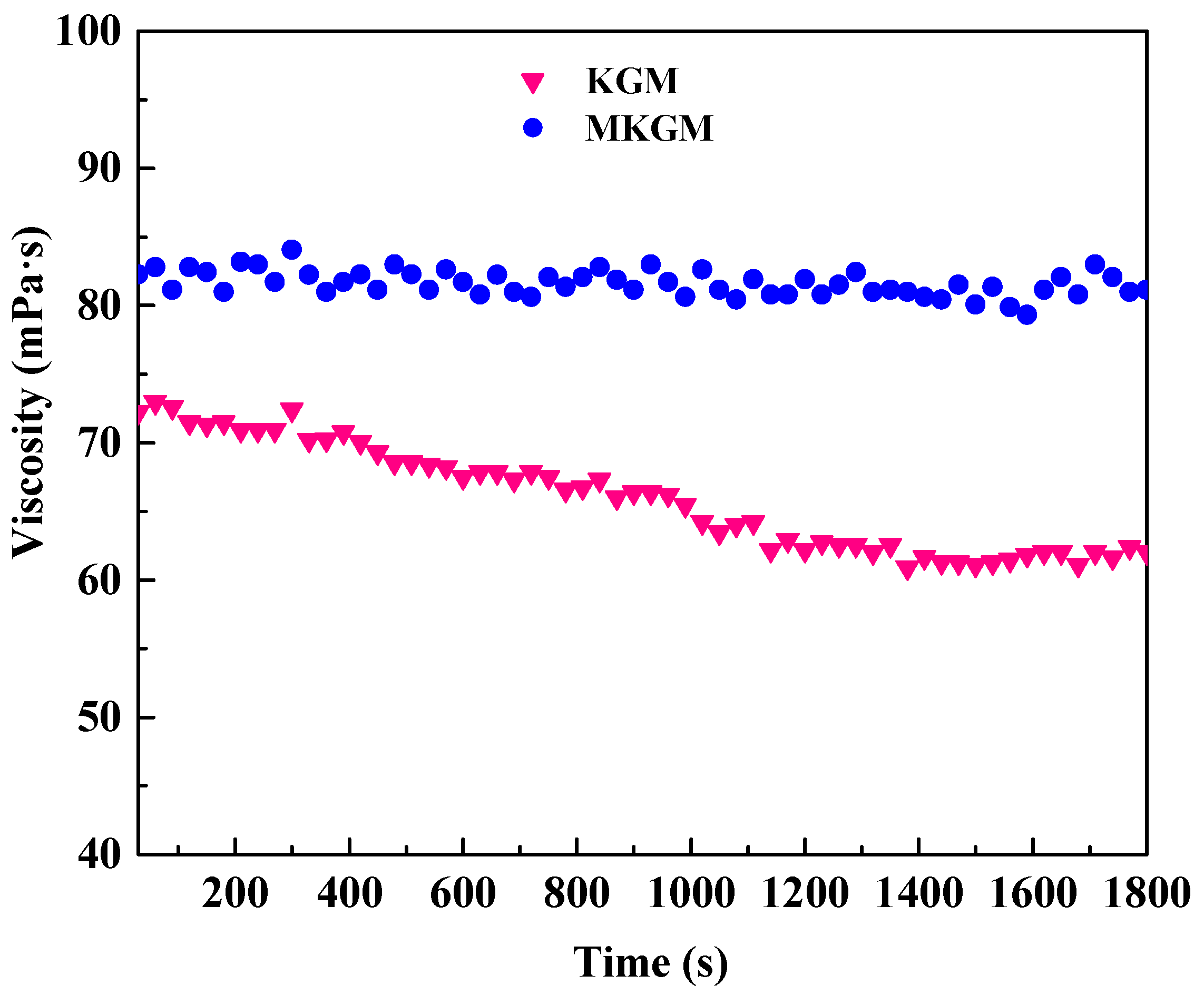
2.4.2. Shear Resistance Test
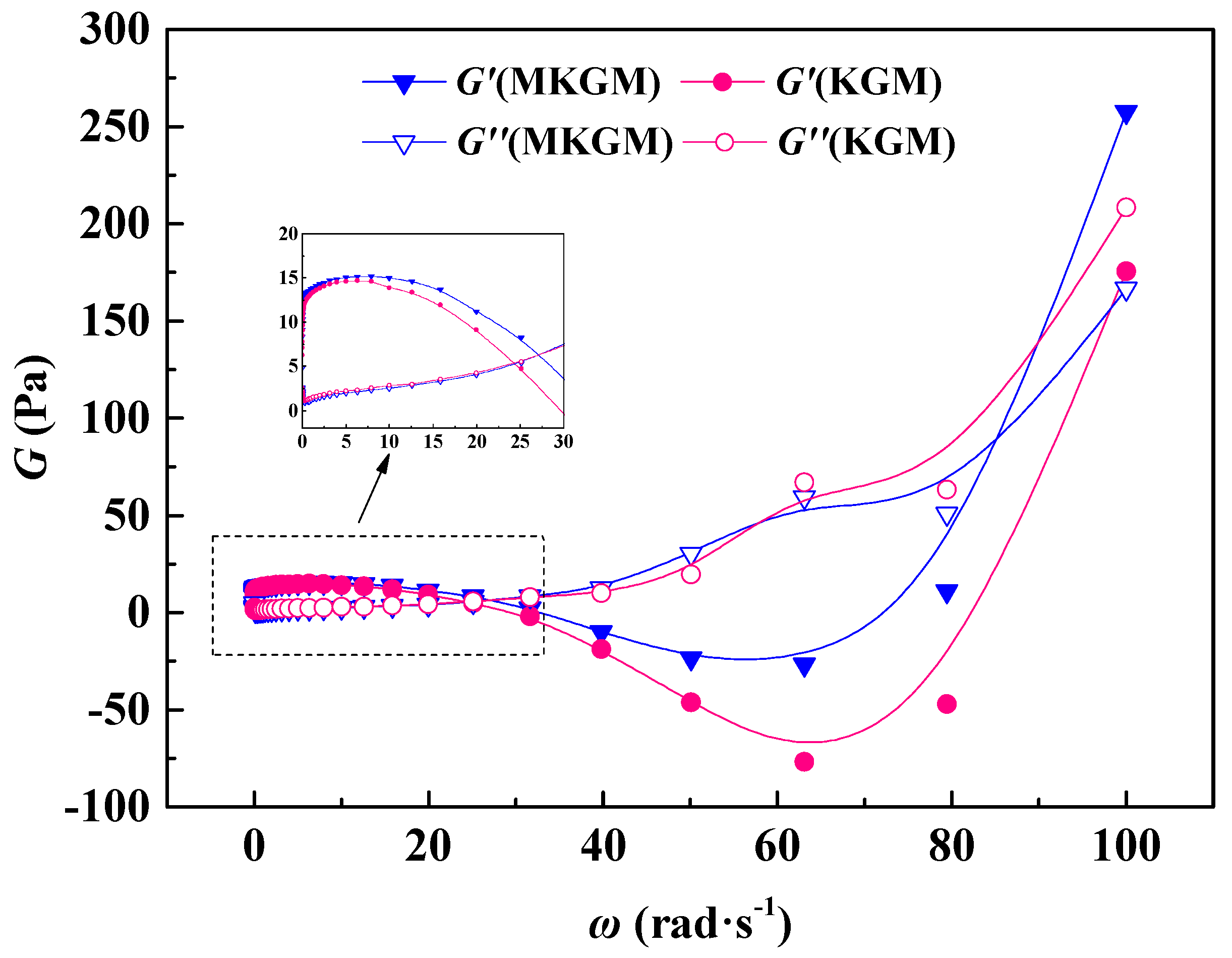
2.4.3. Viscoelastic Properties Test
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Preparation of Modified Konjac Glum (MKGM)
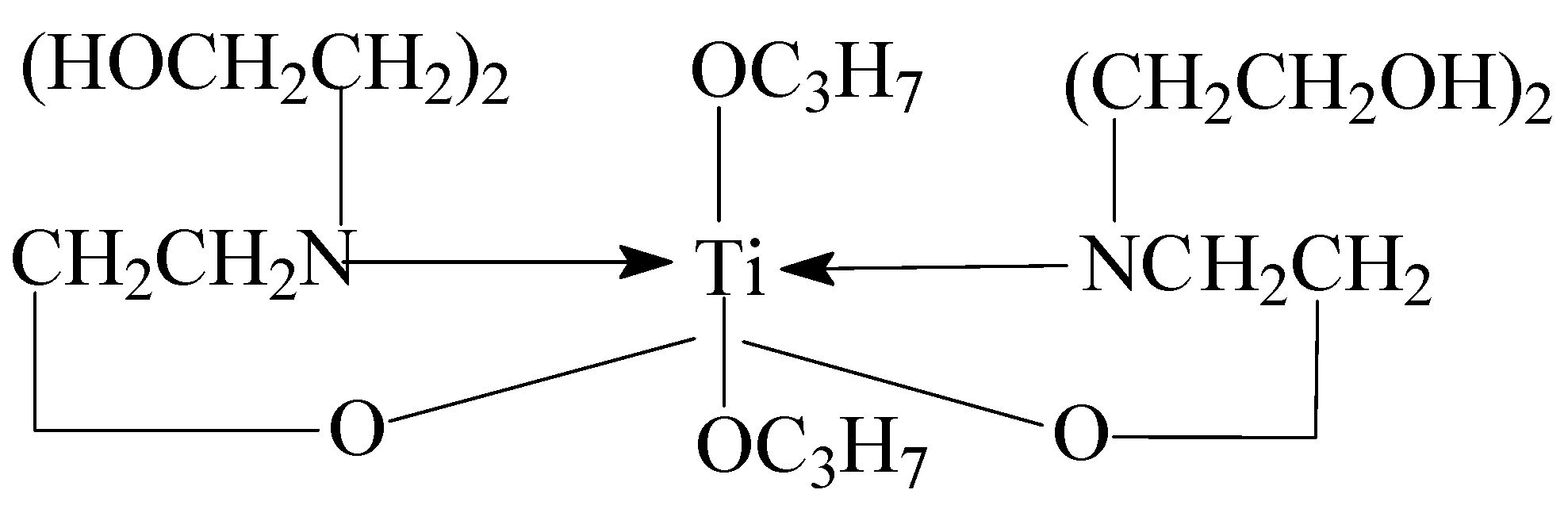
3.2.2. Preparation of Organic Titanium High-Temperature Stabilizer
3.2.3. Preparation of Organic Borate Cross-Linker
3.2.4. Preparation of the Fracturing Fluid System
- (1)
- Preparation of MKGM and KGM base solution. A total of 0.35 g of MKGM was slowly added to 100 mL of water under vigorous stirring for 30 min after MKGM had uniformly dissolved in the water. The MKGM solution was then standing for 2 h before use. The KGM solution was also prepared following the above steps.
- (2)
- Preparation of MKGM and KGM gels. Totals of 0.3 g of organic titanium high-temperature stabilizer and 0.8 g of organic borate cross-linker were both placed in MKGM base solutions (100 mL). A cross-linked MKGM gel was formed by manually stirring the mixture until the gel could be hung up easily. The KGM gel was also prepared following the above steps. Once the gels were prepared, they could immediately be used for evaluation tests [16].
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hudiyanti, D.; Al Khafiz, M.F.; Anam, K.; Siahaan, P.; Christa, S.M. In vitro evaluation of curcumin encapsulation in gum arabic dispersions under different environments. Molecules 2022, 27, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.D.; Yang, F.Q. Konjac glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide for OCDDS. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zong, M.; Li, G. Lipase-catalyzed acylation of konjac glucomannan in organic media. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatirat, O.; Charoenrein, S.; Kerr, W.L. Physicochemical properties of extrusion-modified konjac glucomannan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gan, J.; Nirasawa, S.; Tatsumi, E.; Yin, L.; Cheng, Y. Effects of sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate on colloidal properties and molecular characteristics of konjac glucomannan hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, Q.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S.; Luo, X. Synthesis of konjac glucomannan acetate with high degree of substitution and of its rheological and thermoplastic properties. Acta Polym. Sin. 2010, 41, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y. Gelation mechanism of alkali induced heat-set konjac glucomannan gel. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zongo, A.W.S.; Shah, B.R.; Li, J.; Li, B. Konjac Glucomannan (KGM), deacetylated KGM (Da-KGM), and degraded KGM derivatives: A special focus on colloidal nutrition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12921–12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Nakaya, M.; Kondo, T.; Nakazawa, M.; Ueda, M.; Naganawa, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sakamoto, T. Gelation of konjac glucomannan by acetylmannan esterases from Aspergillus oryzae. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2022, 160, 110075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; You, J.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Q. Gelling properties of silver carp surimi incorporated with konjac glucomannan: Effects of deacetylation degree. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zou, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Zhan, F.; Li, B. Partial removal of acetyl groups in konjac glucomannan significantly improved the rheological properties and texture of konjac glucomannan and κ-carrageenan blends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Modifications of konjac glucomannan for diverse applications. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.H.; Karim, A.; Seow, C.C. Effects of acid modification on physical properties of konjac glucomannan (KGM) films. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Zhuo, X.; Liang, L. Preparation and characterization of polylactide/thermoplastic konjac glucomannan blends. Polymer 2009, 50, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Lai, J.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Qi, Y. A study of relation between suspension behavior and microstructure and viscoelastic property of guar gum fracturing fluid. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 124, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; Lei, S.; Yi, H.; Guo, J. Influence of Nanomaterial Morphology of Guar-gum Fracturing Fluid, Physical and Mechanical Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, N.; Wen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; He, W.; Chen, Y. Polymer flooding in high-temperature and high-salinity heterogeneous reservoir by using diutan gum. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 188, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix da Silva, D.; Ogawa, C.Y.L.; Sato, F.; Neto, A.M.; Larsen, F.H.; Matumoto-Pintro, P.T. Chemical and physical characterization of Konjac glucomannan-based powders by FTIR and 13C MAS NMR. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Synthesis and characterization of polycationic chitosan-graft-poly (l-lysine). Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Peng, S.; Wen, C.; Wang, X.; Fan, L.; Deng, R.; Pang, J. Structural characterization and properties of konjac glucomannan/curdlan blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Li, B.; Kennedy, J.F.; Xie, B.J.; Huang, M. Characterization of konjac glucomannan–gellan gum blend films and their suitability for release of nisin incorporated therein. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, K.; Xiao, M.; Kuang, Y.; Corke, H.; Ni, X.; Jiang, F. Structural characterization and properties of konjac glucomannan and zein blend films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Huang, Y.; Ying, H.; Xiao, C. Preparation and characterization of a quaternary ammonium derivative of konjac glucomannan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M. Effects of konjac glucomannan on pasting and rheological properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 89, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Jiang, L.; Yang, K. Preparation, rheological and drag reduction properties of hydrophobically associating polyacrylamide polymer. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; He, P.; Lin, X. The mechanism of sodium hydroxide solution promoting the gelation of Konjac glucomannan (KGM). Food Hydrocolloid. 2013, 30, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Cui, B.; Yuan, C.; Zou, Y.; Liu, W.; Pan, Y. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the rheological, microstructure and digestibility properties of debranched corn starch. Food Hydrocolloid. 2020, 100, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, G.; Wang, L.; Hao, C.; Du, C.; Ma, H. Thermal and Rheological Performances Evaluation of a Modified Biopolymer for Fracturing Fluid System. Molecules 2022, 27, 7776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227776
Ma G, Wang L, Hao C, Du C, Ma H. Thermal and Rheological Performances Evaluation of a Modified Biopolymer for Fracturing Fluid System. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227776
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Guoyan, Le Wang, Chao Hao, Chunbao Du, and Hongfei Ma. 2022. "Thermal and Rheological Performances Evaluation of a Modified Biopolymer for Fracturing Fluid System" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227776
APA StyleMa, G., Wang, L., Hao, C., Du, C., & Ma, H. (2022). Thermal and Rheological Performances Evaluation of a Modified Biopolymer for Fracturing Fluid System. Molecules, 27(22), 7776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227776






