Understanding the Role of the Lateral Dimensional Property of Graphene Oxide on Its Interactions with Renal Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
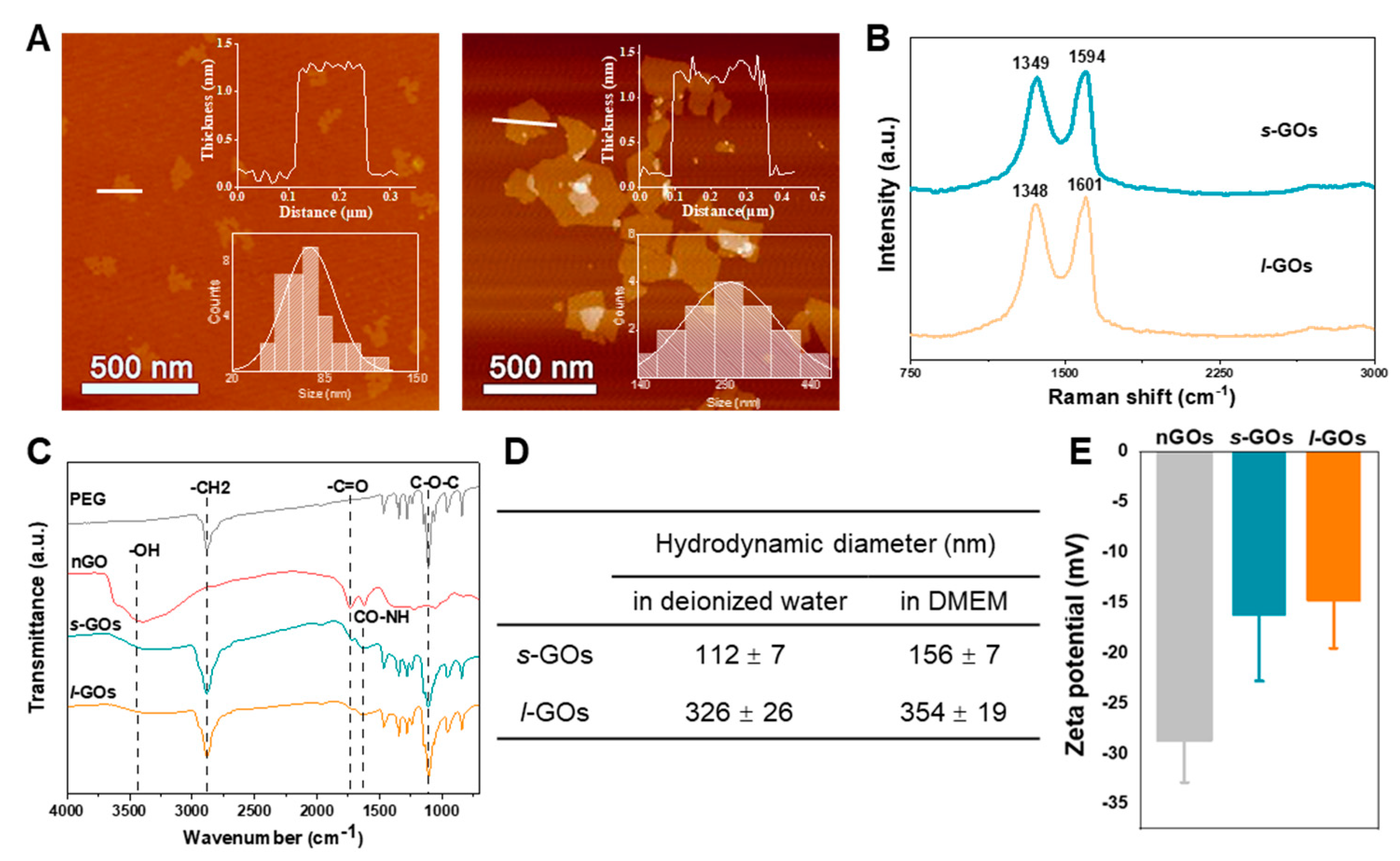
2.1. Physiochemical Properties of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets (GOs)
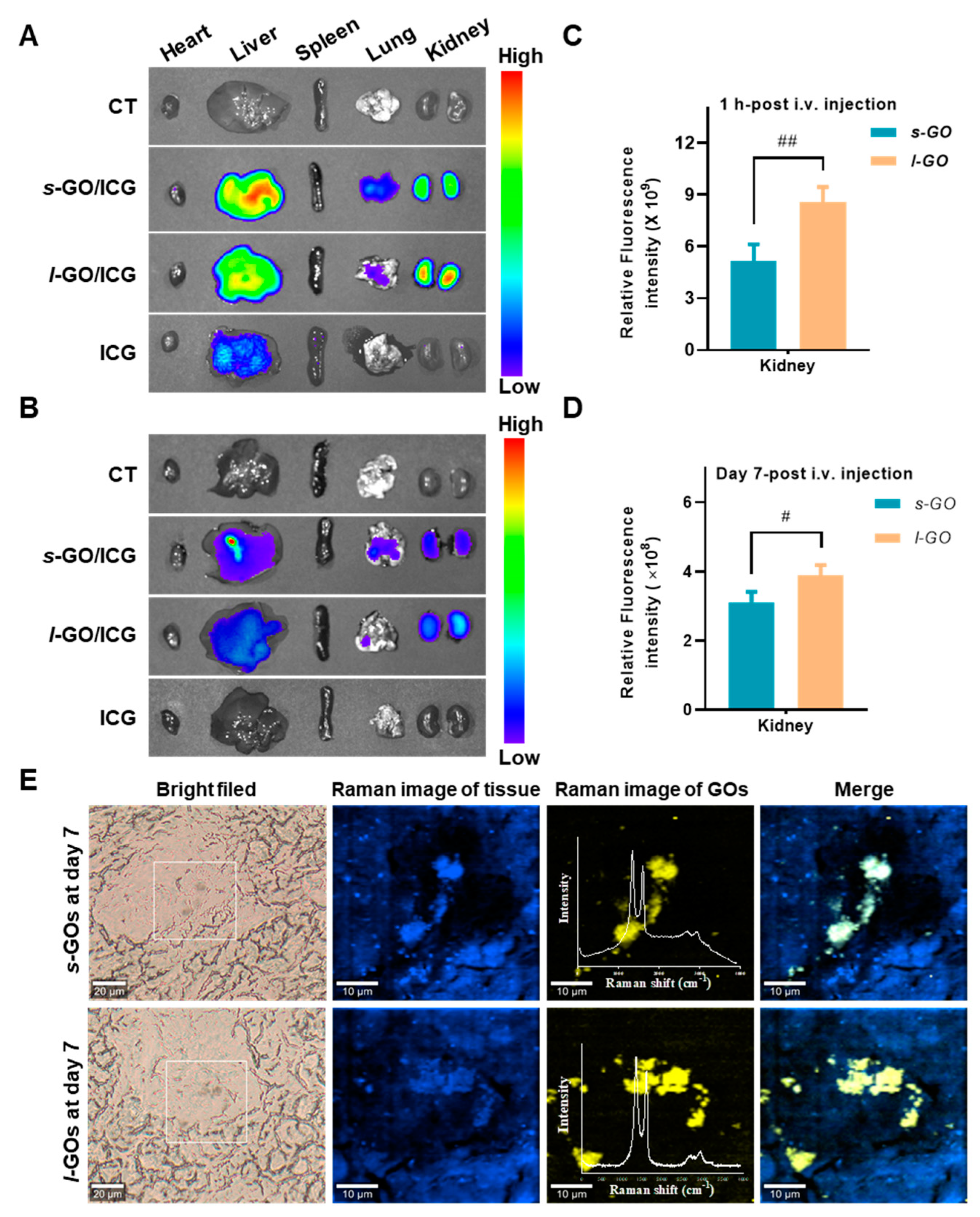
2.2. Renal Clearance of GOs after i.v. Injection
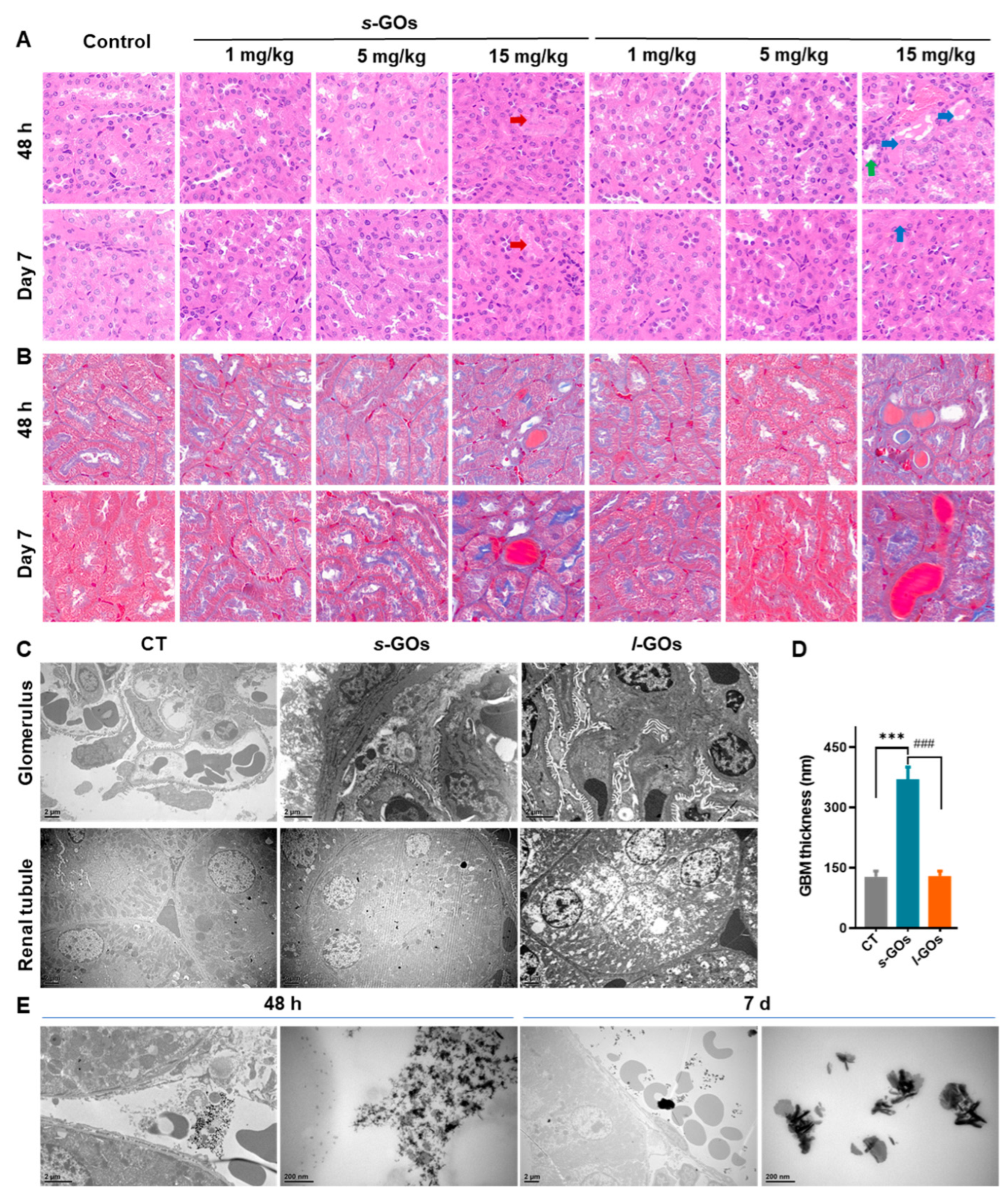
2.3. Pathological Changes in the Glomeruli and Renal Tubules
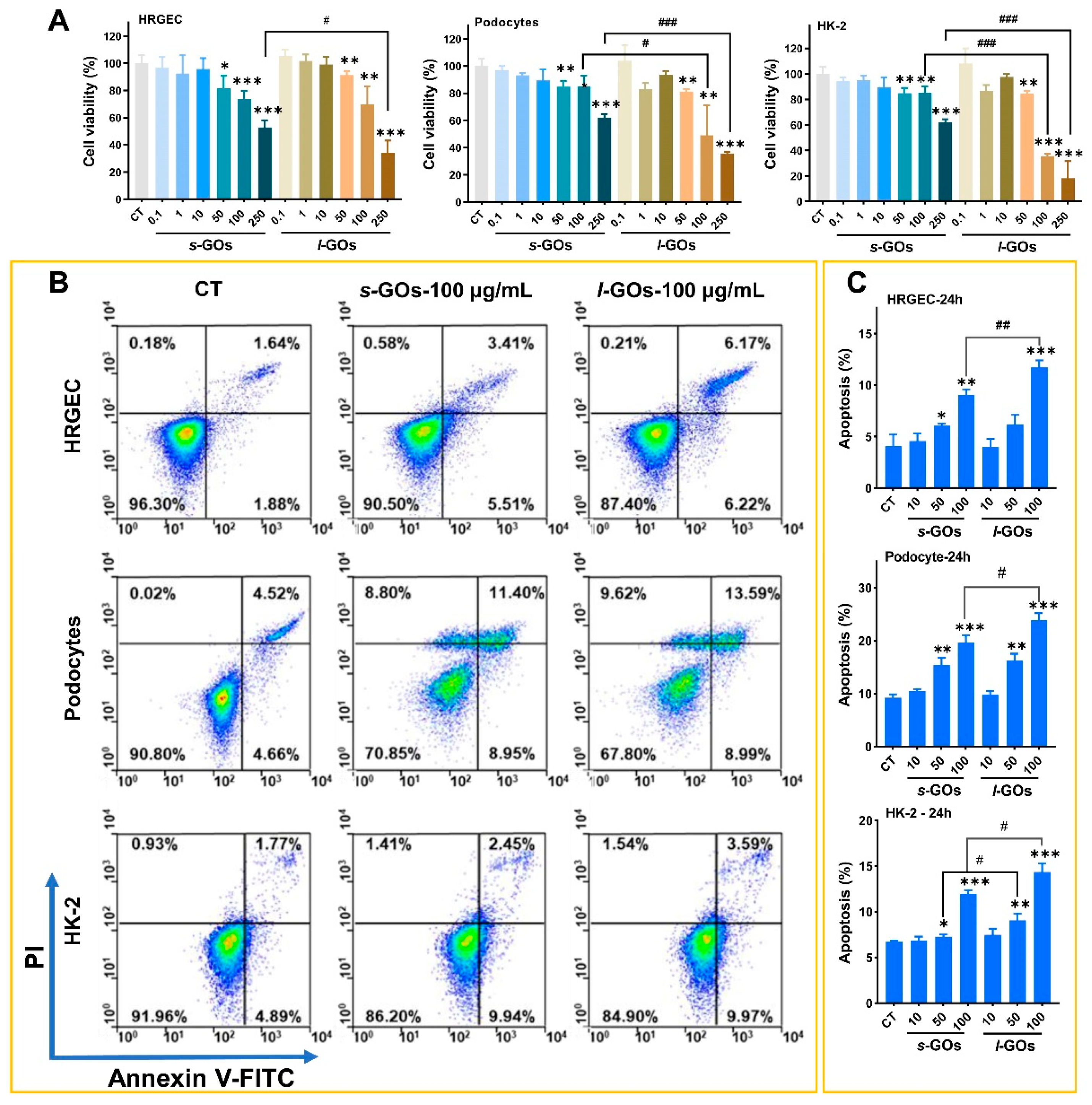
2.4. High-Dose GO-Treatment-Induced Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in HRGECs, Human Podocyte Primary Cells, and HK-2 Cells
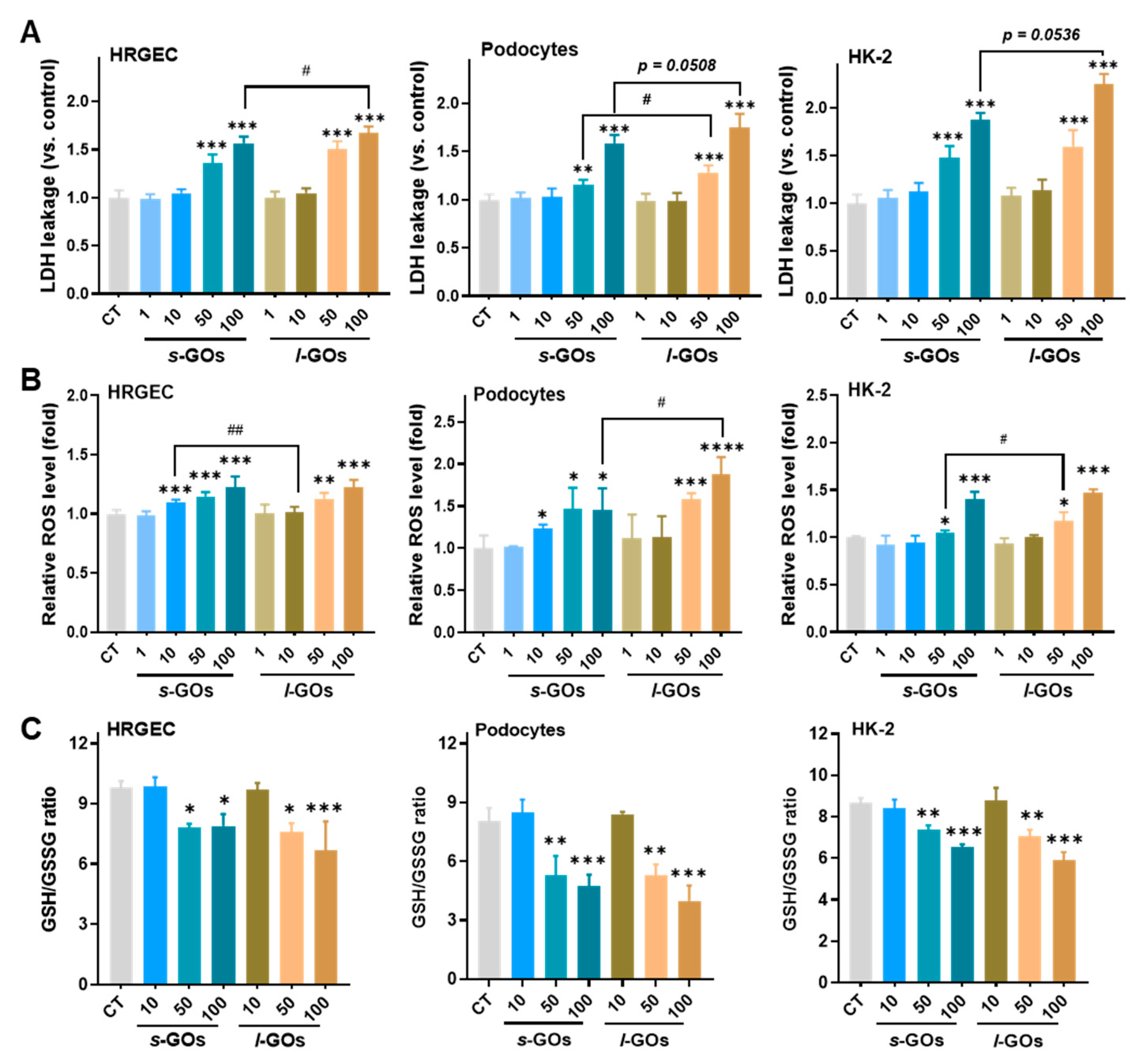
2.5. High Dose of GO Treatments Induced Intracellular LDH Release and Oxidative Stress in HRGECs, Podocytes, and HK-2 Cells
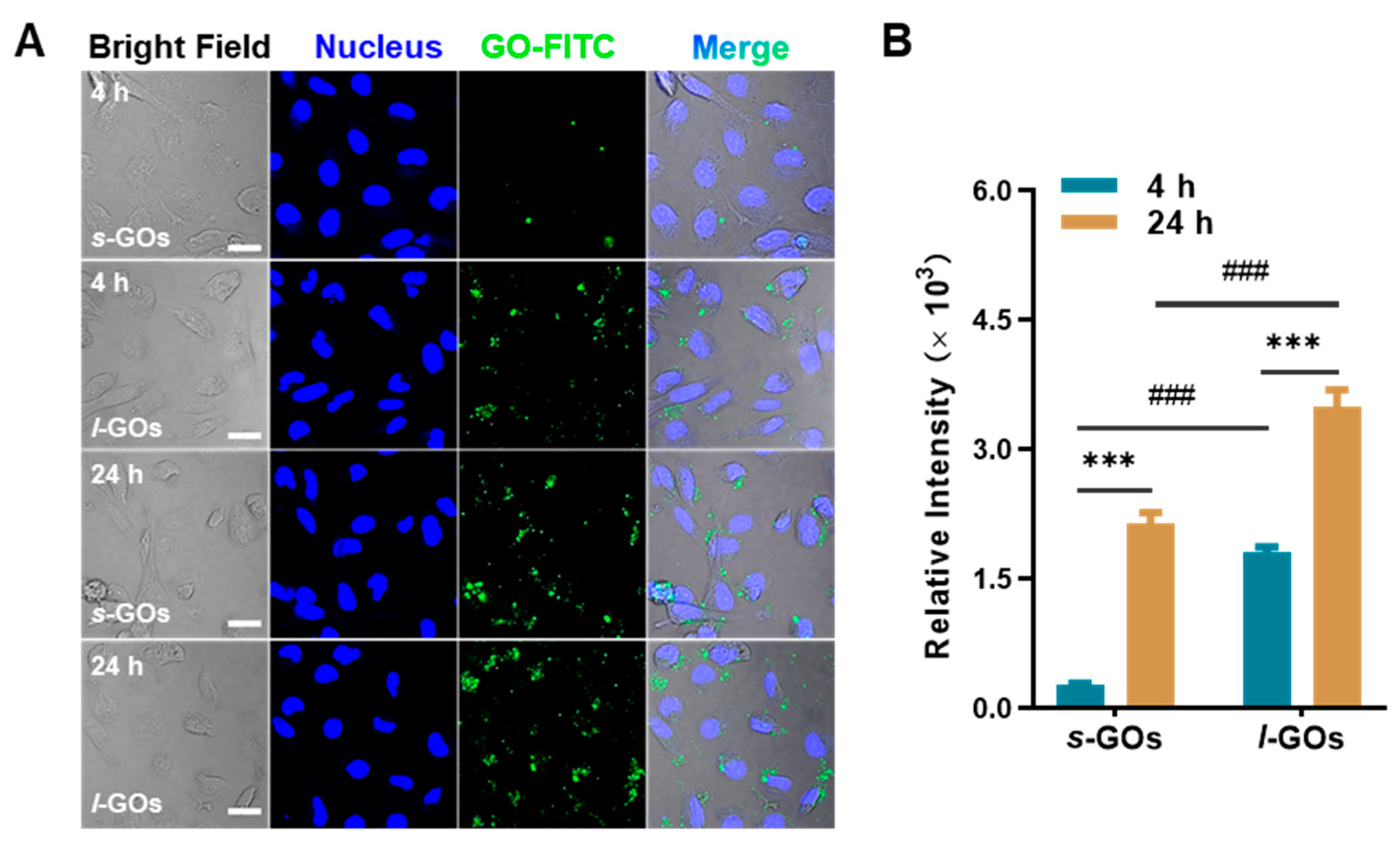
2.6. Cellular Uptake of GOs in HK-2 Cells
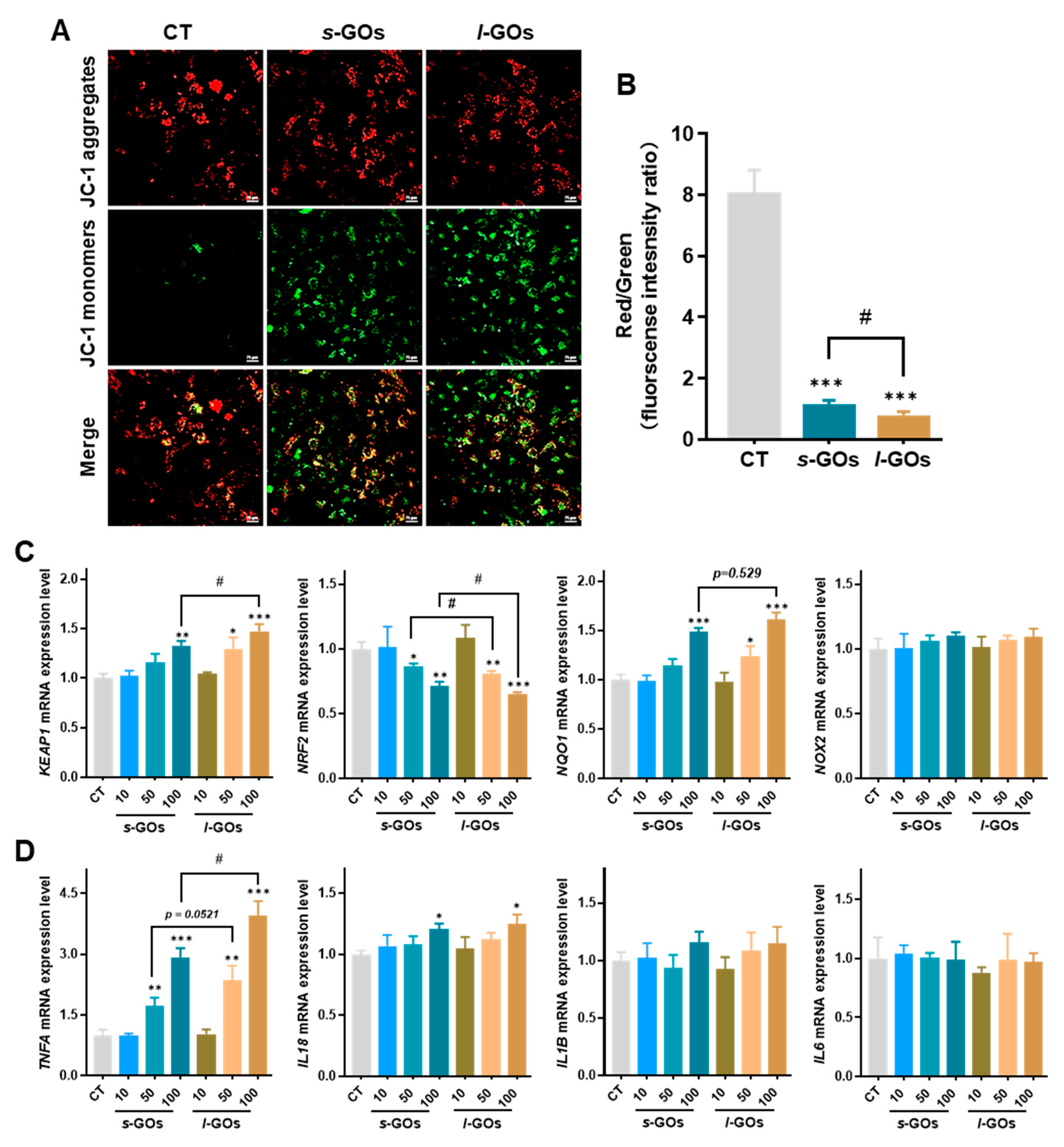
2.7. High Dose of GO Treatments Induced Decrease in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, Elevation of mRNA Expression for Oxidative Stress, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Preparation and Physiochemical Characterization of s-GOs and l-GOs
4.2. Animals and GO Treatments
4.3. In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging of GO Distribution
4.4. In Situ Analysis of GO Renal Deposition by Confocal Raman Microscopy
4.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Imaging
4.7. Histological Analysis
4.8. Cell Culture
4.9. Detection of Cell Viability
4.10. Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
4.11. Detection of LDH Release in Treated Renal Cells
4.12. Measurement of Intracellular ROS, GSH, and GSSG
4.13. Measurement of Cellular Uptake of GOs
4.14. Detection of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.15. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Johnson, A.P.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Pramod, K. Graphene nanoribbons: A promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, G.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, J.M.; Criado, A.; Vazquez, E.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Promises, facts and challenges for graphene in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4400–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.T.; Shah, S.; Chhowalla, M.; Lee, K.B. Design, synthesis, and characterization of graphene-nanoparticle hybrid materials for bioapplications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2483–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emadi, F.; Emadi, A.; Gholami, A. A Comprehensive Insight Towards Pharmaceutical Aspects of Graphene Nanosheets. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Bahrani, S.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.-H.; Yousefi, K.; Omidifar, N.; Rao, N.V.; Ramakrishna, S.; Babapoor, A.; et al. Bio-enhanced polyrhodanine/graphene Oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite with kombucha solvent supernatant as ultra-sensitive biosensor for detection of doxorubicin hydrochloride in biological fluids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 279, 125743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Liang, S.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L.; et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone functionalization induces deformable structure of graphene oxide nanosheets for lung-targeting delivery. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Gu, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, P.; Lv, L.; Aji, S.; et al. Large-Sized Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Increase DC-T-Cell Synaptic Contact and the Efficacy of DC Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Choi, T.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Wang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.D.; Lu, N.; Hyeon, T.; et al. A graphene-based electrochemical device with thermoresponsive microneedles for diabetes monitoring and therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Yang, W.; Zhong, B.; Qing, X.; Shao, Z. Delivery of MutT homolog 1 inhibitor by functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles for enhanced chemo-photodynamic therapy triggers cell death in osteosarcoma. Acta Biomater. 2020, 109, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, C.; Zhi, X.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, X.; Ding, C.; Ma, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, D.; et al. Graphene oxides decorated with carnosine as an adjuvant to modulate innate immune and improve adaptive immunity in Vivo. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Gholami, A.; Mazraedoost, S.; Chiang, W.-H.; Arjmand, O.; Omidifar, N.; Babapoor, A.; Manjunatha, J.G. Precise blood glucose sensing by nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for tight control of diabetes. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 5580203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Yu, M.; Zheng, J. Transport and interactions of nanoparticles in the kidneys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, W. Metabolism of nanomaterialsin vivo: Blood circulation and organ clearance. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Rosenkrans, Z.T.; Ni, D.; Lin, J.; Cai, W. Nanomedicines for Renal Management: From Imaging to Treatment. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, D.A.; Murphy, S.; Newman, L.; Mironov, A.; Prestat, E.; McCaffrey, J.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Bianco, A.; Haigh, S.; et al. The Effects of Extensive Glomerular Filtration of Thin Graphene Oxide Sheets on Kidney Physiology. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10753–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Chu, R.; Yu, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, L.; Chai, Z.; et al. In vivo pharmacokinetics, transfer and clearance study of graphene oxide by La/Ce dual elemental labelling method. NanoImpact 2020, 17, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, D.A.; Newman, L.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Vacchi, I.A.; Lucherelli, M.A.; Lozano, N.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. The impact of graphene oxide sheet lateral dimensions on their pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution profiles in mice. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroojalian, F.; Charbgoo, F.; Hashemi, M.; Amani, A.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Ramezani, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Recent advances in nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the kidney. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 442–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Sun, H.; Fang, C.; Xia, F.; Liao, H.; Lee, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, A.; Ren, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Catalytic activity tunable ceria nanoparticles prevent chemotherapy-induced acute kidney injury without interference with chemotherapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lv, M.; Xiu, P.; Huynh, T.; Zhang, M.; Castelli, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C.; Fang, H.; et al. Destructive extraction of phospholipids from Escherichia coli membranes by graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Guiney, L.M.; Chang, C.H.; Mansukhani, N.D.; Ji, Z.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.P.; Jiang, W.; Sun, B.; Hersam, M.C.; et al. Surface Oxidation of Graphene Oxide Determines Membrane Damage, Lipid Peroxidation, and Cytotoxicity in Macrophages in a Pulmonary Toxicity Model. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1390–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Kostarelos, K.; Fadeel, B. Cytokine Profiling of Primary Human Macrophages Exposed to Endotoxin-Free Graphene Oxide: Size-Independent NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, A.; Emadi, F.; Amini, A.; Shokripour, M.; Chashmpoosh, M.; Omidifar, N. Functionalization of graphene oxide nanosheets can reduce their cytotoxicity to dental pulp stem cells. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 6942707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, F.; Amini, A.; Gholami, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Functionalized graphene oxide with chitosan for protein nanocarriers to protect against enzymatic cleavage and retain collagenase activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Mei, K.C.; Chang, C.H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Guiney, L.M.; Hersam, M.C.; Liao, Y.P.; et al. Lateral size of graphene oxide determines differential cellular uptake and cell death pathways in Kupffer cells, LSECs, and hepatocytes. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Wei, W.; Yue, Z.; Wang, B.; Luo, N.; Gao, Y.; Ma, D.; Ma, G.; Su, Z. The role of the lateral dimension of graphene oxide in the regulation of cellular responses. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4013–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Weber, J.K.; Wang, S.; Luan, B.; Yue, H.; Xi, X.; Du, J.; Yang, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhou, R.; et al. PEGylated graphene oxide elicits strong immunological responses despite surface passivation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Kestenbaum, B. Proximal Tubular Secretory Clearance: A Neglected Partner of Kidney Function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Valle, R.P.; Zuo, Y.; Xia, T.; Liu, S. Crucial role of lateral size for graphene oxide in activating macrophages and stimulating pro-inflammatory responses in cells and animals. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10498–10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Mao, J.; Yan, L.T. Computer simulation of cell entry of graphene nanosheet. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4296–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Guo, R.; Yan, L.T. Simulation and analysis of cellular internalization pathways and membrane perturbation for graphene nanosheets. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6069–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gies, V.; Zou, S. Systematic toxicity investigation of graphene oxide: Evaluation of assay selection, cell type, exposure period and flake size. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Bomback, A.S.; Perazella, M.A. Drug-induced glomerular disease: Direct cellular injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, S.; Shimizu, S.; Tatara, Y.; Mimura, J.; Itoh, K. Regulation of Nrf2 by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in physiology and pathology. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panieri, E.; Saso, L. Inhibition of the NRF2/KEAP1 axis: A promising therapeutic strategy to alter redox balance of cancer cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 34, 1428–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Yu, J.; Cui, R.; Liu, R.; Lei, R.; Chang, Y.; Geng, H.; Qin, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Lipid- and gut microbiota-modulating effects of graphene oxide nanoparticles in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31366–31371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Shim, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Choe, Y.S.; Oh, Y.K. Safety and tumor tissue accumulation of pegylated graphene oxide nanosheets for co-delivery of anticancer drug and photosensitizer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3402–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Weng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, S. Improved in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of graphene oxide through surface modification: Poly(Acrylic Acid)-functionalization is superior to PEGylation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3267–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Gao, L.; Fang, S.; Li, Y.; Pan, H.; et al. Targeted graphene oxide for drug delivery as a therapeutic nanoplatform against Parkinson’s disease. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakia, S.; Toussaint, J.D.; Mullick Chowdhury, S.; Tembulkar, T.; Lee, S.; Jiang, Y.P.; Lin, R.Z.; Shroyer, K.R.; Moore, W.; Sitharaman, B. Dose ranging, expanded acute toxicity and safety pharmacology studies for intravenously administered functionalized graphene nanoparticle formulations. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7022–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, F.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, S. Low-dose exposure to graphene oxide significantly increases the metal toxicity to macrophages by altering their cellular priming state. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaldini, A.; Spano, R.; Catalano, F.; Villa, F.; Poggi, A.; Sabella, S. Sub-lethal concentrations of graphene oxide trigger acute-phase response and impairment of phase-I xenobiotic metabolism in upcyte((R)) hepatocytes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 867728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Wang, B.; Liang, S.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Fang, H.; Yang, P.; Feng, W. Understanding the Role of the Lateral Dimensional Property of Graphene Oxide on Its Interactions with Renal Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227956
Chen W, Wang B, Liang S, Wang M, Zheng L, Xu S, Wang J, Fang H, Yang P, Feng W. Understanding the Role of the Lateral Dimensional Property of Graphene Oxide on Its Interactions with Renal Cells. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227956
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei, Bing Wang, Shanshan Liang, Meng Wang, Lingna Zheng, Si Xu, Jiali Wang, Hao Fang, Pu Yang, and Weiyue Feng. 2022. "Understanding the Role of the Lateral Dimensional Property of Graphene Oxide on Its Interactions with Renal Cells" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227956
APA StyleChen, W., Wang, B., Liang, S., Wang, M., Zheng, L., Xu, S., Wang, J., Fang, H., Yang, P., & Feng, W. (2022). Understanding the Role of the Lateral Dimensional Property of Graphene Oxide on Its Interactions with Renal Cells. Molecules, 27(22), 7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227956





