A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Correlation between PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway and Ischemic Stroke
2.1. Structural Characteristics and Activation of PI3K and Akt
2.2. Ischemic Stroke Activates PI3k/Akt Signaling Pathway, Link to the Relevant Cascade Reaction
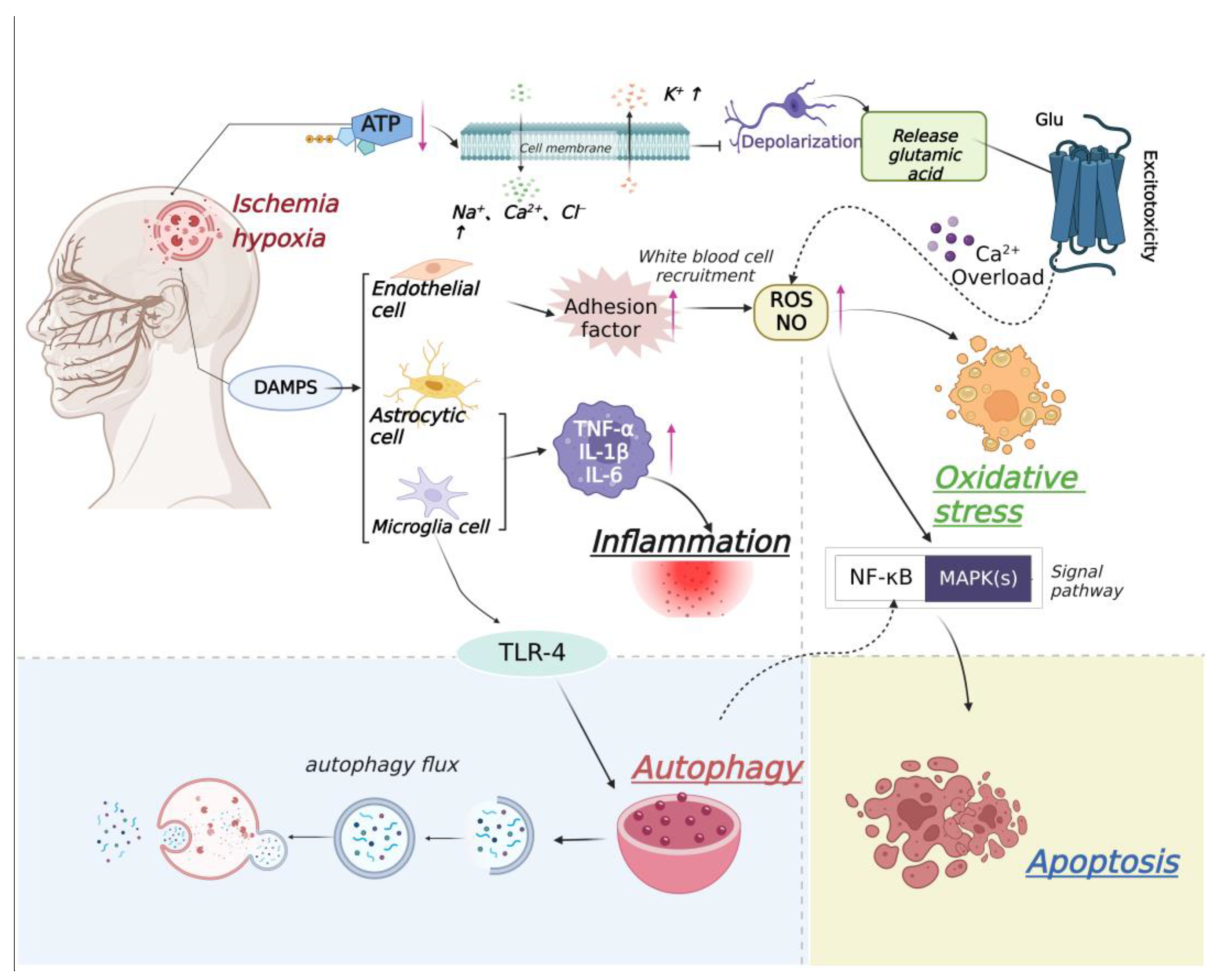
2.2.1. The Pathological Mechanism of Ischemic Stroke
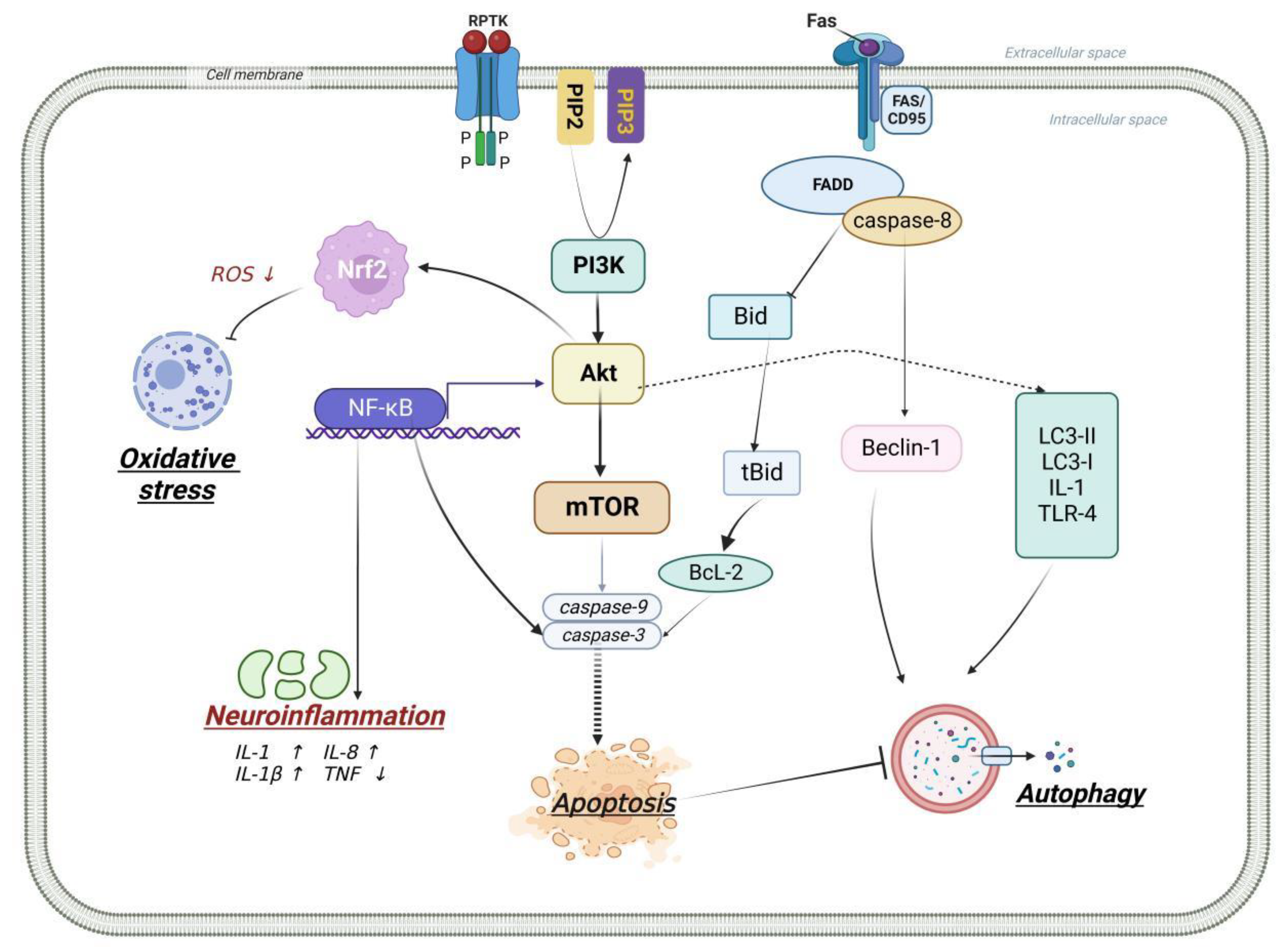
2.2.2. Neuroinflammation Caused by Ischemic Stroke with PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
2.2.3. Apoptosis Caused by Ischemic Stroke with PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
2.2.4. Oxidative Stress Caused by Ischemic Stroke with PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
2.2.5. Autophagy Caused by Ischemic Stroke with PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
3. Natural Medicine for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
3.1. Herbal Medicine
3.1.1. Chuanxiong
3.1.2. Salvia miltiorrhiza
3.1.3. Radix Angelicae sinensis
3.1.4. Astragalus membranaceus
3.1.5. Safflower
3.1.6. Ginkgo biloba leaf
3.1.7. Erigeron breviscapus
3.1.8. Ginseng
3.1.9. Radix Paeoniae Rubra
3.1.10. Panax notoginseng
3.2. Herbal Prescriptions
3.2.1. Buyang Huanwu Decoction
3.2.2. Taohong Siwu Decoction
3.2.3. Xiaoyao San
3.2.4. Danhong Injection
3.2.5. Sanhua Decoction
3.2.6. Xingnaojing Injection
3.3. Animal Medicine
3.3.1. Earthworm
3.3.2. Leech
3.3.3. Scorpion
3.4. Commonly Used Prescriptions of Traditional Chinese Medicine Containing Insects
3.4.1. Tongxinluo Capsule
3.4.2. Naoxintong Capsule
3.4.3. Shuxuetong Injection
3.5. Dosage of Natural Medicine in Animals and Humans
4. Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Qiao, O.; Ji, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Autophagy in vascular dementia and natural products with autophagy regulating activity. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, M.; Vieira, L.E.; Buttari, B.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. The Nrf2 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y. Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: From mechanisms to treatment (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, C.P.; Bienstock, S.W.; Miller, M.; Giustino, G.; Danilov, T.; Kukar, N.; Kocovic, N.; Sperling, D.; Singh, R.; Benhuri, D.; et al. Using Clinical and Echocardiographic Characteristics to Characterize the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Patients with COVID-19. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.J.; Yan, F.; Chao, B.H.; Cao, L.; Wang, L. Treatment and 1-Year Prognosis of Ischemic Stroke in China in 2018: A Hospital-Based Study From Bigdata Observatory Platform for Stroke of China. Stroke 2022, 53, e415–e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, X.T.; Long, N.V.; Van Anh, L.T.; Nga, P.T.; Giang, N.N.; Chien, P.N.; Nam, S.Y.; Heo, C.Y. A Comprehensive Review of Natural Compounds for Wound Healing: Targeting Bioactivity Perspective. Int J. Mol. Sci 2022, 23, 9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Ahmed, W.; Soufiany, I.; Huang, S.; Long, J.; et al. The PI3K/AKT Pathway-The Potential Key Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Stroke. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 900809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Zhao, X.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wan, H.T.; He, Y.; Li, X.H.; Yu, L.; Jin, W.F. Comparison of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Long-Term Secondary Prevention for Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematical Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 722975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Yin, F.T.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, A.H.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.L.; Wang, X.J. The Signaling Pathways and Targets of Natural Compounds from Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Molecules 2022, 27, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mehan, S. Targeting PI3K-AKT/mTOR signaling in the prevention of autism. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 147, 105067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Nie, J.; Chen, C. Activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Causes Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 628690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roudsari, N.M.; Lashgari, N.A.; Momtaz, S.; Abaft, S.; Jamali, F.; Safaiepour, P.; Narimisa, K.; Jackson, G.; Bishayee, A.; Rezaei, N.; et al. Inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Prostate Cancer Chemoprevention and Intervention. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jin, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Gu, S.; Zong, S.; Zhou, J.; et al. Antioxidant effects of ginkgolides and bilobalide against cerebral ischemia injury by activating the Akt/Nrf2 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cell Stress Chaperones 2019, 24, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Li, Y.; Deng, B.; Lin, A.; Zhang, G.; Ma, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Kang, X. The PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in inflammation, cell death and glial scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, P.; Liu, D.; Wang, R.; Cui, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, D. TCM Regulates PI3K/Akt Signal Pathway to Intervene Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 4854755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Botchway, B.O.A.; Zhang, J.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Curcumin can improve Parkinson’s disease via activating BDNF/PI3k/Akt signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 113091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X. The role of PI3K/AKT/FOXO signaling in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 311, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymonowicz, K.; Oeck, S.; Malewicz, N.M.; Jendrossek, V. New Insights into Protein Kinase B/Akt Signaling: Role of Localized Akt Activation and Compartment-Specific Target Proteins for the Cellular Radiation Response. Cancers 2018, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linton, M.F.; Moslehi, J.J.; Babaev, V.R. Akt Signaling in Macrophage Polarization, Survival, and Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2019, 20, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gong, N. Role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: A narrative review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revathidevi, S.; Munirajan, A.K. Akt in cancer: Mediator and more. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.-J.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.R. Progress in Pathological Mechanism of Ischemic Stroke and Prevention and Treatment of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. 2020, 26, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Song, P.; Gu, X.; Liang, W.; Sun, W.; Hua, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z. Comprehensive Landscape of Immune Infiltration and Aberrant Pathway Activation in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 766724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.K.; Zhang, H.B.; Shi, S.S.; Liang, R.S.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, C.M.; Yang, W.Z. 5-LOX Inhibitor Zileuton Reduces Inflammatory Reaction and Ischemic Brain Damage Through the Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.T.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.M.; Cao, Y.; Yang, N.N.; Lin, L.L.; Fisher, M.; Yang, J.W.; Liu, C.Z. Mechanisms of Acupuncture in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 7875396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Vecchie, A.; Casula, M.; Carbone, F.; Dallegri, F.; Montecucco, F. Update on Inflammatory Biomarkers and Treatments in Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2016, 17, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Nie, D.; Wang, L.J.; Qiu, H.C.; Ma, L.; Dong, M.X.; Tu, W.J.; Zhao, J. Microglial Polarization: Novel Therapeutic Strategy against Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Aaron Howell, G.L.B.I. Targeting the NF-κB pathway for therapy of ischemic stroke. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.U.; Orset, C.; Engelhardt, B.; Baumgart-Vogt, E.; Gerriets, T.; Vivien, D.; Kanse, S.M. Deficiency of Factor VII activating protease alters the outcome of ischemic stroke in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 41, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Hawkins, K.E.; Dore, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C135–C153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Li, J.; Che, Y.Q. CXCL8 gene silencing promotes neuroglial cells activation while inhibiting neuroinflammation through the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB-signaling pathway in mice with ischemic stroke. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 7341–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Hou, S.; Feng, L.; Shen, P.; Nan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, D.; Feng, J. Vinpocetine Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Targeting Astrocytic Connexin43 via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mao, L.-L.; Hao, D.-L.; Mao, X.-W.; Xu, Y.-F.; Huang, T.-T.; Wu, B.-N.; Wang, L.-H. Neuroprotective effects of bisperoxovanadium on cerebral ischemia by inflammation inhibition. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 602, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.-J.; Ge, J.-W.; Xia, S.-N.; Zou, X.-X.; Bao, X.-Y.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Meng, H.-L. Fraxetin alleviates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrabi, S.S.; Parvez, S.; Tabassum, H. Ischemic stroke and mitochondria: Mechanisms and targets. Protoplasma 2020, 257, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Q.Z.; Zhang, S.T.; Lei, P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 259–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Peng, J.; Sherchan, P.; Ma, Y.; Xiang, S.; Yan, F.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.H.; et al. TREM2 activation attenuates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via PI3K/Akt pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tian, Q.; Han, S.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, M. The neuroprotective effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 via the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway are mediated by the PI3K/AKT cascade following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 177, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Zhang, M.; Feng, Y.S.; Xing, Y.; Tan, Z.X.; Li, W.B.; Dong, F.; Zhang, F. Electroacupuncture Inhibits Neuronal Autophagy and Apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT Pathway Following Ischemic Stroke. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, K.; Wan, W.; Cheng, Y.; Pu, X.; Ye, X. Resveratrol provides neuroprotection by regulating the JAK2/STAT3/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway after stroke in rats. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dringen, R. Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 62, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.X.; Li, C.; Yan, X.L.; Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.N. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Ferroptosis/Oxytosis in Ischemic Stroke: Possible Targets and Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6643382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Ma, S.-X.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Ko, Y.-H.; Seo, J.-Y.; Lee, B.-R.; Lee, S.-Y.; Jang, C.-G. The Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Bark. Involves NF-kappa B Suppression and Nrf2-Dependent HO-1 Induction in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Jin, H. Collagen peptides from Acaudina molpadioides prevent CCl4-induced liver injury via Keap1/Nrf2-ARE, PI3K/AKT, and MAPKs pathways. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samakova, A.; Gazova, A.; Sabova, N.; Valaskova, S.; Jurikova, M.; Kyselovic, J. The pi3k/Akt Pathway Is Associated With Angiogenesis, Oxidative Stress and Survival of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Pathophysiologic Condition in Ischemia. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, S131–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Shi, H.X.; Yu, X.C.; Wang, X.J.; Yan, Y.B.; Fu, X.B.; Hu, H.W.; Li, X.K.; et al. bFGF inhibits ER stress induced by ischemic oxidative injury via activation of the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Cao, X.; Xiao, L.G.; Zhou, R.J. Aloperine protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Gan, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. SCO-spondin-derived peptide NX210 rescues neurons from cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through modulating the Integrin-beta1 mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Jiang, H.H.; Mao, B.B.; Yu, H. Total Flavonoids of Chuju Decrease Oxidative Stress and Cell Apoptosis in Ischemic Stroke Rats: Network and Experimental Analyses. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 772401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Gao, Y.; Chu, S.; Chen, N. Review of the effects and Mechanisms of microglial autophagy in ischemic stroke. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Liu, P.; Harris, P.D.R.; Sagi, A.; Field, R.E.; Sochart, D.H.; Tucker, K.; Asopa, V. Severe Global Cerebral IschemiaYInduced Programmed Necrosis of Hippocampal CA1 Neurons in Rat Is Prevented by 3-Methyladenine: A Widely Used Inhibitor of Autophagy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 70, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xu, P.; Lenahan, C.; Lu, J.; Zheng, J.; Dong, X.; Shao, A.; Zhang, J. An updated review of autophagy in ischemic stroke: From mechanisms to therapies. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 340, 113684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wan, H.; Liu, W.; Kong, F.; Ma, G. Deltonin Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Correlation with Modulation of Autophagy and Inflammation. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, X.; Zhang, J.; Jing, L. Selenium attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced damage to the blood-brain barrier in hyperglycemia through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway-mediated autophagy inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Lan, R. Nested case-control study on the effect of PI3K autophagy signaling pathway on the recurrence of ischemic stroke. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2021, 36, 3713–3716. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, N.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Seto, S.; Wang, Y. Tong-Qiao-Huo-Xue decoction activates PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to reduce BMECs autophagy after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Mo, Y.; Yue, E.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.Y. Ibrutinib ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through autophagy activation and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in diabetic mice. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7432–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Yan, Y.; Bao, T.H.; Jia, W.J.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yin, M.; Han, J.H. Ischemic postconditioning exerts neuroprotective effect through negatively regulating PI3K/Akt2 signaling pathway by microRNA-124. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Zheng, S.-L.; Fan, Q.-J.; Yuan, J.-C.; Yang, S.-M.; Kong, F.-L. A Fast HPLC Quantitative Determination of Ligustrazine in Rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 5026–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Fu, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, X. Ligustrazine suppresses neuron apoptosis via the Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3 pathway in PC12 cells and in rats with vascular dementia. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Du, J.R.; Wang, J.; Yu, D.K.; Chen, Y.S.; He, Y.; Wang, C.Y. Z-ligustilide extracted from Radix Angelica Sinensis decreased platelet aggregation induced by ADP ex vivo and arterio-venous shunt thrombosis in vivo in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi 2009, 129, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Kong, L.; Luan, S.; Qi, C.; Wu, F. Ligustrazine Suppresses Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB-Induced Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Inflammation by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 437–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Pan, R.; Tang, H.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Jing, F.; Dong, J. Ligustrazine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurocognitive impairment by activating autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Du, J.; Cui, F.; Chen, L.; Li, K. The protective effect of ligustrazine on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.J.; Liu, S.N.; Guo, X.F. Medium- and long-term efficacy of ligustrazine plus conventional medication on ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.-Y.; Ming, Q.-L.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L.-P. Salvia miltiorrhiza: Traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.Y.; Chuang, C.H.; Chern, C.M.; Liou, K.T.; Liu, D.Z.; Hou, Y.C.; Shen, Y.C. Salvianolic acid A alleviates ischemic brain injury through the inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis and the promotion of neurogenesis in mice. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 99, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.J.; Dong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fu, S.J.; Li, C.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xie, F.; Chen, X.Y.; Xu, H.; Cai, X.J.; et al. Salvianolic acid B alleviates neurological injury by upregulating stanniocalcin 1 expression. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, G.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Isaiah, A.O.; Lin, Y.; et al. Direct stimulation of adult neural stem/progenitor cells in vitro and neurogenesis in vivo by salvianolic acid B. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.T.; He, Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Wan, H.T.; Ding, Z.S.; Yang, J.H.; Zhou, H.F. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking-Based Mechanism Study to Reveal the Protective Effect of Salvianolic Acid C in a Rat Model of Ischemic Stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 799448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Han, R.; Xiao, H.; Shen, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, J. Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone IIA and/or tetramethylpyrazine in cerebral ischemic injury in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res. 2012, 1488, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Bian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Tian, J.; Lu, T. The crosstalk signals of Sodium Tanshinone A Sulfonate in rats with cerebral ischemic stroke: Insights from proteomics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.Y.; Zhou, F.; Han, L.J.; Yang, J.; Fan, H.J.; Li, S.S.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; et al. Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Enhances Effectiveness Rt-PA Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Associated with Ameliorating Blood-Brain Barrier Damage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2017, 8, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, T.; Li, H.; Fang, Z.; Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, L.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Polysaccharides from Angelica sinensis alleviate neuronal cell injury caused by oxidative stress. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.B.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.B.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.H.; Zeng, C. The Effect of Angelica sinensis Polysaccharide on Neuronal Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via PI3K/AKT Pathway. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.W.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.H. Overview of therapeutic potentiality of Angelica sinensis for ischemic stroke. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Wang, K.-X.; Cai, J.-Q.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.-L.; Wu, Q.; Meng, W.; Wang, H.-D.; Yin, C.-H.; Wu, J.; et al. Detecting Key Functional Components Group and Speculating the Potential Mechanism of Xiao-Xu-Ming Decoction in Treating Stroke. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 7829341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Mao, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, N. Ligustilide Attenuates Ischemia Reperfusion-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Apoptosis via Activating the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Hsieh, C.L. Proteomics analysis of protein biomarkers in Astragalus membranaceus- and Astragaloside IV-treated brain tissues in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, X.F.; Zhou, X.H.; Dong, X.H.; Yu, W.T.; Gao, W.J. The Role of Astragaloside IV against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis via Promotion of P62-LC3-Autophagy. Molecules 2019, 24, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Han, R.; Guo, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.; Gao, C. Antagonistic effects of IL-17 and Astragaloside IV on cortical neurogenesis and cognitive behavior after stroke in adult mice through Akt/GSK-3beta pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.-L.; Sun, L.-M.; Dong, Y.; Yi, B.-H. Effects of Astragali Radix total flavonoids on oxidative stress inflammation and apoptosis of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.Y.; Yin, L.; Sun, Z.F.; Shao, S.S.; Chen, W.B.; Man, X.; Du, Y.F.; Chen, Y. Astragalus polysaccharide exerts anti-Parkinson via activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to increase cellular autophagy level in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Ke, X.; Wan, X.S.; Yang, Y.B.; Huang, Y.J.; Qin, J.; Hu, C.H.; Shi, L. Astragalus polysaccharides attenuates TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance via suppression of miR-721 and activation of PPAR-gamma and PI3K/AKT in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.Y.; Lin, N.; Shan, G.L.; Zuo, P.P.; Cui, L.Y. Safflower yellow for acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2014, 22, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Li, Y.M.; Qiao, B.Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, X.; Du, H.M.; Han, P.C.; Shi, J. The Value of Safflower Yellow Injection for the Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 478793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chi, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, K. Safflower yellow alleviates osteoarthritis and prevents inflammation by inhibiting PGE2 release and regulating NF-kappa B/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2020, 78, 153305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Z.L.; He, W.D.; Chen, H.F.; Lai, Z.L.; Duan, Y.H.; Cao, X.H.; Tao, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.J.; et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Confers Neuroprotection from Focal Cerebral Ischemia by Modulating the Crosstalk Between JAK2/STAT3 and SOCS3 Signaling Pathways. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Liao, L.; Wang, C.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Hydroxysafflor yellow A, a natural compound from Carthamus tinctorius L with good effect of alleviating atherosclerosis. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan-ping, T. Protection of Hydroxysafflor Yellow-A Combined with Paeoniflorin on CIRI Rats and Its influence on Expression of PI3K and AKT Protein. Anti. Infect. Pharm. 2018, 15, 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.Z.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Lu, H.; Gao, M.; Liu, L.M.; Song, H.Q.; Lin, A.J.; Wu, Q.M.; Zhou, H.F.; et al. Effect and Safety of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A for Injection in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke of Blood Stasis Syndrome: A Phase II, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Multiple-Dose, Active-Controlled Clinical Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Bai, Y.; Hu, D.; Xie, X. The neuroprotective mechanisms of ginkgolides and bilobalide in cerebral ischemic injury: A literature review. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhaocheng, J.; Jinfeng, L.; Luchang, Y.; Yequan, S.; Feng, L.; Kai, W. Ginkgolide A inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human coronary artery endothelial cells via downregulation of TLR4-NF-kappaB signaling through PI3K/Akt pathway. Pharmazie 2016, 71, 588–591. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, J.; Fang, W.; Li, Y. XQ-1H promotes cerebral angiogenesis via activating PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta/beta-catenin/VEGF signal in mice exposed to cerebral ischemic injury. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Protective effects and mechanism of ginkgo flavonoids and ginkgolides on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2019, 30, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Mao, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhou, L. Extracts of Ginkgo flavonoids and ginkgolides improve cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signalling pathway and multicomponent in vivo processes. Phytomedicine 2022, 99, 154028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zheng, H.; Du, Y.W.; Zhang, R.L.; Chen, P.L.; Ren, R.; Wu, S.X. The Clinical Efficacy of Ginkgo biloba Leaf Preparation on Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 4265219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.H.; Tan, L.R.; Liu, P.W.; Tan, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Li, X.H.; Wang, M.J.; He, B.X. Scutellarin regulates osteoarthritis in vitro by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.M.; Li, G.X.; Shen, S.; Wei, X.L. Scutellarin inhibits the invasive potential of malignant melanoma cells through the suppression epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.-q.; Wu, J.-r.; Zhu, Y.-l.; Zhou, W.; Fu, C.-g.; Liu, X.-k.; Liu, S.-y.; Ni, M.-w.; Guo, S.-y. Revealing the Common Mechanisms of Scutellarin in Angina Pectoris and Ischemic Stroke Treatment via a Network Pharmacology Approach. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 27, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liang, Y.; Xu, M.; Sun, M.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Song, W.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z. Protective mechanism of Erigeron breviscapus injection on blood-brain barrier injury induced by cerebral ischemia in rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yang, M.Y.; Le, J.Q.; Luo, B.Y.; Yin, M.D.; Li, C.; Jiang, J.L.; Fang, Y.F.; Shao, J.W. Protective Effects and Therapeutics of Ginsenosides for Improving Endothelial Dysfunction: From Therapeutic Potentials, Pharmaceutical Developments to Clinical Trials. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 749–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Yang, W.; Zheng, P.; Zeng, J.; Tong, W. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on integrity of blood-brain barrier following cerebral ischemia. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.-W.; Lu, P.; Peng, L.; Jiang, W. Ginsenoside Rb1 Inhibits Cardiomyocyte Autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Reduces Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Shang, W.; Xue, J.; Chen, R.; Xing, Y.; Song, D.; Xu, R. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes cerebral angiogenesis via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in ischemic mice. Eur J. Pharm. 2019, 856, 172418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Cai, N.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, S.; Si, Q.; Zhang, W. Neuroprotective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 prevents cognitive impairment induced by isoflurane anesthesia in aged rats via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects mediated by the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3 pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2778–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wen, A.; Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Ren, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Ginsenoside-Rd improves outcome of acute ischaemic stroke—A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Eur J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Ginsenoside Rh1 Exerts Neuroprotective Effects by Activating the PI3K/Akt Pathway in Amyloid-beta Induced SH-SY5Y Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Hou, J.C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.X.; Zheng, Y.Q. Ginsenoside Rd promotes neurogenesis in rat brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2015, 36, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Han, T.; Lan, J.; He, L.X.; Shi, J.Y. Angiogenic Actions of Paeoniflorin on Endothelial Progenitor Cells and in Ischemic Stroke Rat Model. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Huang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Geng, W. Paeoniflorin improves functional recovery through repressing neuroinflammation and facilitating neurogenesis in rat stroke model. Peerj 2021, 9, e10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-C.; Wang, S.-X.; Yan, X.-L.; He, Y.-Y.; Wang, M.-C.; Zheng, H.-Z.; Shi, X.-G.; Tan, Y.-H.; Wang, L.-S. Combination of paeoniflorin and calycosin-7-glucoside alleviates ischaemic stroke injury via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.Z.; Zhao, W.; Yan, K.T.; Huang, P.P.; Zhang, H.W.; Ma, X.C. Preclinical Evidence of Paeoniflorin Effectiveness for the Management of Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, L.; Zou, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Hu, B.; Chen, J. Panax notoginseng Saponins Promotes Stroke Recovery by Influencing Expression of Nogo-A, NgR and p75NGF, in Vitro and in Vivo. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.; Jia, Z.H.; Dong, S.F.; Han, B.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Sun, J.N. Panax notoginseng Saponins Ameliorate Leukocyte Adherence and Cerebrovascular Endothelial Barrier Breakdown upon Ischemia-Reperfusion in Mice. J. Vasc. Res. 2019, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Hu, H.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Du, S. Panax notoginseng Saponins Protect Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion-Induced Barrier Dysfunction via Activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Antioxidant Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, J.; Mai, L.; Shan, Z.; Yu, X.; et al. Panax notoginseng saponins inhibit ischemia-induced apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt pathway in cardiomyocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.T.; Li, S.D.; Li, C.; Xiong, Y.X.; Lu, X.H.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Pu, L.J.; Luo, H.Y. Panax notoginsenoside saponins Rb1 regulates the expressions of Akt/ mTOR/PTEN signals in the hippocampus after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 345, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.D.; Xu, Z.M.; Liang, X.; Qiu, W.R.; Liu, S.J.; Dai, L.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Guo, C.Y.; Qi, X.H.; Wang, J.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Randomized Controlled Trials on Efficacy and Safety of Panax Notoginseng Saponins in Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 4694076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-W.; Xu, F.; Wang, D.; Ye, J.; Cai, S.-Q. Buyang Huanwu Decoction ameliorates ischemic stroke by modulating multiple targets with multiple components: In vitro evidences. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.L.; Dong, L.Y.; Wu, C.Q.; Qin, J.; Li, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, X.; Huang, D.K. Buyang Huanwu Decoction fraction protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating the inflammatory response and cellular apoptosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.J.; Yang, A.L.; Zhou, H.J.; Wang, C.; Luo, J.K.; Lin, Y.; Zong, Y.X.; Tang, T. Buyang huanwu decoction promotes angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 activation through the PI3K/Akt pathway in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; Fu, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J. Proteomics-Guided Study on Buyang Huanwu Decoction for Its Neuroprotective and Neurogenic Mechanisms for Transient Ischemic Stroke: Involvements of EGFR/PI3K/Akt/Bad/14-3-3 and Jak2/Stat3/Cyclin D1 Signaling Cascades. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4305–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xiao, Z.R.; Jia, C.H.; Wang, W. Effect of Buyang Huanwu decoction for the rehabilitation of ischemic stroke patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Jiang, H.J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Zhou, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J.M.; He, Y.; Ren, C.X.; Pei, J. A comparative study on the traditional versus modern yellow rice wine processing methods using Taohong Siwu Decoction for pharmaceutical production. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 290, 115114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Huang, S.; Fei, C.; Wang, N.; Chu, F.; Peng, D.; Duan, X. Network pharmacology and experimental validation-based approach to understand the effect and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction against ischemic stroke. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 294, 115339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Fei, C.; Chu, F.; Huang, S.; Pan, L.; Peng, D.; Duan, X. Taohong Siwu Decoction Regulates Cell Necrosis and Neuroinflammation in the Rat Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Model. Front. Pharm. 2021, 12, 732358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan-Hai, Z. Effect of Taohongsiwu decoction on the angiogenesis and PI3K /AKT signal pathway in brain tissue of rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Bengbu Med. Coll 2017, 42, 36–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.D.; Fu, L.J.; Qin, G.Z.; Shi, P.L.; Fu, W.J. The regulatory effect of Xiaoyao San on glucocorticoid receptors under the condition of chronic stress. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, Z.R.; Huang, M.Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y. Mechanism of Action of Xiaoyao San in Treatment of Ischemic Stroke is Related to Anti-Apoptosis and Activation PI3K/Akt Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Wan, H.F.; Tong, X.; He, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Shao, C.Y.; Ding, Z.S.; Wan, H.T.; Li, C. An integrative strategy for discovery of functional compound combination from Traditional Chinese Medicine: Danhong Injection as a model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhou, H.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shao, C.; Yin, J.; Du, H.; Yang, J.; Wan, H. Danhong injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by improving intracellular energy metabolism coupling in the ischemic penumbra. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 140, 111771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; He, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wan, H. Danhong Injection Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats Through the Suppression of the Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharm. 2021, 12, 561237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Shao, C.; He, Y.; Wan, H.; Jin, W. Neuroprotective Effect of Danhong Injection on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Activation of the PI3K-Akt Pathway. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, M.L.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Tian, J. Observation of the clinical effects of Danhong injections combined with pitavastatin on blood lipid regulation in patients with ischemic strokes complicated with lipid abnormalities. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 12, 3364–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.W.; Wang, X.X.; Zhong, L.Q.; Wu, S.X. Comparative study of the effects of Danhong injection with different doses on ischemic stroke: A substudy of hospital-based Danhong injection registry. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 38, 917–925. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, C.J. Rapid characterization of the chemical constituents of Sanhua decoction by UHPLC coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26109–26119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.-L.; Li, J.-H.; Shi, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-L.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, G.-Q. Sanhua Decoction, a Classic Herbal Prescription, Exerts Neuroprotection Through Regulating Phosphorylated Tau Level and Promoting Adult Endogenous Neurogenesis After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.J.; Ma, S.B.; Wang, M.M.; Yao, M.N.; Li, R.L.; Li, W.W.; Zhao, X.; Hu, D.M.; et al. Network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification to explore the mechanism of Sanhua decoction in the treatment of ischaemic stroke. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.F.; Chu, Y.; Ma, X.H.; Zheng, H.R.; Bai, X.L.; Zhou, S.P.; Yu, B.Y. GC-MS/MS method for the determination and pharmacokinetic analysis of borneol and muscone in rat after the intravenous administration of Xingnaojing injection. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4264–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Qu, X.Y.; Zhai, J.H.; Tao, L.N.; Gao, H.; Song, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.X. Xingnaojing Injection Protects against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via PI3K/Akt-Mediated eNOS Phosphorylation. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 2361046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Pan, S. Network pharmacology to investigate the pharmacological mechanisms of muscone in Xingnaojing injections for the treatment of severe traumatic brain injury. Peerj 2021, 9, e11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fan, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Xingnaojing Injection for Emergency Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharm. 2022, 13, 839305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Lu, H.; Yang, P.; Ye, L. Clinical Research Progress in Insect Chinese Materia Medica in Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Chin. J. Inf. TCM 2019, 26, 142–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, S.A.; Huang, C.H.; Su, H.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, J.H.T.; Huang, S.S. Sirt1 Activation by Post-ischemic Treatment With Lumbrokinase Protects Against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, C.K.; Kuo, W.W.; Shen, C.Y.; Chen, T.S.; Pai, P.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Lo, F.Y.; Ju, D.T.; Huang, C.Y. Dilong Prevents the High-KCl Cardioplegic Solution Administration-Induced Apoptosis in H9c2 Cardiomyoblast Cells Mediated by MEK. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, T.; Jia, Z.; Yin, M.; Hu, L. Exploration of the protective effects of Leech and Earthworm extracts on cerebral ischemic penumbra neurons in MCAO/R mice based on PI3K/AKT pathway. Tianjin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 39, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Wang, L.; Bi, H.; Sun, L.; Cai, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Du, Z. Mechanisms of lumbrokinase in protection of cerebral ischemia. Eur J. Pharm. 2008, 590, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhou, K.H.; Zhang, X.C.; Dai, H.H.; Yang, B.L.; Shang, H.C. Efficacy and safety of lumbrokinase plus aspirin versus aspirin alone for acute ischemic stroke (LUCENT): Study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Trials 2022, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junren, C.; Xiaofang, X.; Huiqiong, Z.; Gangmin, L.; Yanpeng, Y.; Xiaoyu, C.; Yuqing, G.; Yanan, L.; Yue, Z.; Fu, P.; et al. Pharmacological Activities and Mechanisms of Hirudin and Its Derivatives—A Review. Front. Pharm. 2021, 12, 660757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Q.; Qin, Z.S.; Chen, S.; Cheng, D.; Yang, S.C.; Choi, Y.M.M.; Chu, B.; Zhou, W.H.; Zhang, Z.J. Hirudin alleviates acute ischemic stroke by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation: In vivo and in vitro approaches. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, W.J.; Gao, X.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Sun, W. A Molecular Mechanism Study to Reveal Hirudin’s Downregulation to PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway through Decreasing PDGFR beta in Renal Fibrosis Treatment. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5481552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.X.; Lin, W.; Yang, K.; Wei, L.J.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhong, K.; Chen, X.; Pei, M.; Yang, H.T. Transcriptome-Based Network Analysis Reveals Hirudin Potentiates Anti-Renal Fibrosis Efficacy in UUO Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 741801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.G.; Bi, L.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, F.; Jiang, W. The efficacy and safety of Hirudin plus Aspirin versus Warfarin in the secondary prevention of Cardioembolic Stroke due to Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, T.V.; Anh, H.N.; Trang, N.T.T.; Van Trung, P.; Khoa, N.C.; Osipov, A.V.; Dubovskii, P.V.; Ivanov, I.A.; Arseniev, A.S.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. Low-molecular-weight compounds with anticoagulant activity from the scorpion Heterometrus laoticus venom. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 476, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Hoang, A.N.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Van Phung, T.; Nguyen, K.C.; Osipov, A.V.; Ivanov, I.A.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Anticoagulant Activity of Low-Molecular Weight Compounds from Heterometrus laoticus Scorpion Venom. Toxins 2017, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasquini, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Casetta, I.; Laudisi, M.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Adenosinergic System Involvement in Ischemic Stroke Patients’ Lymphocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.J.; Wu, Y.R.; Li, Q.X.; Sheng, W.; Zhou, Q.; Fu, W. Astragalus-Scorpion Drug Pair Inhibits the Development of Prostate Cancer by Regulating GDPD4-2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 895696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.P.; Hu, L.; Wei, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Chinese medicine Tongxinluo capsule protects against blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke by inhibiting the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 pathway in mice. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Luo, H.X.; Zhou, L.H.; Wang, L.X.; Sun, J.B.; Huang, Y.; Luo, E.L.; Cai, Y.F. Neuroprotective effect of the traditional Chinese herbal formula Tongxinluo: A PET imaging study in rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wei, C.; Kang, N.; He, Q.L.; Liang, J.Q.; Wang, H.T.; Chang, L.P.; Chen, D.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chang, C.C.; et al. Chinese medicine Tongxinluo capsule alleviates cerebral microcirculatory disturbances in ischemic stroke by modulating vascular endothelial function and inhibiting leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions in mice: A two-photon laser scanning microscopy study. Microcirculation 2018, 25, e12437. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.H.; Cai, M.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Z.N.; Zhang, J.S.; Song, X.L.; Zhang, W.; Bao, J.; Li, W.W.; Cai, D.F. PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to neuroprotective effect of Tongxinluo against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 181, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, P.; Yang, R.J. Systematic Review of Tongxinluo Capsule on the Therapeutic Effect and Hemorheology of Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5541768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Yin, Z.Q.; Cao, P.C.; Zheng, S.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Yu, M.Y.; Liao, C.Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Duan, Y.J.; Han, J.H.; et al. NaoXinTong Capsule ameliorates memory deficit in APP/PS1 mice by regulating inflammatory cytokines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Deng, L.N.; Xie, T.; Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, W.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Gao, X.M. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pharmcodynamic compoents of naoxintong capsules as a basis of broad spectrum effects. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, X.K.; Zheng, L.F.; Wu, X.Y.; Chen, H. Comparison of Aspirin and Naoxintong Capsule (sic) with Adjusted-Dose Warfarin in Elderly Patients with High-Risk of Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation and Genetic Variants of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 24, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Z.L.; Jiang, J.; Lei, Y. Efficacy and safety of Naoxintong capsule for acute ischemic stroke A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e27120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Wang, F.J.; Guo, H.; Chen, L.; Chai, L.J.; Li, R.L.; Hu, L.M.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.X. Shuxuetong injection protects cerebral microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation reperfusion. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 783–793. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Jiao, J.K.; Shang, J.F.; Bi, L.; Wang, H.H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.W.; Cui, Y.R.; Wang, P.; Liu, X. The Differences of Metabolites in Different Parts of the Brain Induced by Shuxuetong Injection against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion and Its Corresponding Mechanism. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 9465095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.R.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, H.J. In-depth transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of the hippocampus and cortex in a rat model after cerebral ischemic injury and repair by Shuxuetong (SXT) injection. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhou, H.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, R.R.; Huang, X.Q.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, S.; et al. Effects of shuxuetong injection for cerebral infarction A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e21929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Fu, W.J.; Cheng, N.F.; Meng, D.; Gu, Y. Ligustrazine reduces blood-brain barrier permeability in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Z.H.; Gao, Y.H.; Pan, C.H.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.Y. Effect of Tanshinone IIA combined with Rehabilitation Training on Nerve Repair and Expression of Growth-associated Protein-43 of Peri-ischemic Cortex in Ischemic Stroke Rats. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2019, 38, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, S.Q.; Wei, H.D.; Sun, S.S.; Zhao, G.C.; Dong, H.L. Tanshinone IIA Elicits Neuroprotective Effect Through Activating the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor-Dependent Antioxidant Response. Rejuvenation Res. 2017, 20, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.K.; Chen, Y.F.; Feng, F.; Luo, Y. Tanshinone IIA pretreatment attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation induced hippocampal neurons damage. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 10287–10296. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.H.; Li, N.; Gao, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.J.; Ji, X.M.; Ding, Y.C. Ligustilide provides neuroprotection by promoting angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Neurol. Res. 2020, 42, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Wang, L.F.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, Y.N.; He, Q.; Chen, C.; Du, J.R. Ligustilide ameliorates neuroinflammation and brain injury in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats: Involvement of inhibition of TLR4/peroxiredoxin 6 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 71, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, D.P.; Qin, Z.; Wang, P.Y.; Hu, B.H.; Yu, J.G.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, B.; Chen, Y.L.; Lu, M.; et al. Protective cerebrovascular effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) on ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.N.; Qian, Y.S.; Fu, L.S.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhong, H.L.; Wei, X.H. Hydroxysafflor yellow A exerts neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemia reperfusion-injured mice by suppressing the innate immune TLR4-inducing pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Xia, F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.D.; Zhao, G.; Shi, M. Ginsenoside Rd Is Efficacious Against Acute Ischemic Stroke by Suppressing Microglial Proteasome-Mediated Inflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.D.; Yang, Q.Z.; Kong, X.W.; Han, J.L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, P.; Liu, J.F.; Shi, M.; Xiong, L.Z.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd attenuates early oxidative damage and sequential inflammatory response after transient focal ischemia in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.G.; Zhu, Q.S.; Man, X.X.; Guo, L.; Hao, L.M. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits apoptosis following spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Y.; Li, M.H.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, L.O.; Zhou, X.F.; Luo, Y.H.; An, D.; Li, S.D.; Luo, H.Y.; et al. Effects of Panax notoginseng ginsenoside Rb1 on abnormal hippocampal microenvironment in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 202, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; He, W.B.; Chen, C.; Luo, P.; Liu, D.D.; Ai, Q.D.; Gong, H.F.; Wang, Z.Z.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against ischemic/reperfusion-induced neuronal injury through miR-144/Nrf2/ARE pathway. Acta Pharmakoi. Sin. 2019, 40, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.B.; Shi, F.G.; Zhang, R.; Sun, C.L.; Gong, C.T.; Jian, L.Y.; Ding, L. Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Amygdalin and Paeoniflorin After Single and Multiple Intravenous Infusions of Huoxue-Tongluo Lyophilized Powder for Injection in Healthy Chinese Volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.D.; Han, F.; Zhou, L.; Wu, S.X.; Du, Y.W.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Panax Notoginseng Saponins (Xueshuantong) in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (EXPECT) Trial: Rationale and Design. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 648921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, X.F.; Tian, Y.; Sui, J.H.; Sun, Y.; Lin, S.; Gao, X.; Peng, C.; Fan, Y.J. Anti-platelet aggregation of Panax notoginseng triol saponins by regulating GP1BA for ischemic stroke therapy. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tao, Y.W.; Luo, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.B.; Meng, X.L. Dengzhan Xixin injection derived from a traditional Chinese herb Erigeron breviscapus ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via modulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 288, 114988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, X.J.; Shen, J.G. Astragaloside VI Promotes Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Enhances Neurological Function Recovery in Transient Cerebral Ischemic Injuryvia Activating EGFR/MAPK Signaling Cascades. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3053–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.H.; Cai, J.; Zhan, L.C.; Guo, Y.H.; Huang, R.Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, M.C.; Xu, D.D.; Zhan, J.; Chen, H.X. Buyang Huanwu decoction facilitates neurorehabilitation through an improvement of synaptic plasticity in cerebral ischemic rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.L.; Wu, C.Y. Acupuncture combined with Buyang Huanwu decoction in treatment of patients with ischemic stroke. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Peng, D.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guan, L. Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes neurogenesis via sirtuin 1/autophagy pathway in a cerebral ischemia model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Shen, Y.C.; Shiao, Y.J.; Liou, K.T.; Hsu, W.H.; Hsieh, P.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Lin, Y.L. Multiplex Brain Proteomic Analysis Revealed the Molecular Therapeutic Effects of Buyang Huanwu Decoction on Cerebral Ischemic Stroke Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.M.; Liu, Z.Q.; Hu, S.S.; Duan, X.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Peng, C.; Peng, D.Y.; Han, L. Taohong Siwu Decoction Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Injury Via Suppressing Pyroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 590453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgah, J.O.; Ren, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Orgah, E.A.; Gao, X.M.; Zhu, Y. Danhong injection facilitates recovery of post-stroke motion deficit via Parkin-enhanced mitochondrial function. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2019, 37, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, T.T.; Guo, F.F.; Ji, E.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.W.; Tang, S.H.; Wei, J.Y.; Yang, H.J. Systematical Identification of the Protective Effect of Danhong Injection and BuChang NaoXinTong Capsules on Transcription Factors in Cerebral Ischemia Mice Brain. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5879852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.X.; Cao, K.G.; Kong, L.B.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xmas Study, I. Xingnaojing for Moderate-to-severe Acute ischemic Stroke (XMAS): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.F.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yuan, C.X.; Wu, D.H.; Zhao, Y.W.; Yang, J.J.; Wang, C.D.; Wu, W.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; et al. Naoxintong Capsule for Secondary Prevention of Ischemic Stroke: A Multicenter, Randomized, and Placebo-Controlled Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, H.F.; He, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, C.; Yang, J.H.; Wan, H.T. Protective Effect of Naoxintong Capsule Combined with Guhong Injection on Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells during Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 27, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.Y.; Wan, H.F.; Yang, R.B.; Wan, H.T.; Yang, J.H.; He, Y.; Zhou, H.F. Protective effect of Danhong Injection combined Naoxintong Capsule on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats with. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.Q.; Xie, X.W.; Jing, J.; Meng, X.; Lv, W.; Yu, J.D.; Lv, X.P.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.J. Shuxuetong for Prevention of recurrence in Acute Cerebrovascular events with Embolism (SPACE) trial: Rationale and design. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Natural Medicine | Plant Atlas | Active Ingredients | Model | Regulation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway | Main Purposed Effects | Ref(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbal medicine | ||||||
| Chuanxiong |  | Ligustrazine | PC12 Cells SD rats Human amniotic epithelial cells | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation Activating autophagy | [61,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza |  | Tanshinone; Danshensu; Salvianolic Acid. | SD rats Neural stem/precursor cells | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Inhibit apoptosis Anti-inflammation Anti-oxidative stress | [68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| Radix Angelicae sinensis |  | Angelica Polysaccharides; Ferulic Acid; Ligustilide. | PC12 Cells SD rats CIRI rats | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-oxidative stress Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [76,77,78,79,80] |
| Astragalus membranaceus |  | Astragalus Polysaccharides; Astragalus Saponins; Flavonoids. | SD rats OGD/R HT22 cells | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [81,82,83,84,85,86] |
| Safflower |  | Safflower Yellow | SD rats | ↑p-PI3K, p-Akt, GSK3β | Anti-oxidative stress Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [87,88,89,90,91,92,93] |
| Ginkgo biloba leaf |  | Ginkgo Flavonoids; Ginkgolides. | SD rats brain endothelial cell | ↑p-Akt, p-GSK3β, VEGF | Anti-inflammation Anti-oxidative stress | [94,95,96,97,98,99] |
| Erigeron breviscapus |  | Flavonoids Scutellarin (Breviscapine) | SD rats A375 cells | ↑p-Akt, eNOS | Anti-oxidative stress Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [100,101,102,103] |
| Ginseng |  | Ginsenoside | Mice SD rats | ↑p-Akt, p-mTOR, p-ERK | Anti-oxidative stress Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111] |
| Radix Paeoniae Rubra |  | Paeoniflorin | Mice SD rats | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-inflammation Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [112,113,114,115] |
| Panax notoginseng |  | Panax Notoginseng; Saponins. | Mice SD rats bEnd 3 cells H9c2 cells | ↑p-Akt/Akt, p-mTOR, Nrf2 | Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [116,117,118,119,120,121] |
| Herbal prescriptions | ||||||
| Buyang Huanwu Decoction | Propyl Gallate; Formononetin; Hydroxysafflor Yellow A; Formononetin; Astragaloside IV; Inosine, Paeoniflorin; Paeonol; Ligustrazine; Ferulic Acid. | HT22 cells mice | ↑p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-Bad | Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [122,123,124,125,126] | |
| Taohong Siwu decoction | Hydroxysafflor Yellow A; Paeoniflorin; Paeonol; Ligustrazine; Ferulic Acid. | SD rats | ↑p-Akt | Anti-inflammation Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [127,128,129,130] | |
| Xiaoyao San | Saikoside; Ferulic Acid; Ligustilide; Atractylenolide; Paeoniflorin; Albiflorin; Liquiritin; Glycyrrhizic Acid; Pachymic Acid. | PC12 cells | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [131,132] | |
| Danhong injection | Ferulic Acid; Cryptotanshinone; Quercetin; Anhydrosafflor Yellow B. | SD rats | ↑p-PI3K, p-Akt, GSK3β | Anti-inflammation Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [133,134,135,136,137,138] | |
| Sanhua decoction | Flavonoids; Anthraquinones; Coumarins; Phenylpropanoid Glycosides; Alkaloids; Lignans. | SD rats | ↑p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-inflammation Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [139,140,141] | |
| Xingnaojing injection | Turmeric; Moschus; Borneolum Syntheticum; Fructus Gardeniae. | SD rats | ↑p-Akt, eNOS | Anti-oxidative stress Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [142,143,144,145] |
| Natural Medicine | Insect Atlas | Active Ingredients | Model | Regulation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway | Main Purposed Effects | Ref(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insect medicine | ||||||
| Earthworm |  | Lumbrokinase | SD rats mice | ↑: p-PI3K and p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [147,148,149,150,151] |
| Leech |  | Hirudin; Fibrinolysin. | IPF rats SD rats mice | ↑: p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis Anti-inflammation | [152,153,154,155,156] |
| Scorpion |  | Adenosine; Dipeptides. | SD rats K562 cell | ↑: p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [157,158,159,160] |
| Insect prescriptions | ||||||
| Tongxinluo capsule | Ginsenoside; Hirudin; Denosine; Paeoniflorin. | SD rats mice | ↑: p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [161,162,163,164,165] | |
| Naoxintong capsule | Adenosine; Hirudin; Tanshinone; Danshensu; Salvianolic Acid. | SD rats | ↑: p-Akt | Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [166,167,168,169] | |
| Shuxuetong injection | Hirudin; Lumbrokinase. | SD rats | ↑: p-Akt, VEGF | Anti-oxidative stress Anti-neuronal apoptosis | [170,171,172,173] |
| Medicine | Dose in Animals | Dose in Human | Ref(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active ingredients | |||
| Ligustrazine | 20 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) | 80–240 mg/d (i.v.) | [67,174] |
| Tanshinone IIA | 30 mg/kg/d in rat (i.v.) 10 mg/kg/d in mice (i.p.) | 60 mg/d (i.v.) | [75,175,176,177] |
| Ligustilide | 20–40 mg/kg/day in rat (p.o.) 5–20 mg/kg/d in mice (i.p.) | / | [178,179] |
| Hydroxysafflor Yellow A | 10–40 mg/kg/d in rat (i.v.) 2 mg/kg/d in mice (i.v.) | 25–70 mg/d (i.v.) | [93,180,181] |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 25 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) 10–50 mg/kg/d in mice (i.p.) | 10–20 mg/d (i.v.) | [182,183,184] |
| Ginsenoside-Rb1 | 25–100 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) | / | [185] |
| Ginsenoside-Rg1 | 20 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) 10–40 mg/kg/d in mice (i.p.) | / | [107,186] |
| Paeoniflorin | 40 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) | 3–9 g/d (i.v.) | [112,187] |
| Panax notoginseng Saponins | 25–100 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) 45 mg/kg/d in mice (i.p.) | 500 mg/d (i.v.) | [117,188,189] |
| Salvianolic Acid B | 10–20 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) | / | [70] |
| Breviscapus | 3–6 mL/kg in rat (i.v.) | / | [190] |
| Astragaloside IV | 2g/kg/d in rat (i.v.) 20 mg/kg in rat (i.p.) 200 mg/kg in mice (i.p.) | / | [82,83,191] |
| Lumbrokinase | / | 1,800,000 units/d (p.o.) | [151] |
| Hirudin | 10–40 mg/kg in mice (p.o.) | 2.25 g/d (p.o.) | [153,156] |
| Prescriptions | Formula/dose | ||
| Buyang Huanwu Decoction | 10–40 g/kg in rat (p.o.) 1.0 g/kg in mice (p.o), twice daily | raw Astragalus 30 g, angelica 15 g, longan meat 15 g, antler gum 10 g, Salvia miltiorrhiza 10 g, frankincense 10 g, myrrh 10 g, and dried pine 5 g | [192,193,194,195] |
| Taohong Siwu decoction | 4.5–18 g/kg/d in rat (p.o.) | / | [196] |
| Danhong injection | 0.75–3 mL/kg in rat (i.v.), twice daily 3 mL/kg/d in mice (i.m.) | 20–40 mL/d (i.v.) | [134,138,197,198] |
| Sanhua decoction | 10 g/kg/d in rat (p.o.) | / | [140] |
| Xingnaojing injection | 0.75–3 mL/kg/d in rat (i.m.) 6 mg/kg/d in mice (i.m.) | 20 mL/12 h (i.v.) | [143,199] |
| Tongxinluo capsule | 100 mg/kg/d in rat (p.o.) 0.75–3.0 g/kg/d in mice (p.o.) | 1.56–3.12 g/d (p.o.) | [161,162,163] |
| Naoxintong capsule | 0.5 g/kg/d in rat (p.o.) | 2.4 g/d (p.o.) | [200,201,202] |
| Shuxuetong injection | 6 mL/kg/d in rat (i.v.) 0.27–1.08 mg/kg/d in rat (i.p.) | 6–10 mL/d (i.v.) | [171,172,203] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xiao, X.; Han, X.; Yao, L.; Lan, W. A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227963
Liu X, Xiao X, Han X, Yao L, Lan W. A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227963
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xian, Xinyu Xiao, Xue Han, Lan Yao, and Wei Lan. 2022. "A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227963
APA StyleLiu, X., Xiao, X., Han, X., Yao, L., & Lan, W. (2022). A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 27(22), 7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227963






