Paeoniflorin Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via JNK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
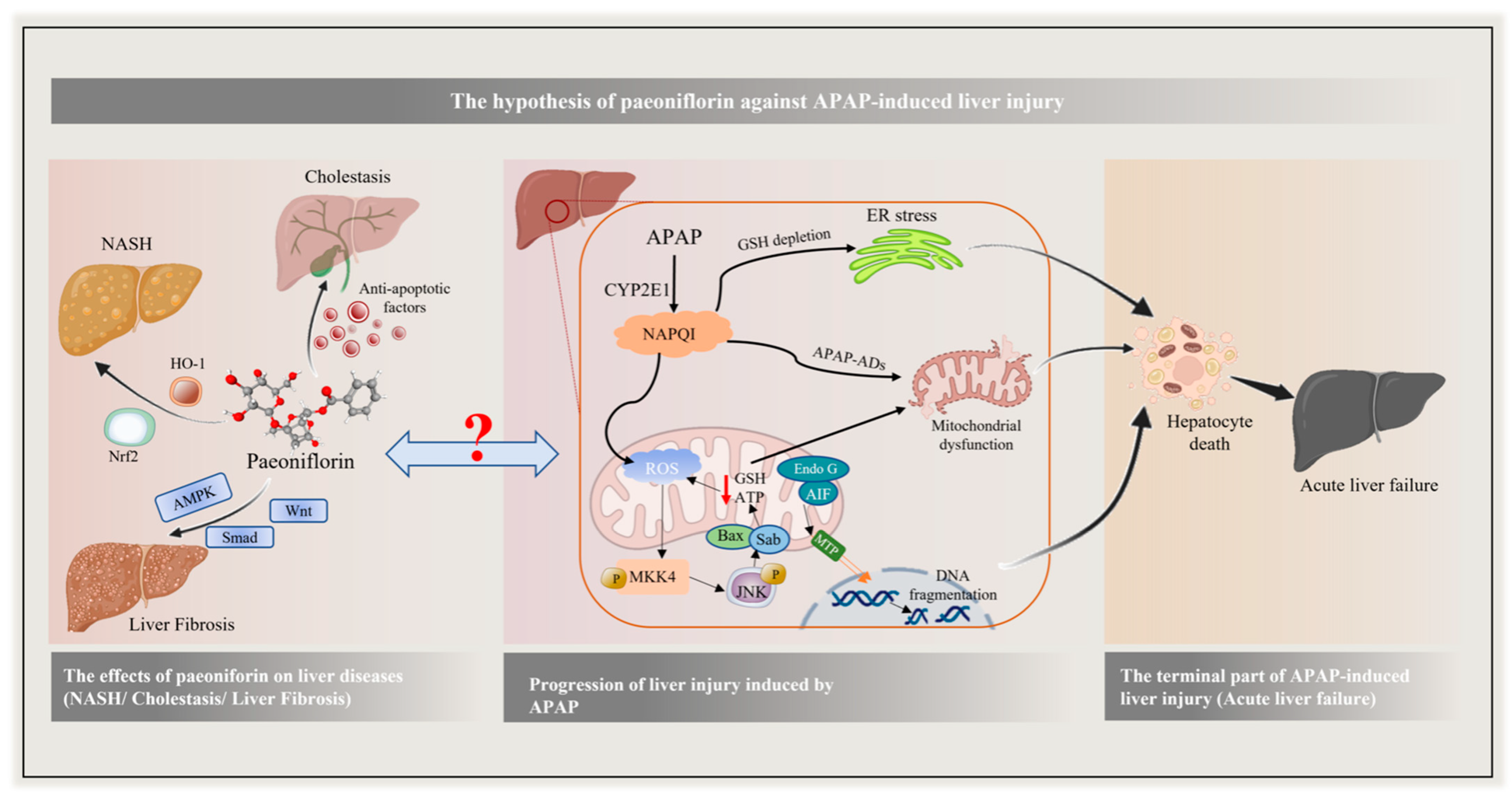
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Investigation of Experimental Conditions and PF Safety
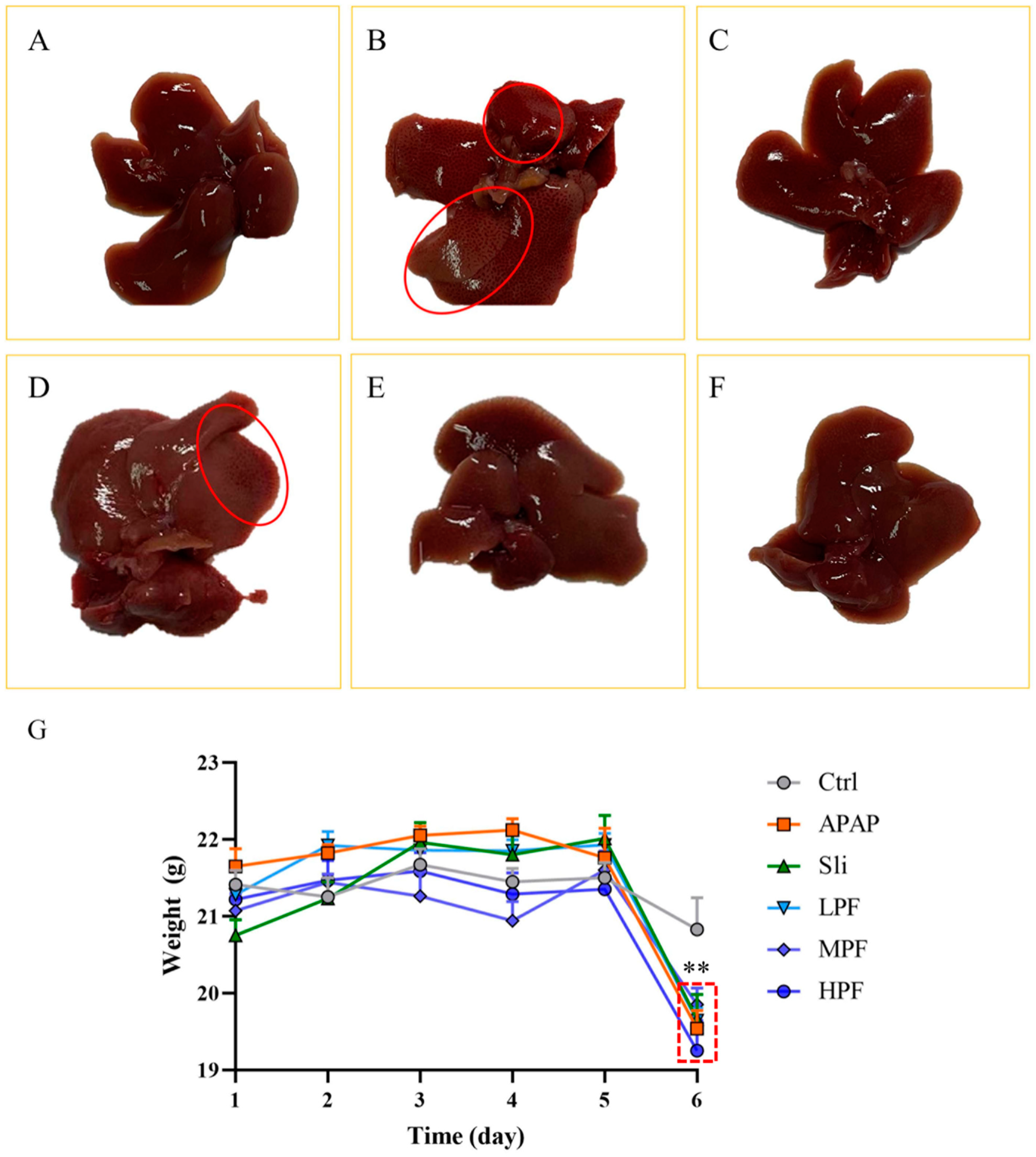
2.2. Effect of PF on Macroscopic Pathological of the Liver
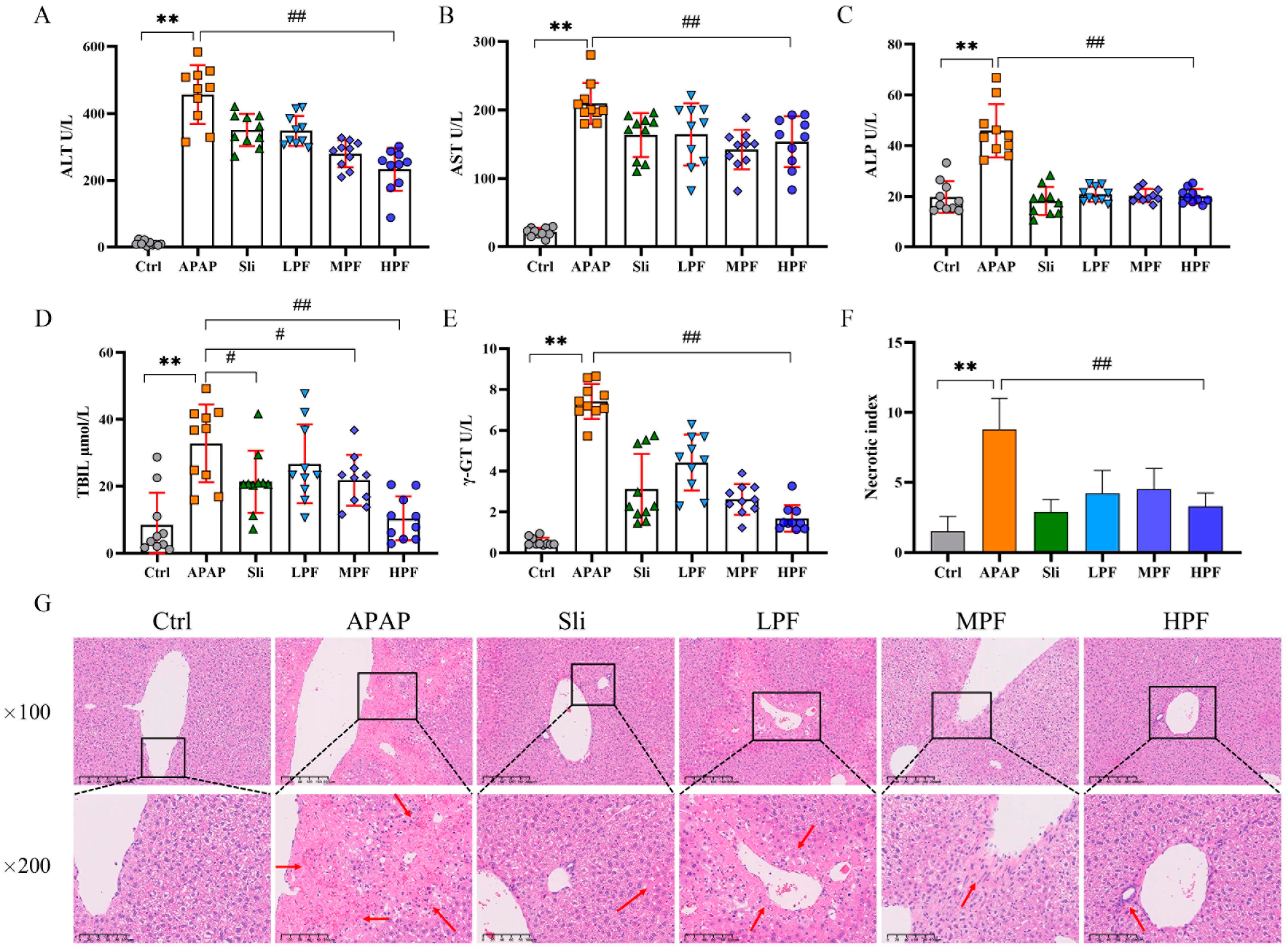
2.3. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of PF on Liver Injury Caused by APAP
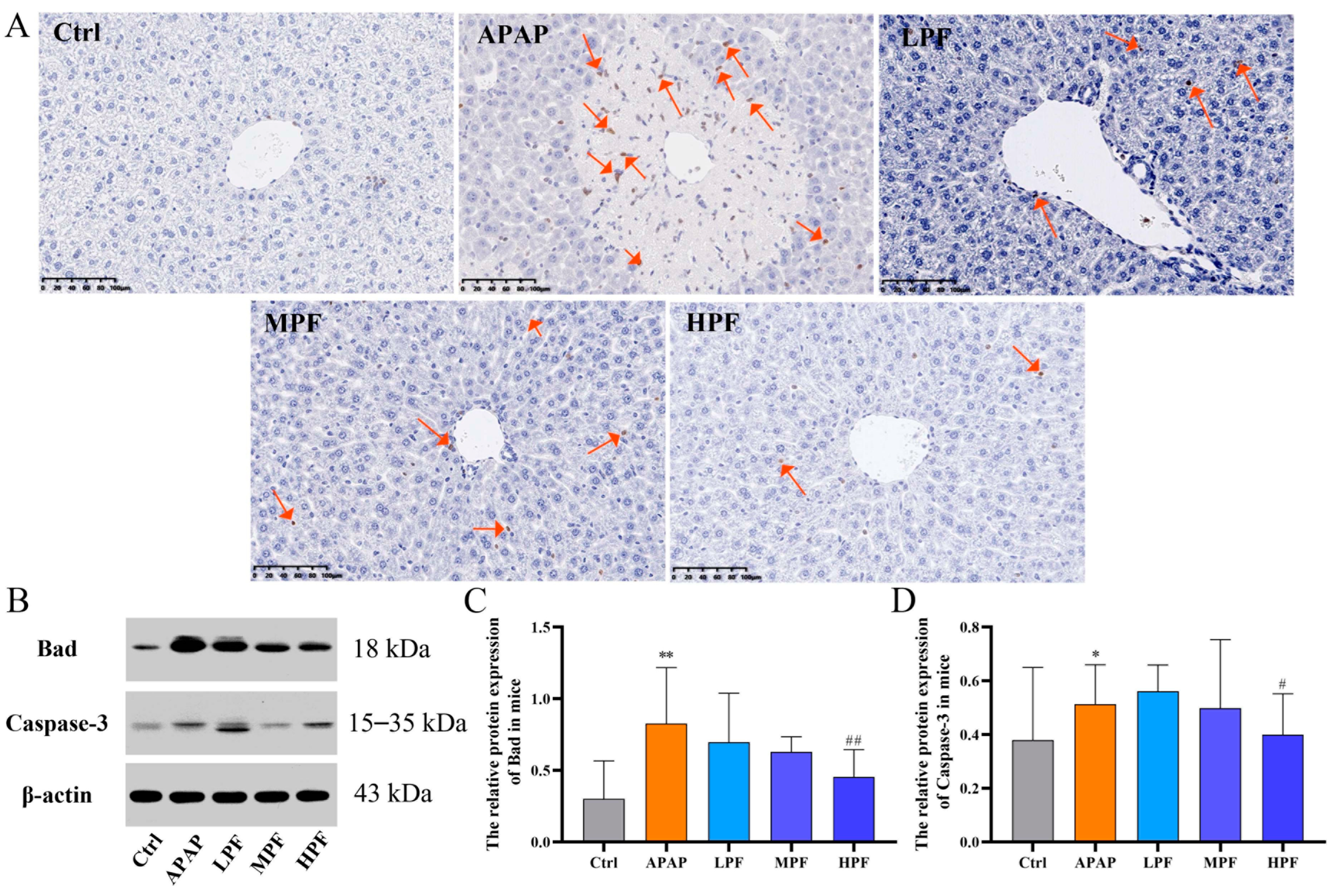
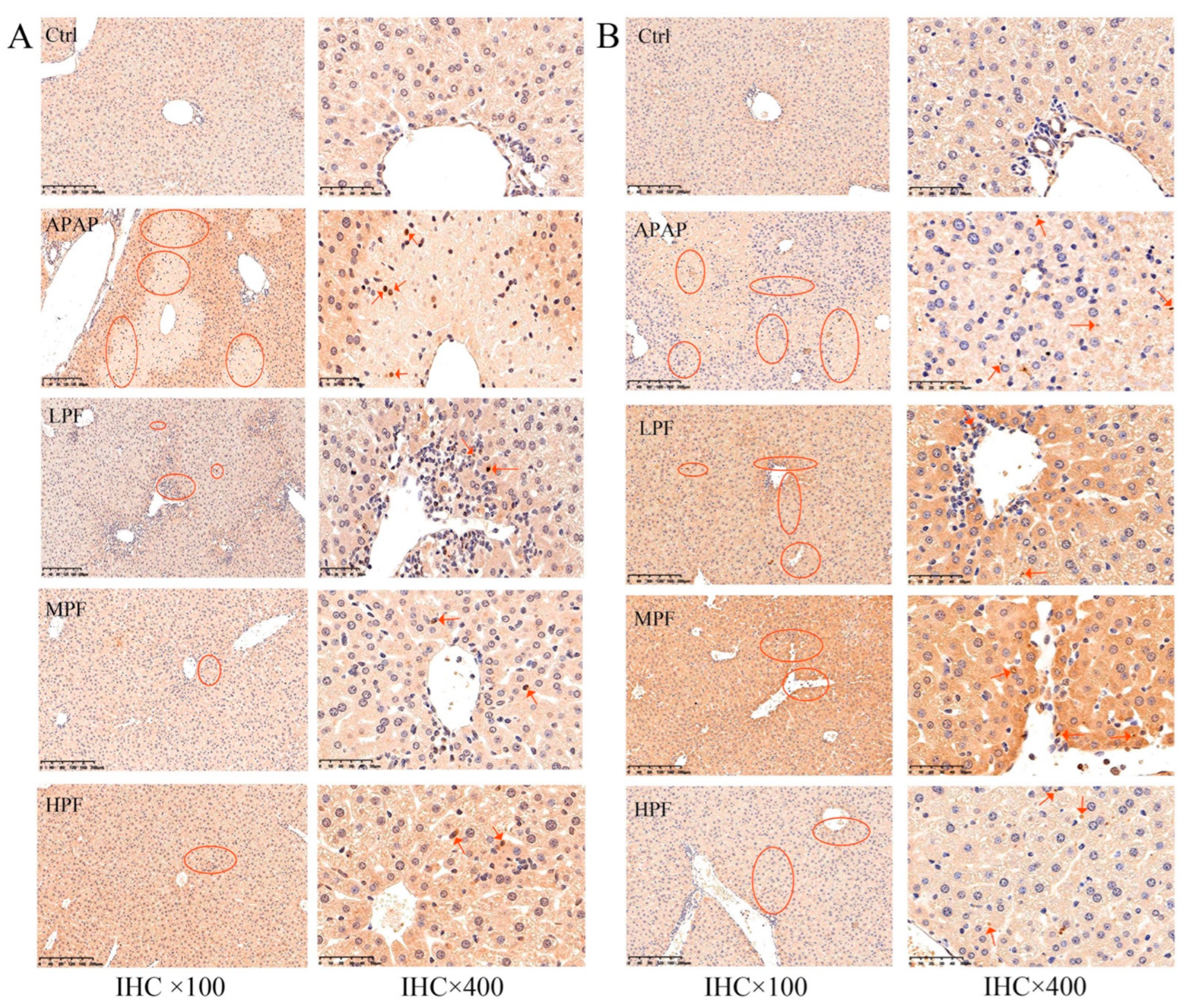
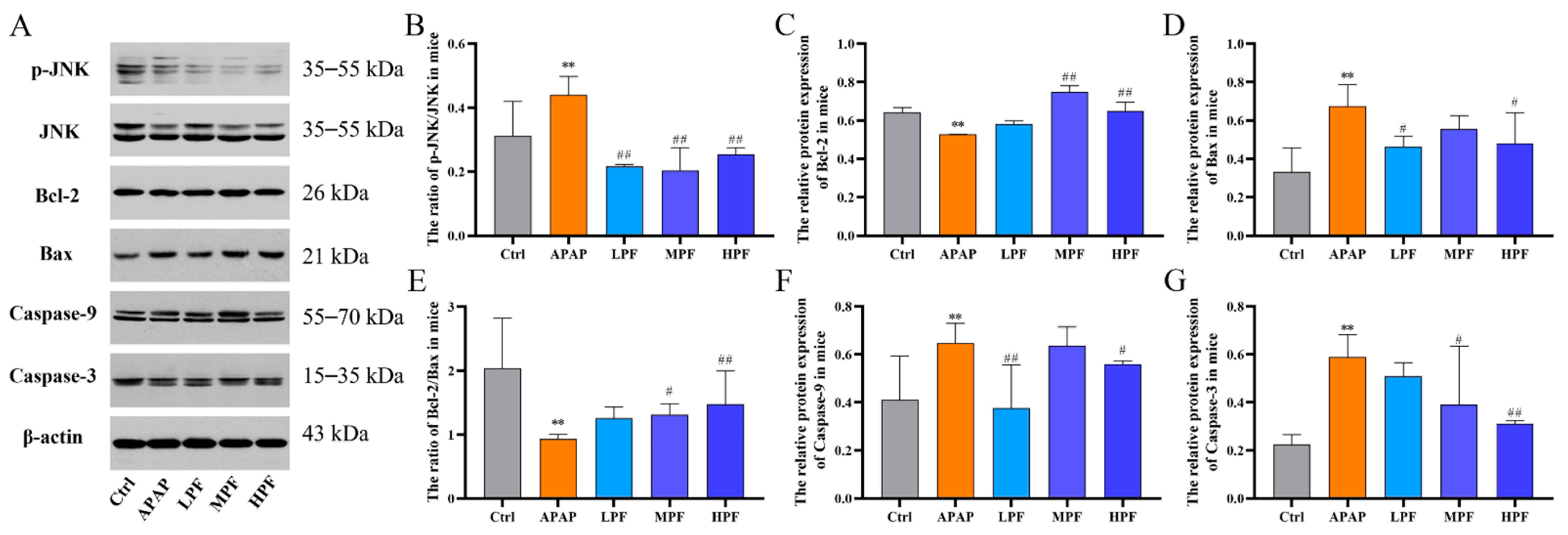
2.4. PF Prevents the Apoptosis in Mice Liver from APAP-Induced Injury
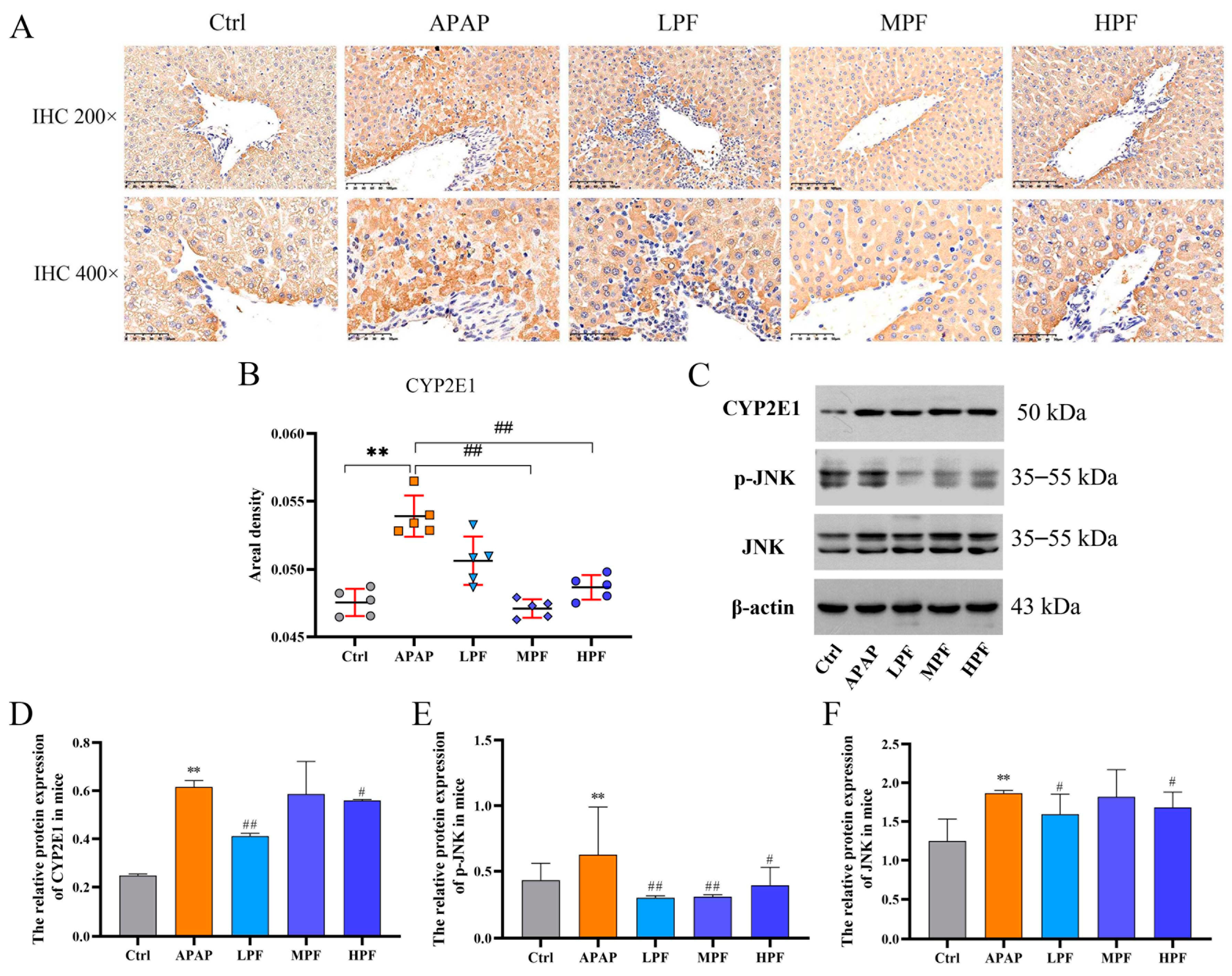
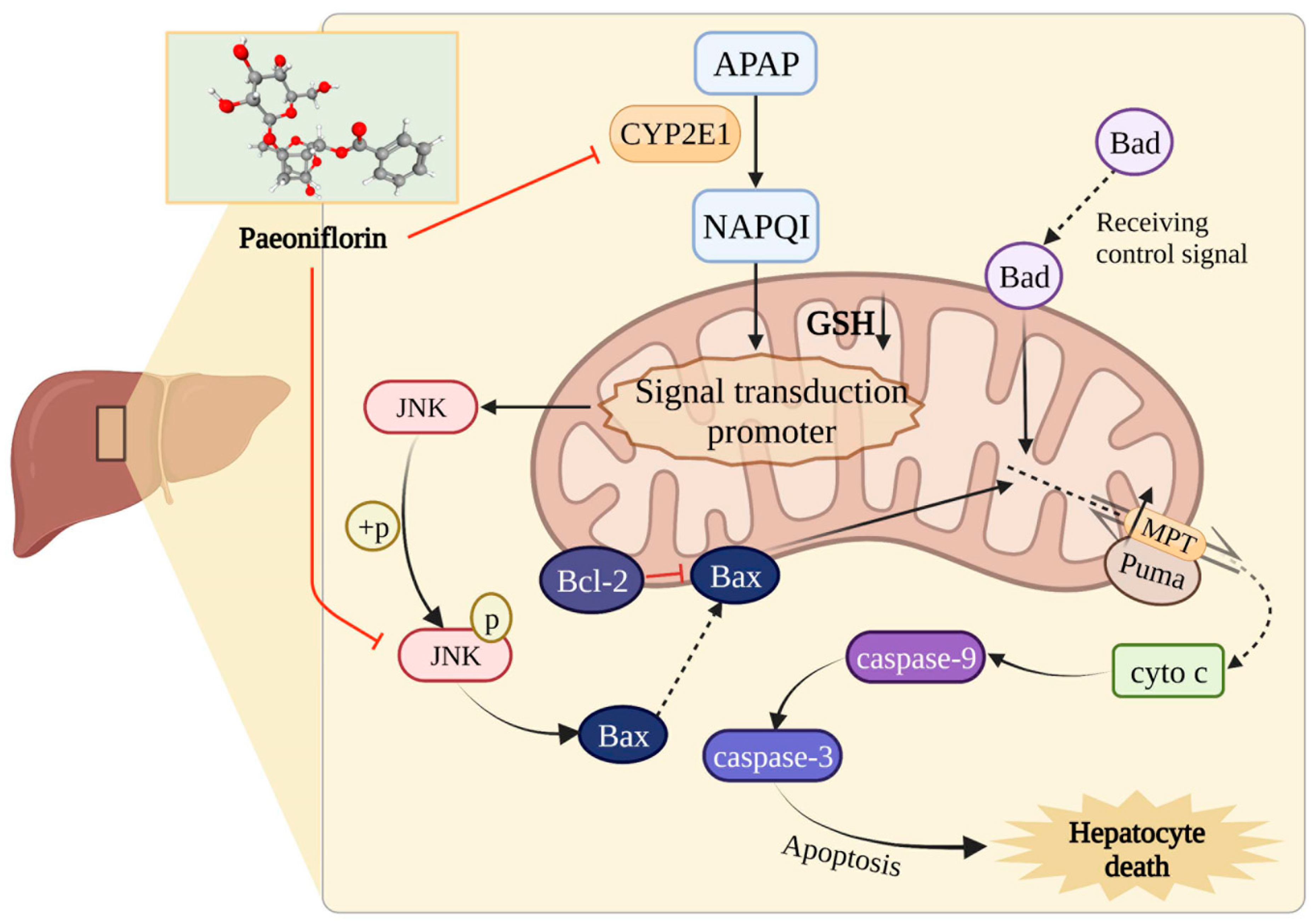
2.5. The Protective Effect of PF on Liver Injury Related to CYP2E1/JNK Signal
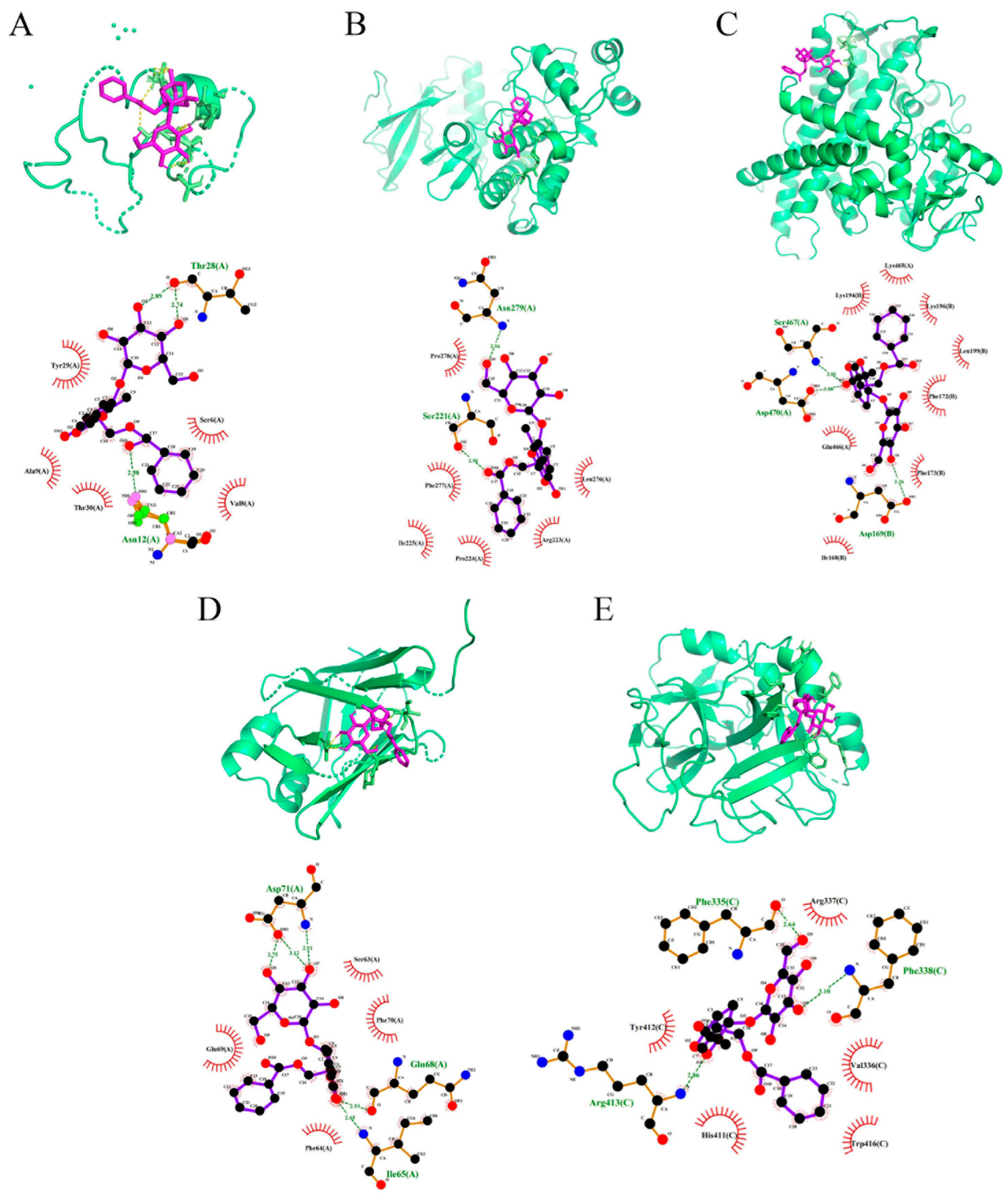
2.6. PF Displays Favorable Affinity in CYP2E1 and JNK
2.7. PF Ameliorates APAP-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Refraining Upregulation of CYP2E1/JNK Signal
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Establishment of Experimental Model and Treatment
4.4. Biochemical Analysis
4.5. Histological Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.6. TUNEL Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Quantification
4.8. Protein Extraction and Western Blot (WB)
4.9. Molecular Docking
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bernal, W.; Wendon, J. Acute Liver Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M. Acute Liver Failure in the United States. Semin. Liver Dis. 2003, 23, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Liu, Y.; Shang, J.; Xie, Q.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Xu, J.; Niu, J.; Liu, J.; Watkins, P.B.; et al. Incidence and Etiology of Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Mainland China. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2230–2241.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnsson, E.S. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, W.; Auzinger, G.; Dhawan, A.; Wendon, J. Acute Liver Failure. Lancet 2010, 376, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunchorntavakul, C.; Reddy, K.R. Acetaminophen (APAP or N-Acetyl-p-Aminophenol) and Acute Liver Failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cortes, M.; Robles-Diaz, M.; Stephens, C.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J. Drug Induced Liver Injury: An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 3381–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Graudins, A. Risk Prediction of Hepatotoxicity in Paracetamol Poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen: Dose-Dependent Drug Hepatotoxicity and Acute Liver Failure in Patients. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M. Acute Liver Failure. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.S.; Curry, S.C. Evaluation and Treatment of Acetaminophen Toxicity. Adv. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, J.A.H.; Clements, J.A.; Prescott, L.F. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Paracetamol. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1982, 7, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trettin, A.; Batkai, S.; Thum, T.; Jordan, J.; Tsikas, D. Trapping of NAPQI, the Intermediate Toxic Paracetamol Metabolite, by Aqueous Sulfide (S2−) and Analysis by GC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 963, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen Toxicity: Novel Insights Into Mechanisms and Future Perspectives. Gene Expr. 2018, 18, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Akakpo, J.Y.; Umbaugh, D.S.; Ramachandran, A. Novel Therapeutic Approaches Against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury and Acute Liver Failure. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 174, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, A.; Schmidt, H.H.J. Silymarin as Supportive Treatment in Liver Diseases: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Qiao, J.Y.; Wang, B.Y.; Bai, M.; Shen, J.D.; Cheng, Y.X. Paeoniflorin Ameliorates Fructose-Induced Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis by Activating LKB1/AMPK and AKT Pathways. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, X.; Kuang, G.; Jiang, R.; Guo, X.; Wu, S.; Wan, J.; Yin, L. Paeoniflorin Modulates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Hepatic Stellate Cells Activation to Alleviate CCl4-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis by Upregulation of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zang, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Paeoniflorin Inhibits Cell Viability and Invasion of Liver Cancer Cells via Inhibition of Skp2. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3165–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chi, Y.H.; Niu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, C.E.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Metabolomics Coupled with Multivariate Data and Pathway Analysis on Potential Biomarkers in Cholestasis and Intervention Effect of Paeonia Lactiflora Pall. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, X.; Niu, M.; Wang, R.; Yang, T.; Wang, D.; Wen, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of Paeoniflorin in the Treatment of Bile Duct Ligation-Induced Cholestatic Liver Injury Using Integrated Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 586806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senior, J.R. Alanine aminotransferase: A clinical and regulatory tool for detecting liver injury-past, present, and future. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Sun, J.; Sullivan, M.A.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, K. Angelica Sinensis Polysaccharide Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury and Cell Death by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Hepatic Apoptosis in Vivo and in Vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zou, K.; Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Seabuckthorn Berry Polysaccharide Extracts Protect against Acetaminophen Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice via Activating the Nrf-2/HO-1-SOD-2 Signaling Pathway. Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Tong, X.; Peng, W.; Wei, S.; Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, W. Network Pharmacology Prediction and Molecular Docking-Based Strategy to Discover the Potential Pharmacological Mechanism of Huai Hua San Against Ulcerative Colitis. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3255–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Zhong, G.Y.; Zhu, J.X. Molecular Mechanism and Research Progress on Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Liver Injury. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Jiang, L.L.; Li, H.Y.; Yan, P.F.; Zhang, Y.L. Chemical Components and Pharmacological Activities of Terpene Natural Products from the Genus Paeonia. Molecules 2016, 21, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, J.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Y. Paeoniflorin, a Natural Product with Multiple Targets in Liver Diseases-A Mini Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Chu, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yao, W.; Yi, J.; Gao, Y. Beneficial Effects of Paeoniflorin on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High-Fat Diet in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chu, L.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Dai, J.; Yi, J.; Gao, Y. Paeoniflorin Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Rats: Involvement with the ROCK/NF-ΚB Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cao, L.; Luo, Y.; Feng, X.; Sun, L.; Wen, M.; Peng, S. Paeoniflorin Protects against Concanavalin A-Induced Hepatitis in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 24, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, D. Paeoniflorin Protects Pancreatic β Cells from STZ-Induced Damage through Inhibition of the P38 MAPK and JNK Signaling Pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, P.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.B.; Ma, X.; Li, R.S.; Wei, S.Z.; et al. Paeoniflorin Attenuates ANIT-Induced Cholestasis by Inhibiting Apoptosis in Vivo via Mitochondria-Dependent Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Ma, X.; Wen, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, S.; Li, H.; et al. Paeoniflorin Ameliorates Cholestasis via Regulating Hepatic Transporters and Suppressing Inflammation in ANIT-Fed Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, F.S.; Wendon, J. Understanding Paracetamol-Induced Liver Failure. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorović Vukotić, N.; Đorđević, J.; Pejić, S.; Đorđević, N.; Pajović, S.B. Antidepressants- and Antipsychotics-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossanen, J.C.; Tacke, F. Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Shinohara, M.; Ybanez, M.D.; Saberi, B.; Kaplowitz, N. Signal Transduction Pathways Involved in Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 196, 267–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallunki, T.; Deng, T.; Hibi, M.; Karin, M. C-Jun Can Recruit JNK to Phosphorylate Dimerization Partners via Specific Docking Interactions. Cell 1996, 87, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.J. Signal Transduction by the JNK Group of MAP Kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M. A Liver Full of JNK: Signaling in Regulation of Cell Function and Disease Pathogenesis, and Clinical Approaches. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.D.; Hou, J.G.; Liu, W.; Ren, S.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3, a rare saponin from red ginseng, ameliorates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 59, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, C.F.A.; Wong-Brown, M.W.; Bowden, N.A. BCL-2 Family Isoforms in Apoptosis and Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Duan, L.; Akakpo, J.Y.; Farhood, A.; Ramachandran, A. The Role of Apoptosis in Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y. Mechanisms of Caspase Activation and Inhibition during Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentnall, M.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; de Guevara, R.L.; Cepero, E.; Boise, L.H. Caspase-9, Caspase-3 and Caspase-7 Have Distinct Roles during Intrinsic Apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knockaert, L.; Descatoire, V.; Vadrot, N.; Fromenty, B.; Robin, M.A. Mitochondrial CYP2E1 Is Sufficient to Mediate Oxidative Stress and Cytotoxicity Induced by Ethanol and Acetaminophen. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, J.; Begriche, K.; Hartman, J.H.; Fromenty, B. Role of Mitochondrial Cytochrome P450 2E1 in Healthy and Diseased Liver. Cells 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Tong, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W. Preclinical Validation of Silibinin/Albumin Nanoparticles as an Applicable System against Acute Liver Injury. Acta Biomater. 2022, 146, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudich, N.; Zamir, G.; Pappo, O.; Shlomai, Z.; Faroja, M.; Weiss, I.D.; Wald, H.; Galun, E.; Peled, A.; Wald, O. Focal Liver Necrosis Appears Early after Partial Hepatectomy and Is Dependent on T Cells and Antigen Delivery from the Gut. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Dosage (mg·kg−1) | Liver Index (mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | None | 30.78 ± 1.44 |
| APAP | None | 38.24 ± 4.09 * |
| Sli | 60 | 33.43 ± 5.03 |
| LPF | 50 | 34.83 ± 7.69 |
| MPF | 100 | 31.45 ± 3.51 # |
| HPF | 200 | 32.27 ± 2.08 # |
| Compound | Target | Target (PDB ID) | Target Structure | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paeoniflorin | JNK | 3NIR | 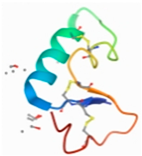 | −9.59 |
| CYP2E1 | 2FDV | 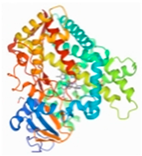 | −3.59 | |
| MAPK1 | 4ZZN |  | −3.66 | |
| Bcl-2 | 3P6H |  | −7.30 | |
| Bad | 5PAX | 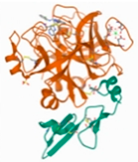 | −4.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, J.; et al. Paeoniflorin Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via JNK Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238534
Deng X, Li Y, Li X, Zhang Z, Dai S, Wu H, Zhang F, Hu Q, Chen Y, Zeng J, et al. Paeoniflorin Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via JNK Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238534
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Xinyu, Yubing Li, Xing Li, Zhenpeng Zhang, Shu Dai, Hefei Wu, Fangling Zhang, Qichao Hu, Yuan Chen, Jinhao Zeng, and et al. 2022. "Paeoniflorin Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via JNK Signaling Pathway" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238534
APA StyleDeng, X., Li, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Dai, S., Wu, H., Zhang, F., Hu, Q., Chen, Y., Zeng, J., & Ma, X. (2022). Paeoniflorin Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via JNK Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 27(23), 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238534




